HOSA Pharmacology
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Pure Food and Drug Act (1906)
Forbade the manufacture, sale, and transportation of adulterated or mislabeled foods and drugs.
Shirley Amendment of 1912
Prevented fraudulent therapeutic claims by drug manufacturers
Harrison Act of 1914
Established the word narcotic and required the use of a stamp on narcotic drug containers. Also regulated the importation, manufacture, sale, and use of opium, codeine, and their derivatives
Schedule II drugs
Accepted for medical use but with severe restrictions (high potential for abuse)
Schedule III drugs
Have low potential for abuse with an accepted medical use. Perscription only
Schedule IV
Abuse potential exists, but less than Sch III. Examples are: Ambien, Darvocet and Lorazepam.
Schedule V drugs
Lowest potential for abuse. May be sold OTC to people that show ID
Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act of 1938
A New drug could not be marketed until proven safe, tested for toxicity, and required adverse drug effects to be reported.
Durham-Humphrey Amendment (1951)
Replaced Laws of 1938. Required designation of whether or not the drug was prescription or OTC
Schedule I
This type of drug has no accepted medical use in the United States and has a high potential for abuse
Kefauver-Harris Amendment (1962)
Requires proof of safety and efficacy of a drug for approval before marketing
Controlled Substances Act (1970)
Replaced all laws passed prior to it concerning drug control. 5 drug schedules put in place based on potential for abuse.
Poison Prevention Packaging Act (1970)
Implemented child resistant packaging
Drug Listing Act of 1972
drugs must have a National Drug Code number.
Drug Regulation and Reform Act of 1978
Quicker development and distribution of new drugs
Orphan Drug Act of 1983
Established funding for research of rare chronic illnesses for new and old drugs.
Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984
Eased requirements for marketing generic drugs
Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (OBRA 1990)
Mandated that OTC drugs be documented
Anabolic Steroid Control Act of 1990
placed all into category III drugs (CSA)
Prescription Drug Amendments of 1992
Allowed rapid approval of drugs for life-threatening diseases
Food and Drug Administration Modernization Act of 1997
Allowed rapid approval of drugs by the FDA
Pharmacokinesis
the movement of drugs through the body via absorbtion, distribution, metabolism, and excretion
drug blood level
amount of a drug present in the blood
plasma binding
when proteins bind to drugs and decrease the amount of free-flowing drug in the bloodstream allowing the drug to stay in the body for longer.
Examples of Sulfonamides
Sulfamethoxazole, sulfisoxazole, sulfadiazine
Uses for Sulfonamides
Treating UTIs, Ulcerative colitis, 2nd and 3rd degree burns
Drugs that interact with Sulfonamides
Oral anticoagulants, methotrexate, and hydantoins
What are the 4 groups of penicillin?
Natural penicillins, penicillinase-resistant penicillins, aminopenicillins, extended-spectrum penicillins
Uses for Penicillins
UTIs, Septicemia, Meningitis, Intra-Abdominal infections, Sexually Transmitted Infections (syphilis), Pneumonia and other respiratory infections
What variables can effect drug dosage?
Weight, Age, Height, Gender, Genetics, Diet
Another name for antianxiety drugs
Anxiolytics
Benzodiazepines
category 4 meds
3 Examples of antianxiety drugs
alprazolam, doxepin, lorazepam
Acroynm for cancer in adults?
CAUTION
What are the common signs of childhood cancer and the abbriviation?
CHILD CANCER
C ontinued unexplained weight loss
H eadaches, often with early morning vomiting
I ncreased swelling or persistant pain in bones,
joints, back, or legs
L ump or mass, especially in the abdomen, neck,
chest, pelvis, or armpits
D evelopment of excessive bruising, bleeding, or
rash
C onstant infection
A whitish color behind the pupil
N ausea that that persists or vomiting without
nausea
C onstant tiredness or noticeable paleness
E ye or vision changes that occur suddenly and
persist
R ecurrent and persistent fevers of unknown origin
What chemotherapy targets?
Fast-dividing cells
What is the difference between stage and grade in cancer diagnosis?
Stage is how invasive a tumor is, grade is used to classify how abnormal a cancer cell looks under a microscope
Benign Tumor
localized, is smooth and freely movable, and do not break the skin
Malignant Tumor
A tumor that metastasizes to different parts of the body through the lymph nodes and blood vessels
What is another name for antineoplastic agents?
chemotherapeutic agents
What is an anticonvulsant?
A drug used to treat seizures, neuropathic pain, Bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorder
How do anticonvulsants work?
By depressing abnormal nerve impulse discharges in the CNS (central nervous system)
A person taking oral contraceptive should not take
anticonvulsants
anticonvulsants?
diazepam
Which name (trade or generic) starts with a lowercase letter?
Generic
What are the 5 stages of the cell cycle?
G1, S, G2, M, G0
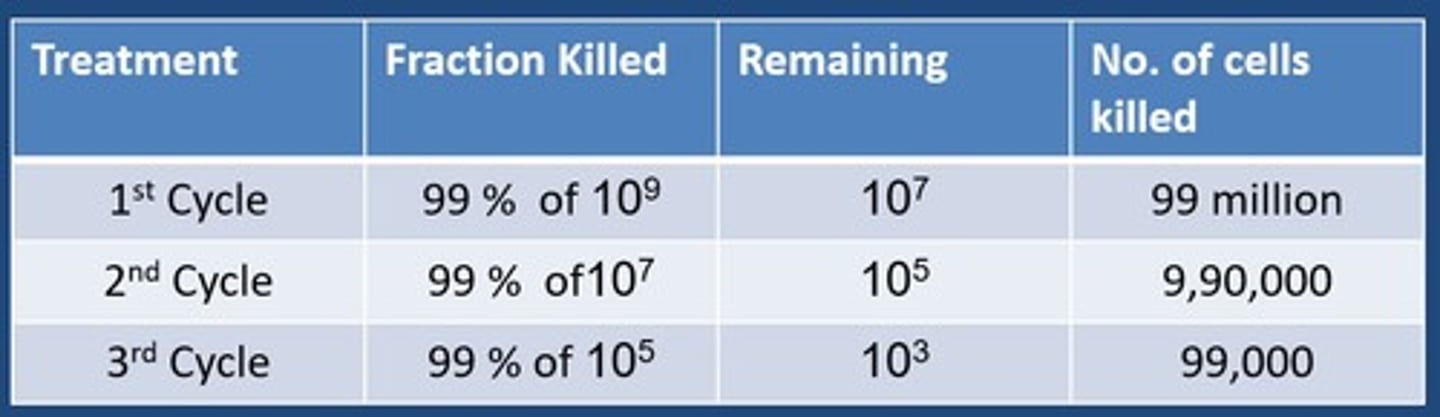
Select the option that shows the cell kill theory.
90% of 100% Killed, 10% left
90% of 10% Killed, 1% left
Body attacks rest of cancer
gemcitabine
Used for
Solid tumors: pancreatic, NSCLC
nelarabines
C11H15N5O5
platinum-based drugs
cisplatin, oxaliplatin, carboplatin
What drug has the chemical formula of C16H20FN3O4?
linezolid
What is one example of a Topical Anti inflammatory or Corticosteroid Agent?
hydrocortisone
Pharmacodynamics
the branch of pharmacology concerned with the effects of drugs and the mechanism of their action.
Pharmacology
the branch of medicine concerned with the uses, effects, and modes of action of drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
the branch of pharmacology concerned with the movement of drugs within the body.
Pharmacotherapeutics
beneficial and adverse effects of drugs.
Polypharmacy
the simultaneous use of multiple drugs to treat a single ailment or condition.
Potentiation
the increase in strength of nerve impulses along pathways that have been used previously, either short-term or long-term.
Receptor site
A molecular site or the docking port on the surface of, or within, a cell, usually involving proteins that are capable of recognizing and binding with specific molecules. Supplement. For example: CD4 receptor on the surface of certain cells is the receptor site that HIV binds with and uses to enter cells.
Recombinant DNA technology
segments of two or more different DNA molecules.
Replacement therapy
treatment aimed at making up a deficit of a substance normally present in the body.
Safe drug
a drug that causes no harmful effects when taken in high doses over a long period of time.
Solubility
Ability of particles to be dissolved.
Distribution
is a branch of pharmacokinetics which describes the reversible transfer of a drug from one location to another within the body.
Drug blood level
The concentration of drug and/or its active metabolite(s) or chemical present in the blood (serum or plasma).
Drug half
when 0.5 concentration or amount of drug in the body reduced.
Drug interaction
affects the activity of a drugs when both are administered together.
Excretion
any one of a number of processes by which a drug is eliminated (that is, cleared and excreted) from an organism either in an unaltered form (unbound molecules) or modified as a metabolite.
First pass
metabolism of a drug before it reaches the systemic circulation or through absorption.
unbound Drug
a drug is kept in the bloodstream
Glycoside
a sugar is bound to another functional group
Habituation
tolerance to the effects of a drug acquired through continued use.
Hypersensitivity reaction
an immune-mediated reaction to a drug.
Ideal drug
effective and safe, producing no side effects or adverse reactions
Idiosyncratic
An unexpected, unusual response to a Drug.
Indication
reason to use a particular drug for a particular disorder.
Alkaloid
A drug that is combined with acids to make salts
Distribution
a branch of pharmacokinetics which describes the reversible transfer of a drug from one location to another within the body.
Antagonist
Medication that binds to a receptor
allergic reaction
Hypersensitivity to a drug
antiinflammatory
a drug that reduces inflammation
Biotransformation
Chemical changes that a substance undergoes in the body
Curative
Medication prescribed to kill the causative agents
Demulcent
Drug used to soothe a body part or to relieve symptoms of irritation
Pharmacology
the branch of medicine concerned with the uses, effects, and modes of action of drugs.
Pharmacotherapeutics
a branch of Pharmacology, which is defined by Merriam-Webster as "the study of the therapeutic uses and effects of drugs" this is a study of beneficial and adverse effects of drugs.
Denominator
Part of a fraction representing the total number of parts
Dosage strength
Amount of drug in the given form, such as tablet or capsule
Gram
Mass metric measure equivalent to one thousandth of a kilogram
Liter
Metric measure of volume, roughly equivalent to quart in household measure
Adverse reaction
Undesirable drug effect.
Dimensional analysis
Newer method of calculating drug dosages based on fractions
metric system
System of measurement based on units of 10.
Numerator
Part of a fraction representing the number of parts taken (the number above the line).
Solvent
Fluid in which a solid dissolves; also called the diluent.
antagonism
Cancellation or reduction of one drug's effect by another drug
nonprescription drugs
safe when taken as directed, can be obtained without a prescription.
prescription drugs
potentially harmful unless their use is supervised by a licensed health care provider, such as a nurse practitioner, physician, or dentist.
What is a common adverse reaction to chemotherapy drugs?
Hair loss
In what drug schedule would you find heroine and other specialty drugs?
Schedule 1