The structure of the heart
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Describe the general structure of the heart
It is 2 pumps deoxygenated blood on the right side and oxygenated on the left side.
Made of cardiac muscle, supplied with oxygen for regular rhythmic contraction by coronary artery
Pericardial membranes surround heart, they can’ stretch so heart does not over distend with blood
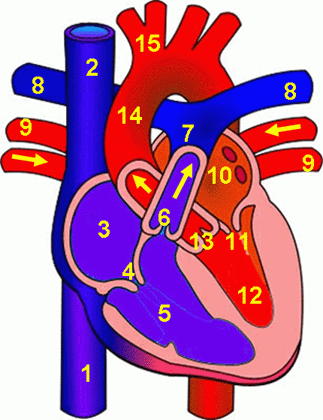
Name each part of the heart
Superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Right atrium
Tricuspid valve (Right AV valve)
Right ventricle
Interventricular septum
Aorta
Left and right pulmonary artery
Left atrium
Bicuspid valve (Left AV valve)
Left ventricle
Papillary muscles
Pulmonary valve (semilunar)
Aortic valve (semilunar)
External view of heart
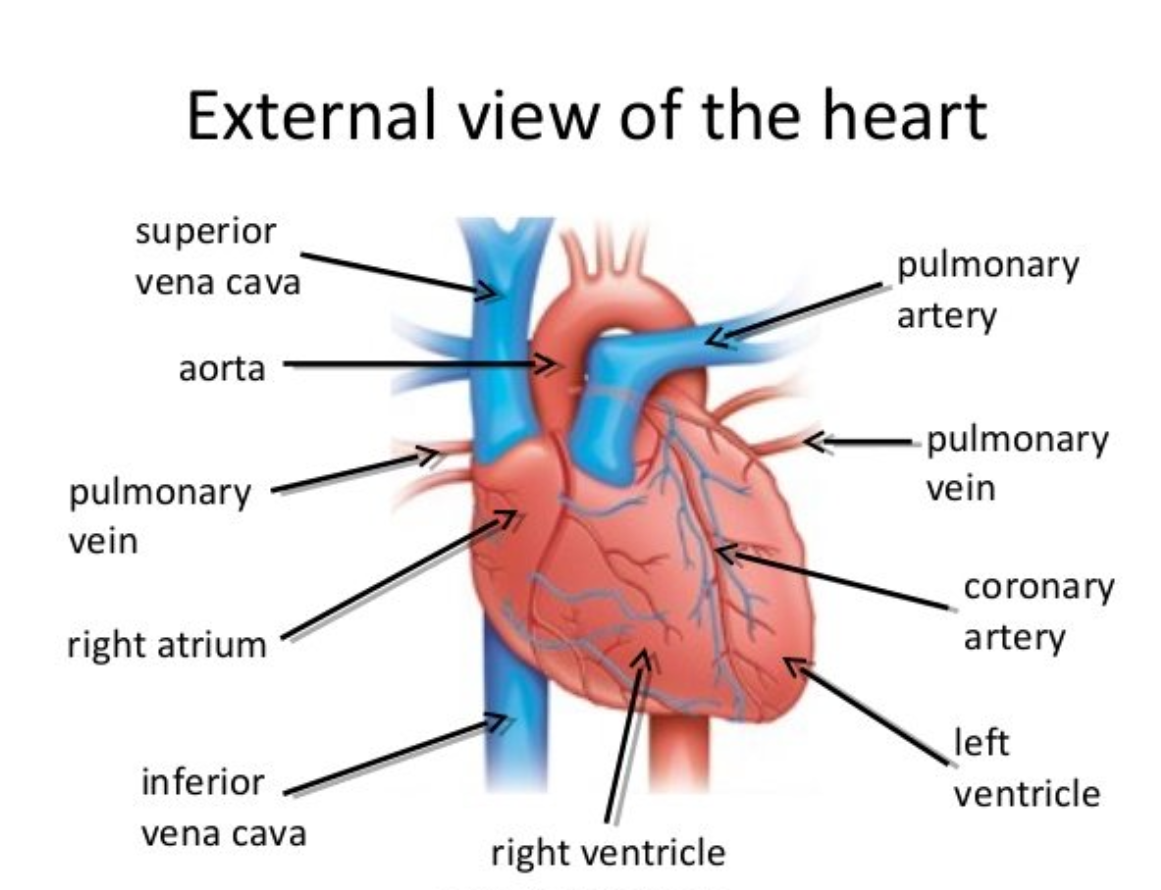
Why is the left ventricle thicker than the right
This is because the left side pumps blood around body, whereas right ventricle pumps blood to lungs (reduced pressure to prevent rupture of capillaries surrounding alveoli)
Why are the atria thinner walled than ventricles
Atria only have to pump to the ventricles which are nearby whilst ventricles have to pump blood to lungs or rest of body which is a larger distance away.
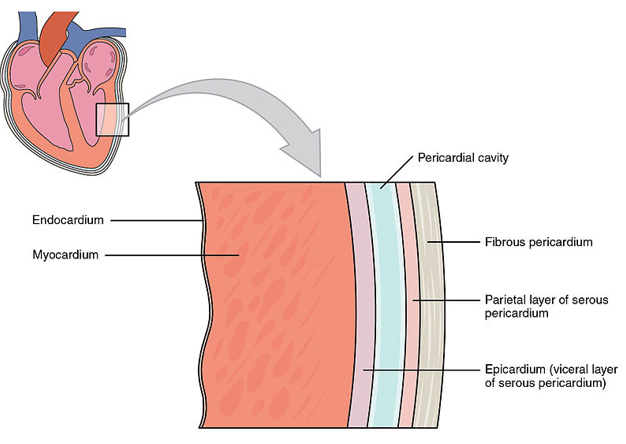
What are the 3 main layers
Epicardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
Describe epicardium
Outer layer of the heart wall and thin protective layer
Describe myocardium
Thick middle layer of cardiac muscle, responsible for contracting and pumping blood.
Thickest in the left ventricle as that is where blood is pumped to whole body
Describe endocardium
Inner lining of the heart chambers. Thin, smooth layer that reduces friction as blood flows through heart.
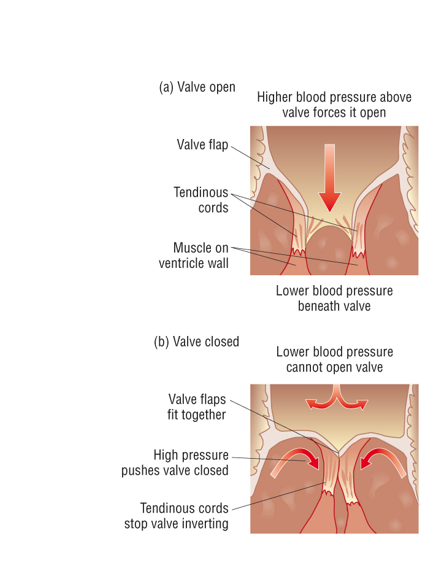
How the AV valves work
What is the importance of the septum
It separates deoxygenated blood in the right side from the oxygenated blood in the left side.
A heart murmur is an indication there is a hole in the septum meaning deoxygenated and oxygenated blood will mix reducing oxygen delivery.