biology final study guide
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Genetic engineering
Tech that involves manipulating genes of an organism
Ex: adding or removing traits
What is the result of the polymerase chain reaction
Millions of copies of a specific DNA segment
Scientists use the process of genetic engineering to __________?
Create organisms with new traits, make medicines, improve agriculture, treat genetic disorders
DNA typing
Way to identify individuals based on their unique DNA
What is the human genome project specifically trying to find?
The exact sequence of 5 billion nucleotides in human DNA
Took 10 years and international scientists
What are the benefits of pharmocagenomics
Stronger safer medicine
More accurate drug dosages
Improvements on drug discovery
Decrease healthcare costs
Explain why Darwin said that many organisms seemed well suited to survive their environment in which they lived.
The organism adapted to its environment which helped them thrive and reproduce
Explain how similar DNA sequences in genes can be evidence of common ancestry
The more DNA organisms have in common, the more likely they are to have a common ancestor
Fitness
How well an organism can survive and reproduce in its environment
Biogeography
The study of where a species lives around the world and how they got there
Vestigial structures
Body parts that are not mandatory to survive
Ex: appendix, tailbone
Homologous structures
Body parts that are the same in 2 different species, most likely from a common ancestor
Explain how fossil records supported Charles Darwin’s theory
Showed that the earth is super old, and how animals have changed over the years
Adaptation
A trait that helps an organism to survive and reproduce better
Mutation
A random change in genetic material
Can be beneficial or harmful
Genetic drift
Change in allele frequencies by chance
Chance of loosing alleles is greater in smaller populations
More favorable in larger population
Temporal isolation
2 groups of the same species don’t mate because they reproduce during different times
Gene pool
Total collection of genes and alleles in a population
Explain why genetic drift tends to occur in populations that are small
With fewer individuals, random changes have bigger impact
Explain why founders would be the first step that occurred in the speciation of the Galapagos finches
Because a few finches (founders in this case) flew to a new island, and now most of their population resides there
Binomial nomenclature
2 name system used to name organisms
Genus+species
Ex:homo sapiens
Scientific names
Latin names for animals
Used for no confusion
Puma - puma con color
Phylum
3rd level of classification
Backbone - phylum chordata (vertebrates)
Genus
Group before species, 2nd most specific
HOMO sapiens
Explain why common names are not useful to biologists, and that they need to refer to the
species scientific name.
They could possibly cause confusion between scientists
What are the two parts of scientific names composed of
Genus+species
What are the two things that traditional classification tended to take into account
Physical characteristics and behavior
Kingdoms
2nd biggest category
Ex: animalia, plantae, fungi
Domain
Biggest category
Ex: bacteria, archaea, eukaryotic
Archea
Prokaryotes
Ancient bacterium
Species
Most specific level of classification Backbone, same species CAN mate
Cladogram
Family tree based on shared traits
What do nodes on a cladogram represent
Node - where branches split
Shows a common ancestor
Motor neurons
Carry signals from the brain or spinal cord to your muscles and glands
Neurons
Nerve cells that send messages throughout your body via electrical signals
Sensory neurons
Carries info from receptors in the skin to your brain
Nervous system
Controls all body responses, thoughts, feelings, movements
2 parts - CNS and PNS
CNS
Processes info and forms a response
Made of brain and spinal cord
Which part of the ear do sound waves first enter
Auditory canal, creates vibrations
Stimulant
All drugs that increase alertness and physical activity
Ex: nicotine, caffeine
What are the components of the circulatory system
Blood, vessels, heart
Arteries
Vessels carrying oxygen rich blood from the heart to the body - thickest vessel
EXCEPT pulmonary
Capillaries
Microscopic vessels that filter waste in blood
Connects veins and arteries
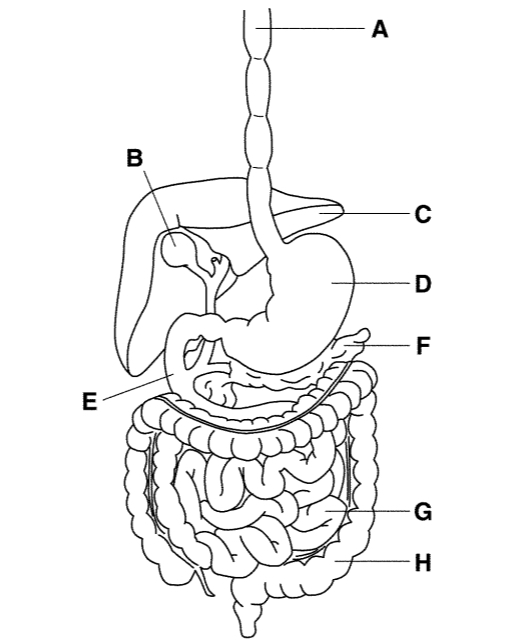
A
Esophagus
B
Gallbladder
C
Liver
D
Stomach
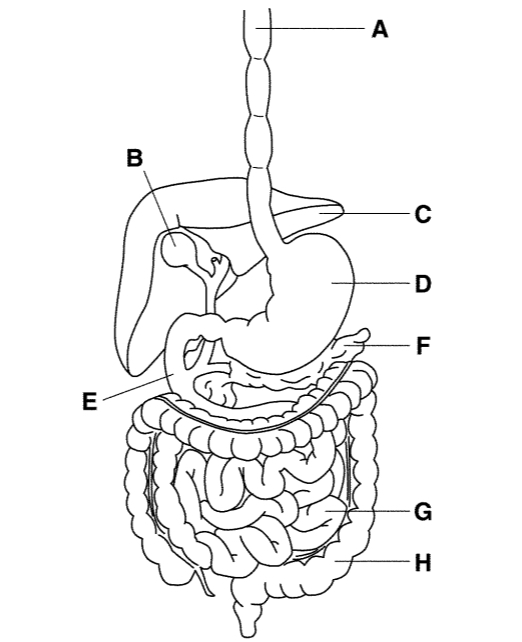
E
Small intestine
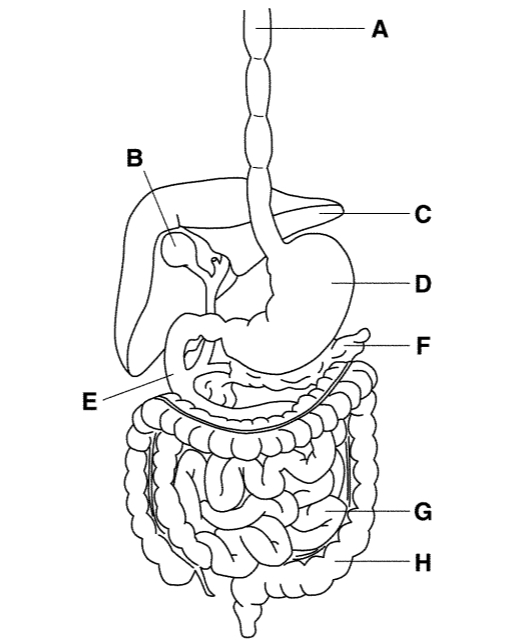
F
Pancreas
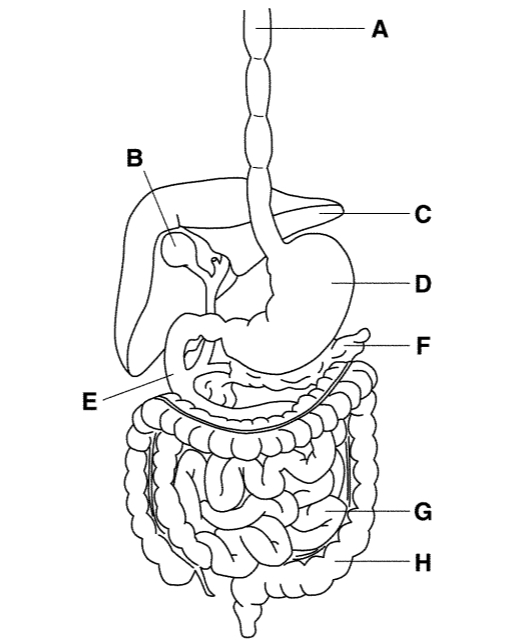
G
Small intestine
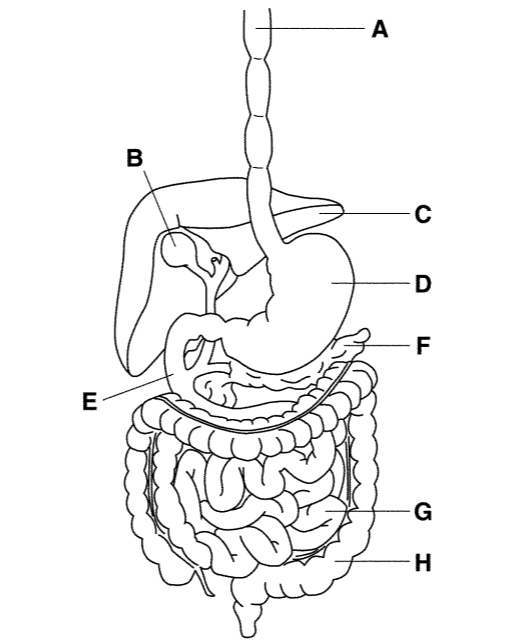
H
Large intestine
Where does the process of chemical digestion begin?
In the mouth with saliva
Pancreas
Creates digestive enzymes and sends them out
Makes insulin and glucagon to keep blood sugar regulated
Explain what role does the pancreas play in regulating glucose in the blood
When blood sugar is high it releases insulin to regulate
Zygote
A fertilized egg cell
The placenta contains tissue from who
Mom and baby
Lymph nodes and what does it mean when the lymph nodes are swollen
Swollen means sign of infection
Lymph nodes are the body’s immune defense
Inflammatory response
Signs - redness, heat, swelling, body sends out white body cells
B cells
Creates antibodies to attach and neutralize antigens (invaders)
Orders T cells to attack
T cells
Immune system’s defense
Active immunity and include an example
Your body builds its own army of antibodies after being exposed to a pathogen
Ecology
The study of how living things interact with each other and their environment
Biomes
Big area with similar climate plans and animals
Habitat
the place an organism lives
Niche
An organisms role in an ecosystem
Biotic factors
Living factors of an environment
Food web
Complex map of the transfer of energy in an environment
Food chain
Simple line of who eats who
Water cycle
The movement of water through an environment
Tundra
super cold, dry, windy, permafrost
Renewable resources
Unlimited or naturally replenished my nature
Non renewable resources
Once used up, takes millions of years to replenish