HS EOY Biology Revision
1/337
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
338 Terms
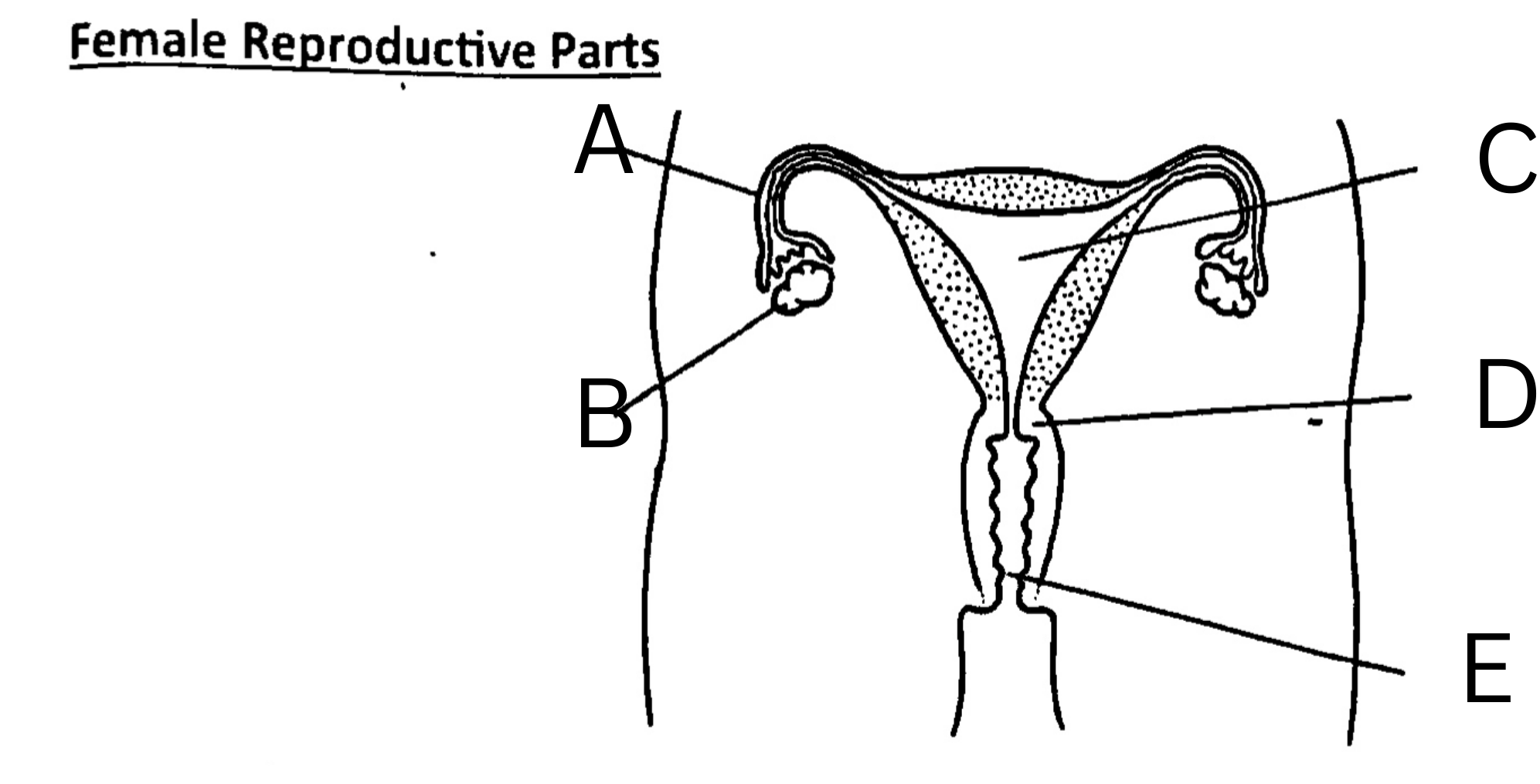
What is A on the diagram?
Fallopian Tube, or oviduct
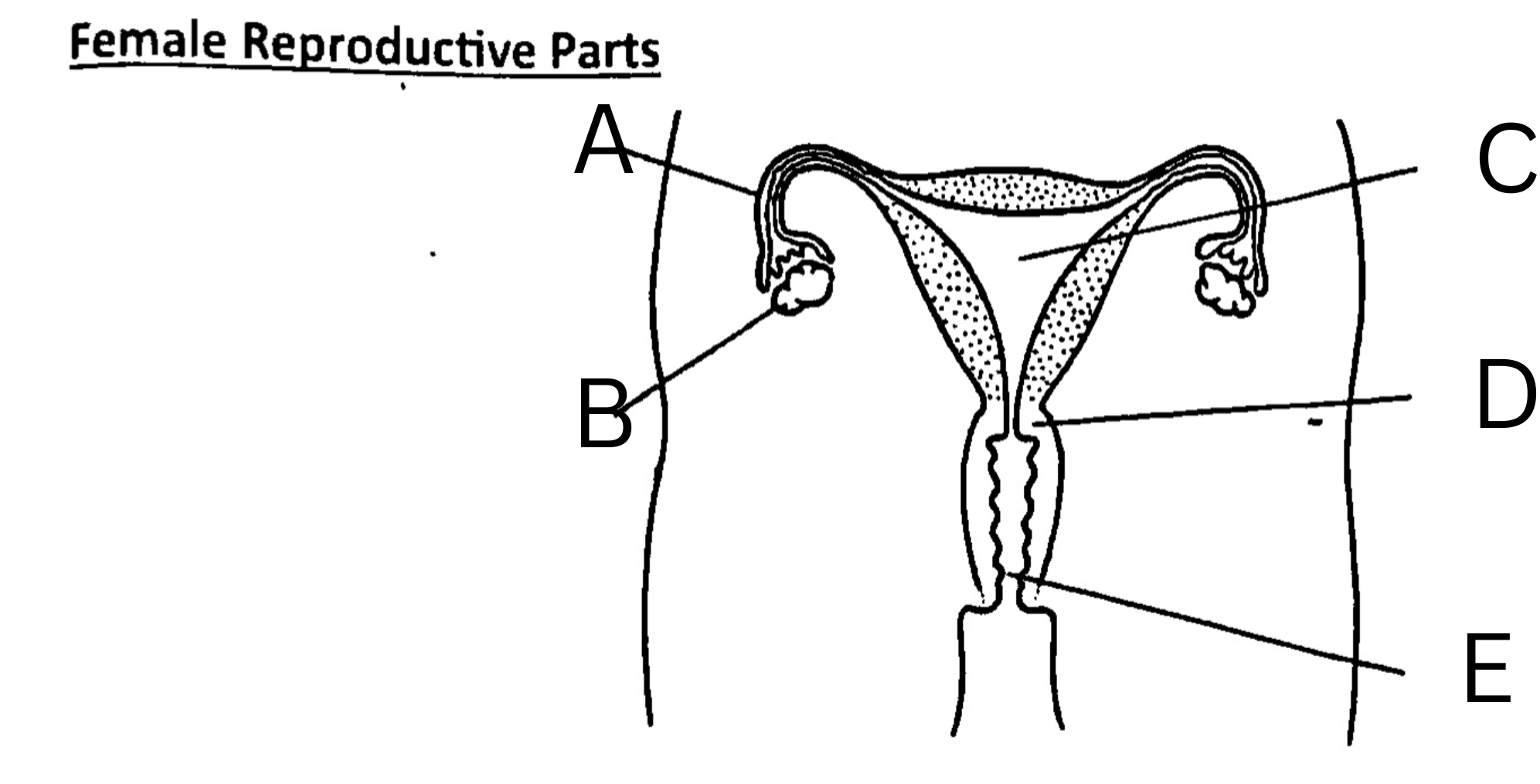
What is B on the diagram?
Ovary
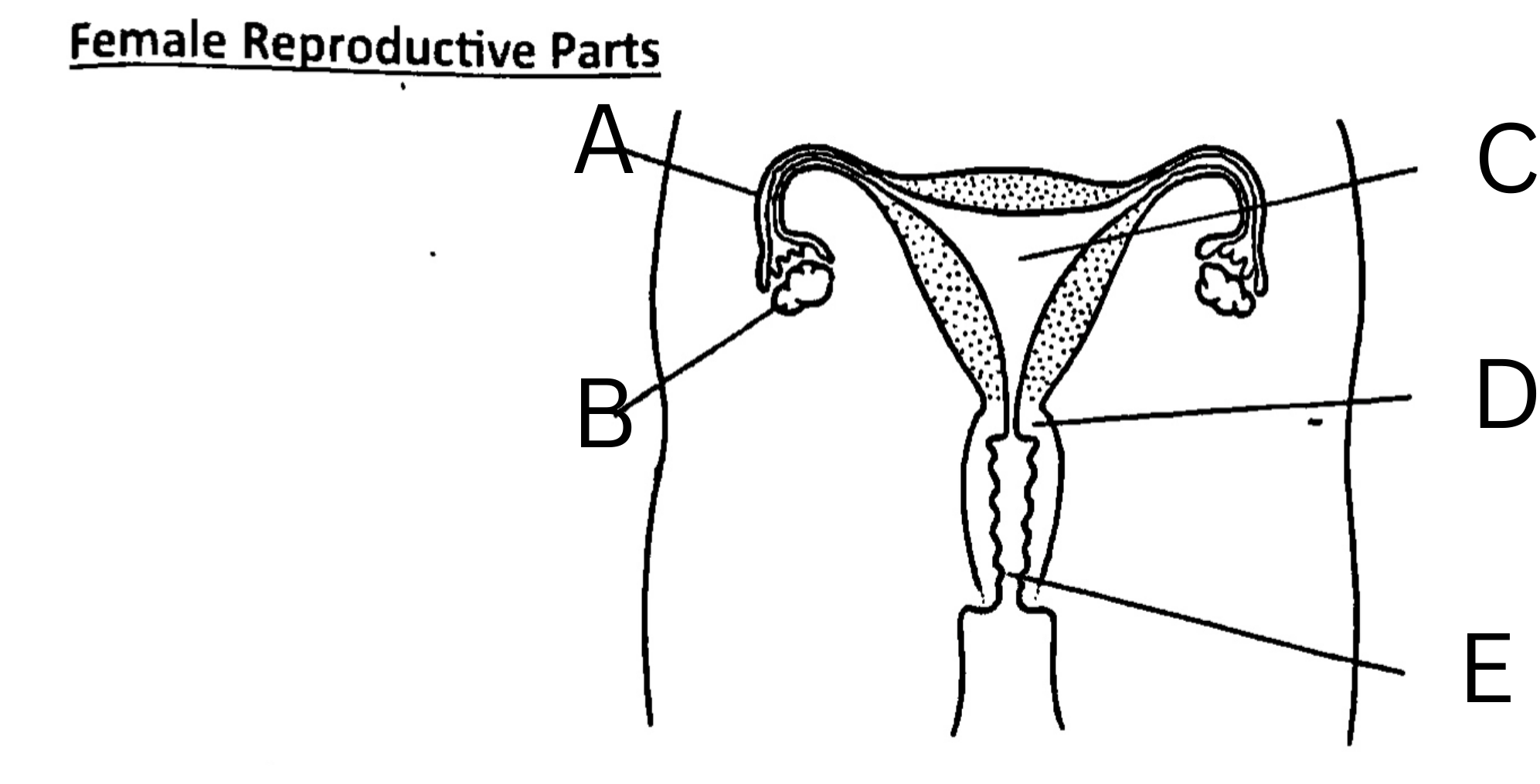
What is C on the diagram?
Womb, or uterus
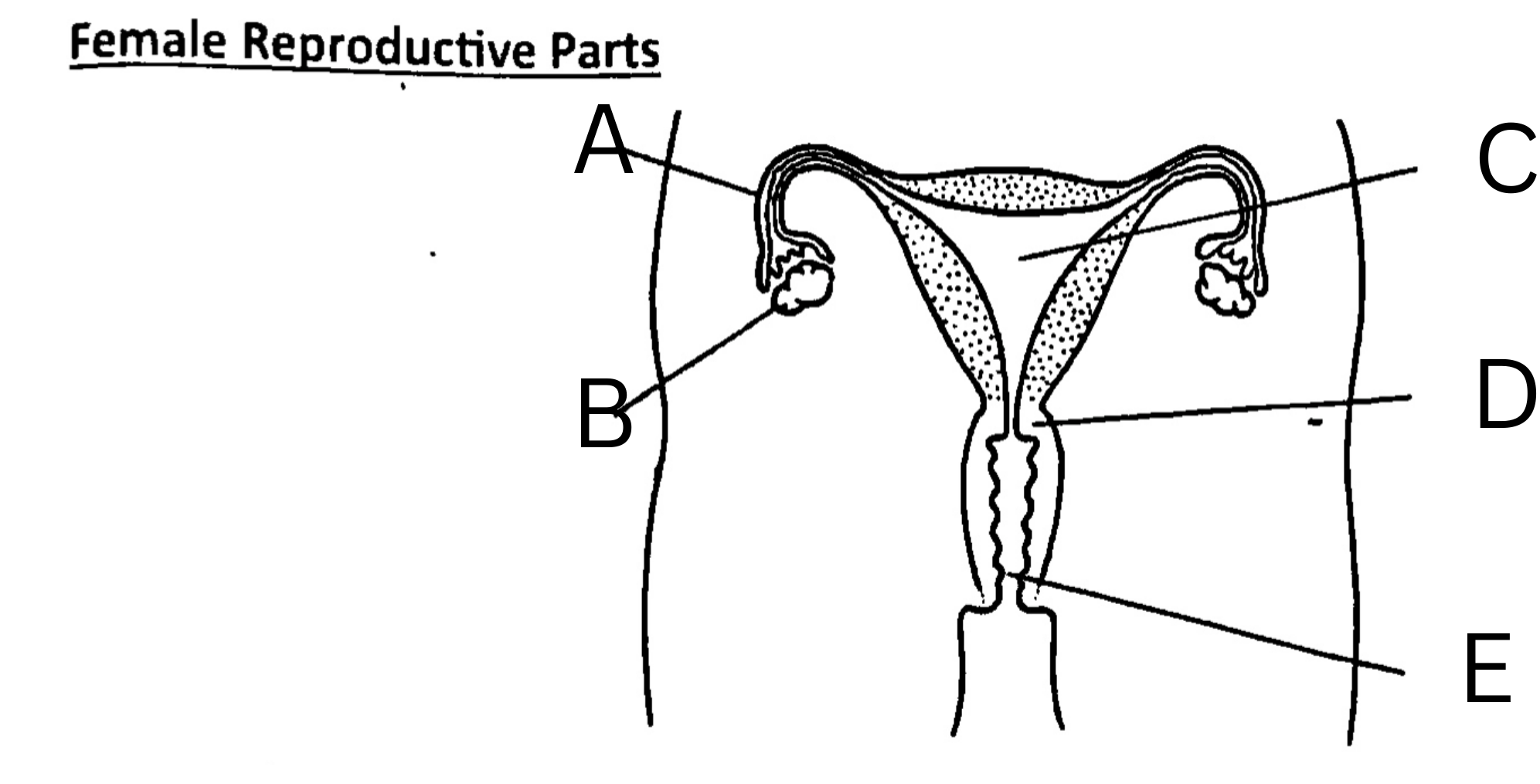
What is D on the diagram?
Cervix
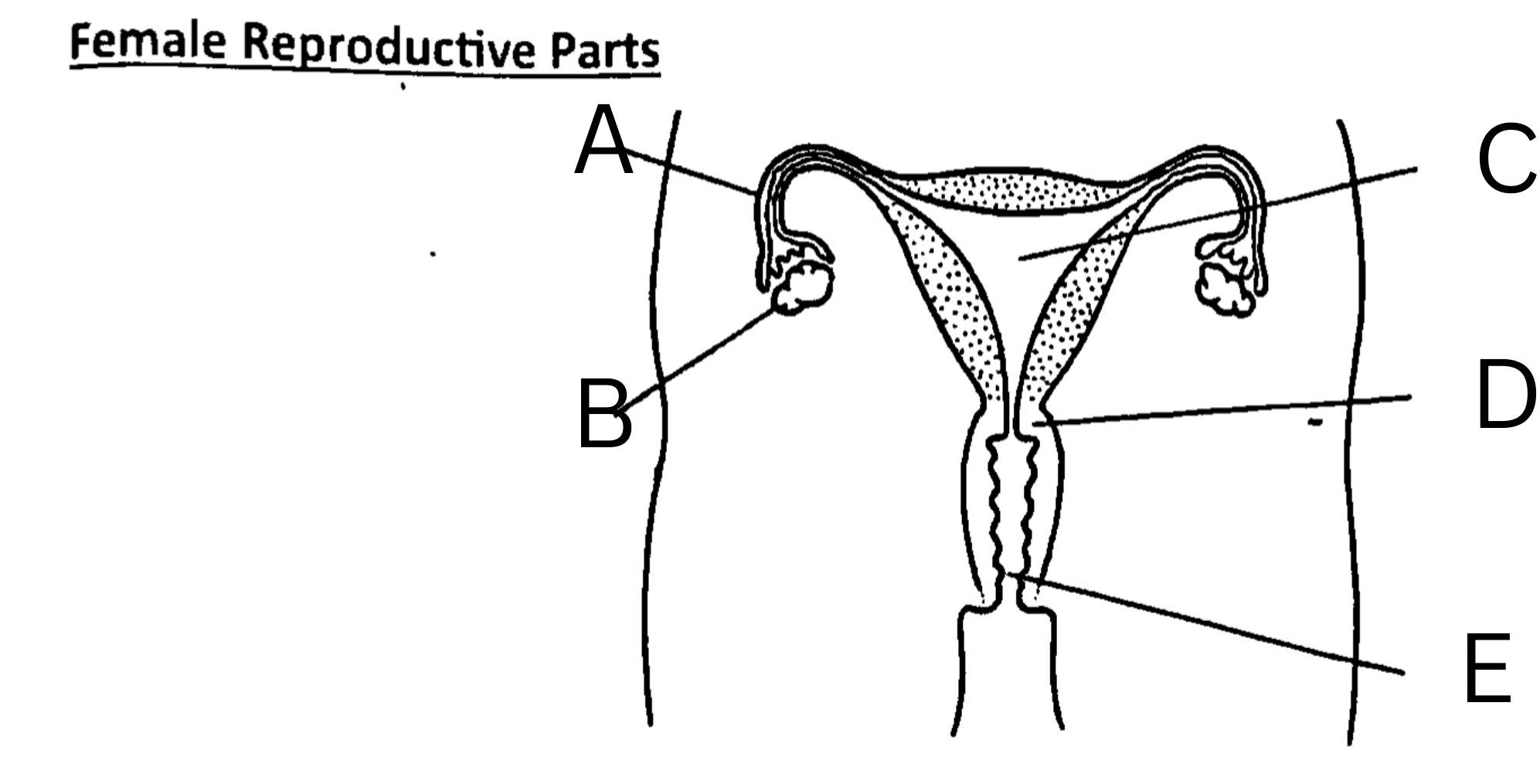
What is E on the diagram?
Vagina
Define vagina:
Tube leading from uterus to outer body
Define cervix:
Neck of the womb that leads to vagina
Define Oviduct (fallopian tubes):
Pair of tubes that lead from the ovaries to the womb
Where does fertilisation take place?
The oviduct/fallopian tubes
What is the tube that leads from the uterus to outside the body?
Vagina
What is the ‘neck of the womb’ that connects the womb to the vagina?
Cervix
What are the tubes that lead from the ovaries to the womb called?
Oviducts/fallopian tubes
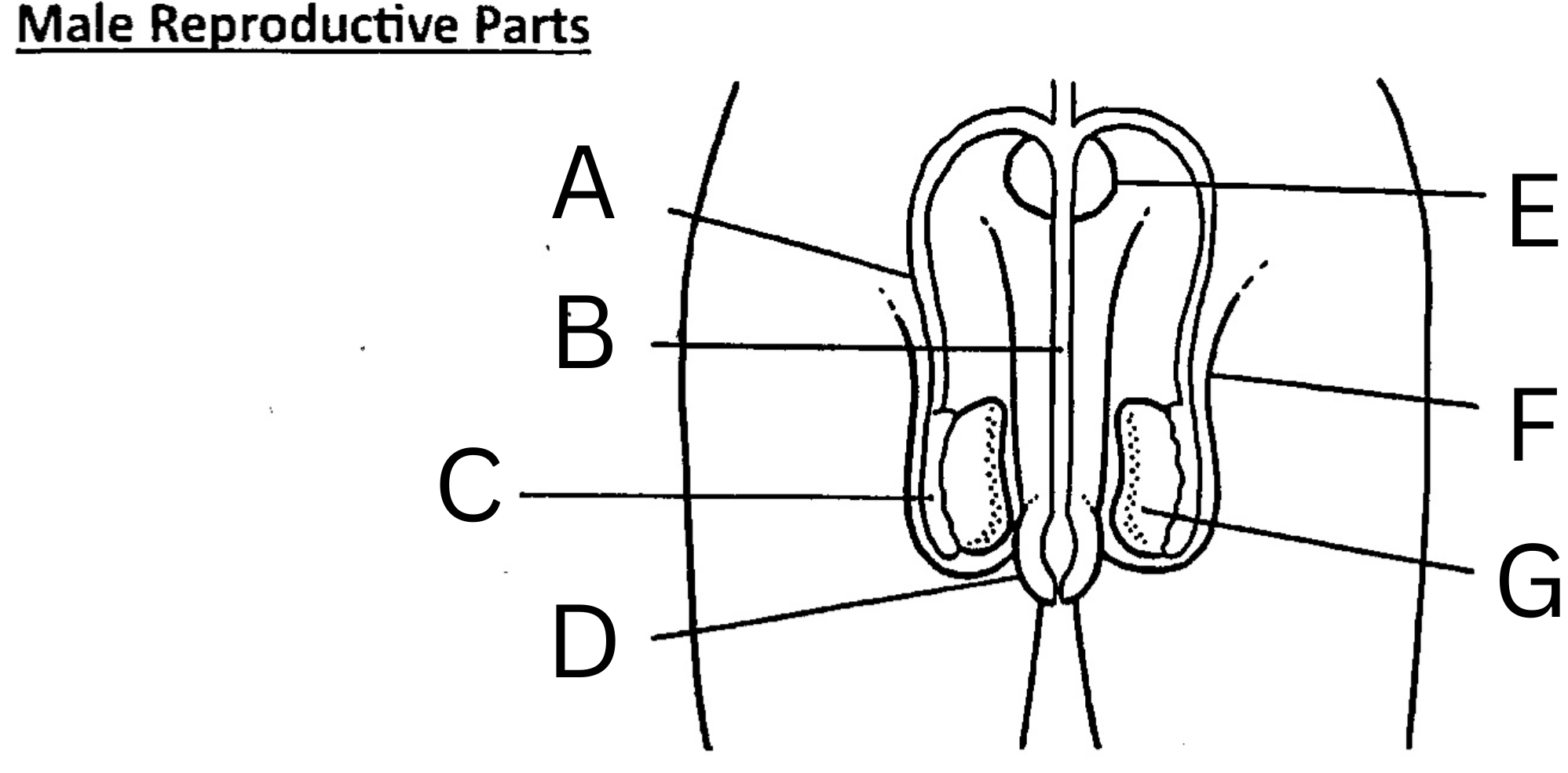
What is A on the diagram?
Vas deferens
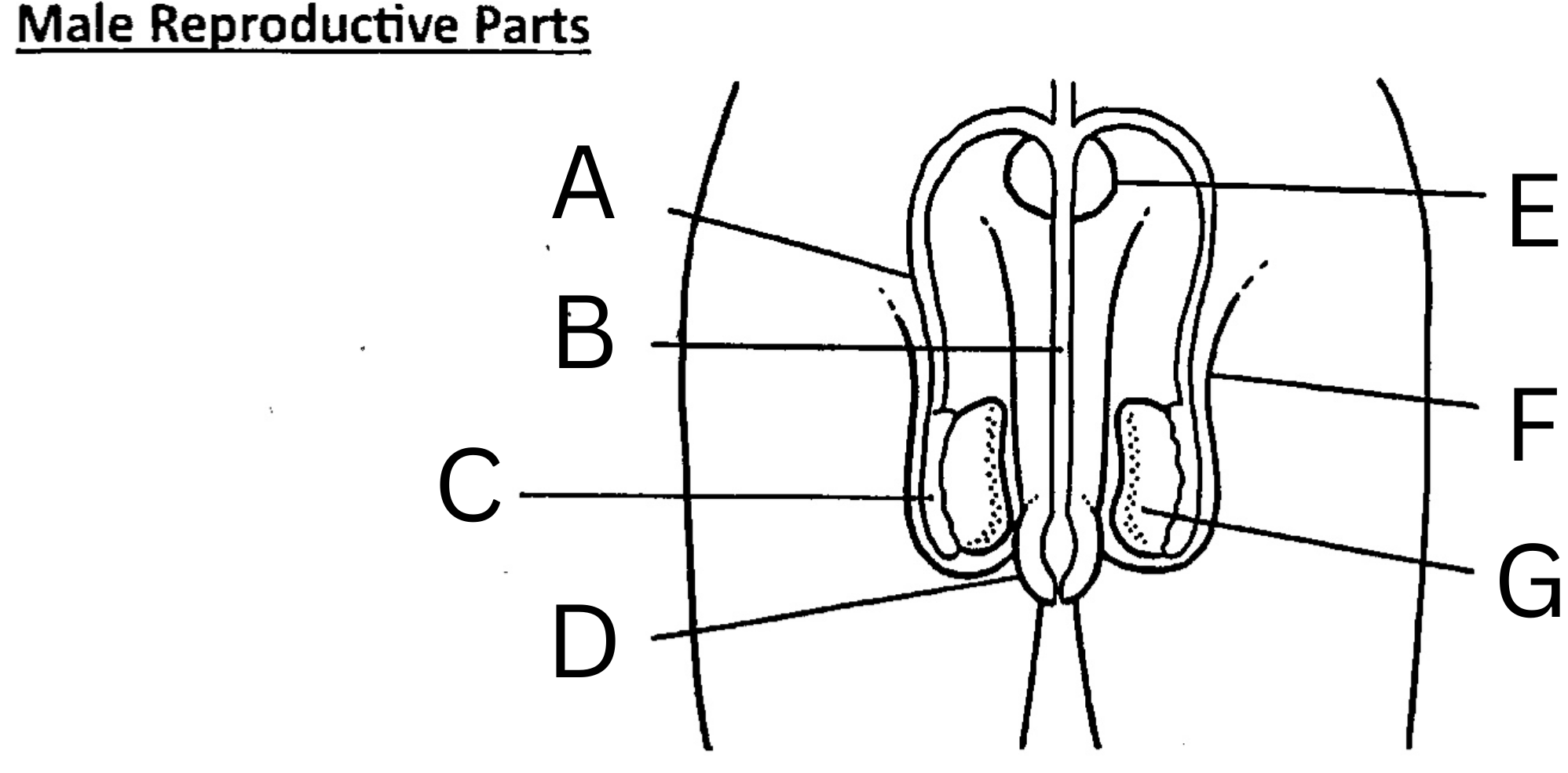
What is B on the diagram?
Urethra
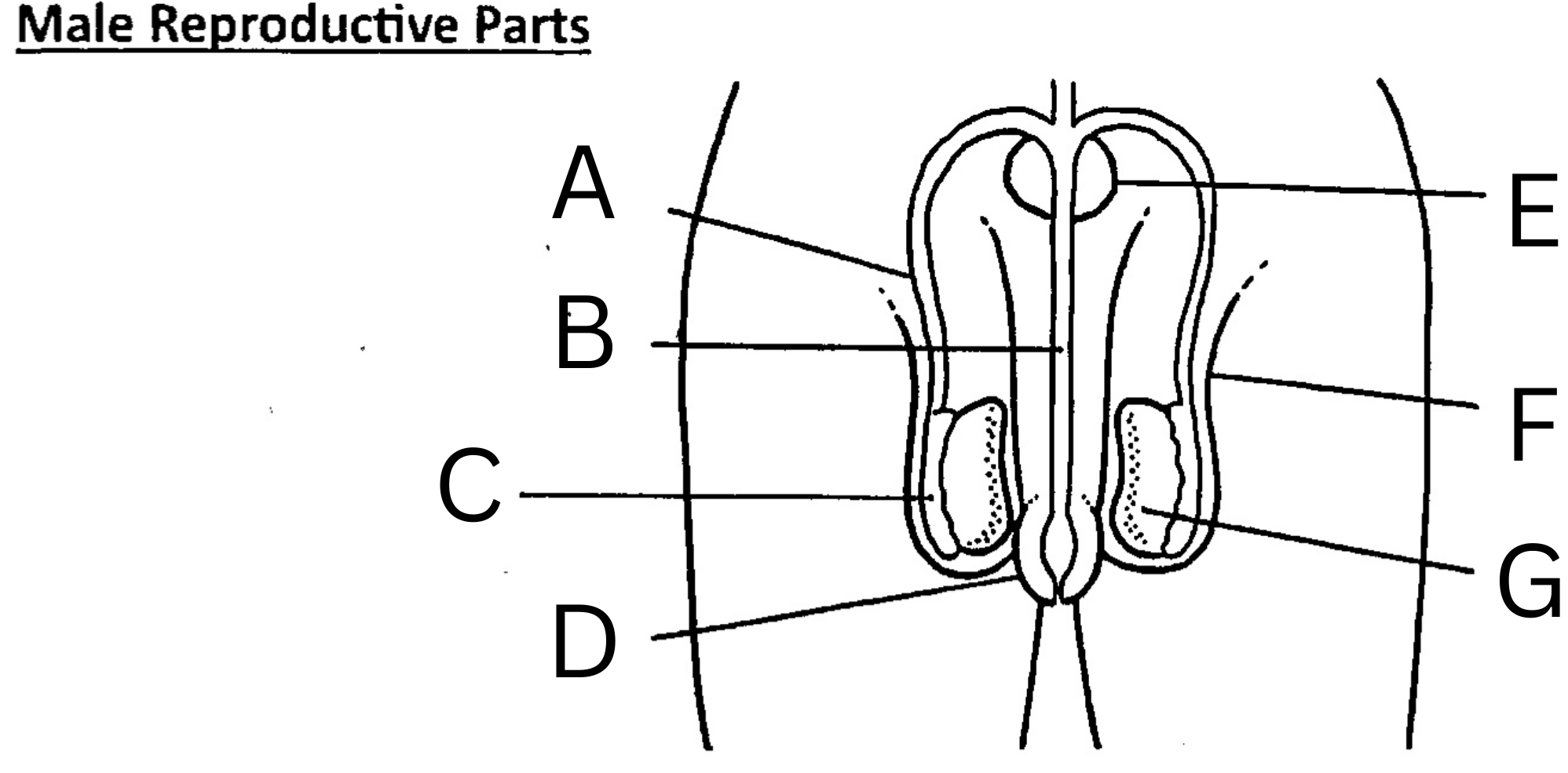
What is C on the diagram?
Epididymis
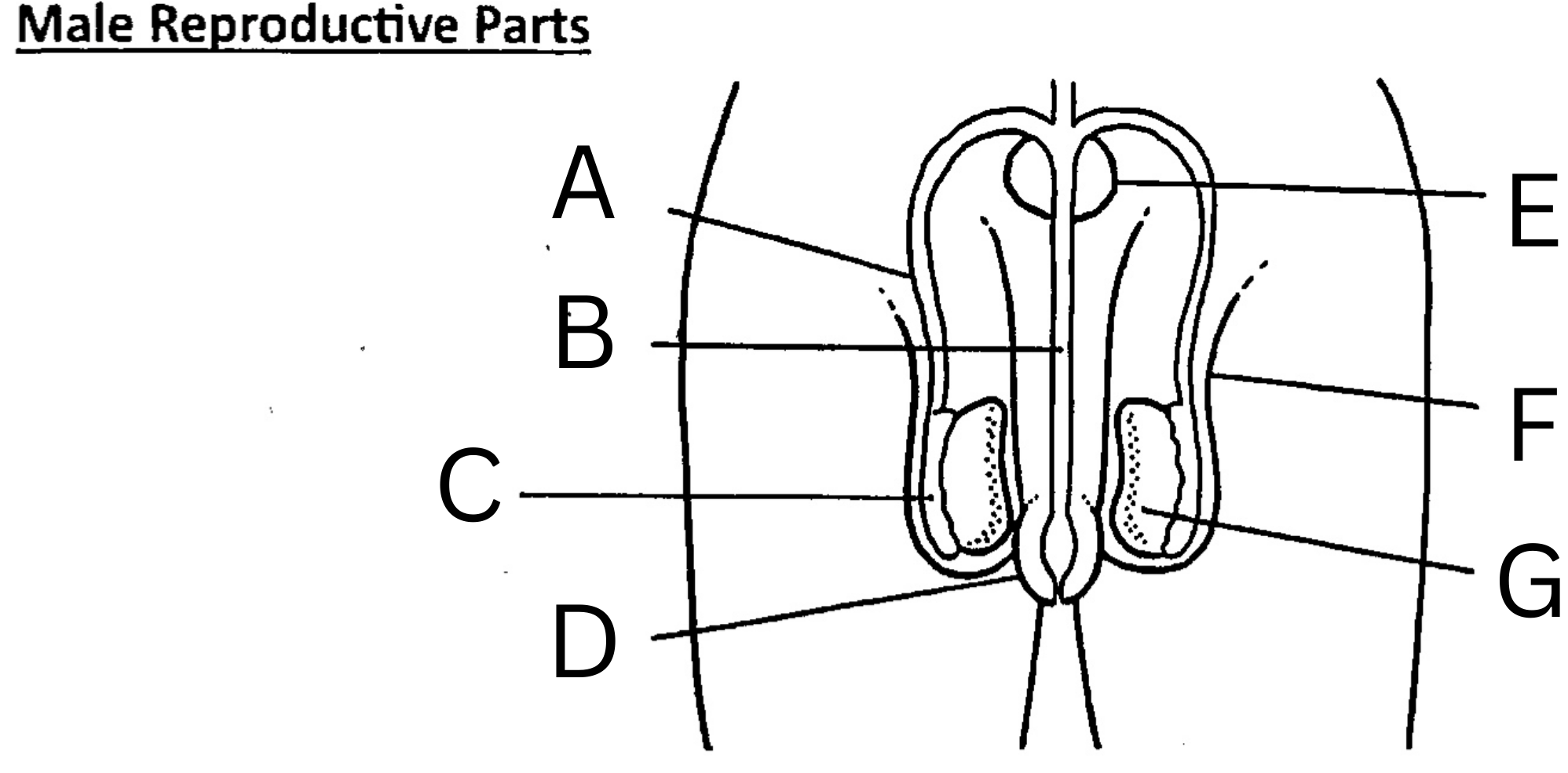
What is D on the diagram?
Foreskin
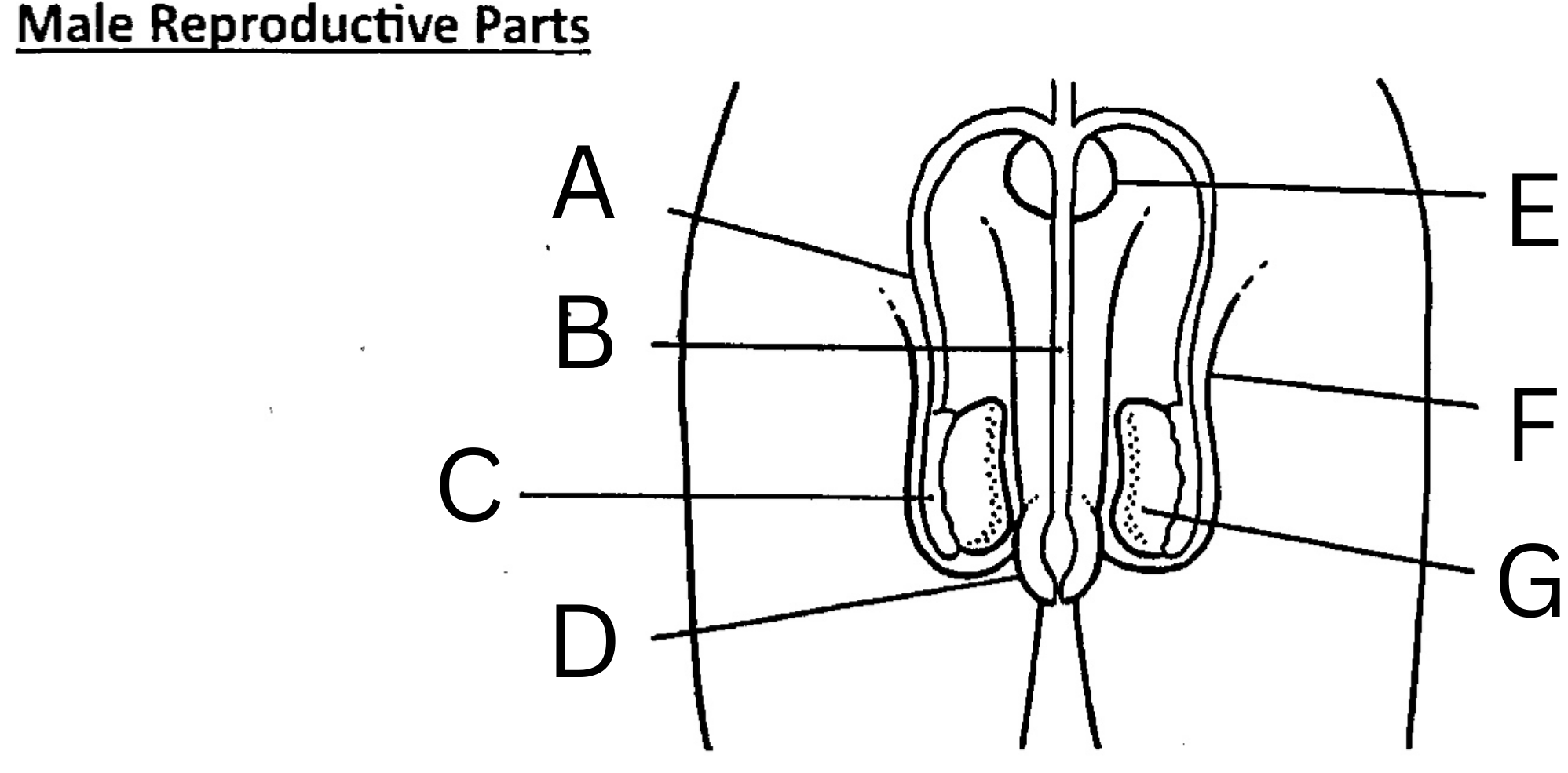
What is E on the diagram?
Prostate gland
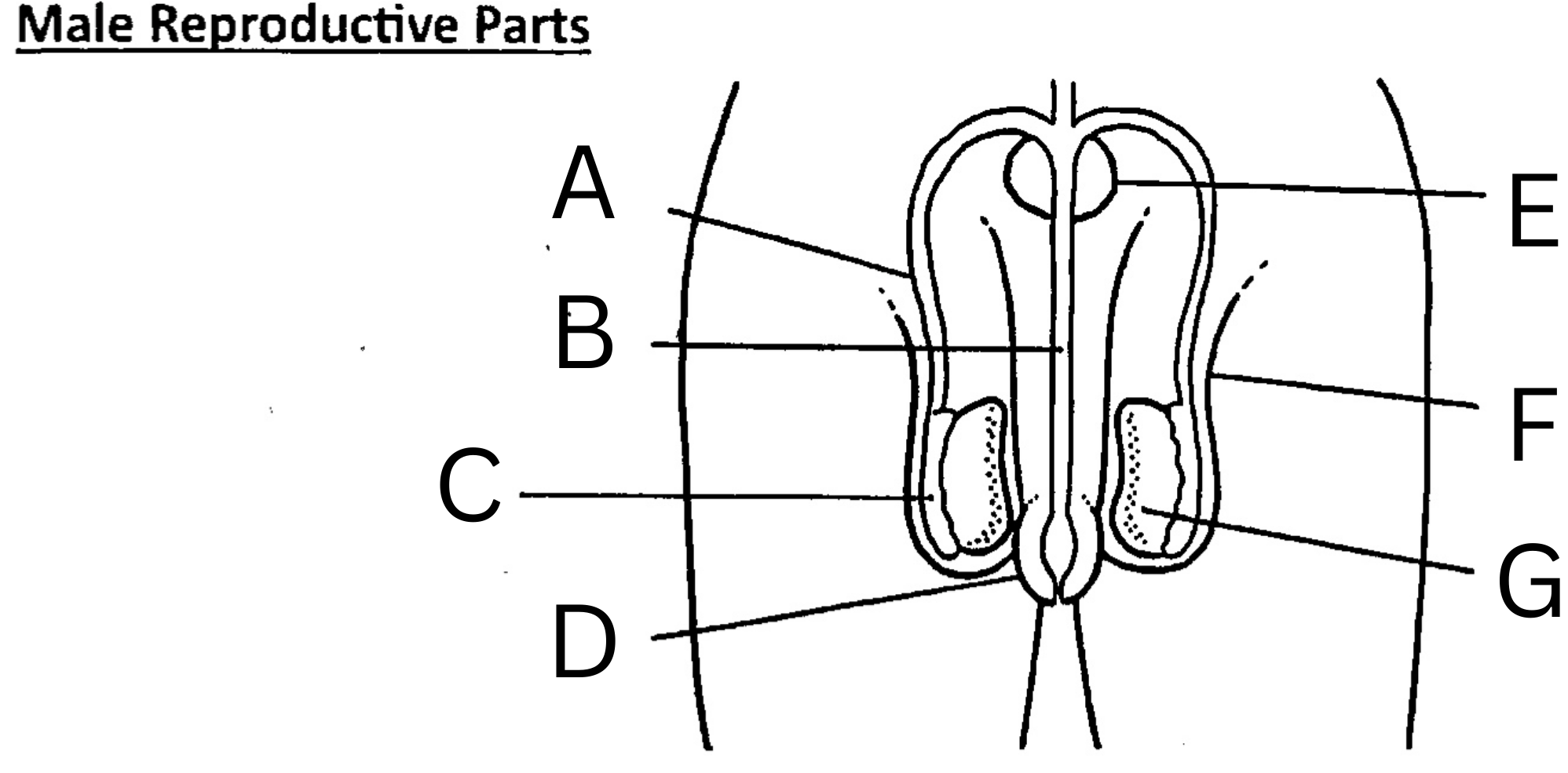
What is F on the diagram?
Scrotum
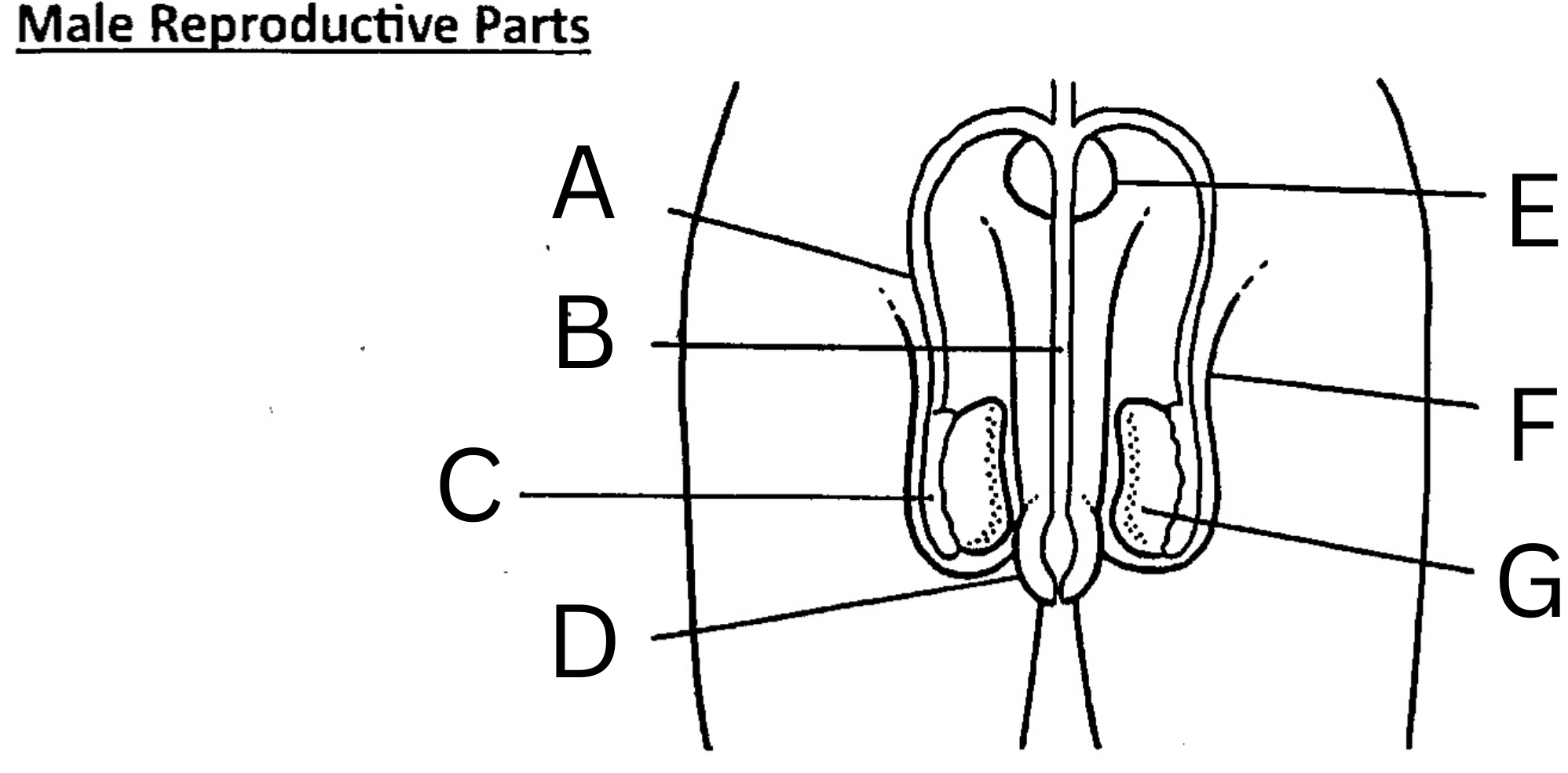
What is G on the diagram?
Testis
What is the plural of testis?
Testes
What is the penis?
Male sex organ
What is the penis used for?
To deliver sperm into female during sexual intercourse; to facilitate urination
Which male sex organ delivers sperm into the female during sexual intercourse?
The penis
What happens when the erectile tissue is filled with blood?
The penis is erect
What fills the penis to make it erect?
Blood
What do the testes do?
Produce sperm
What male reproductive part produce sperm?
The testes
What is the scrotum?
Sac of skin that holds testes
Why are the testes carried outside the body?
Sperm production requires lower temperature
What is the vas deferens?
Tube that carries sperm out of the testes
What is the tube that carries sperm out of the testes called?
Vas deferens
What is the epididymis?
Where sperm are stored after production
Where are sperm stored after production?
The epididymis
What is the urethra?
Tube that carries urine and sperm to the outside
What do the seminal vesicles do?
Makes the fluid sperm swim in
What is the tube that carries sperm and urine to the outside?
Urethra
What makes the fluid that sperm swim in?
Seminal Vesicles
What do the prostate gland do?
Secretes semen (with sugar)
Define semen:
A fluid containing both sperm and nourishing substances
What is the gland that secretes semen with sugar?
Prostate gland
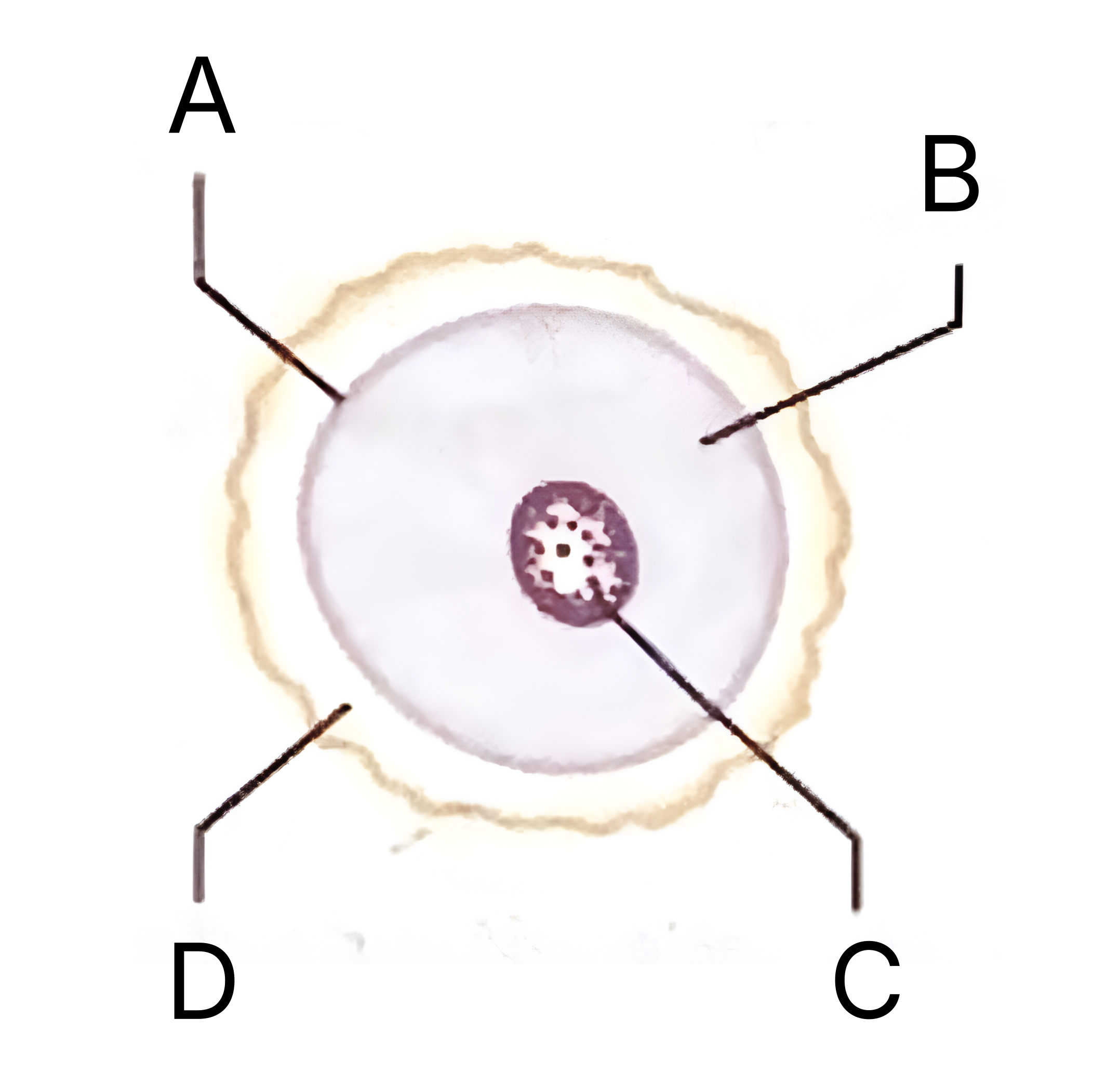
What is A on the egg cell diagram?
Cell membrane
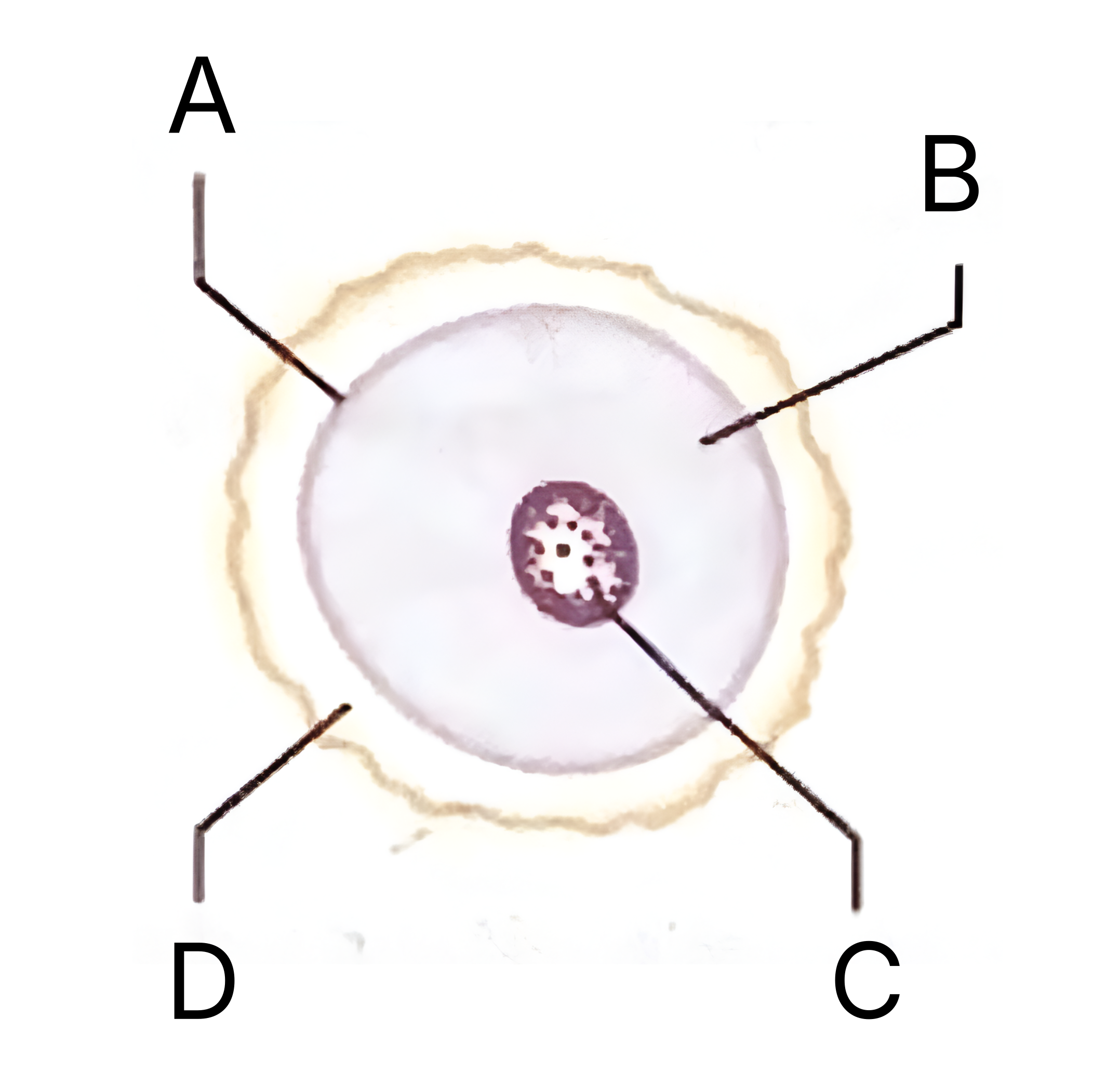
What is B on the egg cell diagram?
Cytoplasm
In an egg cell, what does the cytoplasm contain?
A yolk
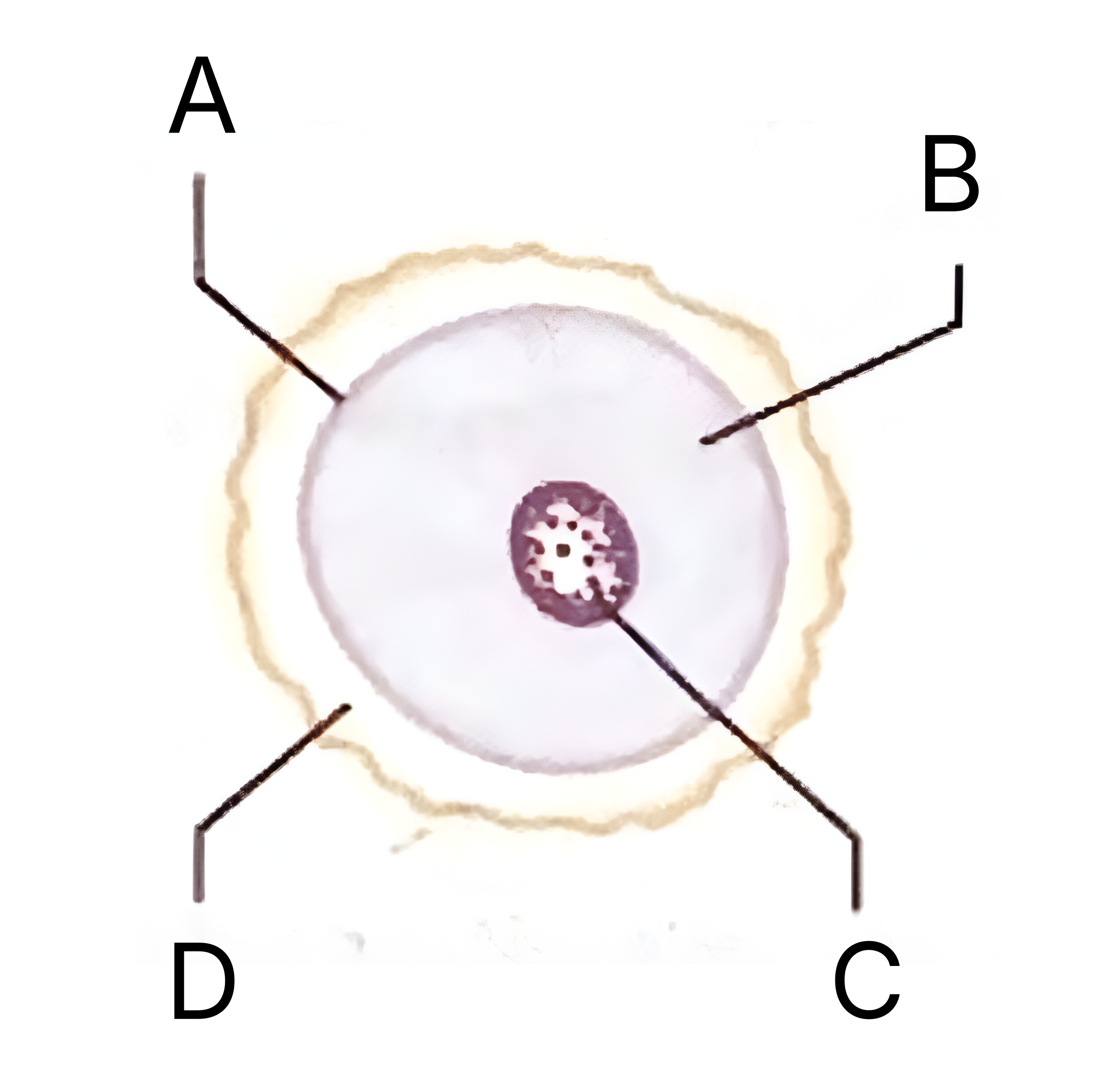
What is C on the egg cell diagram?
Nucleus
What does the nucleus in an egg cell contain?
Chromosomes
How many chromosomes do egg/sperm cells have each?
23
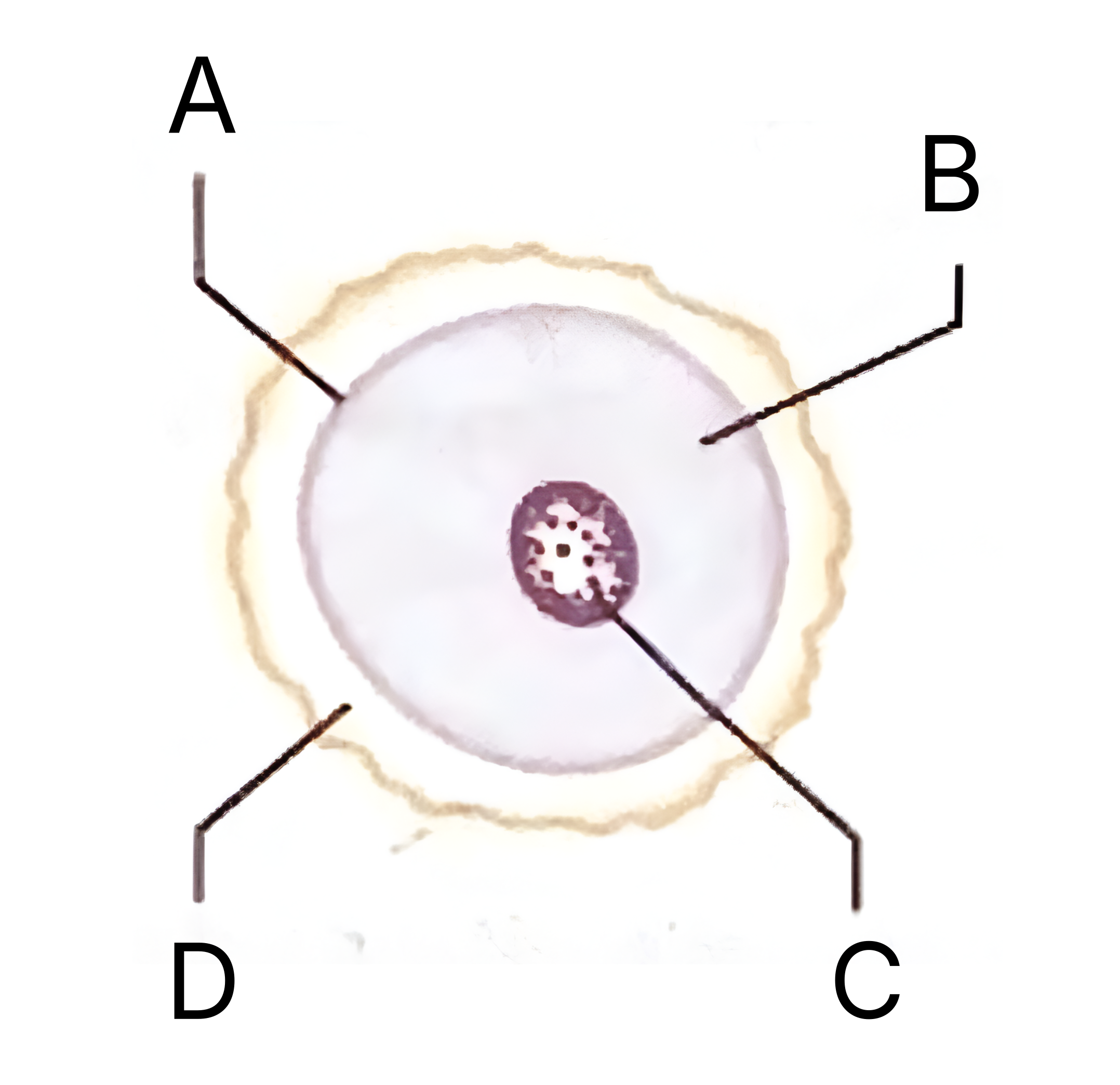
What is D on the egg cell diagram?
Layer of jelly
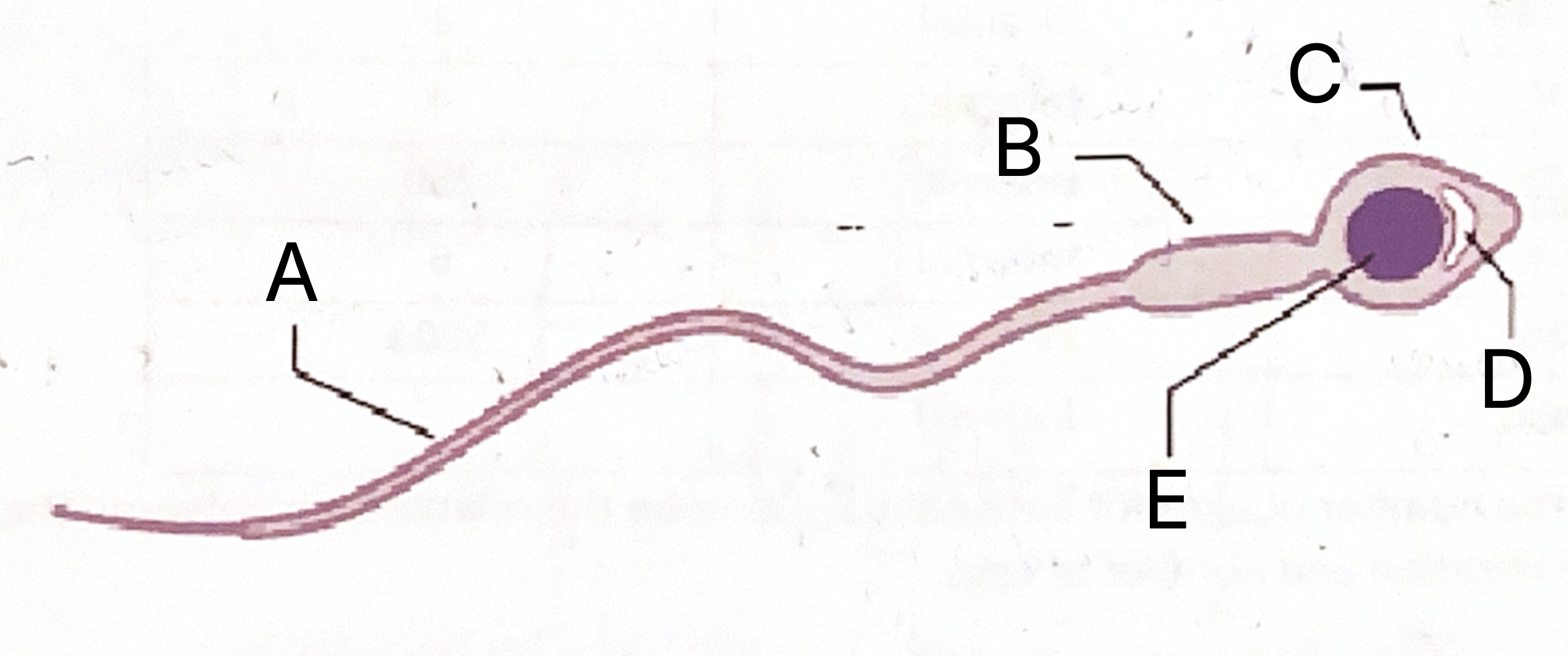
What is A on the sperm cell diagram?
Flagellum
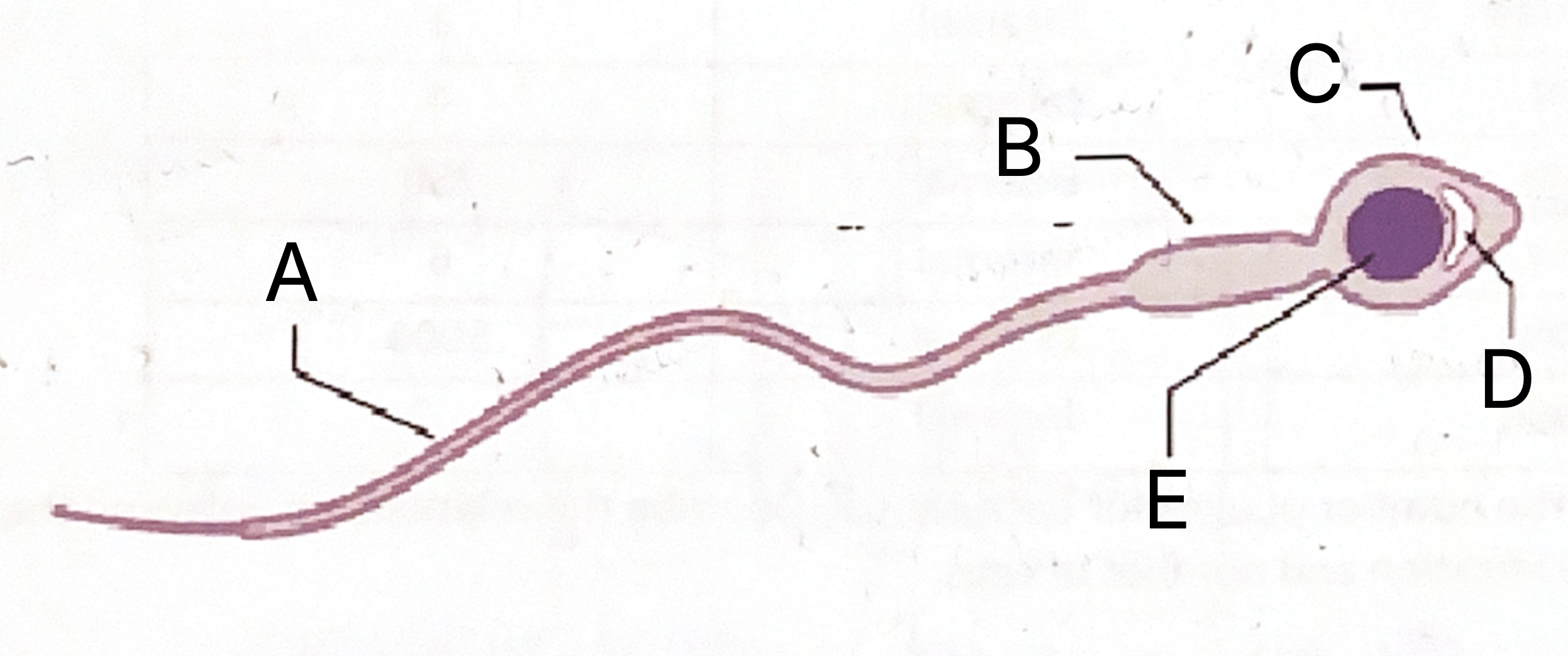
What is B on the sperm cell diagram?
Middle piece
What does the middle piece contain?
Mitochondria
Which part of the sperm contains mitochondria?
Middle piece
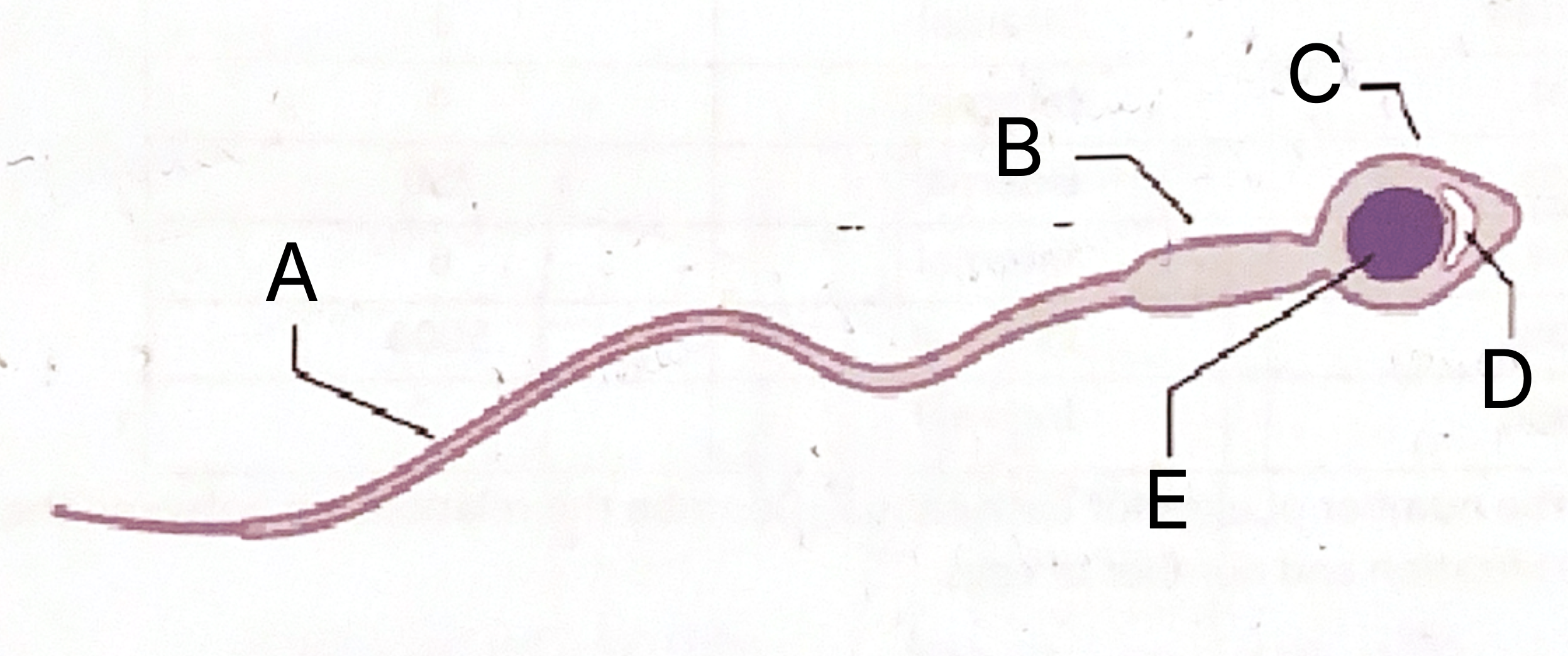
What is C on the sperm cell diagram?
Acrosome
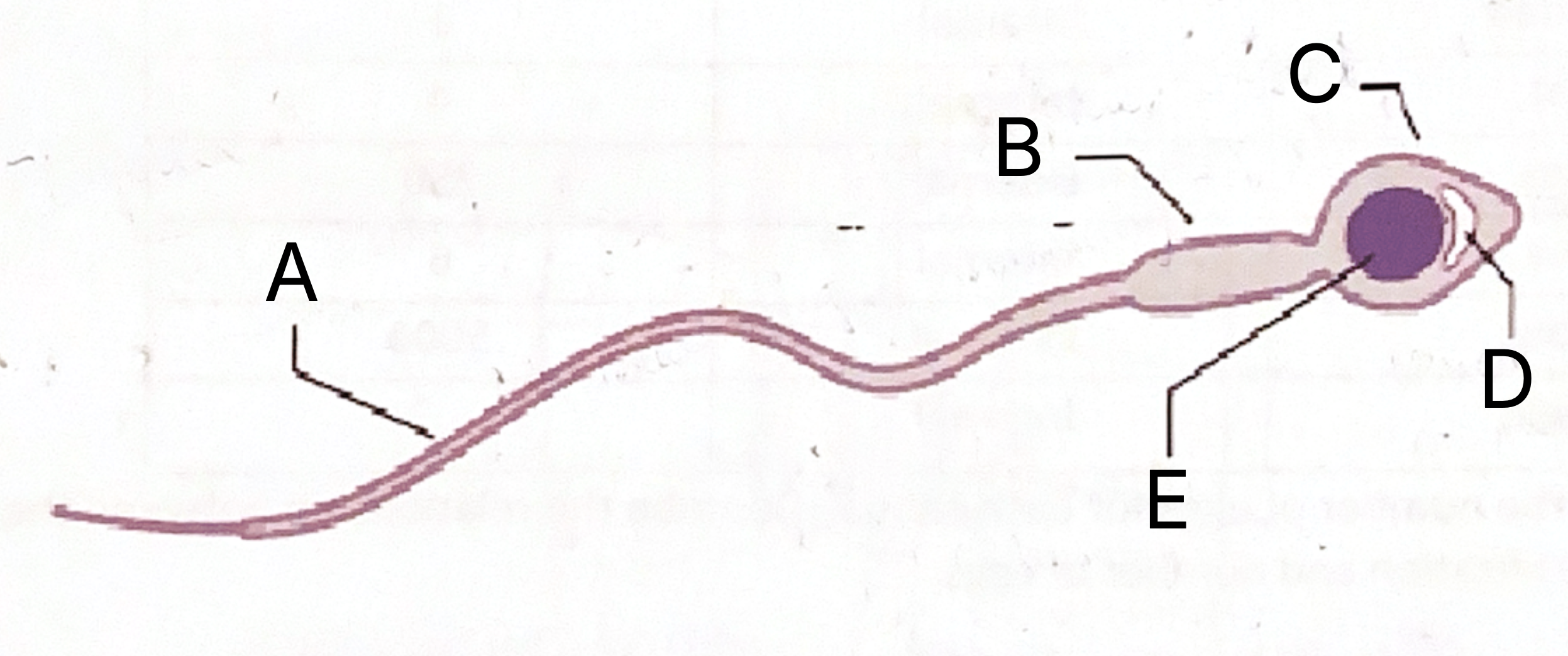
What is D on the sperm cell diagram?
Vesicle
What does the sperm vesicle contain?
Enzymes
What do sperm enzymes do?
Dissolve into egg
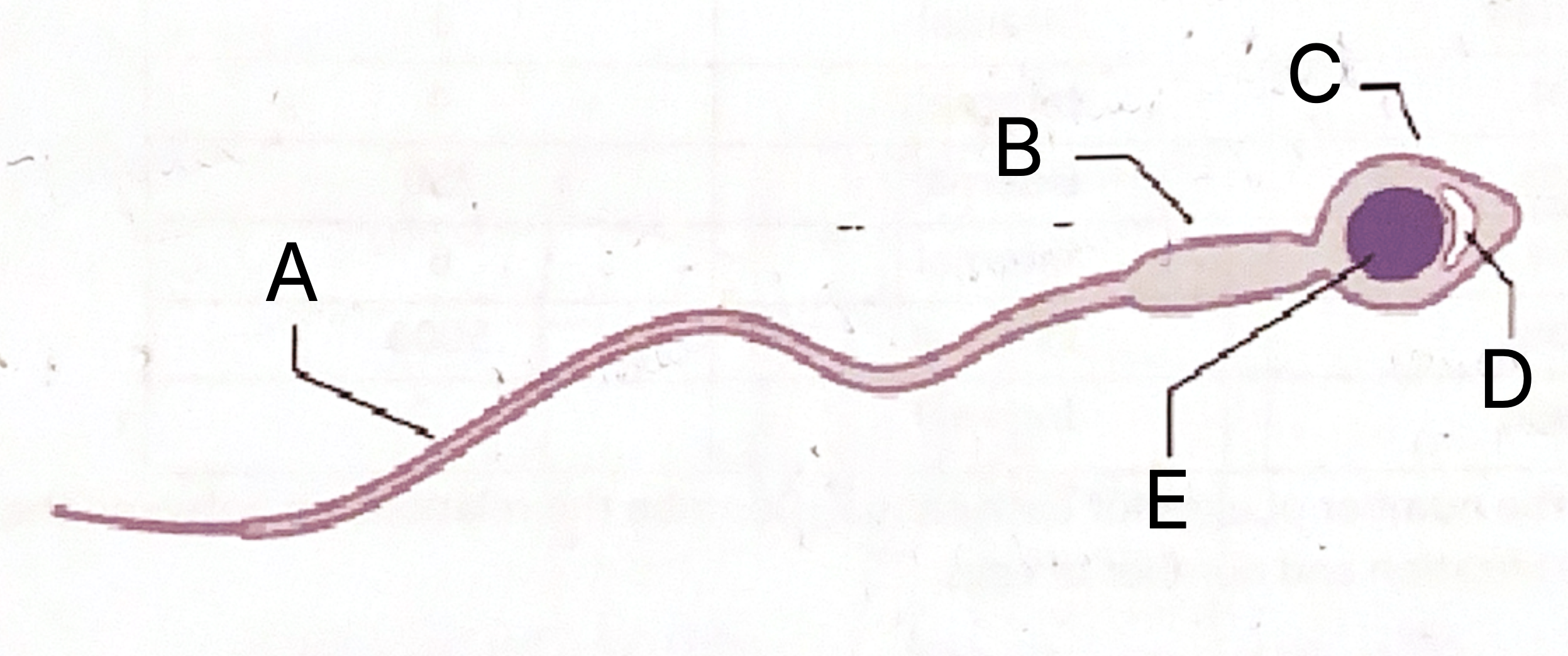
What is E on the sperm celldiagram?
Nucleus
How many mm are in a m?
1000 mm
How many μm are in a mm?
1000 μm
How many nanometres are there in a μm?
1000 nm
What is μm short for?
Micrometre
What is mm short for?
Millimetre
What is m short for?
Metre
What is nm short for?
Nanometre
What does the term microbe refer to?
Microscopic organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
What are bacteria?
Unicellular (single-celled) organisms.
Where are bacteria found?
Almost everywhere.
How do bacteria reproduce?
By binary fission.
Define binary fission
Splitting in two
Can bacteria survive extreme conditions?
Yes
How do bacteria obtain food?
Some photosynthesise, but most live on or in their food.
Are all bacteria harmful?
No, many are harmless or even useful, but some cause diseases.
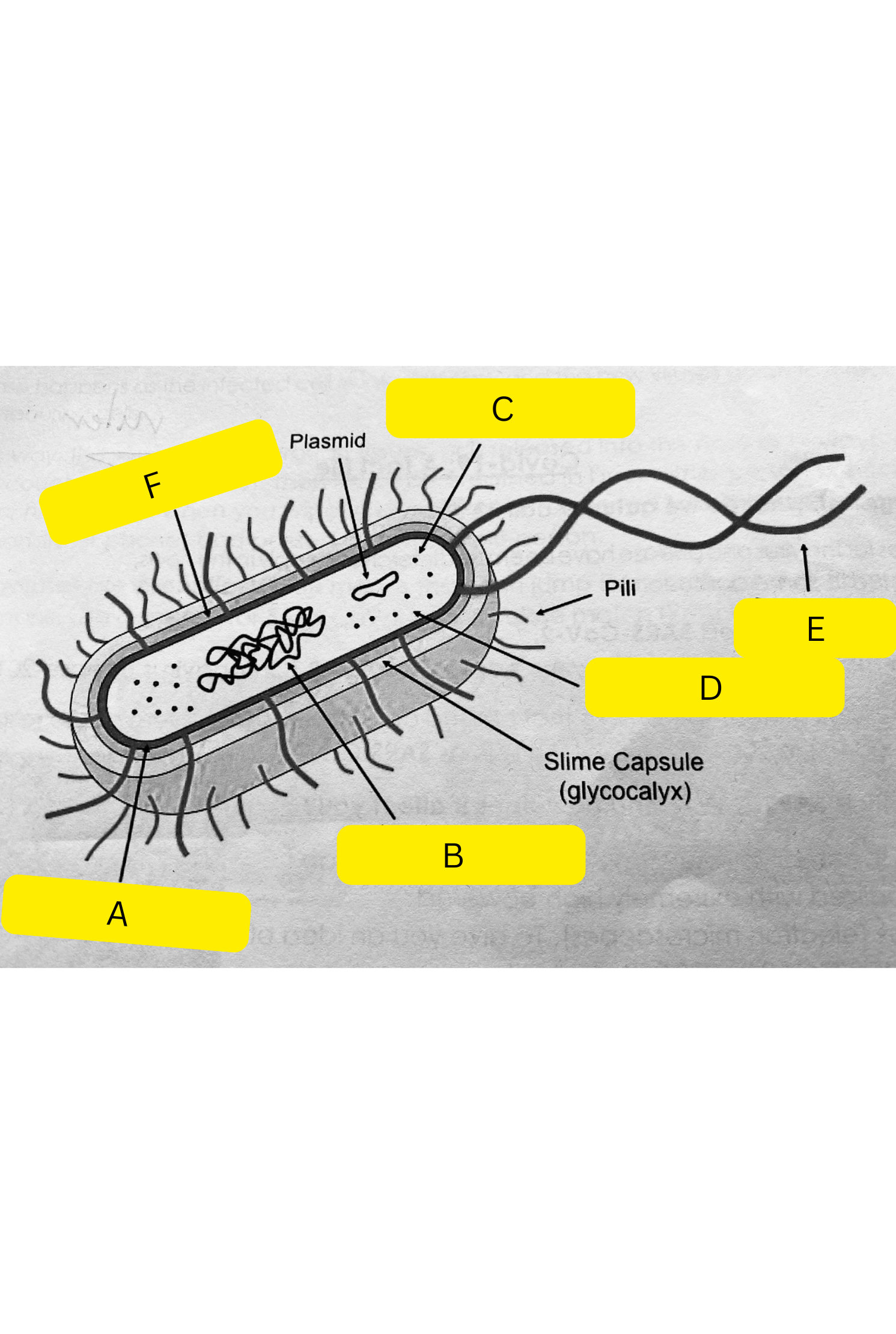
What is A on the bacterium diagram?
Cell membrane
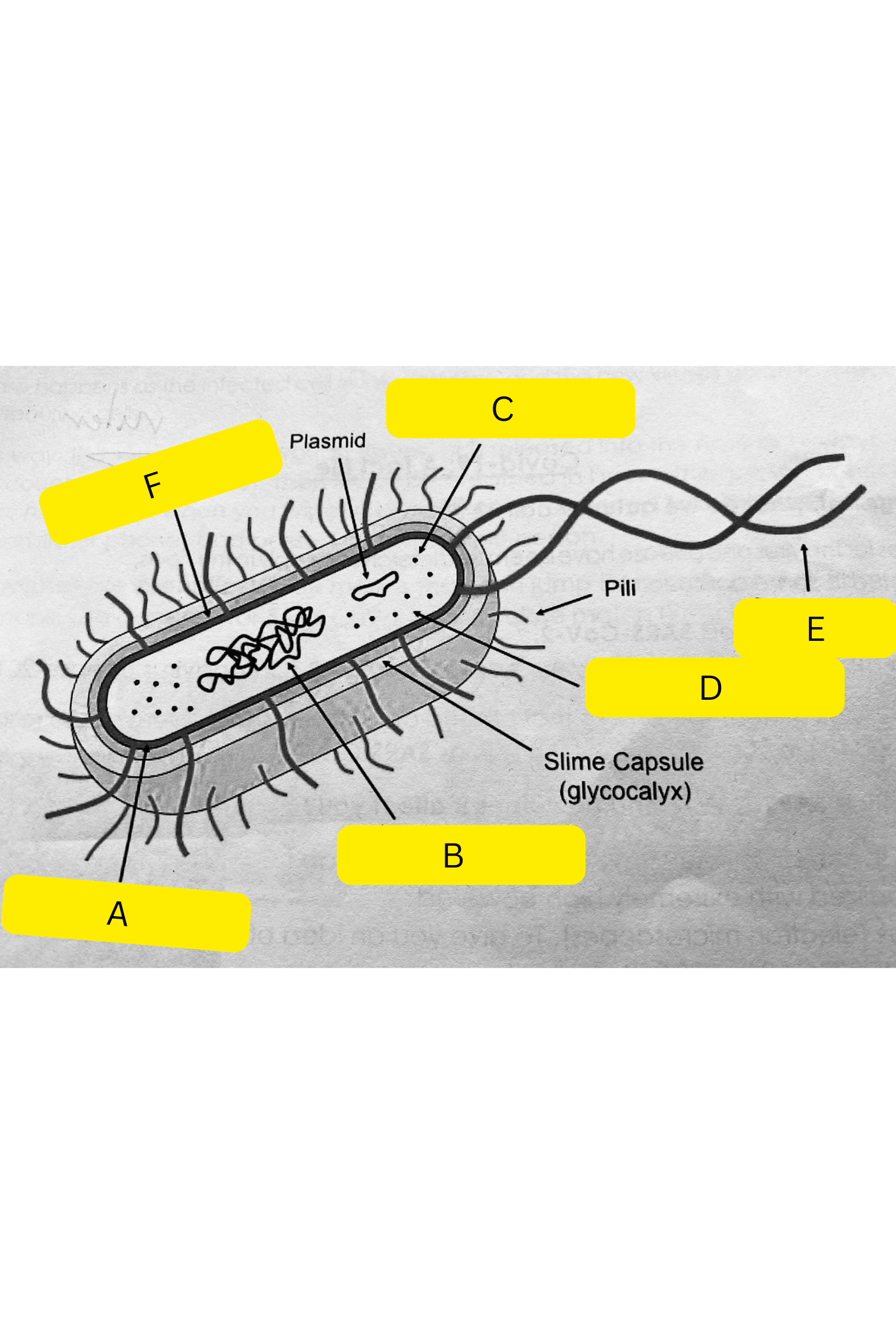
What is B on the bacterium diagram?
Nucleoid
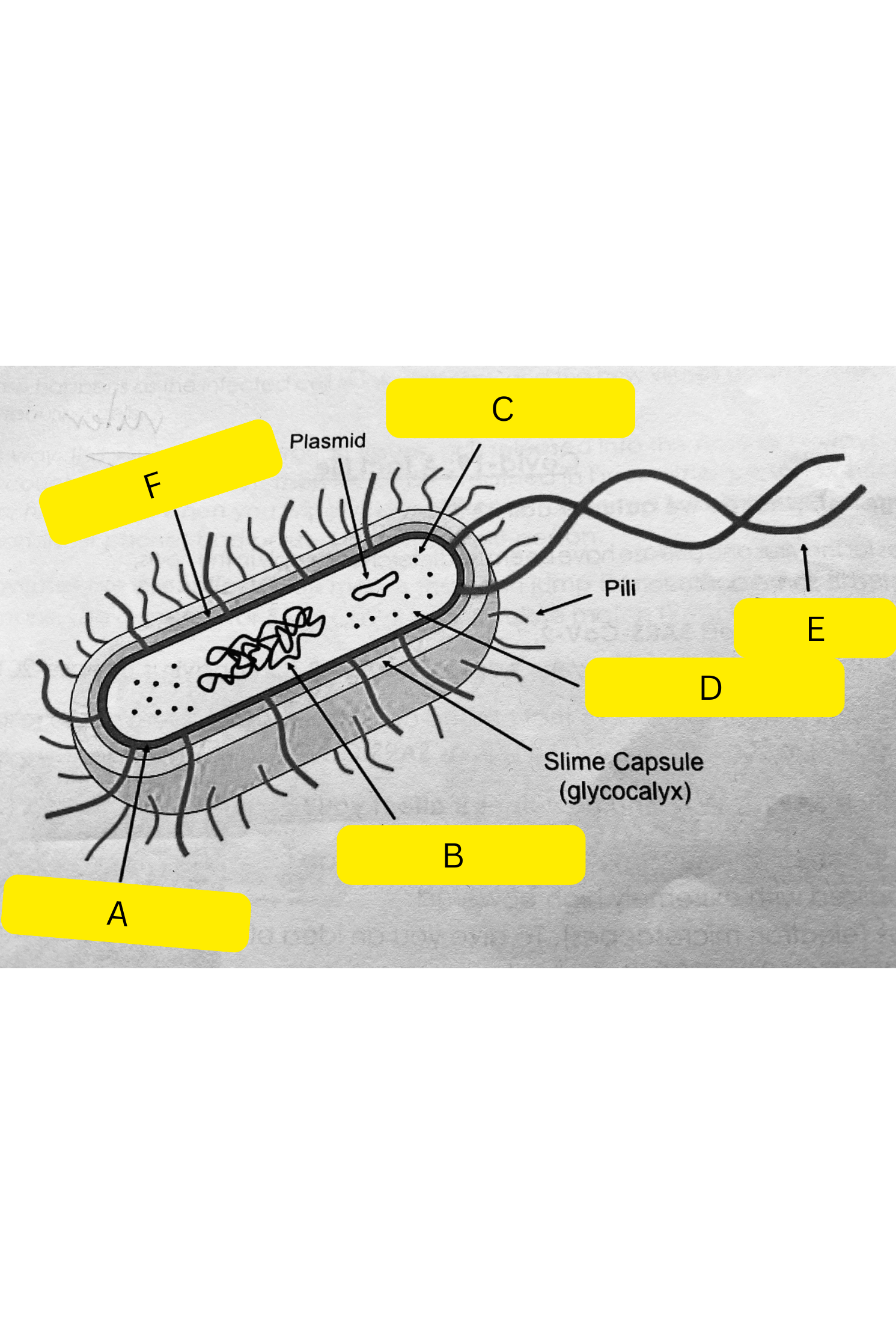
What is C on the bacterium diagram?
Ribosomes
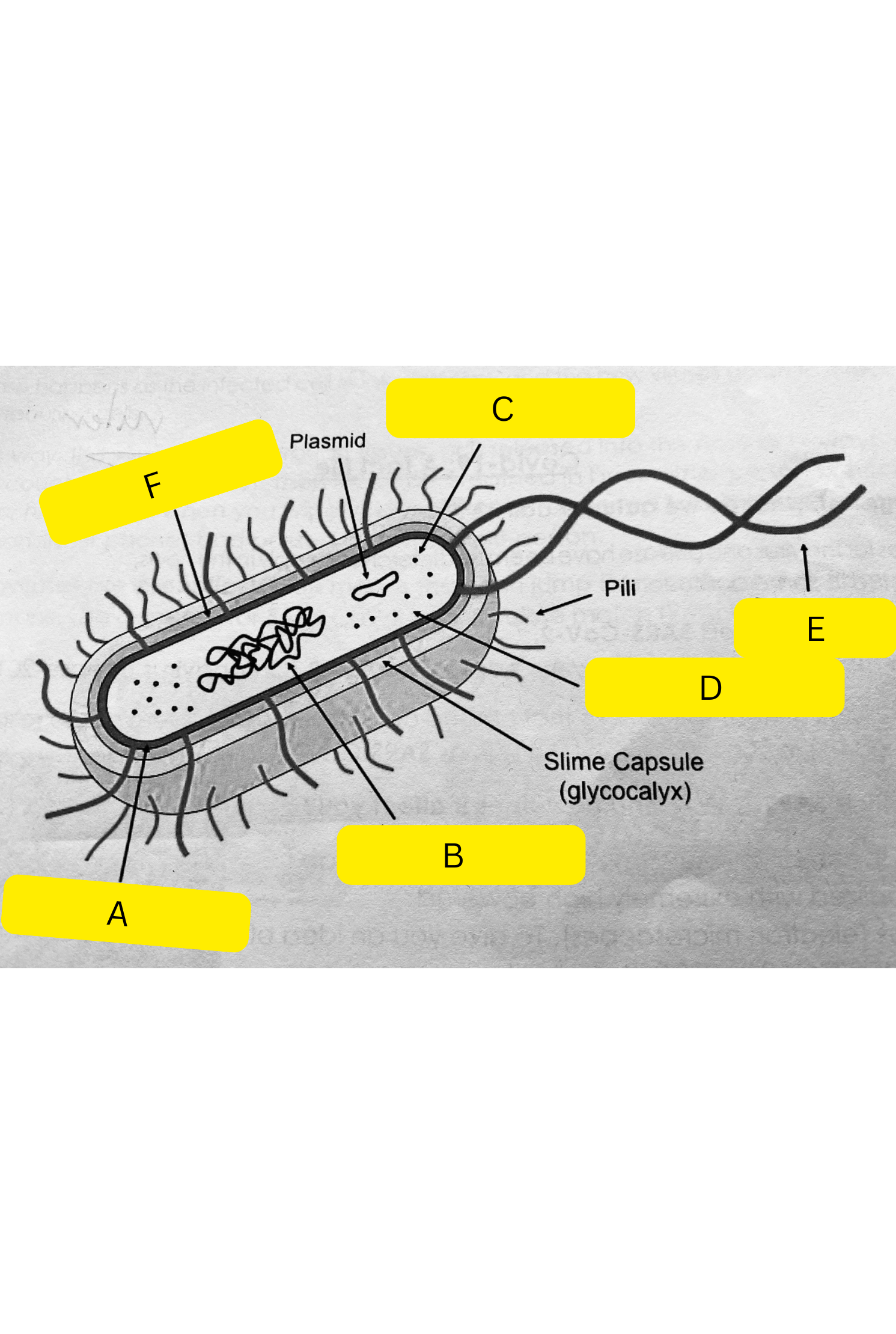
What is D on the bacterium diagram?
Cytoplasm

What is E on the bacterium diagram?
Flagellum
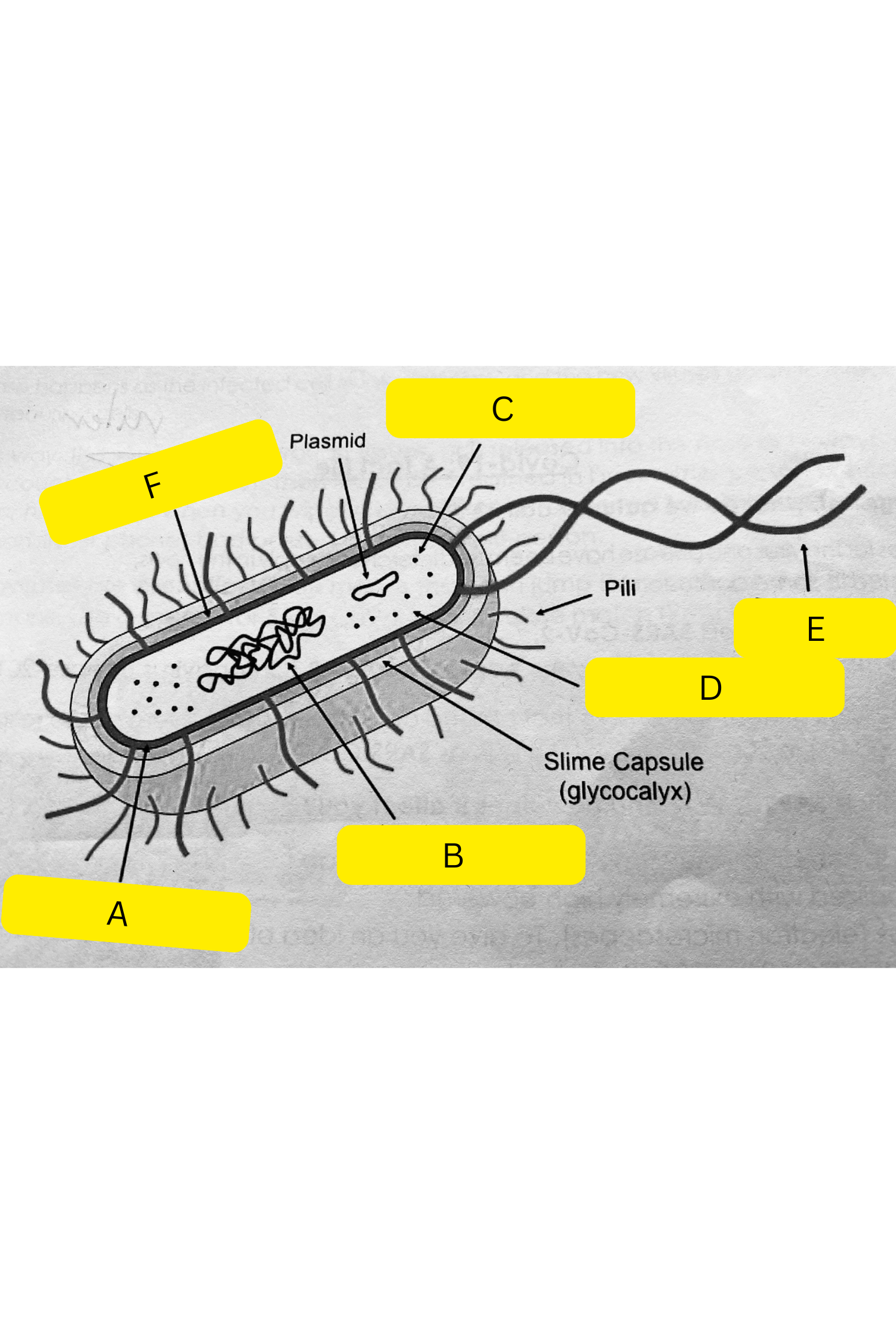
What is F on the bacterium diagram?
Cell wall
Are viruses living organisms?
No, viruses are not considered living.
Which characteristics of life do viruses show?
Reproduction, though this is inside a host cell only.
How do viruses reproduce?
By infecting a host cell and using it to make more viruses.
Which types of living organisms can viruses infect?
All types
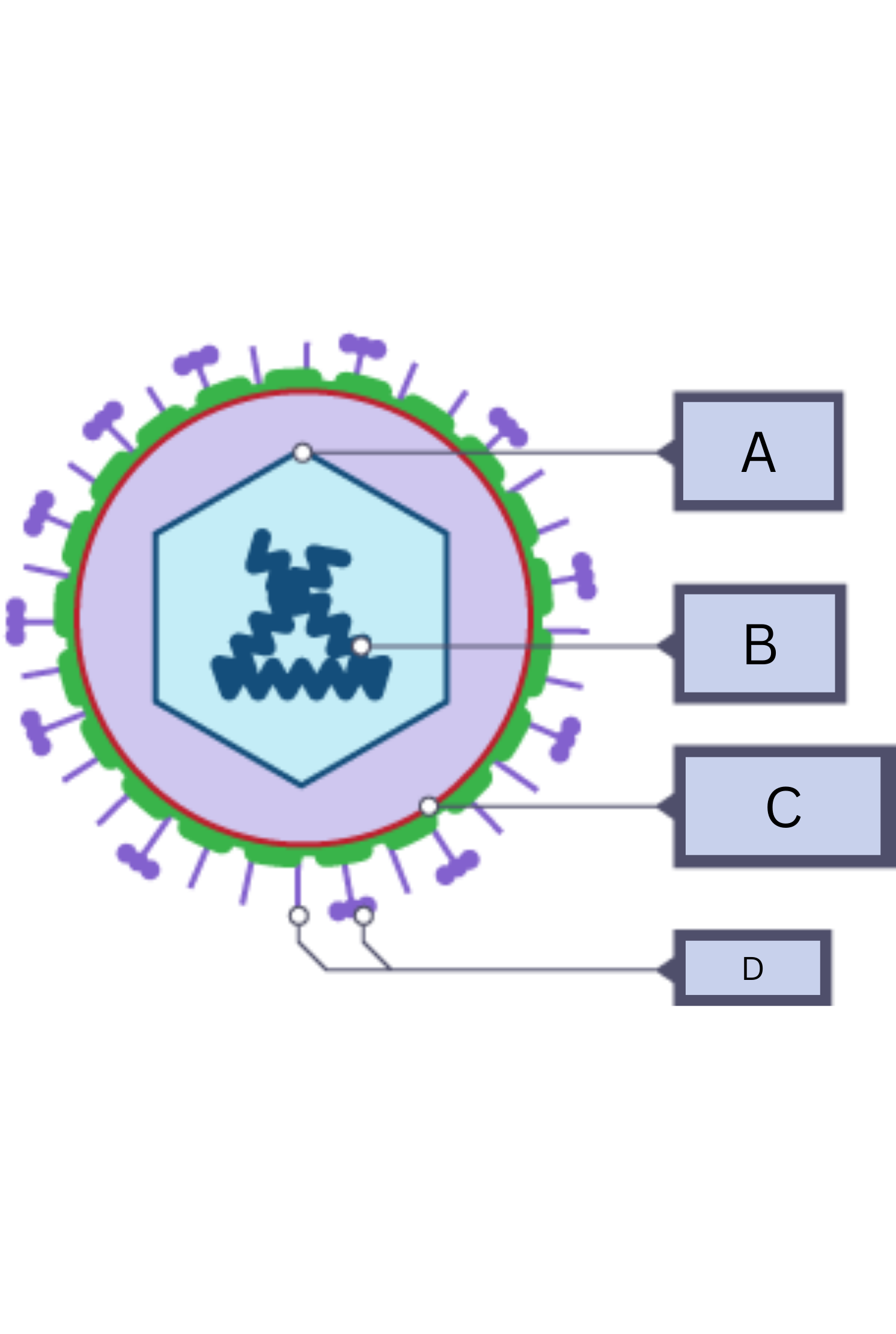
What is A on the virus diagram?
Protein coat
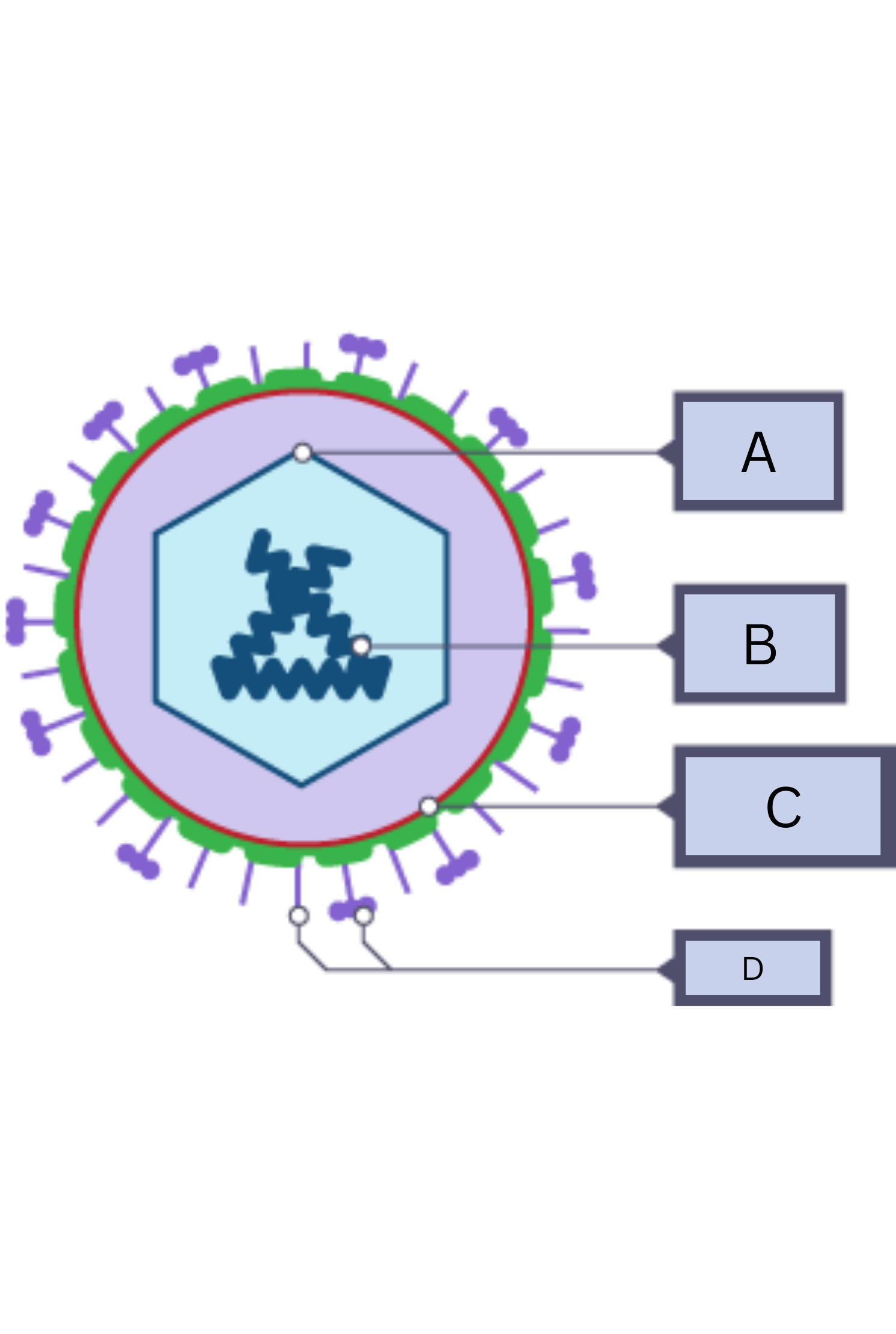
What is B on the virus diagram?
Nucleic Acid/RNA
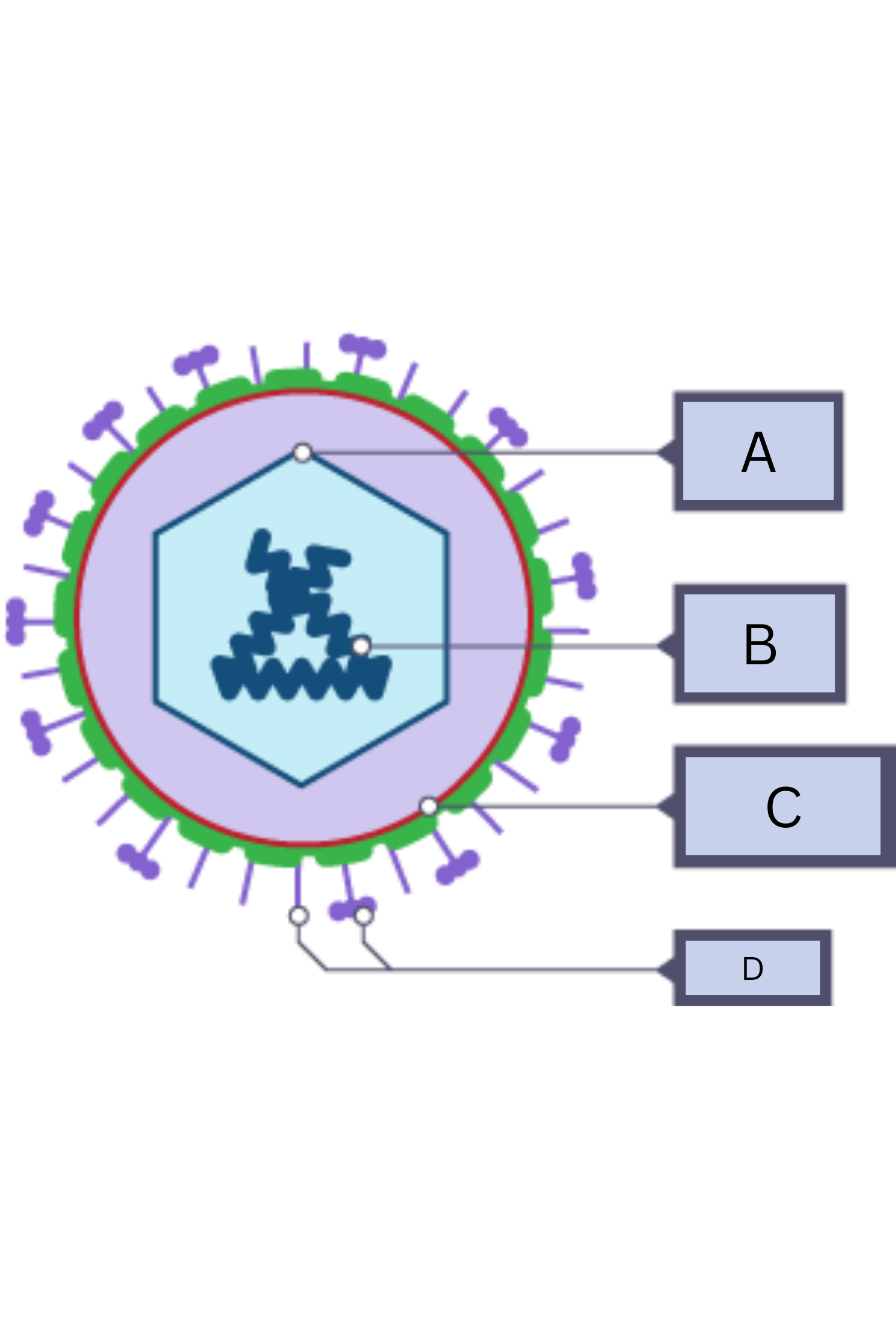
What is C on the virus diagram?
Membrane envelope
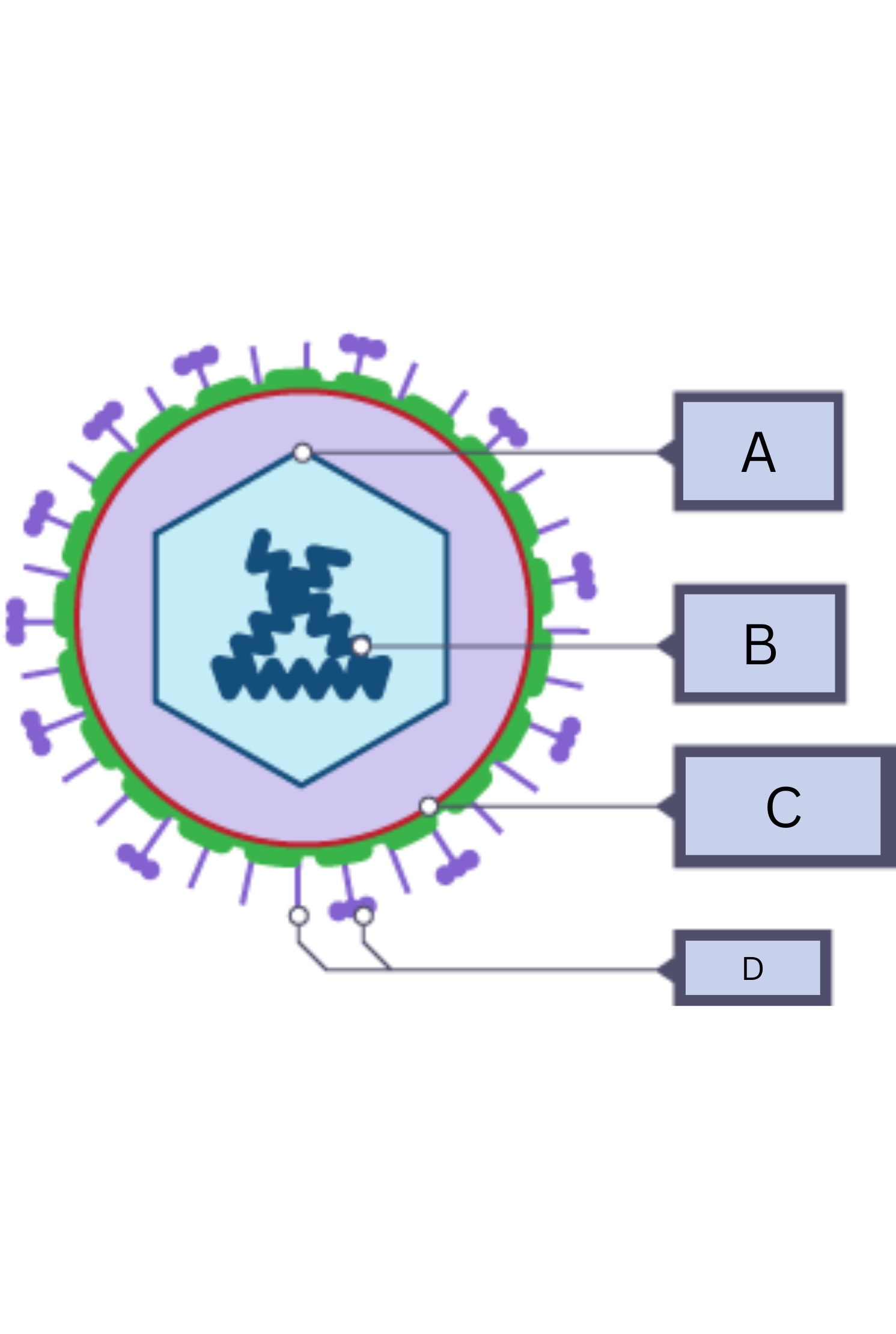
What is D on the virus diagram?
Spikes
Are fungi multicellular or unicellular?
Some fungi are unicellular, others are multicellular.
What are fungal cell walls made of?
Chitin
How do fungi feed?
Extracellularly by releasing digestive enzymes onto their food.
What is saprophytic nutrition?
A feeding method where dead material is broken down externally before nutrients are absorbed.
What is the term for organisms that feed saprophytically?
Saprophytes
Name some uses of fungi.
Yeast is used to make bread and beer, and Penicillium produces the penicillin antibiotic.
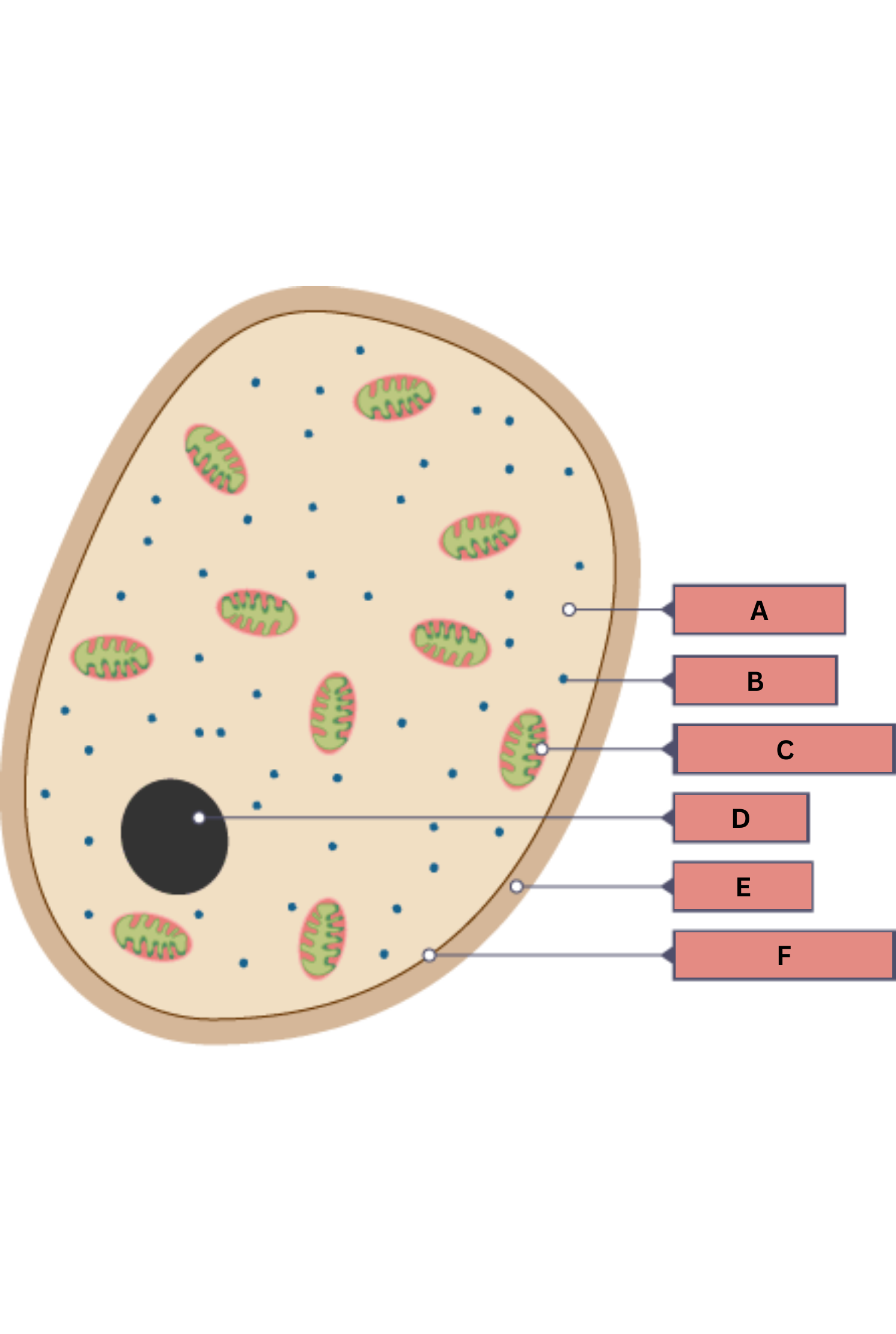
What is A on the fungi diagram?
Cytoplasm
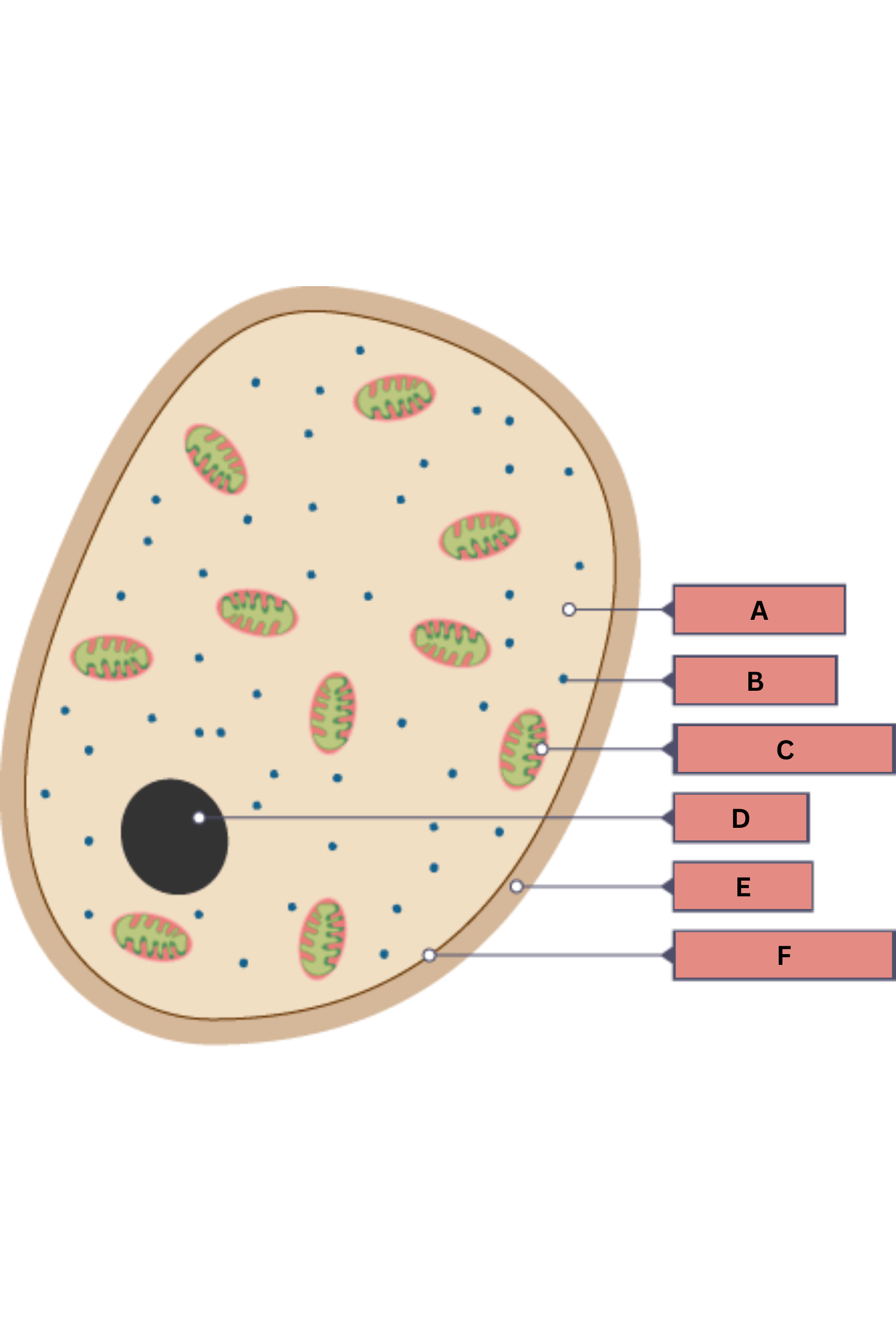
What is B on the fungi diagram?
Ribosome
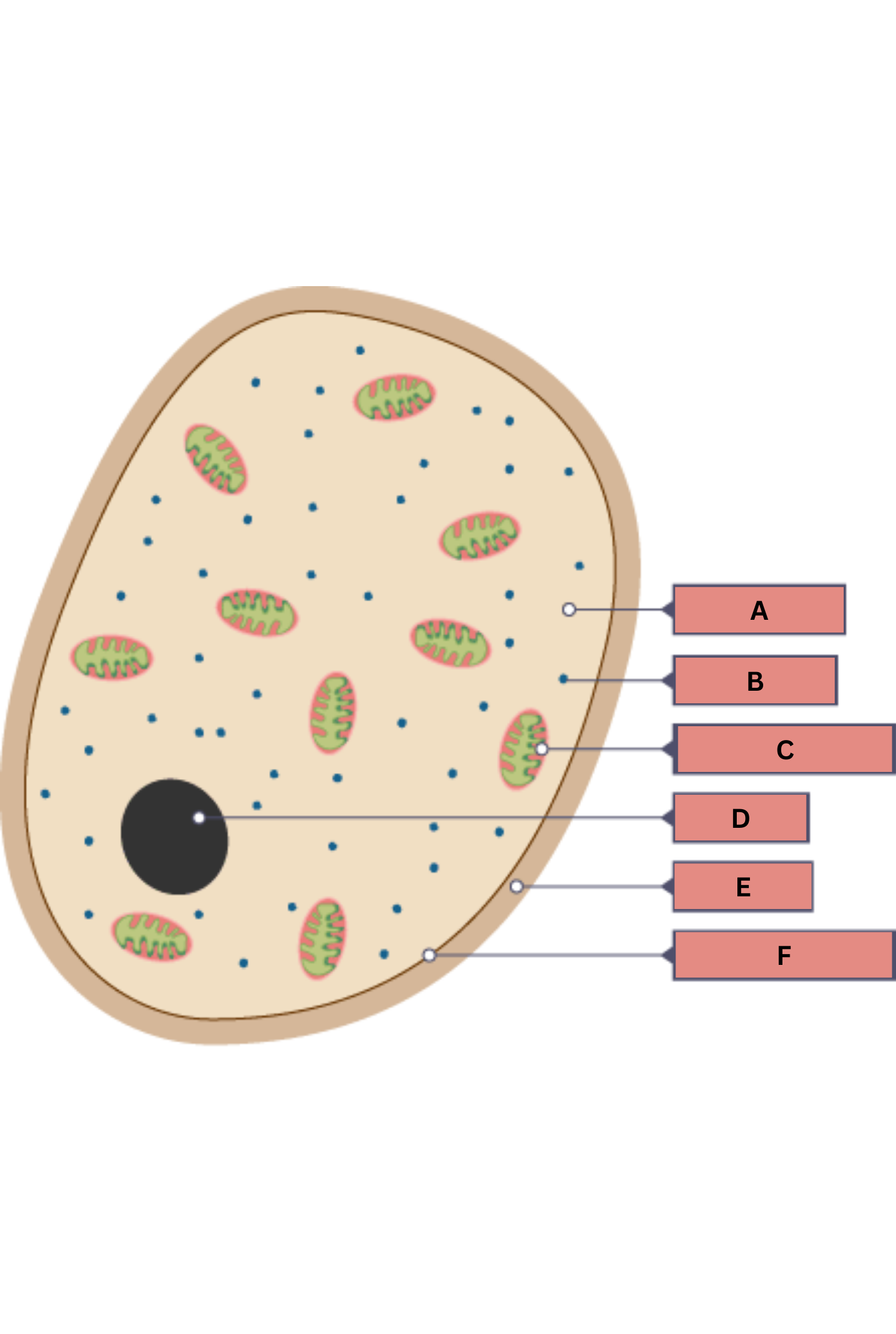
What is C on the fungi diagram?
Mitochondria
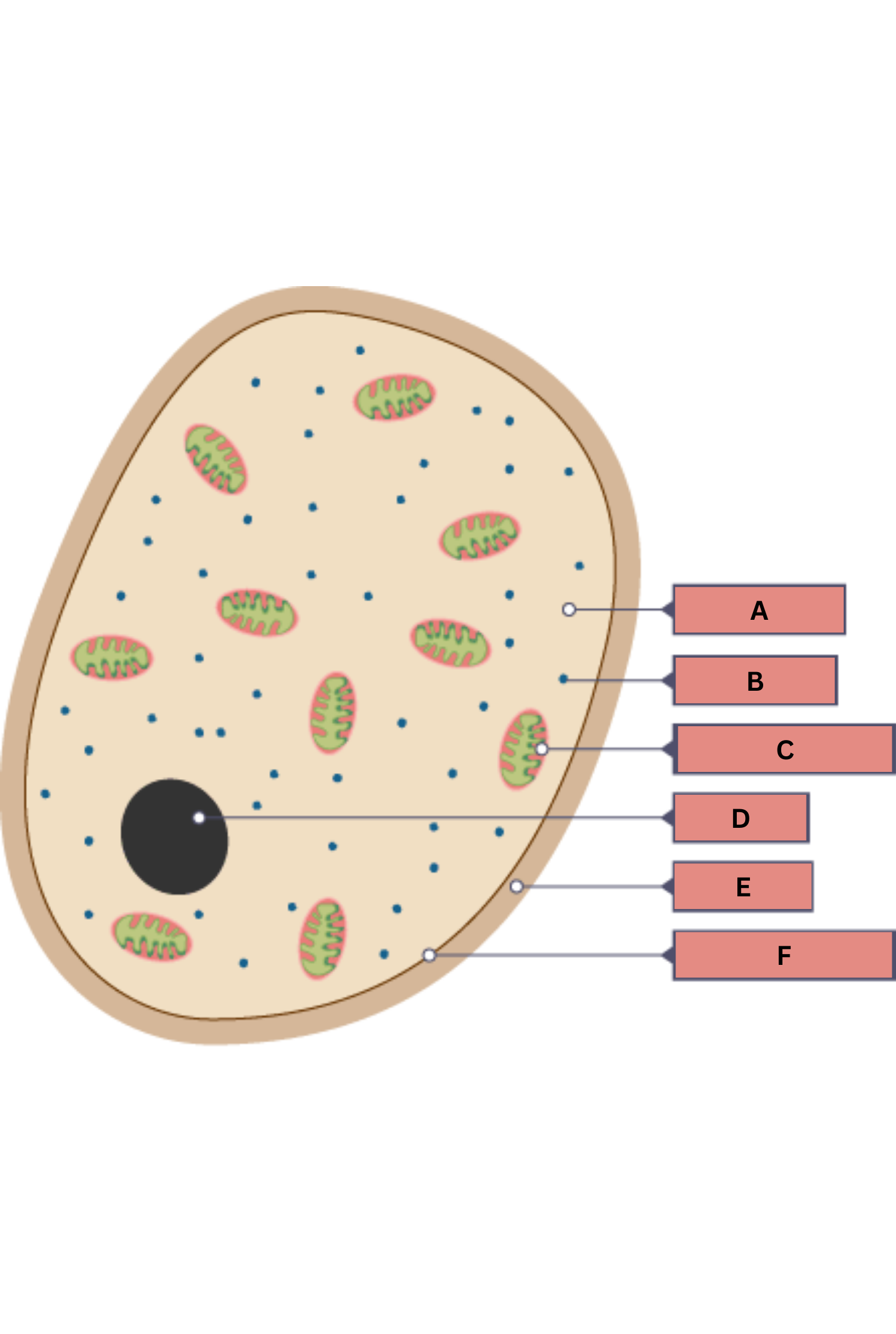
What is D on the fungi diagram?
Nucleus
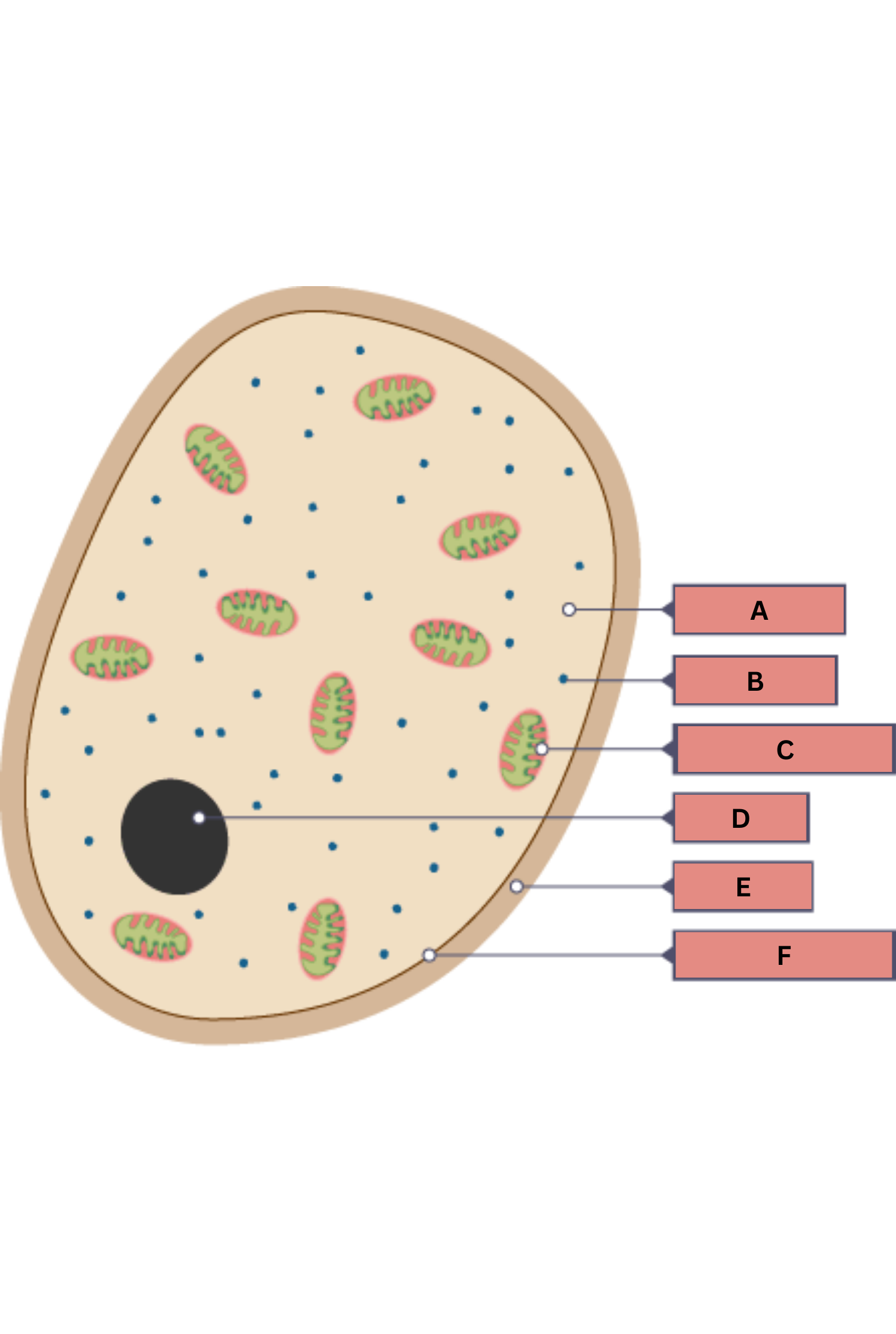
What is E on the fungi diagram?
Cell wall
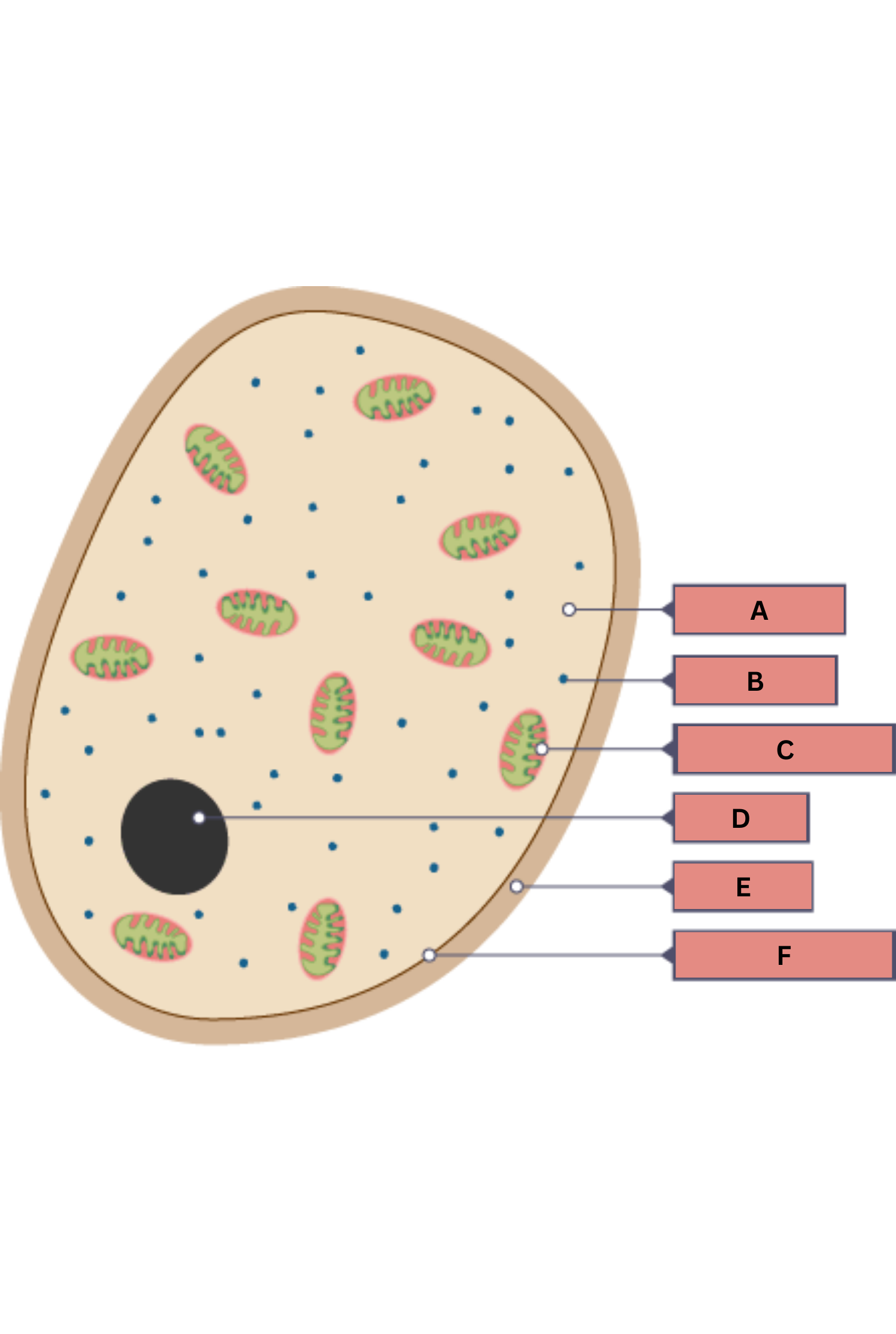
What is F on the fungi diagram?
Cell membrane
What are protoctista?
Simple organisms with varied characteristics.
How do protoctista feed?
Some take in and digest solid food, while others photosynthesise.
Give an example of a protoctist that feeds like an animal.
Amoeba takes in and digests solid food.