AP Psychology Midterm Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/215
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:33 AM on 1/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
216 Terms
1
New cards
structuralism
idea proposed by Wundt that the mind operates by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations; aimed to uncover the basic structures that make up mind and thought
2
New cards
functionalism
theory presented by William James; emphasizes adaptiveness of the mental or behavioral processes
3
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
set up first psychological laboratory in Leipzig, Germany in 1879; known for training subjects in introspection and for his theory of structuralism
4
New cards
Sigmund Freud
revolutionized psychology with his psychoanalytic theory; believed the unconscious mind must be examined through dream analysis, word association, and other psychoanalytic therapy techniques; criticized for being unscientific and creating unverifiable theories
5
New cards
behaviorism
theory that states psychologists should look at only behavior and causes of behavior, and not concern themselves with describing elements of consciousness; dominant school of thought in psychology from the 1920s through the 1960s
6
New cards
Psycho-dynamic Psychology
study of how unconscious drives and conflicts influence behavior, and uses that information to treat people with psychological disorders
7
New cards
biology psychology
the scientific study of the links between biological (genetic, neural, hormonal) and psychological processes
8
New cards
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
9
New cards
behavioral psychology
the scientific study of observable behavior, and its explanation by principles of learning
10
New cards
Sociocultural Psychology
study of influence of cultural and ethnic similarities and differences on behavior and social functioning
11
New cards
humanistic psychology
study of reaching full potential and personal growth
12
New cards
Cognitive Psychology
study of mental processes, including perception, thought, memory, and reasoning
13
New cards
operational definitions
a researcher's explanation how the variable of an experiment will be measured
14
New cards
illusory correlation
perception of a relationship where none exists, or perception of a stronger relationship than actually exists
15
New cards
confirmation bias
the tendency to attend to evidence that complements and confirms our beliefs or expectations, while ignoring evidence that does not
16
New cards
cognitions
mental processes, such as thinking, memory, sensation, and perception
17
New cards
longitudinal study
non-experimental method; a type of study in which one group of subjects is followed and observed (or examined, surveyed, etc.) for an extended period of time (years.)
18
New cards
cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another
19
New cards
hindsight bias
people's tendency upon hearing about research findings to think that they knew it all along
20
New cards
Case Study
An observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
21
New cards
Informed Consent
an ethical principle requiring that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
22
New cards
Debriefing
an ethical principle in which the post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants
23
New cards
confidentiality
an ethical principle in which researchers may not release or publish the names of anyone participating in the experiment.
24
New cards
protection of participants
an ethical principle in which All participants are protected from physical mental and emotional harm.
25
New cards
Right to discontinue
an ethical principle in which Participants have the right to end their participation during any phase of an experiment.
26
New cards
minimum of deception
an ethical principle in which Researchers have an obligation to avoid deceiving participants whenever possible.
27
New cards
Skewed distribution to the left
negatively skewed
28
New cards
Skewed distribution to the right
positively skewed
29
New cards
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving cites on the receiving neuron
30
New cards
action potential steps
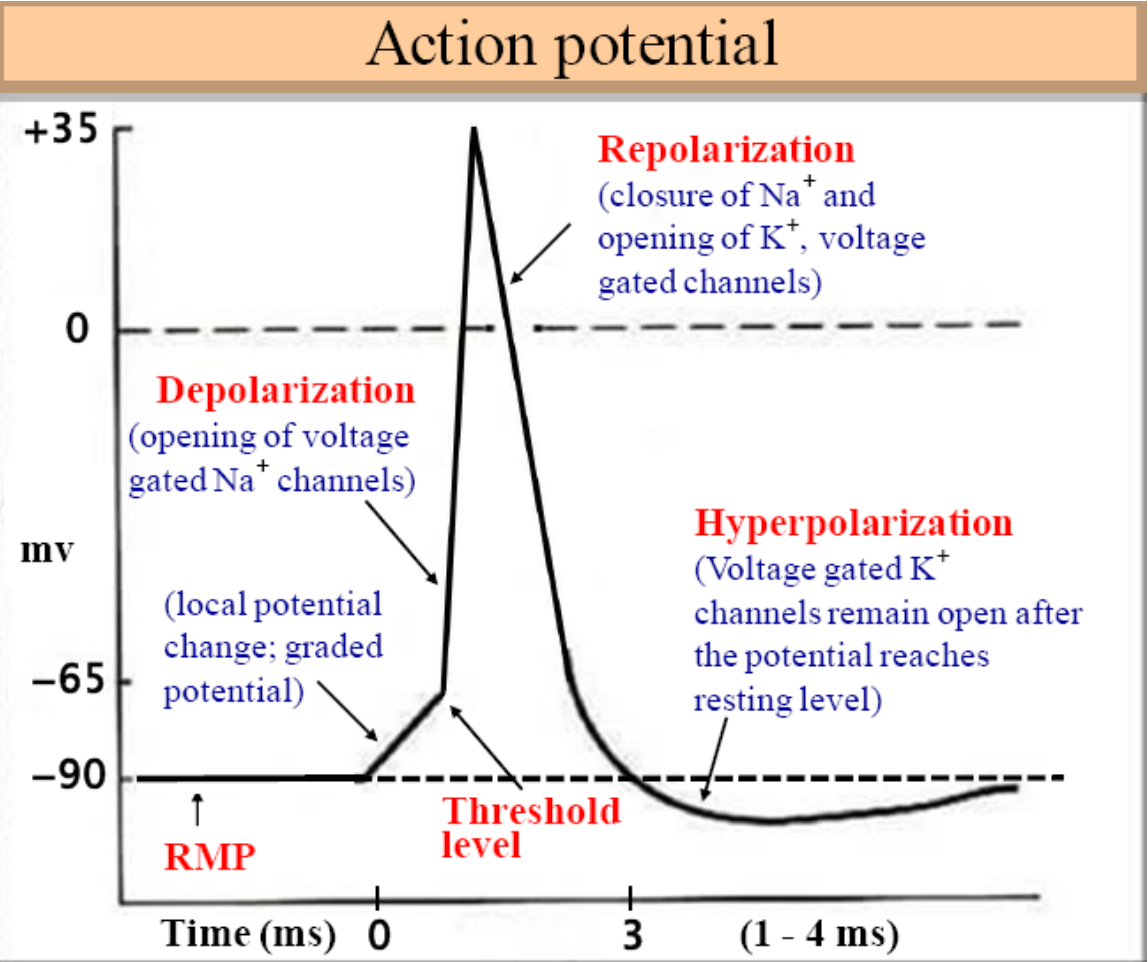
31
New cards
Acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning, and memory
32
New cards
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter influences movement, attention, learning, and emotion
33
New cards
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.
34
New cards
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
35
New cards
Endorphins
neurotransmitter that influence the perception of pain and pleasure
36
New cards
types of neurons
sensory, motor, interneurons
37
New cards
sensory neurons
carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord and brain
38
New cards
motor neurons
carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
39
New cards
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
40
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
connects the body to the CNS by gathering information from the senses and transmitting messages to the CNS
41
New cards
autonomic nervous system
involuntary controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs
42
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations fight, flight, or freeze impulse accelerates heartbeat, raise blood pressure, slows digestion, raise blood sugar, cools body
43
New cards
parasynthetic nervous system
calms the body, conserving its energy rest and digest decelerates heartbeat, lowers blood pressure, stimulates digestion, processes waste, and calms the body
44
New cards
somatic nervous system
controls skeletal muscles
45
New cards
reflex arc
A relatively direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron that allows an extremely rapid response to a stimulus, often without conscious brain involvement.
46
New cards
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
47
New cards
nervous system
neurons releases neurotransmitters neurotransmitters move across the synapse neural transmission is nano-fast
48
New cards
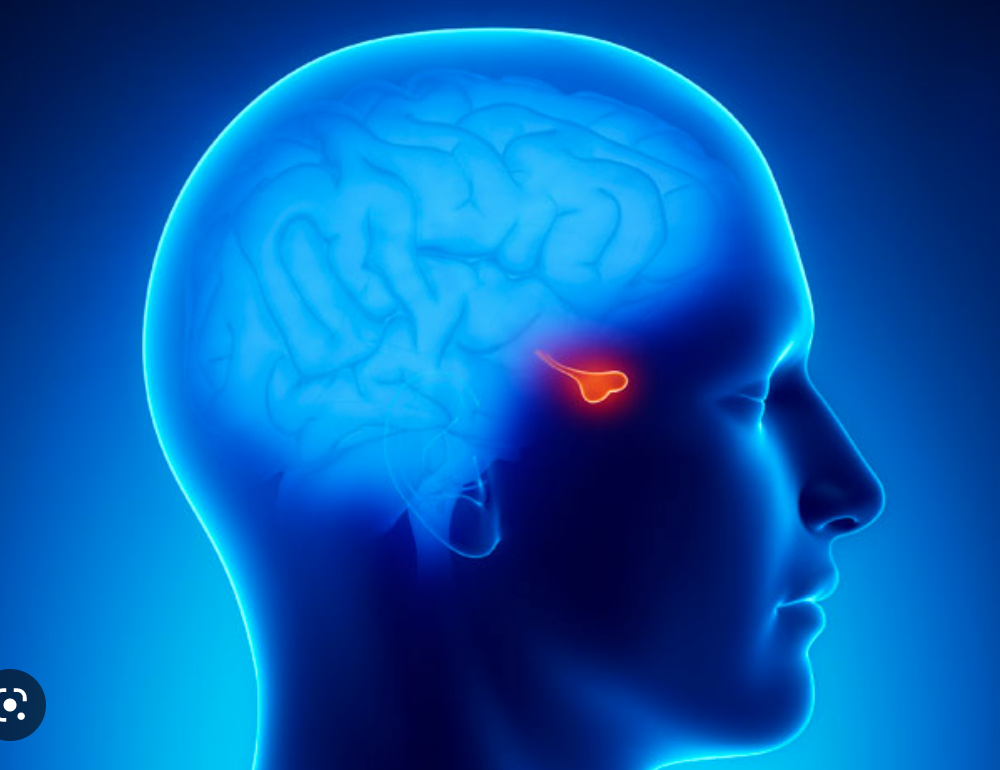
pituitary gland
master gland regulates growth and metabolism
49
New cards
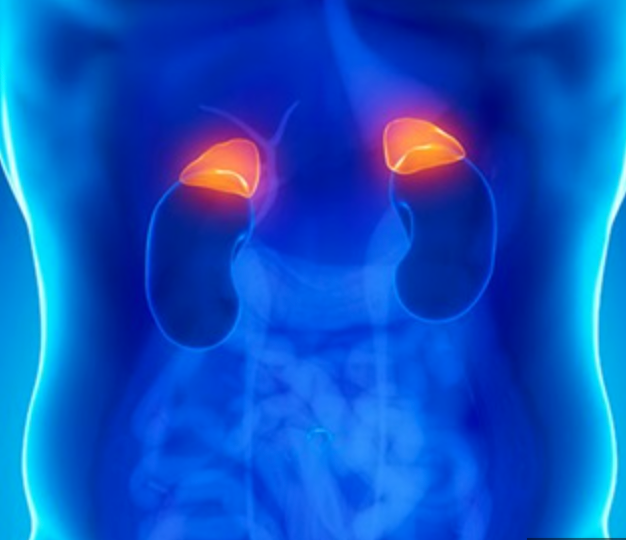
adrenal glands
helps trigger fight or flight response
50
New cards
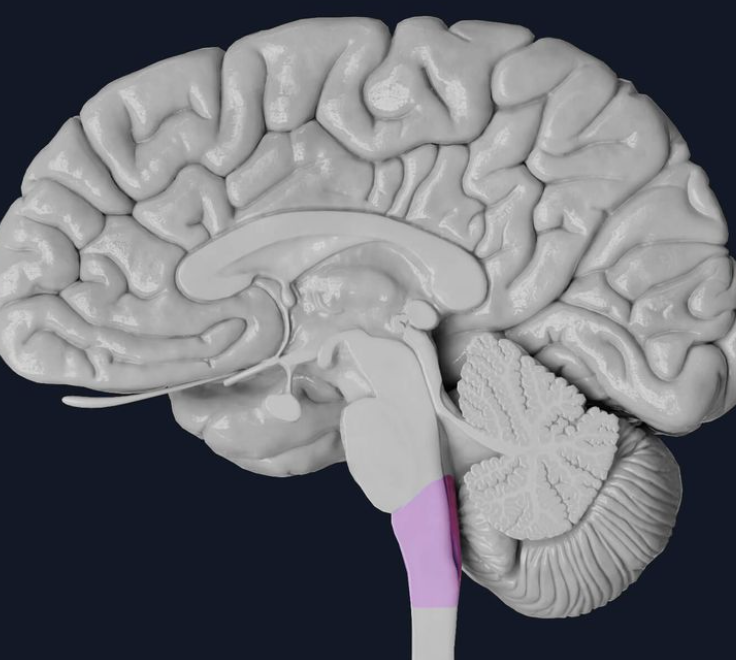
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
51
New cards
Pons
controls sleep and coordinate movement
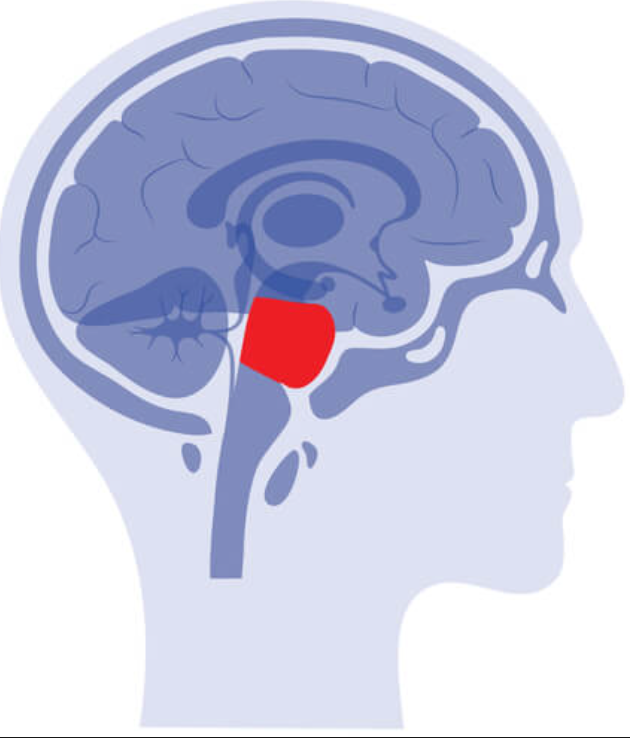
52
New cards
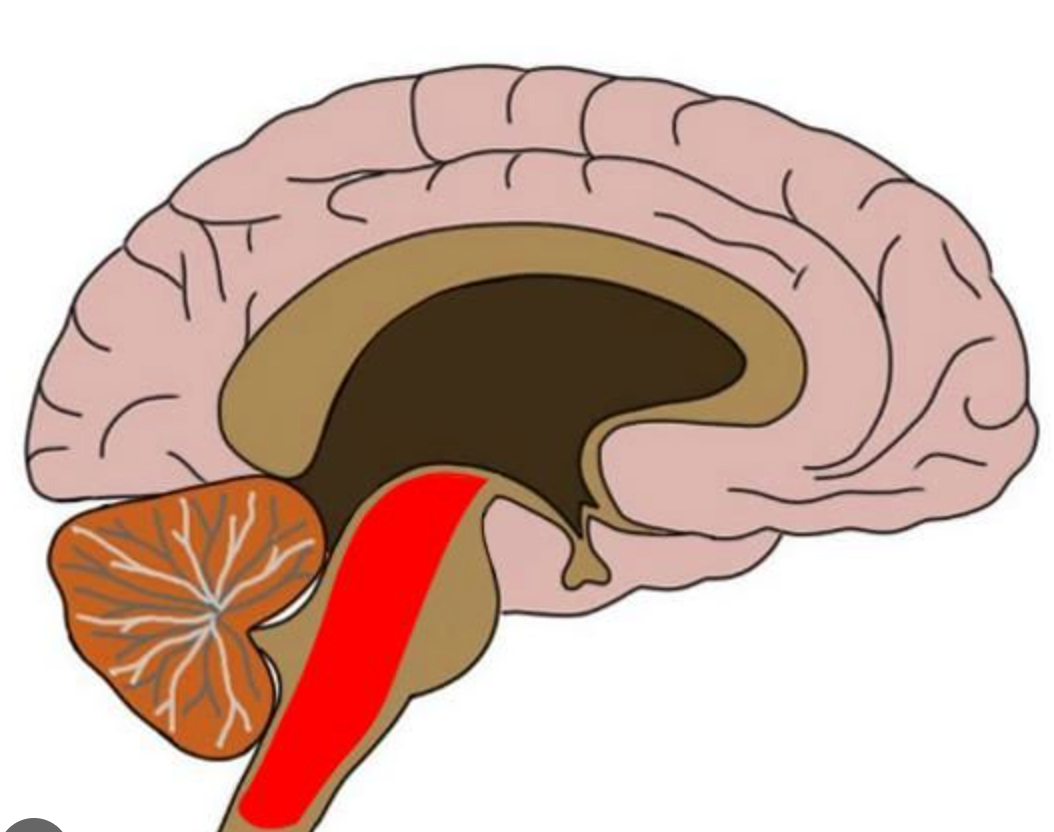
recticular formation
helps control arousal and filters incoming sensory stimuli Nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus
53
New cards
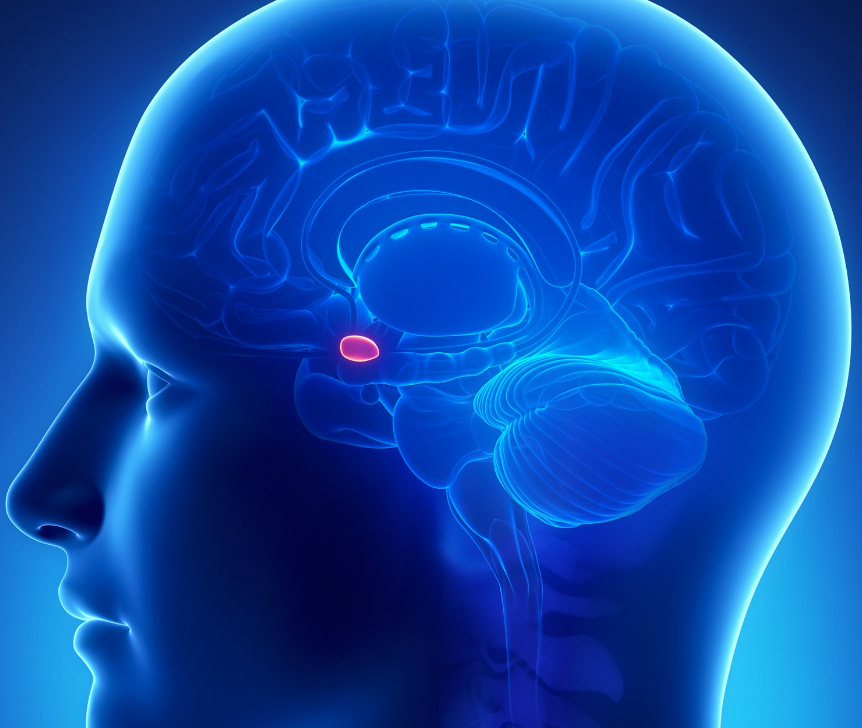
Thalamus
relay station for incoming and outgoing sensory information (with the exception of smell)
54
New cards
Cerebellum
processing sensory input, coordinating movement and balance, nonverbal learning and memory Judging time, modulating emotions, discriminating sound and textures Coordinated voluntary movement
55
New cards
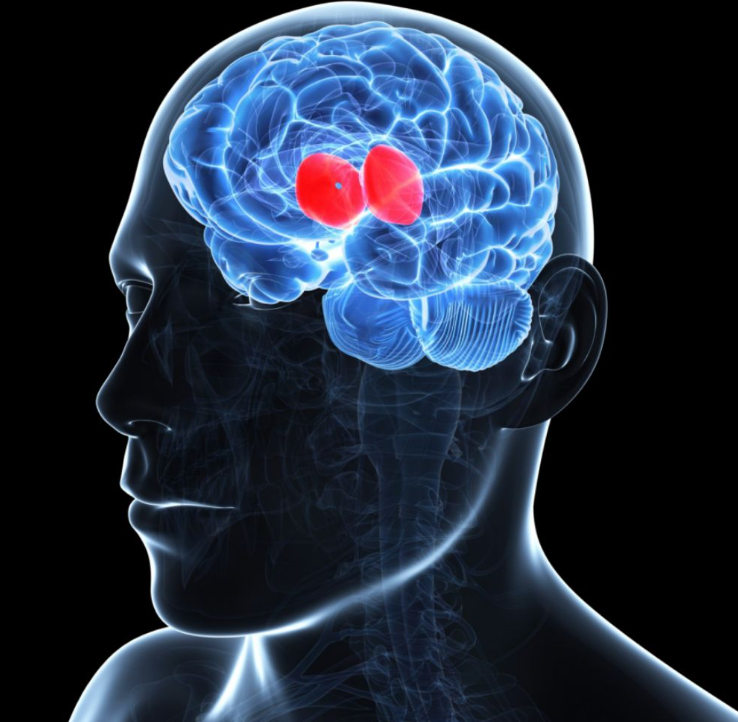
amygdala
linked to emotion, fear, and aggression (Two lima-bean-sized neural cluster )
56
New cards
Hypothalamus
directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
57
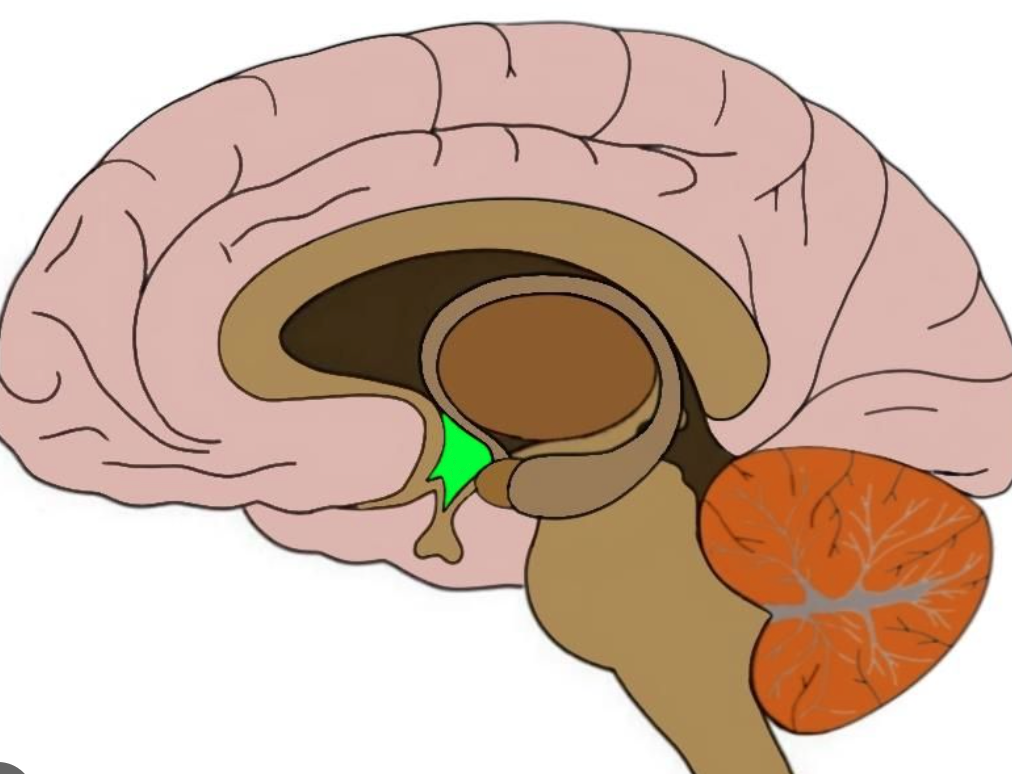
New cards
Hippocampus
helps process for storage explicit (conscious) memories of facts and events Small structure with two "arms" that wrap around the thalamus Decreases in size and function with age
58
New cards
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center Is divided into four regions called lobes
59
New cards
frontal lobe
involved in speaking, motor movements, judgment, and decision making
60
New cards
parietal lobe
receives and processes sensory input for touch and body position
61
New cards
temporal lobe
each lobe receives auditory information, primarily from opposite ear
62
New cards
occiptical lobe
each lobe receives visual information, primarily form opposite visual field
63
New cards
motor cortex
controls voluntary movements
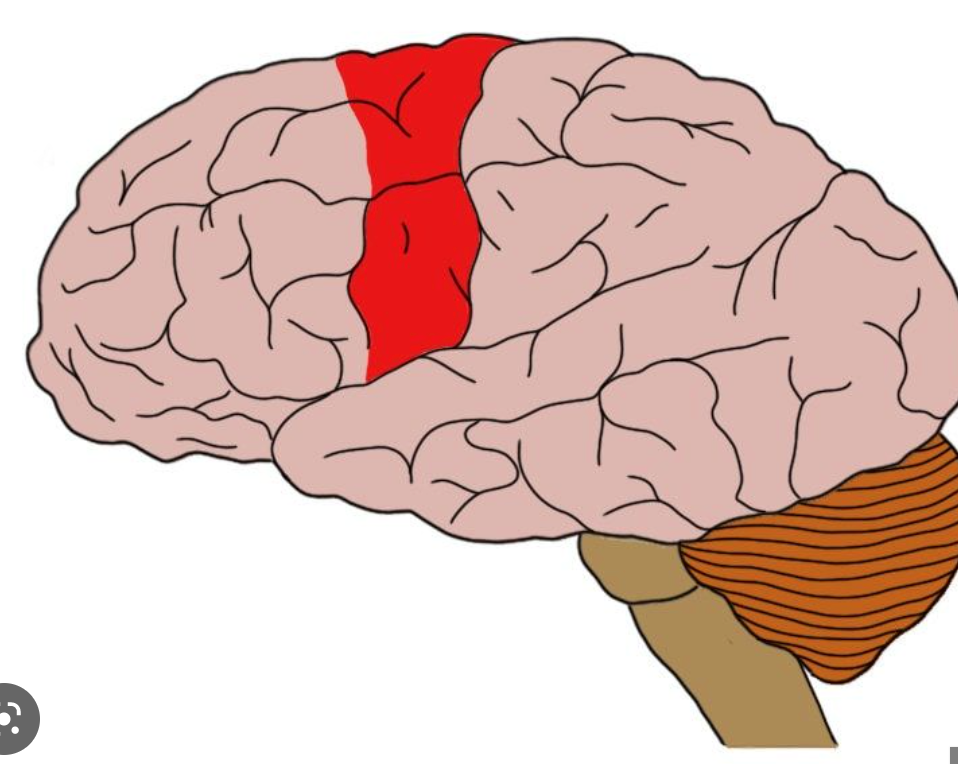
64
New cards
somatosensory cortex
registers and processes body touch and movement sensations
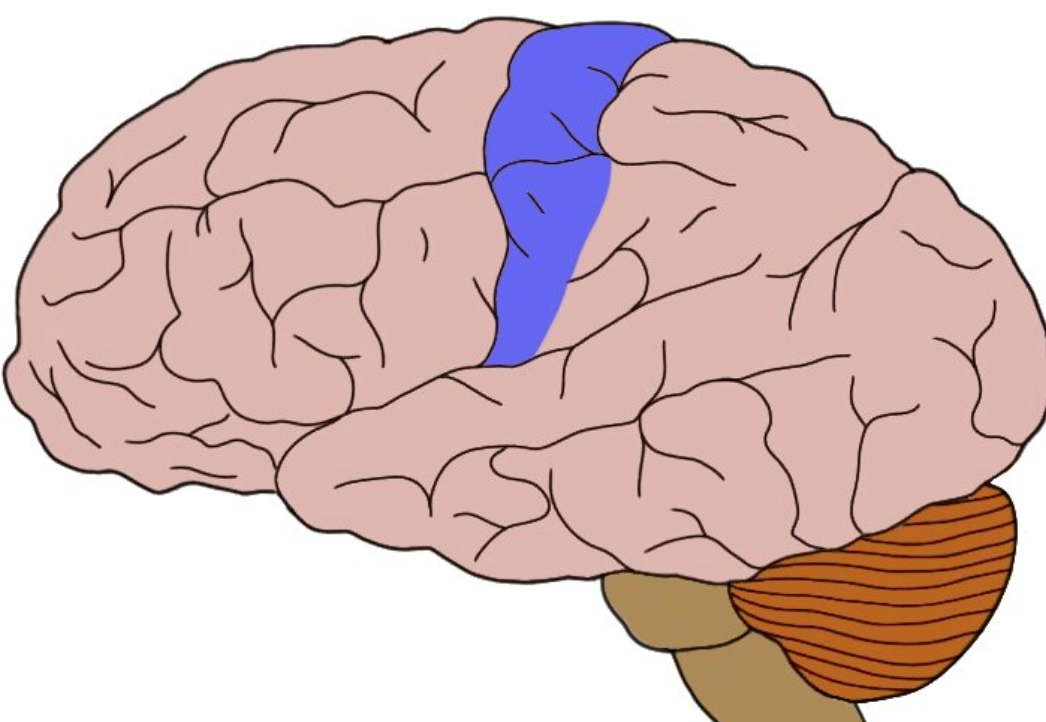
65
New cards
association areas
most of the brain's cortex which integrates information involved in learning, remembering, thinking, and other higher-level functions Attention is shifted, planning occurs Not specifically devoted to motor or sensory cortex functions
66
New cards
broca's area
language center located in the left frontal lobe Involved in expressive language
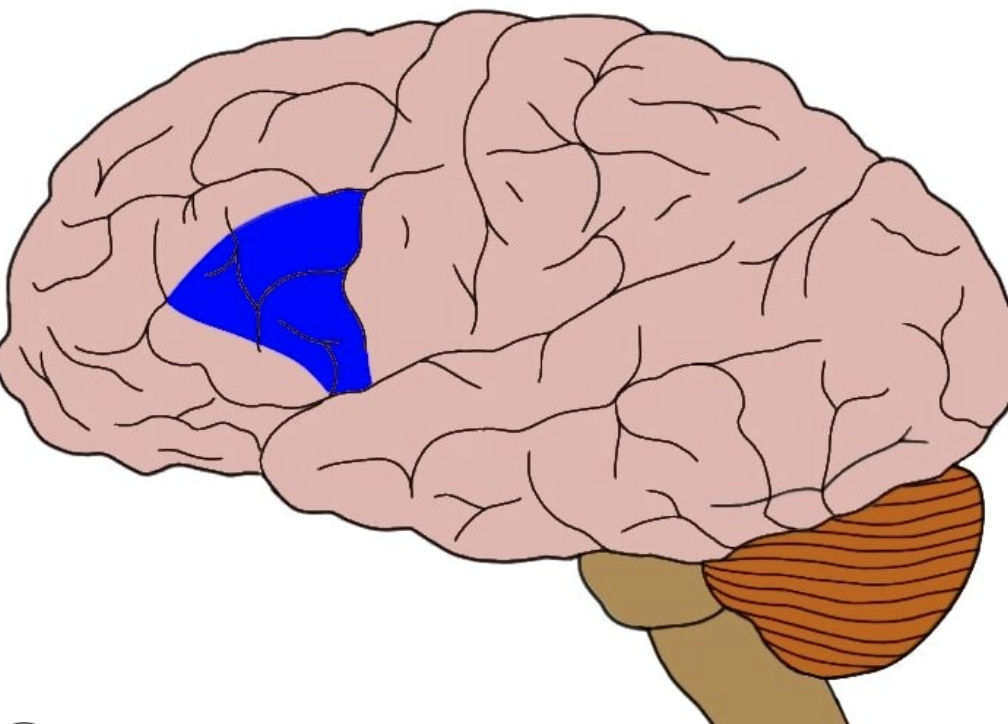
67
New cards
Wernicke's area
language center located in the left temporal lobe Involved in receptive language
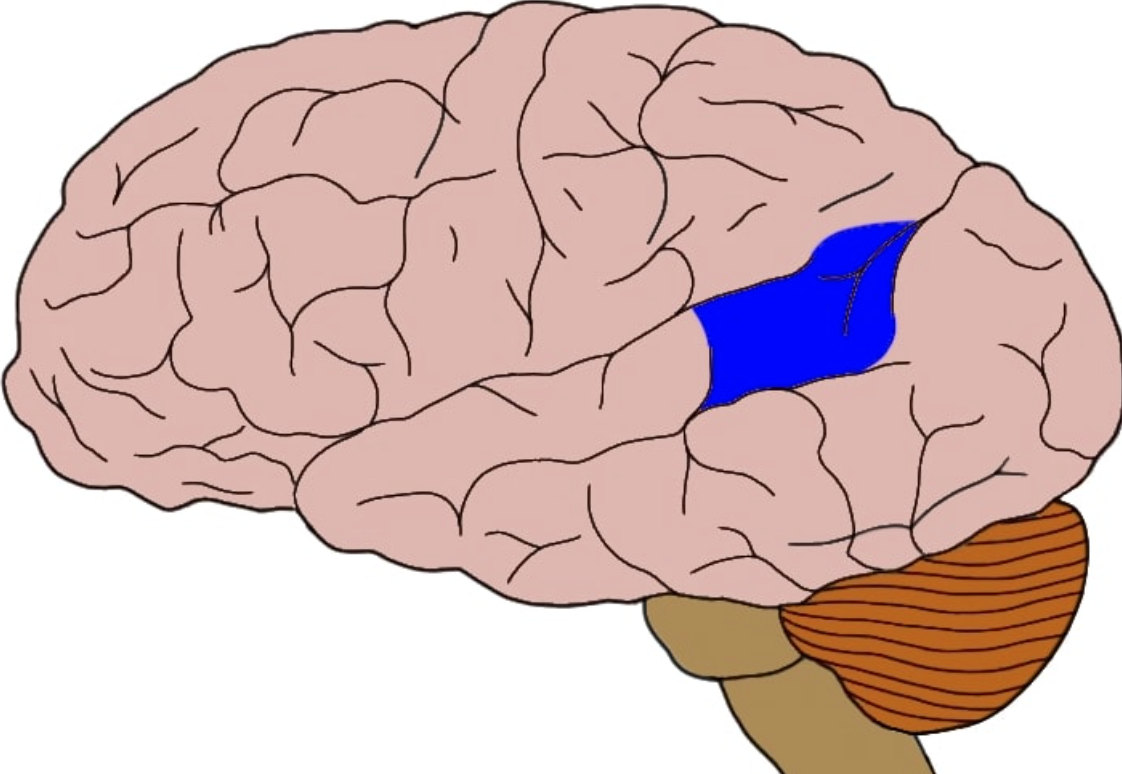
68
New cards
Neuroplasticity
the brain's ability to change, especially during childhood, by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience E.g. blind people have increase sensitivity in fingertips
69
New cards
Neurogenesis
although the brain often attempts self-repair by reorganizing existing tissue, it sometimes attempts to mend itself through neurogenesis
70
New cards
corpus callosum
a wide band of nerve fibers connecting the right and left cerebral hemispheres
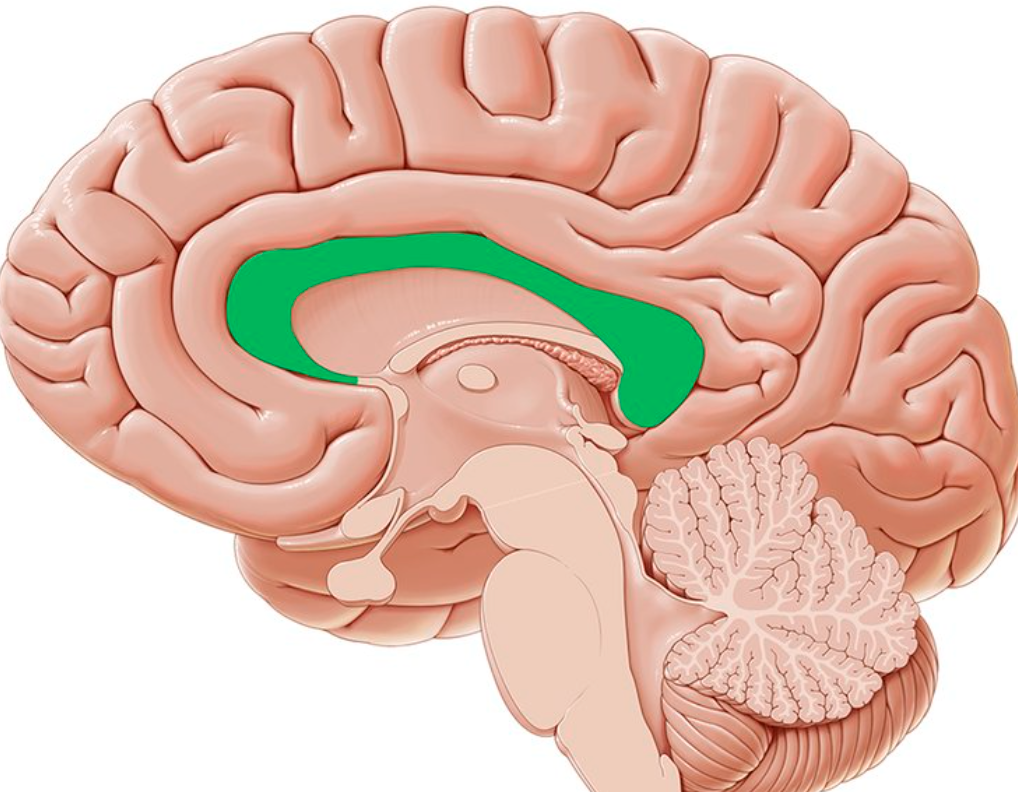
71
New cards
left hemipshere
Speaking and language Math calculations Making literal interpretations Controlling the right side of the body
72
New cards
right hemisphere
Perceptual tasks Making inferences Modulating speech Visual perception Recognition of emotion Controlling the left side of the body
73
New cards
parallel processing
unconscious processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously
74
New cards
sequential processing
conscious processing or one aspect of a problem at a time; generally used to process new information or to solve difficult problems
75
New cards
Heredity
the genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring
76
New cards
Heritability
The proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. The heritability of a trait may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied.
77
New cards
Epigenetics
the study of changes in organisms caused by modification of gene expression rather than alteration of the genetic code itself.
78
New cards
attribution theory
proposed by Psychologist Fritz Heider
we can credit/blame (attribute) the behavior to the person's internal stable, enduring traits (a dispositional attribution), or we can attribute it to the external situation (a situational attribution) e.g. if Jack eats an entire cake, do we explain that behavior by noting that Jack has not eaten in days (situational) or that Jack is greedy and glutinous (dispositional)
we can credit/blame (attribute) the behavior to the person's internal stable, enduring traits (a dispositional attribution), or we can attribute it to the external situation (a situational attribution) e.g. if Jack eats an entire cake, do we explain that behavior by noting that Jack has not eaten in days (situational) or that Jack is greedy and glutinous (dispositional)
79
New cards
fundamental attribution error
the tendency for observers, when analyzing others' behavior, to underestimate the impact of the situation and to overestimate the impact of personal disposition e.g. when passing a homeless person on the street, the fundamental attribution error suggests that we might be more likely to attribute their homelessness to their own personality (Lazy? unmotivated?) rather than to the situation (loss of job? break up of the family? schizophrenia?)
80
New cards
factor that affect attributions
culture: individualist westerners more often attribute behavior to people's person traits. people in the east asian collectivist cultures are more sensitive to the power of the situation.
81
New cards
peripheral route persuasion
occurs when people are influenced by incidental cues, such as a speaker's attractiveness.
uses attention-getting cues to trigger emotion-based snap judgments.
e.g. endorsements by beautiful or famous people can influence people's attitudes, whether the judgement is about choosing a political candidate or buying the latest smart phone
uses attention-getting cues to trigger emotion-based snap judgments.
e.g. endorsements by beautiful or famous people can influence people's attitudes, whether the judgement is about choosing a political candidate or buying the latest smart phone
82
New cards
central route persuasion
occurs when people are influenced by arguments and respond with favorable thoughts.
offers evidence and arguments that trigger careful thinking
e.g. to persuade buyers to purchase a particular phone, an ad might itemize the phone's great features. to increase support for climate change intervention, effective arguments have focused on accumulating greenhouse gases, melting Arctic ice, rising world temperatures and seas, and extreme weather.
offers evidence and arguments that trigger careful thinking
e.g. to persuade buyers to purchase a particular phone, an ad might itemize the phone's great features. to increase support for climate change intervention, effective arguments have focused on accumulating greenhouse gases, melting Arctic ice, rising world temperatures and seas, and extreme weather.
83
New cards
foot-in-the-door phenomenon
the tendency for people who have first agreed to a small request to comply later with a larger request. Succumb to a temptation and you will find the next temptation harder to resist
84
New cards
door-in-the-face phenomenon
tendency for people who won't agree to a large task, but then agree when a smaller request is made
85
New cards
what did the Standford Prison study demonstrate about roles?
every time we act like the people around us, we slightly change ourselves to be more like them, and less like who we used to be although the volunteers in Zimbardo's study knew it was a research set up, they eventually began to act more like their assigned role of prisoner or guard. they took on the roles and performed the behaviors expected in that role (norms)
86
New cards
cognitive dissonance
Leon Festinger's theory
we act to reduce the discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two of our thoughts (cognitions) or our thoughts and behaviors are inconsistent.
when we become aware that our attitudes and our actions clash, we can reduce the resulting dissonance by changing our attitudes e.g. a person who smokes and enjoys the sensation, may also know that smoking cigarettes is correlated with lung cancer. this disconnect between a belief (smoking causes cancer) and a behavior (continuing to smoke cigarettes) causes tensions...or dissonance.
to relieve the dissonance, a person must either change the behavior (stop smoking) or change the thought ("i may die young, but at least i am enjoying myself today!")
we act to reduce the discomfort (dissonance) we feel when two of our thoughts (cognitions) or our thoughts and behaviors are inconsistent.
when we become aware that our attitudes and our actions clash, we can reduce the resulting dissonance by changing our attitudes e.g. a person who smokes and enjoys the sensation, may also know that smoking cigarettes is correlated with lung cancer. this disconnect between a belief (smoking causes cancer) and a behavior (continuing to smoke cigarettes) causes tensions...or dissonance.
to relieve the dissonance, a person must either change the behavior (stop smoking) or change the thought ("i may die young, but at least i am enjoying myself today!")
87
New cards
social contagion
behavior is contagious. if one yawns, laughs, coughs, scratches, stares at the sky, or checks our phone, others in our group will often do the same
88
New cards
chameleon effect
unconscious mimicry of the postures, mannerisms, facial expressions, and other behaviors of one's interaction partners e.g. Tanya Chartrand and John Bargh's research: found that students tended to rub their face when with the face-rubbing person and shake their foot when with the foot-shaking person
89
New cards
how does social contagion lead to empathy and fondness?
this natural mimicry enables us to empathize--to feel what others are feelings. this helps explain why we feel happier around happy people than around depressed people
90
New cards
confromity
adjusting our behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard because of real or imagined pressure to fit in
91
New cards
Solomon Asch's Experiment
1955, Asch devised a simple study to research conformity
the subject of the study is given the line test and his accuracy scores are recorded. then the subject is asked to join five other men in a room to complete the line test together. the five other men in the study are all confederates of Asch.
results: 1/3 of the time, the subjects went along with the group, even though they knew the confederates were wrong
the subject of the study is given the line test and his accuracy scores are recorded. then the subject is asked to join five other men in a room to complete the line test together. the five other men in the study are all confederates of Asch.
results: 1/3 of the time, the subjects went along with the group, even though they knew the confederates were wrong
92
New cards
normative social influence
influence resulting from a person's desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval we are sensitive to social norms because the price we pay for being different can be severe
93
New cards
informational social influence
influence resulting from one's willingness to accept others' opinions about reality when we accept others' opinions about reality, as when reading online movie and restaurant reviews
94
New cards
obedience was highest in Milgram's when...
the person giving the orders was close at hand and was perceived to be legitimate authority figure (donning a white lab coat) the authority was supported by a prestigious institution. conducting the study on Yale campus, versus downtown Bridgeport, increased obedience the victim was depersonalized or at distance, even in another room there were no role models for defiance
95
New cards
social facilitation
improved performance on simple or well-earned tasks in the presence of others e.g. skilled athletes often find they are "on" before an audience (what they do well, they do even better when people are watching)
96
New cards
social loafing
the tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts towards attaining a common goal than when individually accountable
97
New cards
deindividuation
the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity
e.g. during England 2011 riots and looting, rioters were disinhibited by social arousal and by the anonymity provided by darkness and their hoods and masks. later, some of those arrested expressed bewilderment over their own behavior
e.g. during England 2011 riots and looting, rioters were disinhibited by social arousal and by the anonymity provided by darkness and their hoods and masks. later, some of those arrested expressed bewilderment over their own behavior
98
New cards
group polarization
the enhancement of a group's prevailing inclinations through discussion within the group the beliefs and attitudes we bring to a group grow stronger as we discuss them with like-minded others
99
New cards
groupthink
the mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives often when a group is involved in decision making, the hope that the group can arrive at a decision may subtly influence dissenters of the group decision to remain sile
100
New cards
prejudice
an unjustifiable (and usually negative) attitude toward a group and its members generally involves stereotyped beliefs, negative feelings, and a predisposition to discriminatory action is an unjustifiable and usually negative attitude toward a group and its members--who often are people of a particular racial or ethnic group, gender, sexual orientation, or belief system