Ch 52: Rheumatic Disorders
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the most common disabling musculoskeletal disorder in the US?
Arthritis
What is the most common arthritis?
Osteoarthritis
What is osteoarthritis characterized by?
Loss of articular cartilage
Cartilage calcifies
Wear of underlying bone
Formation of bone spurs
Noninflammatory
Weight-bearing joints
What is osteoarthritis caused by?
Abnormal “wear and tear” on joints
What are the factors that increase the abnormal wear and tear in joints?
Obesity
Joint trauma
Congenital disorders
Genu Valgus/Varus
Lifestyle and occupation (abnormal stress to joints)
Genetic predisposition
Hormonal status
Postmenopausal
Is osteoarthritis degenerative?
Is osteoarthritis inflammatory or not?
Noninflammatory
Is osteoarthritis local or systemic?
Localized
For osteoarthritis, what does the initial injury cause?
Chondrocytes release of enzymes
Proteolytic and collagenolytic (Breakdown of the matrix of proteoglycan and collagen)
Collagen fatigue and microfractures
For osteoarthritis, what does the progressive injury cause?
Structural breakdown of cartilage
Osteophyte spur formation
Joint effusion
Inflammation of synovial membrane → joint distention
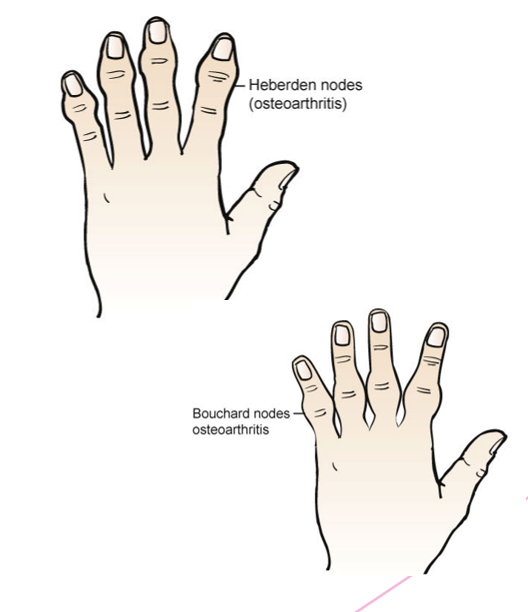
List the clinical manifestations of osteoarthritis.
Localized
Joint pain
Crepitus with movement
Bony enlargement
Morning stiffness
Hand deformity
Heberden
Bouchard nodes
What are the radiologic changes seen with osteoarthritis?
Bony proliferation at the joint margins (bone spurs)
Asymmetric narrowing of the joint space
Subchondral bone sclerosis
Malalignment of joints
Cyst formation
How is osteoarthritis treated?
Acetaminophen → reduce pain
NSAID drug therapy → decrease swelling and pain
Selective NSAID → COX-2 inhibitor (Celebrex)
Inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme
Fewer gastrointestinal side effects
Intraarticular injection of hyaluronan or derivatives
Increase joint lubrication
Reduce inflammation
Physical therapy
Improve range of motion, muscle strength, and joint conditioning
Surgery
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Systemic autoimmune inflammatory disease
What is rheumatoid arthritis triggered by?
Bacterial or viral antigen in genetically susceptible individuals
Describe each phase of rheumatoid arthritis.
Initial phase
Immune response localizes in synovial tissue
Activation of B cells, T cells, and macrophages
Activated B cells produce auto-antibodies
What are the clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis? (Think cardiac, pulmonary, and ophthalmic)
Cardiac →
Pulmonary →
Ophthalmic →
Which body parts are usually involved in rheumatoid arthritis?
Hands
Wrists
Knees
Feet
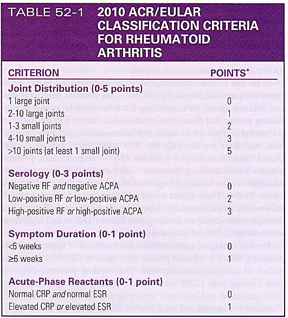
How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
Based on guidelines from:
The American College Rheumatology
European League Against Rheumatism
The patient must have
At least one documented swollen joint
Absence of alternative diagnosis that better explains the joint swelling
A total score on the criteria scale of ≥6
What is the goal of treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Alleviation of pain and swelling
Prevention of structural damage
Preservation of function
How is rheumatoid arthritis treated?
Anti-inflammatory medication (NSAIDS, COX-2 inhibitors, corticosteroids)
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (biological agents, tyrosine kinase inhibitors)
Joint dysfunction is secondary to what other diseases?
Neurovascular, hematologic, and metabolic disorders
What is gouty arthritis?
Heterogenous disorder in which disturbance of uric acid metabolism → deposition of uric acid crystals in joints
What is gouty arthritis characterized by?
Hyperuricemia
Urate crystal → induced arthritis
Recurrent attacks of articular and periarticular inflammation
Accumulation of tophi
Renal impairment
Uric acid calculi
List the clinical manifestations for all four phases of gouty arthritis.
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia → no treatment required
No clinical signs
Serum urate levels are elevated
Acute gouty arthritis
Weight-bearing joints most commonly affected
Warm, red, and tender
Great toe most often involved
Initial attacks can last 1-14 days
Later attacks tend to become more frequent
Intercritical gout
Intervals between acute attacks, no symptoms
Which of the phases of gouty arthritis have no symptoms?
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Gouty arthritis is most common in ___ men and ___ women.
Middle-aged; postmenopausal
When does tophi appear and what tissue can it affect?
About 10 years after initial onset of gout
Affects tissues of the ears and eyes, and cardiac and renal structures
How is gouty arthritis diagnosed?
Joint fluid (synovial) test
Blood test
Uric acid and creatinine
X-ray imaging (can be helpful to rule out other causes of joint inflammation)
Ultrasound (detects urate crystals in a joint or in a tophus)
What is the treatment of gouty arthritis?
Colchicine
NSAIDs
Corticosteroids
Medications to correct hyperuricemia and prevent gout flares
Uricosuric agents or block uric acid production