Bacterial Morphology
1/118
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
is the branch of microbiology that studies bacteria: their structure, classification, physiology, genetics, ecology, and their roles in health, disease, industry, and the environment.
Bacteriology
Bacteriology is the study of bacteria, especially those that cause disease in humans, and their prevention and control.
True
small rod
Bakterion
study of
Logos
are cellular and prokaryotic microorganism with simpler structure compare with eukaryotic organisms.
Bacteria
Is used for identification
Bacterial Shapes
are rod-shaped bacteria
Bacilli
are spherical bacteria
Cocci
corkscrew-shaped microorganisms.
Spiral

Single cocci
Coccus

Pairs
Diplococci

chains
Streptococci

clusters
Staphylococci

groups of four
Tetrads

cubical groups
Sarcinae

Single bacilli
Bacillus

pairs
Diplobacilli

chains
Streptobacilli

short, oval rods
Coccobacilli

side by side
Pallisades

comma-shaped
Vibrios

rigid spiral forms
Spirilla
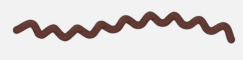
thin, flexible spirals
Spirochetes
is the unit of measurement used in bacteriology and is equal to one-thousandth of a millimeter.
Micrometer
Bacteria are generally one-tenth the size of eukaryotic cells.
True
smallest pathogenic bacillus
Haemophilus
largest pathogenic bacillus
Bacillus anthracis
Bigger size helps bacteria survive and adapt.
False
They can thrive in diverse environments, including marine sediments.
True
is a sticky, gelatinous layer that surrounds the cell wall of some bacteria.
Glycocalyx
well-organized, firmly attached; protects bacteria from phagocytosis
Capsule
loosely attached; helps in adhesion to surfaces
Slime layer
protects bacteria from antibiotic and immune response
Biofilm
Protects bacteria against osmotic pressure
Gives shape to the bacteria
Confer the gram’s reaction of the bacteria
A usual target of anti-microbial drugs
Cell Wall
Cell wall is important for identification.
True
Composed of very thick peptidoglycan layer
Gram-Positive Cell Wall
Negatively charge and contributes to the negativity of cell wall; may also bind and regulate the movement of cation in and out of the cell.
Teichoic Acids
includes acidic and neutral sugars
Polysaccharides
Composed of a thin layer of peptidoglycan.
Gram-Negative Cell Wall
Gram-negative cell walls have no teichoic acids.
True
fluid filled space between outer membrane and gram-negative cell wall
Periplasmic Space
anchor the outer membrane to the peptidoglycan layer and stabilizes the outer membrane
Lipoprotein
only in Gram (-) bacteria
Outer membrane
outer membrane major constituent; toxic
Lipid A
allows small molecules (nutrients, ions, antibiotics) to pass into or out of the cell
Porins
vital to evade the host defenses; contributes to negative charge of the bacterial surface and also comprises endotoxins.
Lipopolysaccharides
Causes Gram-negative sepsis
Can trigger fever, inflammation, hypotension, and septic shock.
Activate the immune system, sometimes excessively (dangerous in severe infections).
Endotoxins
Has a Gram-Positive Reaction
Specialized bacterial cell wall that resists decolorization by acid-alcohol after staining
Acid-Fast Cell Wall
three layered/triple unit membrane instead of wall
Sterols
causing atypical pneumonia
Mycoplasma
causes urogenital infection
Ureaplasma
possess flagella for locomotion
Motile Bacteria
no flagella
Atrichous

single flagellum at one pole
Monotrichous

single flagellum at each pole
Amphitrichous

tuft of flagella at one or both poles
Lophotrichous

flagella all over the organism
Peritrichous
Monotrichous and Peritrichous bacteria are most common pathogen.
True
Hair-like extension that extend into the environment Relatively shorter and finer than a flagella.
Fimbriae
its structural protein
Pilins
for attachment
Common Pili
for bacterial gene exchange
Conjugate Pili
Specialized flagella located within the periplasmic space of certain bacteria; found in Spirochetes
Endoflagella
Site of energy production / energy metabolism
Essential component for Gram(+) and Gram(-) bacteria
Also called as Cell Sac
Cell Membrane
Region containing the bacterial DNA; No nuclear membrane; Controls cell replication and function
Nucleoid
An invagination of the cell wall for cell respiration and division.
Mesosome
Protein synthesis
Ribosome
Storage materials for nutrients; Help bacteria survive during unfavorable conditions
Granules
Survival response to certain adverse nutritional condition such as depletion of a certain resource
Endospore
spore production
Sporulation
return to vegetative state when environmental condition is favorable
Germination
The endospore is helpful in identifying some species of bacteria.
True
Clostridium tetani
Terminal Spores
Clostridium botunilum
Subterminal Spores
Bacillus anthracis
Central Spores
cutaneous, inhalation, or gastrointestinal
Anthrax
flaccid paralysis due to neurotoxins
Botulism
muscle rigidity and spasm
Tetanus
It involves replication of cellular structures and components.
Bacterial Growth
refers to an increase in the number of cells, not cell size.
Microbial Growth
consists of thousands of bacteria.
Bacterial Colony
Visible colonies on culture media actually contain ________ of bacterial cells.
billions
Bacteria require specific nutrients and physical conditions to ___________.
grow
Understanding growth requirements is important for culturing bacteria and controlling infections.
True
Main source of energy and cell structure
Required for synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
Carbon
do not require preformed organic compound for growth because they can synthesize them from inorganic compound and carbon dioxide
Autotrophs/Lithotrophs
required preformed organic compound like sugar and amino acids, for growth. This includes most medical important bacteria
Heterotrophs/Organotrophs
needed for proteins and nucleic acids
Nitrogen
required for some amino acids and enzymes
Sulfur
essential for ATP, nucleic acids, and phospholipids
Phosphorus
is a component of cytochromes essential for electron transport in cellular respiration
Important for enzyme function, osmotic balance, and cell metabolism
Iron
Include iron, potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium
Inorganic Ions
Essential to promote the growth and development of the bacterial cell
Includes Vitamin B complex and amino acids.
Growth Factor
Serves as the medium from which bacteria acquire their nutrients.
Moisture/Water
Bacterial cell is composed mainly of water.
True
>40°C, typically 50°C - 55°C
Thermophiles
Optimal Temperature of 20°C - 40°C, best at 30°C - 37°C
Mesophiles
<10°C, optimum at 10°C - 20°C
Psychrophiles
grows in the presence of atmospheric (free) oxygen
Aerobe
cannot grow without oxygen, which serves as final electron acceptor. Contain superoxide dismutase, which protects from toxic oxygen
Obligate Aerobes