Biochem Final
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
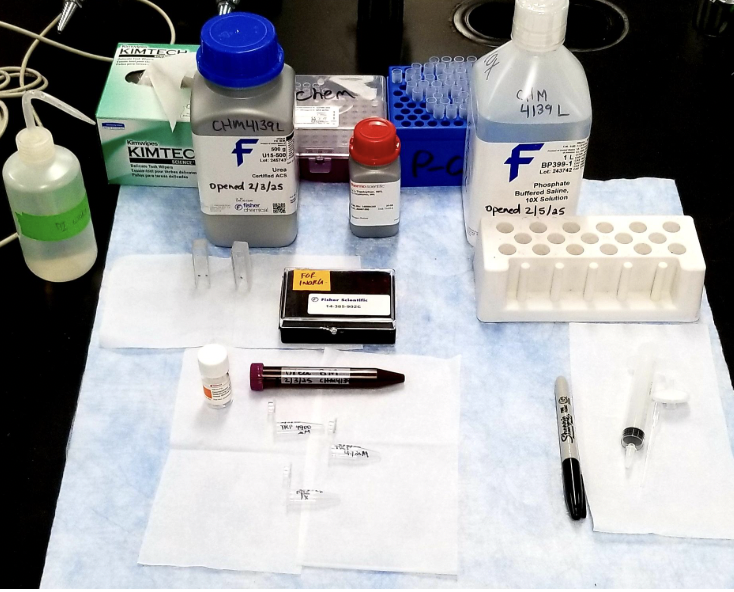
What reagents are shown in the image?
Urea
PBS
Tryptophan
Protein
If a protein is made of 635 amino acids and each amino acid is approximately 110 Daltons or 110 g/mol, what is the molecular weight of the protein?
69,850 g/mol
While rarely in the news, these pictured ice cage formations have garnered attention because of their potential to affect climate change. during offshore drilling, methane ice can get stuck in pipes, causing them to freeze and burst. in fact, the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill is thought to have been caused by a buildup of methane entrapped ice cages. What is the appropriate name of these methane entrapped ice cages?
Clathrates
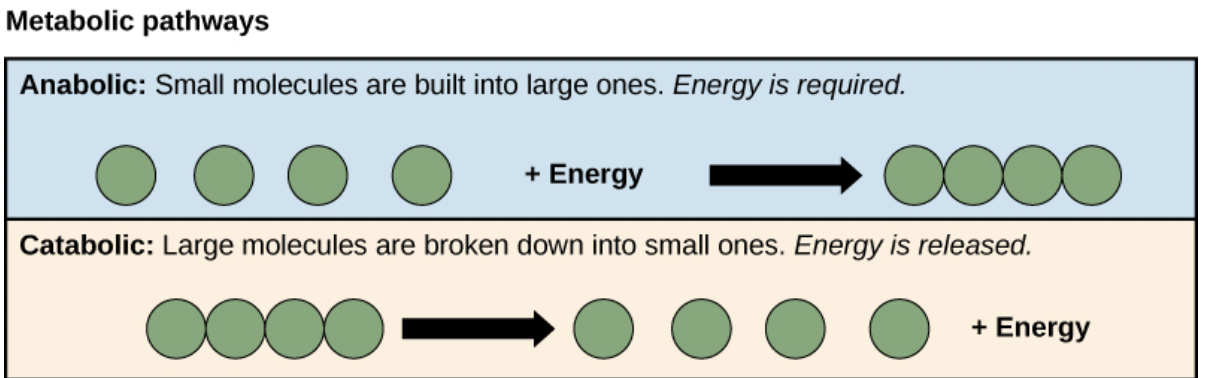
Review the image and select which reaction is spontaneous.
Catabolic; select black arrow
What is the [H+] of a solution with a pH of 11.11
7.762e-12
What is the concentration of OH- in a solution with an H+ concentration of 1.3×10^-4 M?
7.7e-11 M
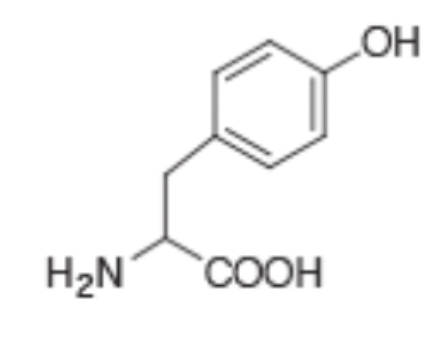
What is the single letter code for the amino acid shown?
Y
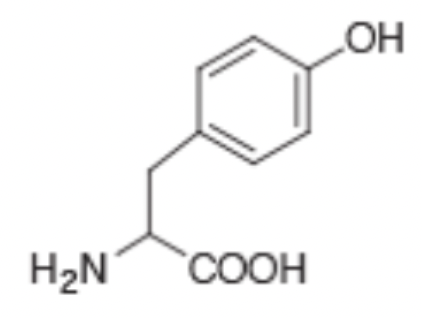
What is the three letter code of the amino acid shown?
Tyr
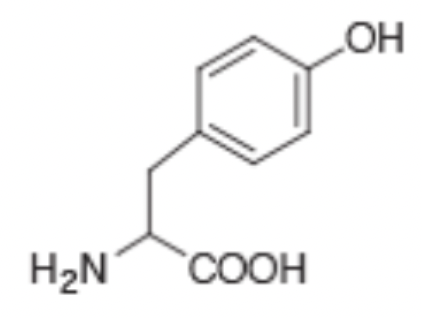
The amino acid shown has an R group that is slightly basic
False
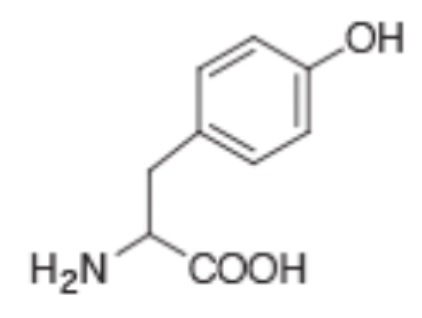
The R group on the amino acid shown is protonated and can be deprotonated under the right conditions. This is because the R group has a low pka.
False
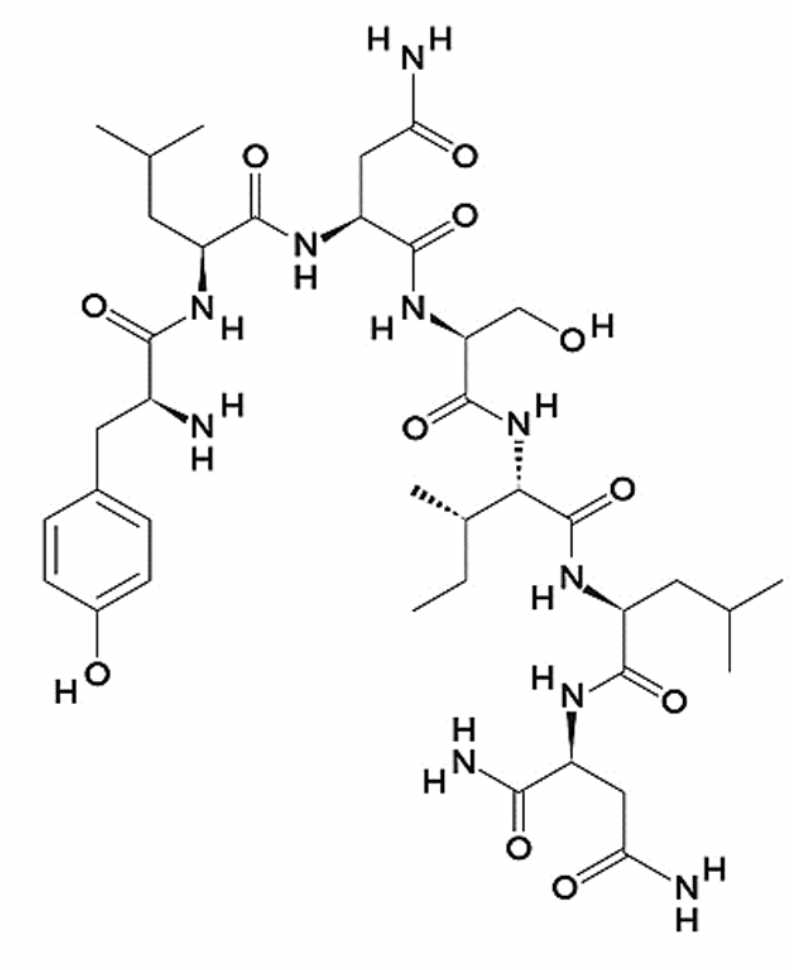
Which of the following amino acids are present in the peptide shown?
N
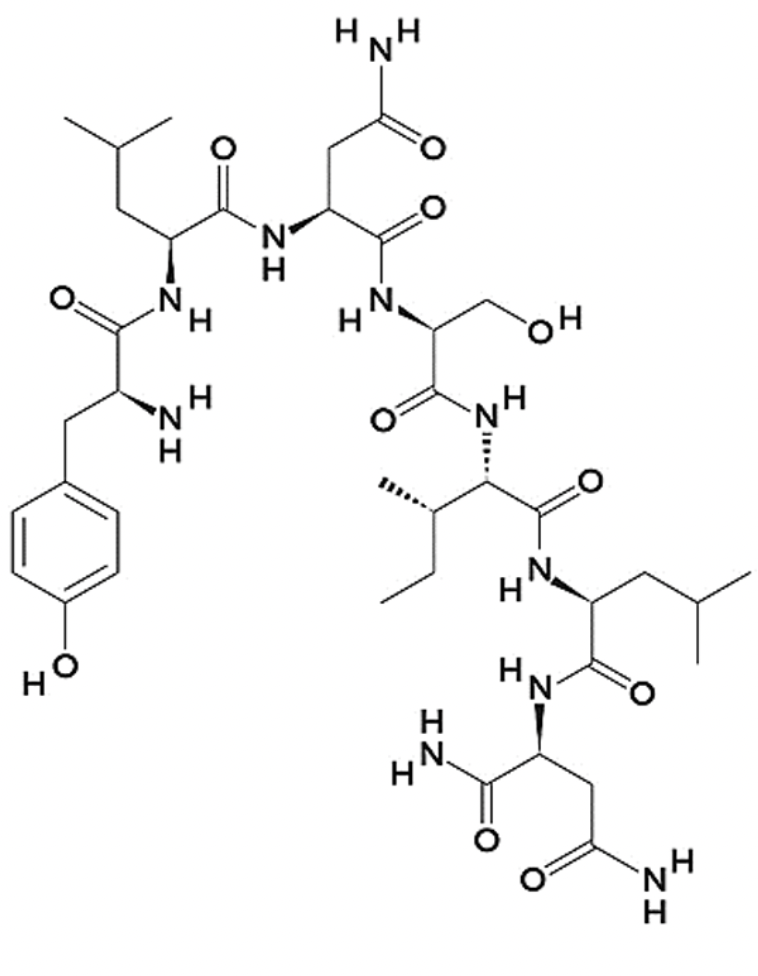
How many amino acids are in this peptide?
7
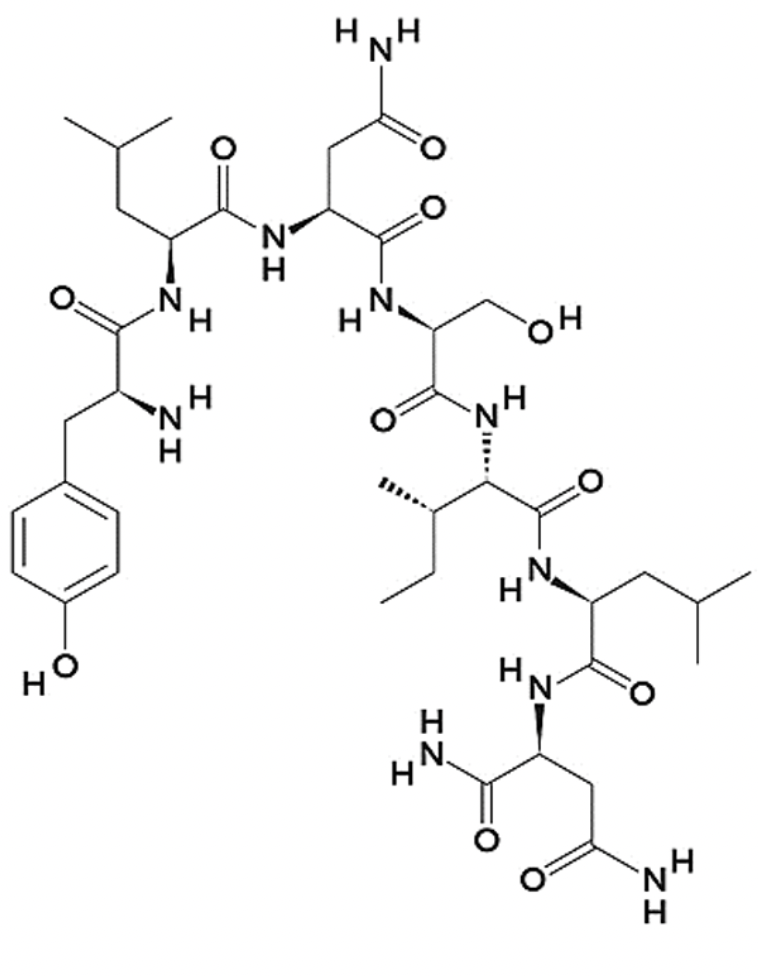
The sequence of the peptide shown is: NLISNLY
False
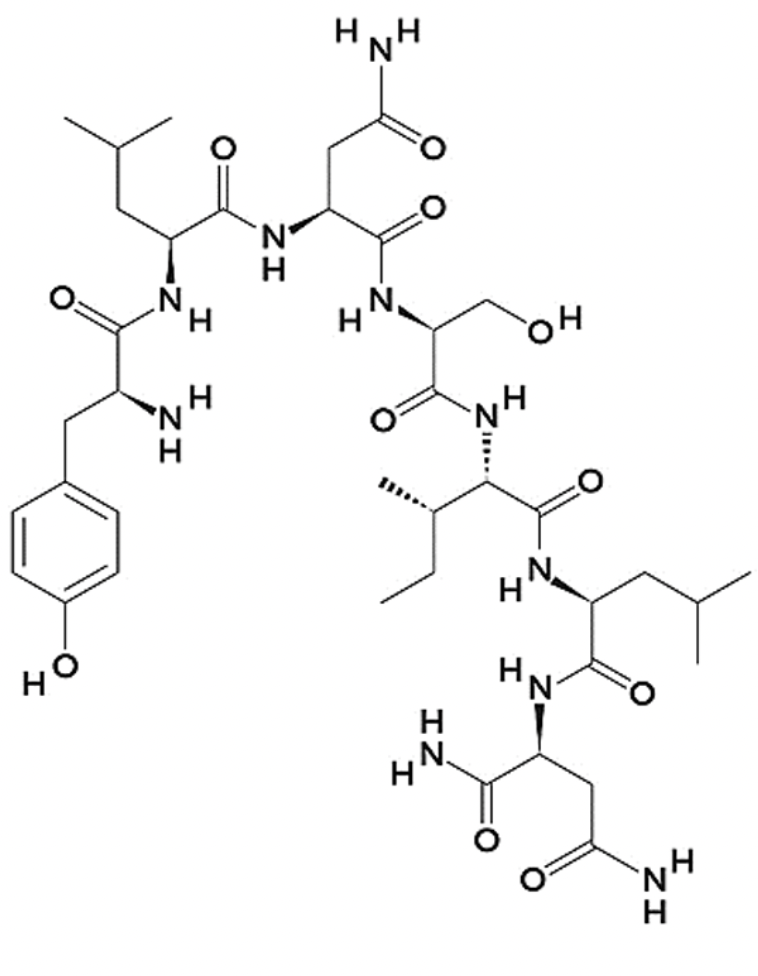
The C-terminal is capped with an amino group
True
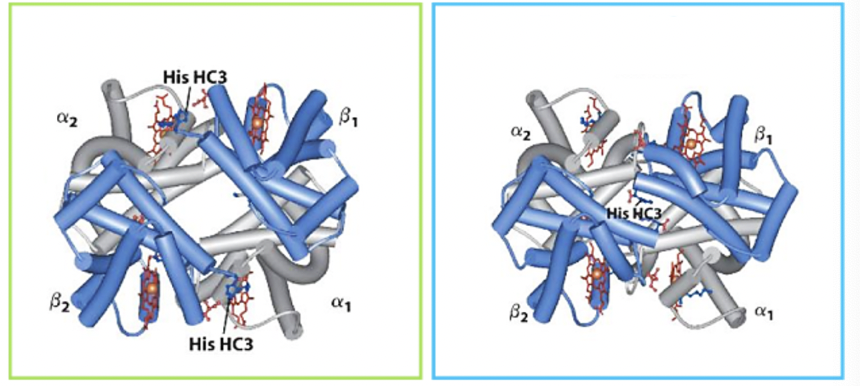
Does the image depict myoglobin or hemoglobin?
hemoglobin
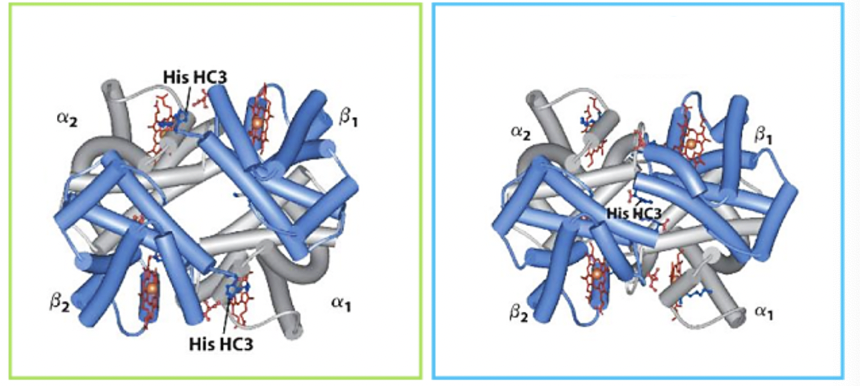
Does the green boxed protein represent the T state or the R state?
T state
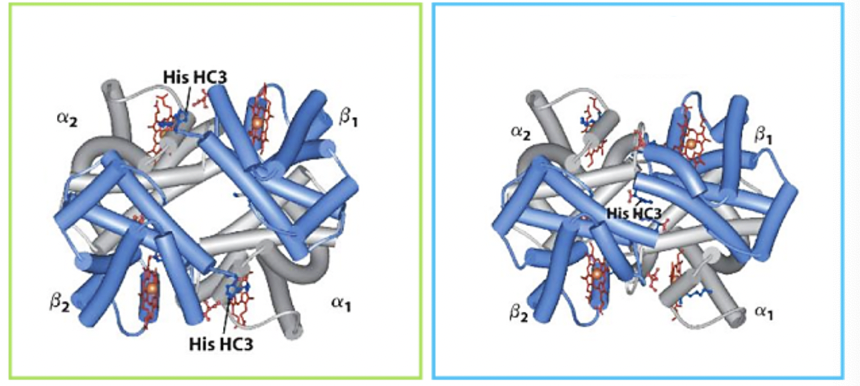
The T state is most stable with oxygen
False
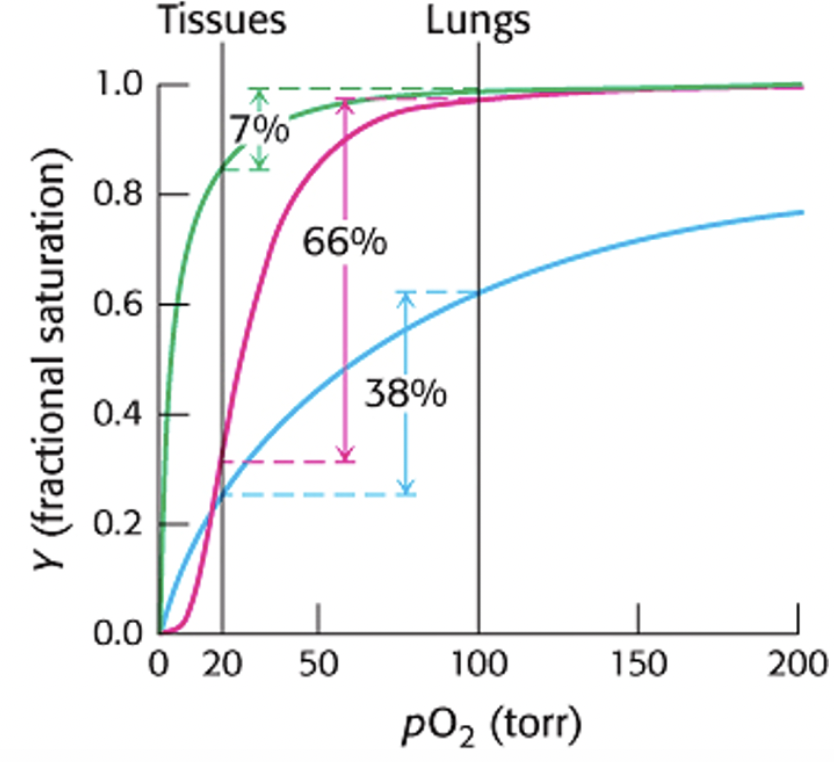
Cooperativity enhances oxygen delivery by hemoglobin. Because of cooperativity between O2 binding sites, hemoglobin delivers more O2 to actively metabolizing tissues than would myoglobin or any noncooperative protein, even one with optimal O2 affinity. Evaluate the graph and determine which line on the graph represents no cooperativity?
Blue line
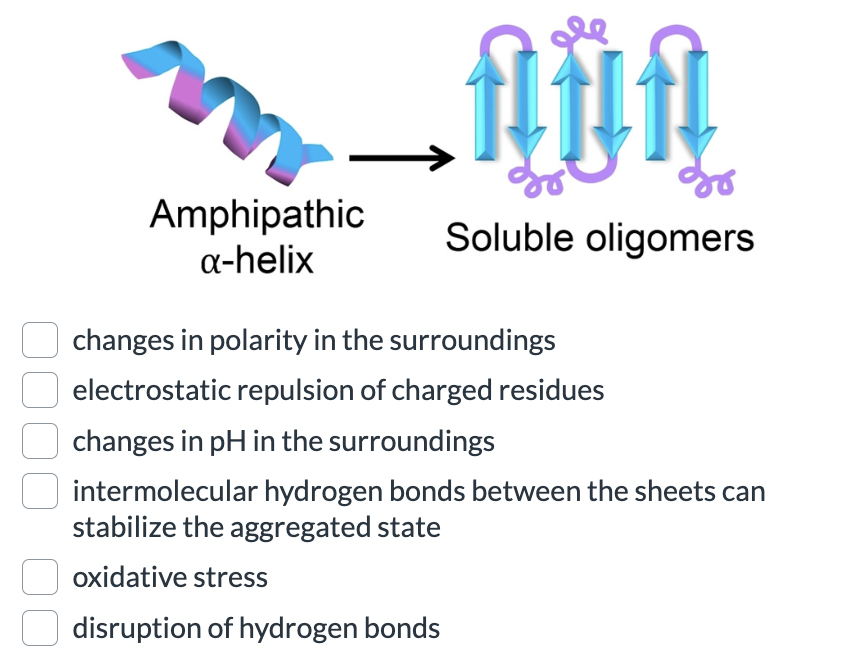
What may cause an alpha helix secondary structure to transition to a beta sheet, like in Alzheimer's disease (amino acid sequence is the same).
all of the above
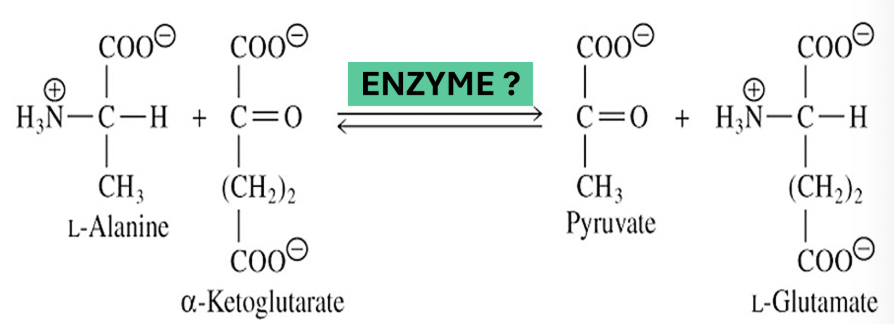
What class of enzyme facilitates the reaction shown?
transferases
What class of enzyme facilitates the reaction below?
translocases

Let us consider a simple reaction. If x=1, what can be determined about this reaction?
the reaction rate is directly proportional to the concentration of one substrate
the units will be s-1
this is a first order reaction
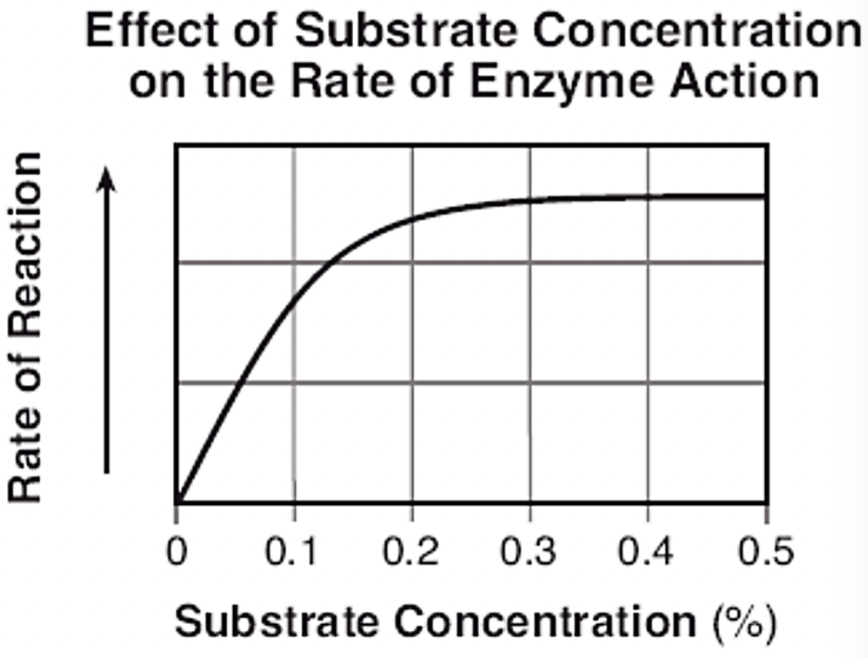
The graph to the left shows the effect of substrate concentration on the action of enzyme P. This enzyme is functioning at its optimal temperature, 28 C, and at its optimal pH 5.5. When the substrate concentration increases from 0.4% to 0.5% , the rate of the reaction
remains the same
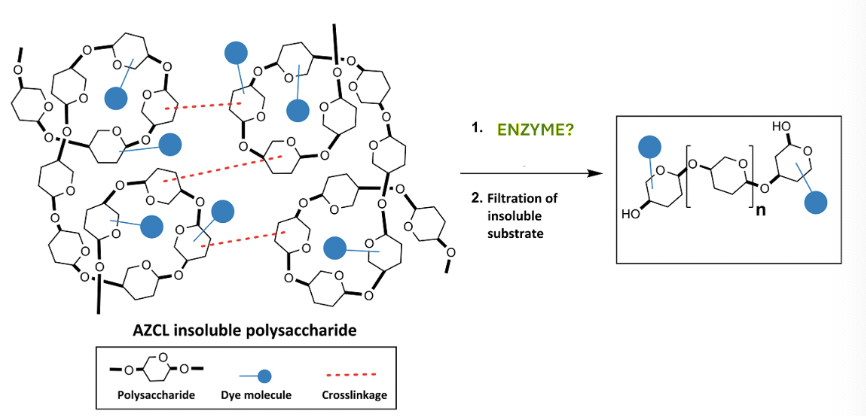
Select the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction
hydrolases
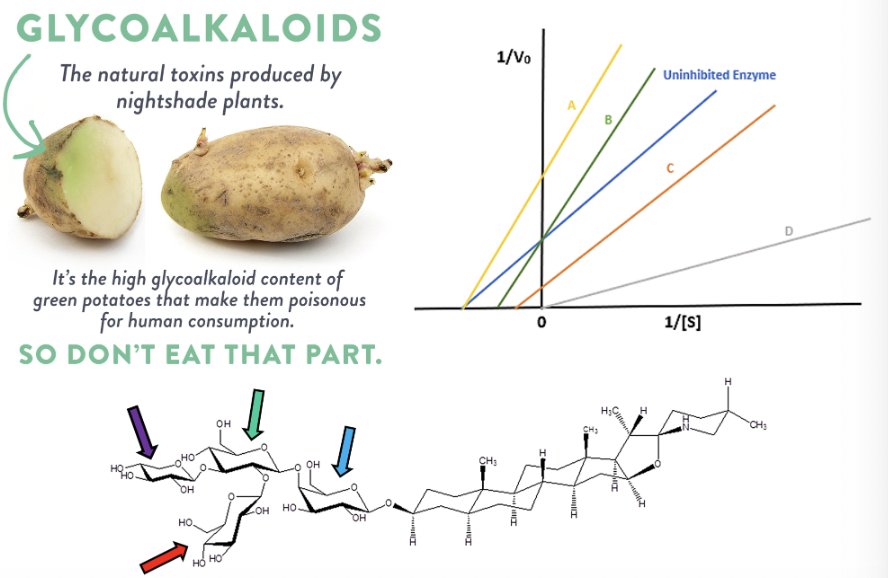
Glycoalkaloids can act as either competitive or non-competitive enzyme inhibitors depending on the specific enzyme and their interactions with the enzyme's active and allosteric sites. Some glycoalkaloids, like solanine and chaconine, are known to inhibit enzymes important in neurotransmitter break down. The buildup of this neurotransmitter causes muscular paralysis and even death for many predators and pests that dare try and eat the potato.
Using the Lineweaver Burk plot shown, determine which line represents competitive inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) by glycoalkaloids.
green (B)
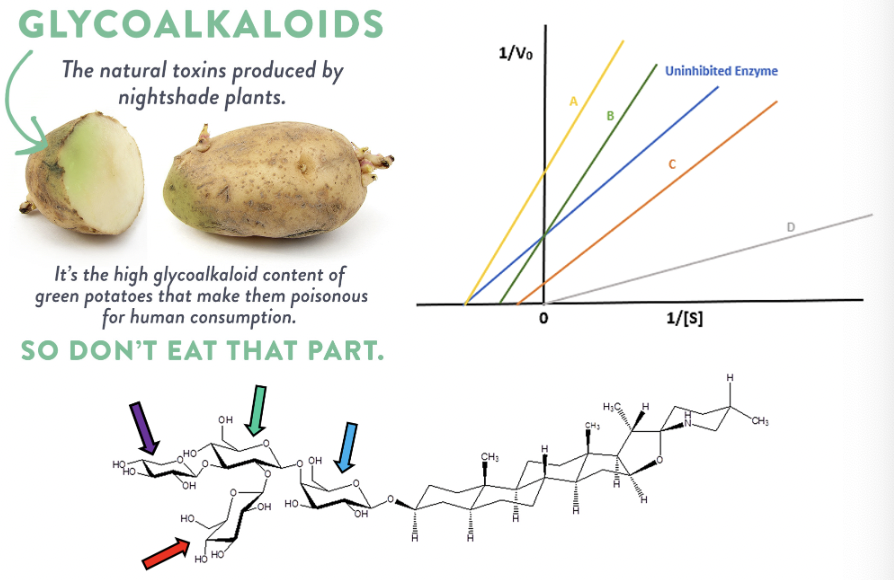
Analyze the carbohydrate structure shown to answer the following question.
The purple arrow is pointing at a structure of glucose.
False
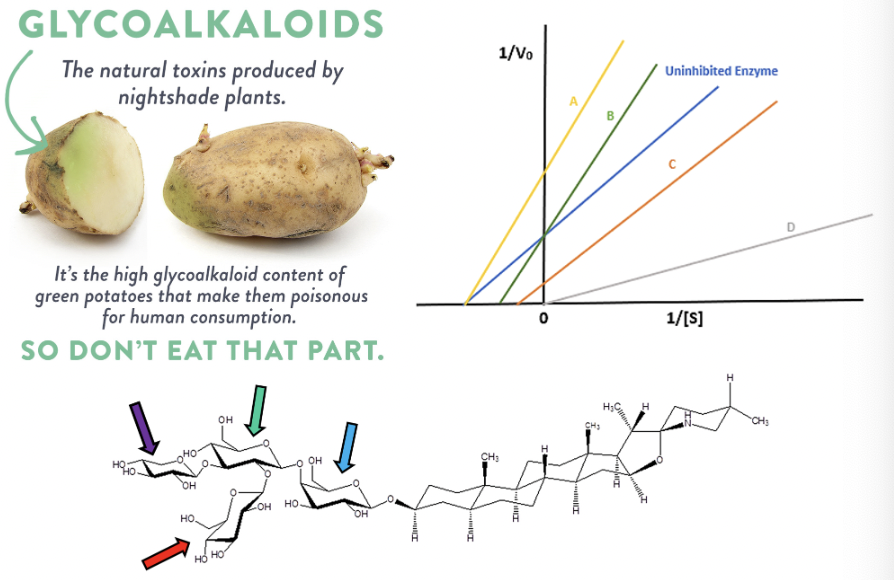
Analyze the carbohydrate structure shown to answer the following question.
What carbohydrate structure (monosaccharide) is the red arrow pointing at?
glucose
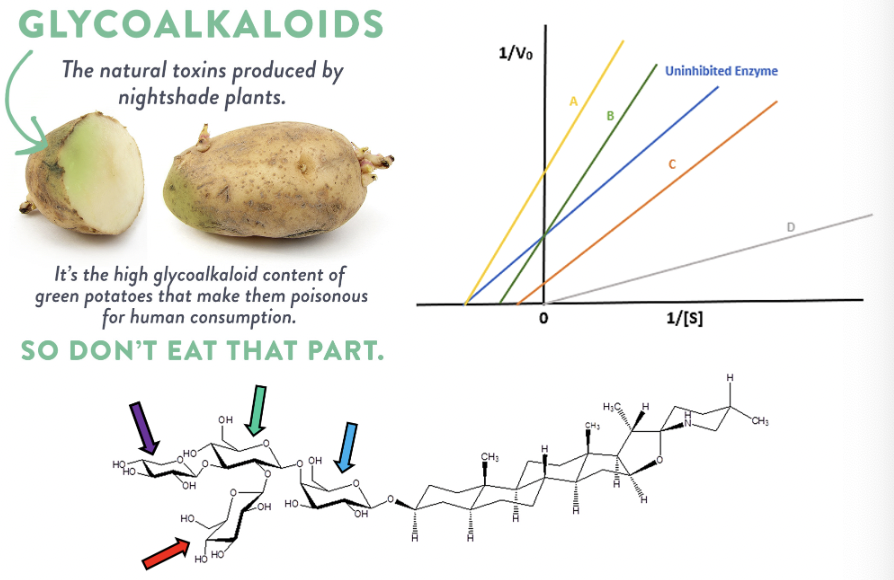
Analyze the carbohydrate structure shown to answer the following question.
Which arrow is pointing at a structure of galactose?
blue
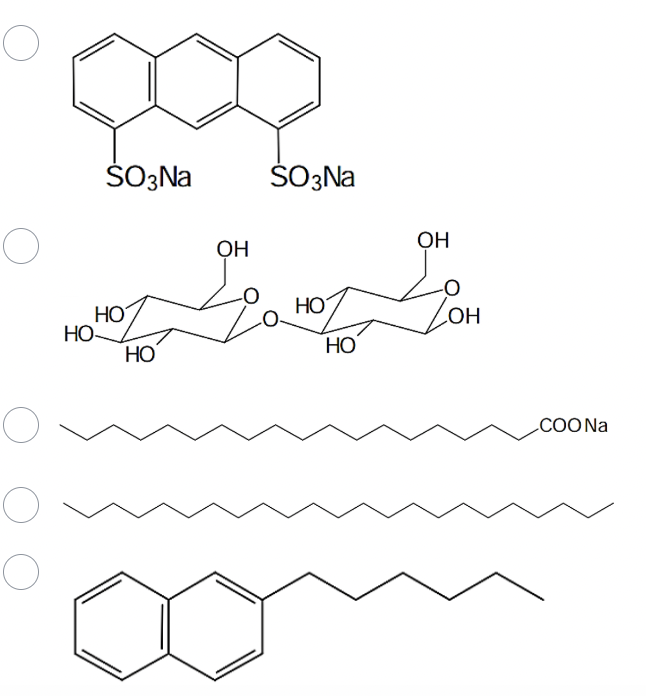
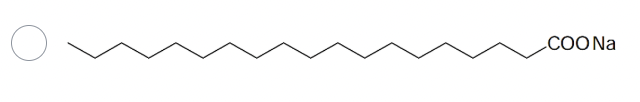
Which one of the following compounds will most likely form micelles in water?
The one with COONa
The following fatty acid is a polysaturated fatty acid. 18:2(∆9,12)
False
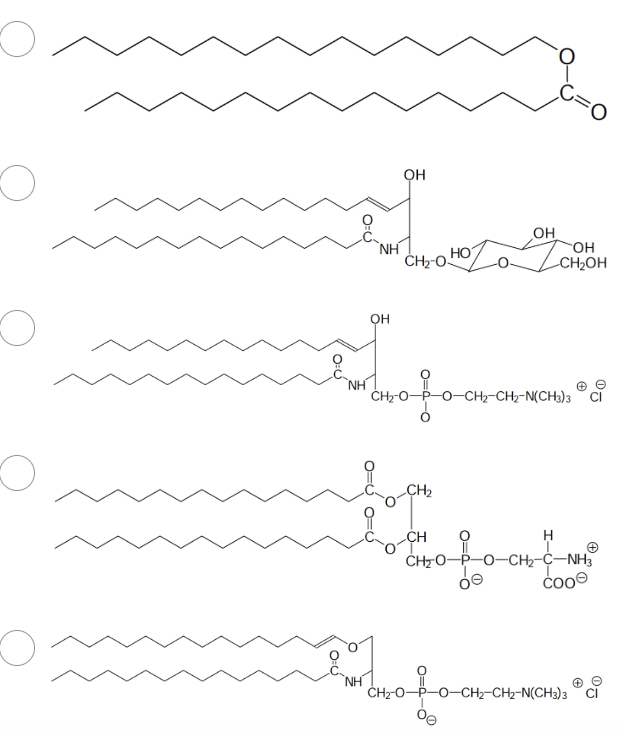
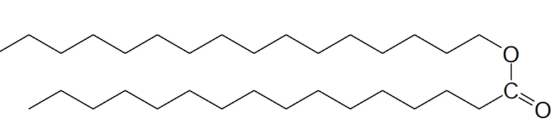
Which one of the following would not be found as part of a biological membrane?
The one with Ester only
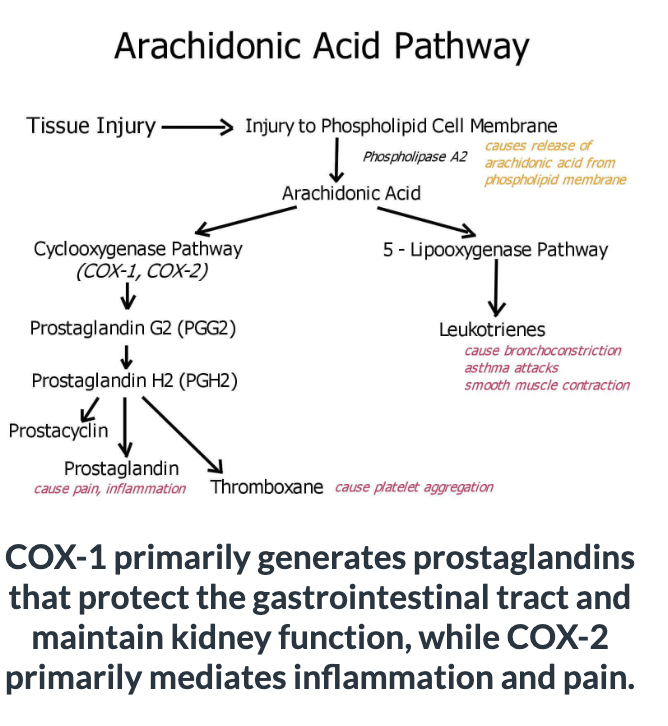
Analyze the Arachidonic Acid Pathway and suggest how the NSAID Ibuprofen (not aspirin) might relieve pain caused by an injury to your knee?
Ibuprofen acts as competitive inhibitor towards the COX1/2 enzyme preventing the production of various eicosanoids, including prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes.
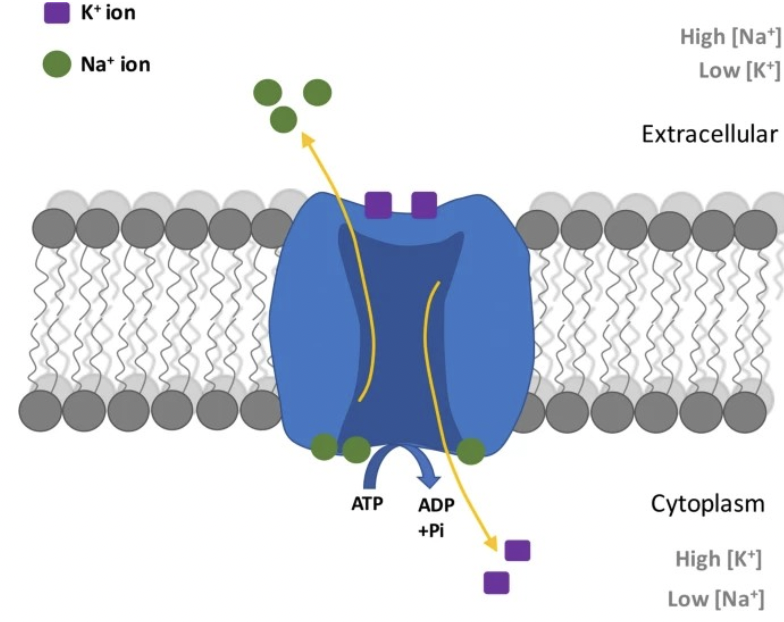
Which of the following is an example of an antiporter?
Na+/K+ ATPase on all cells (sodium potassium pump)
Lipid transport proteins facilitate the movement of lipids across the plasma membrane by binding to specific lipid molecules allowing them to move across the hydrophobic barrier within the plasma membrane.
True
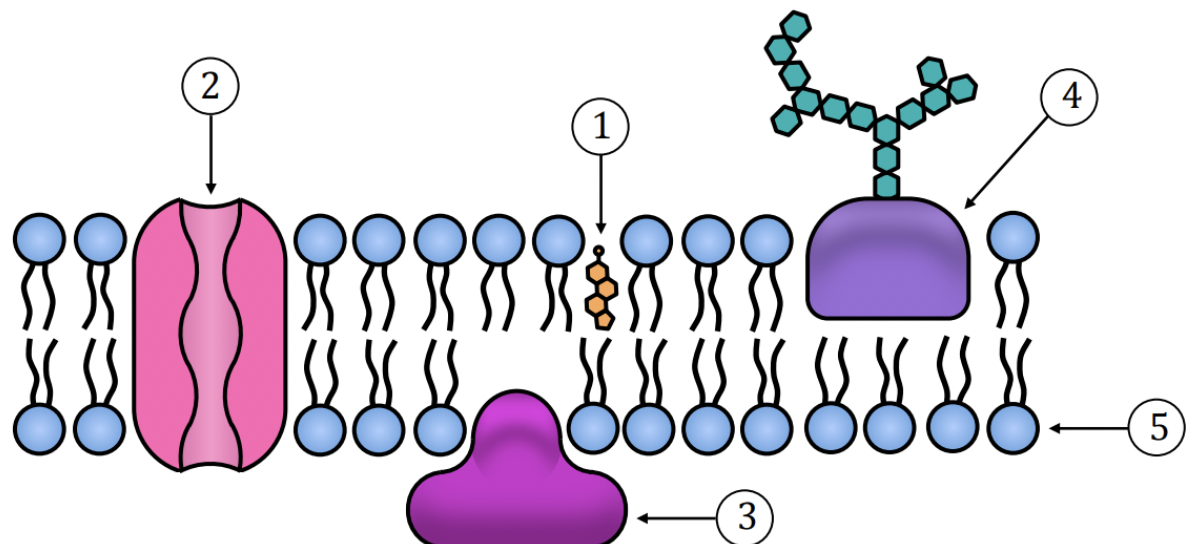
Examine the plasma membrane illustration and determine the structure labeled as #2.
integral protein
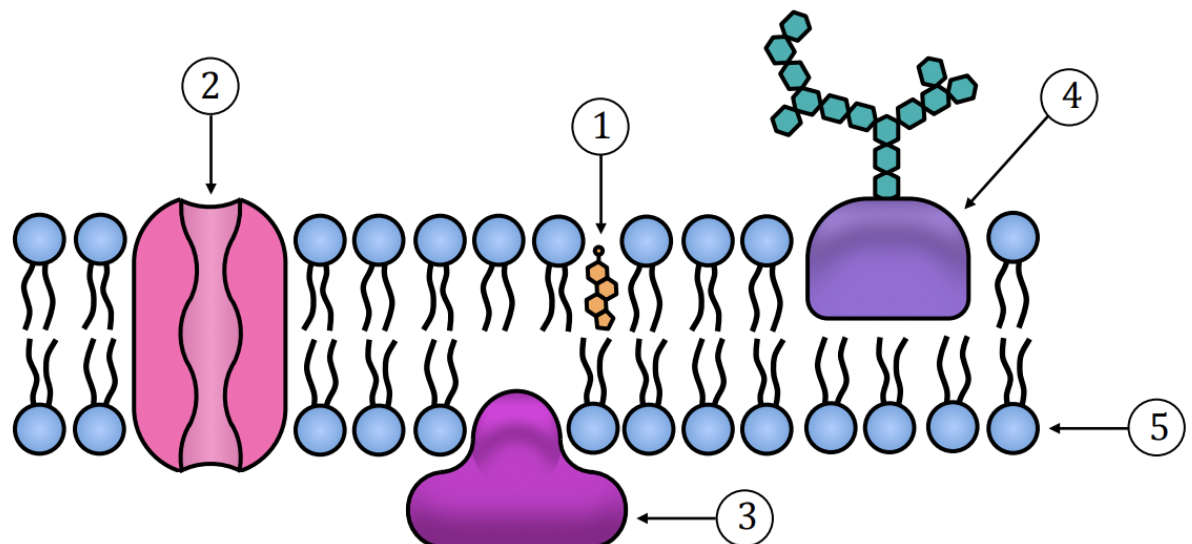
Examine the plasma membrane illustration and determine the structure labelled as #3.
none of these answers are correct
Deoxycytidylate is found in DNA and RNA
False
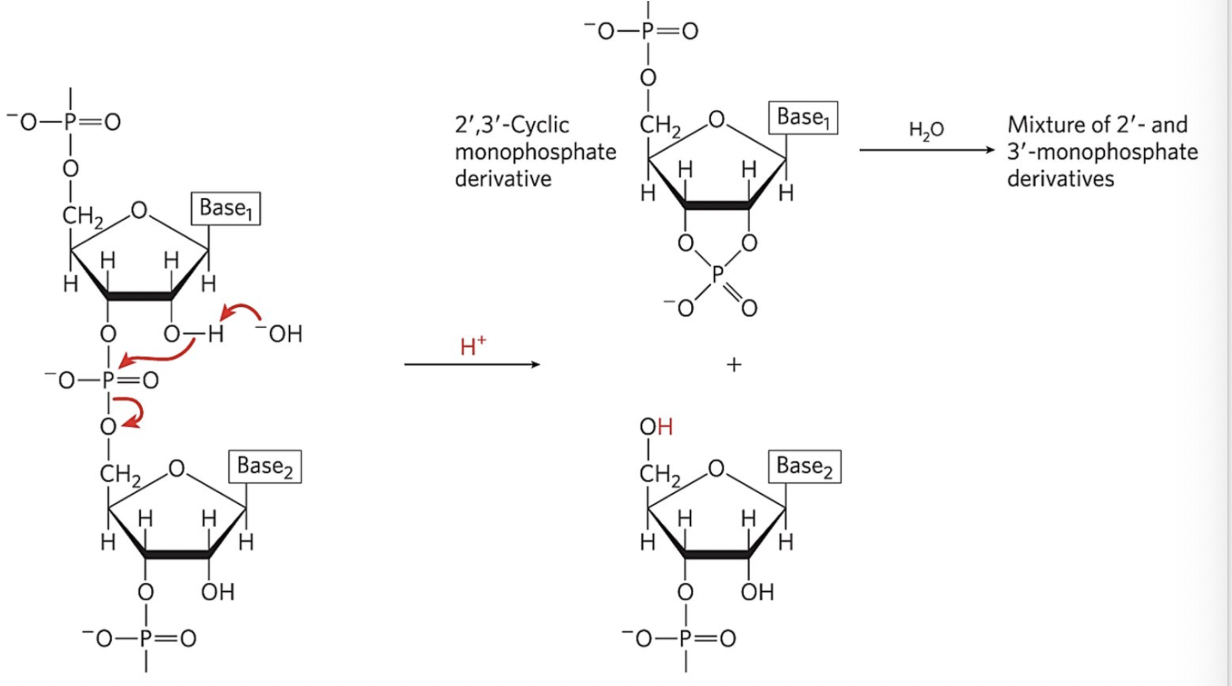
Examine the reaction in the illustration and determine the reaction speed.
fast
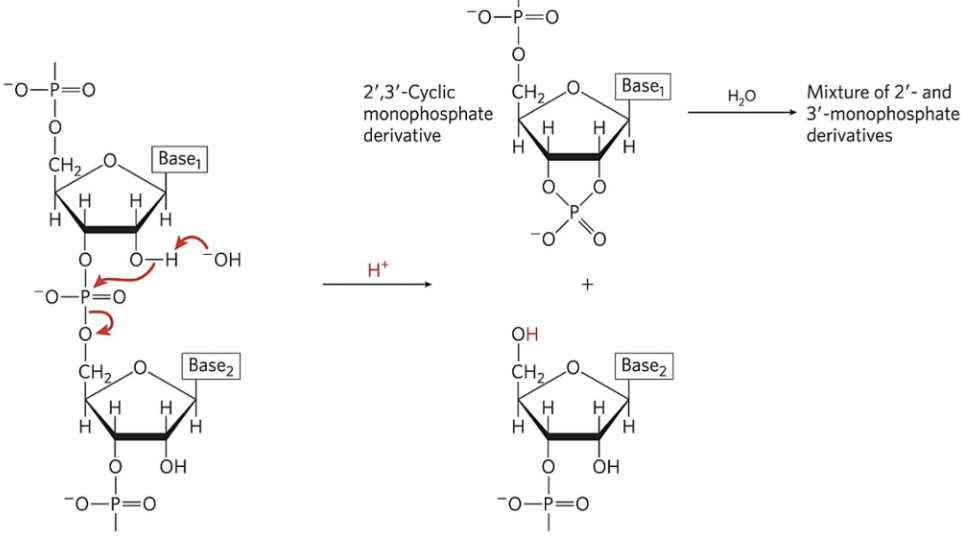
Examine the reaction in the illustration and determine the type of reaction represented.
hydrolysis
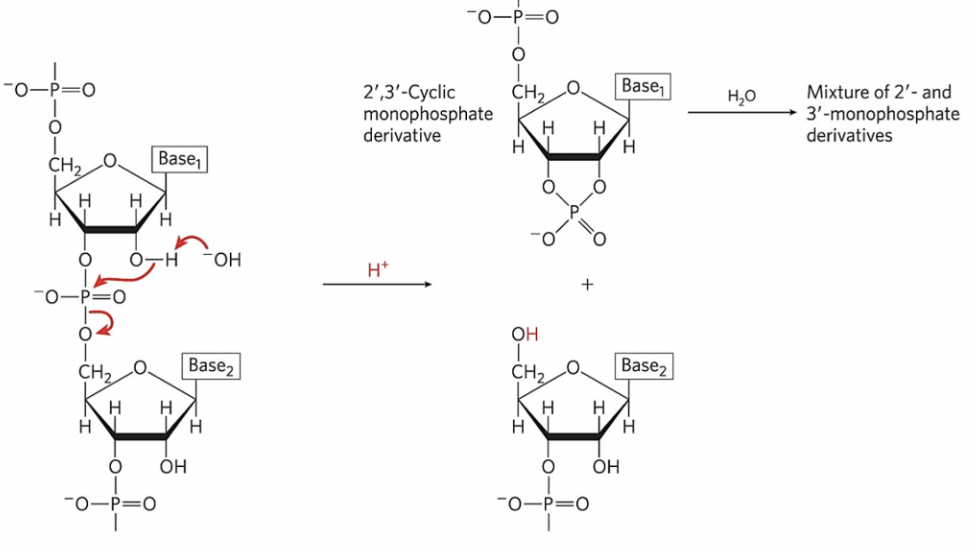
select all the possible ways in which the reaction in the illustration can occur?
enzyme catalyzed
acid catalyzed
base catalyzed

Put the seven basic steps of PCR in order
bring the parent DNA to 95 degrees C
primers become involved at the initiation of annealing
adjust temp to 72 degrees C
taq-man and nucleotides interact with the primers
four DNA strands are present
20 cycles repeated
10^6 fold dna strands present
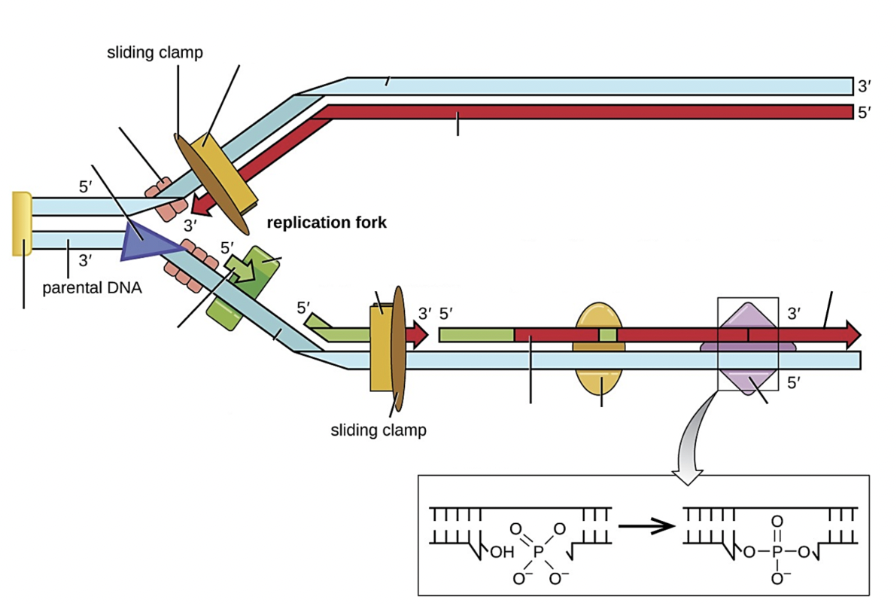
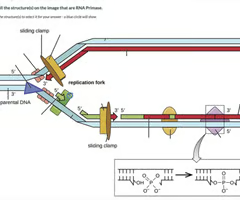
Select all the structure(s) on the image that are DNA ligase
Purple diamond
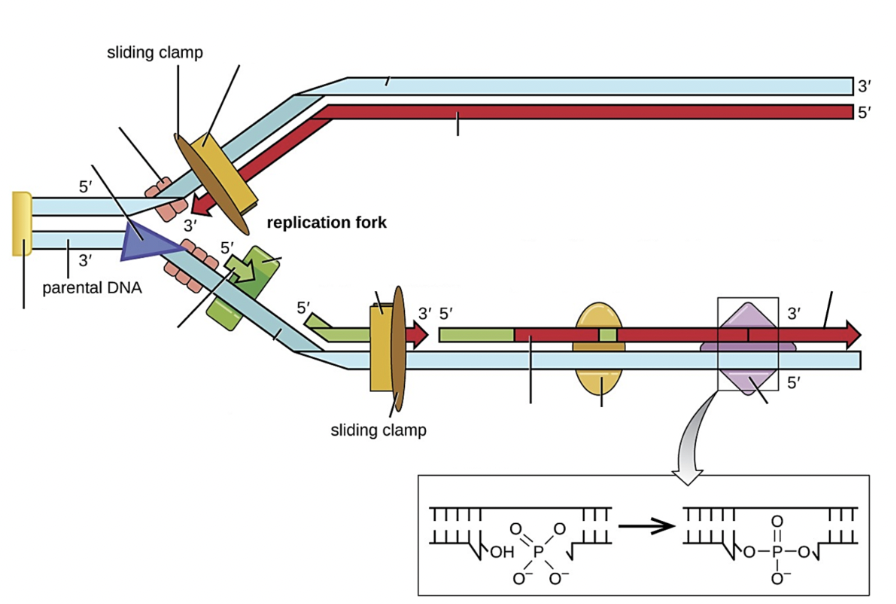
Select all the structure(s) on the image that are DNA polymerase III
yellow rectangle next to sliding clamp
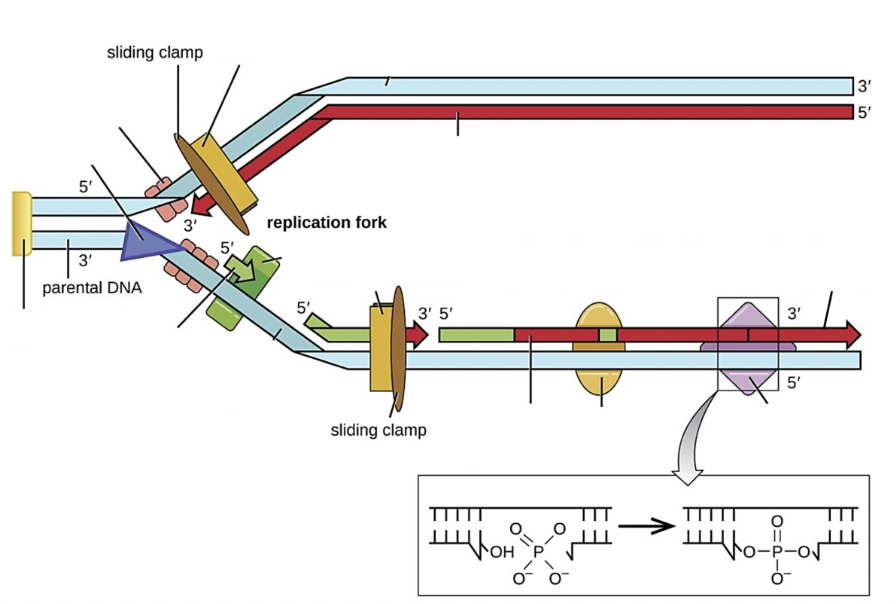
Select all the structure(s) on the image that are DNA polymerase I
yellow oval
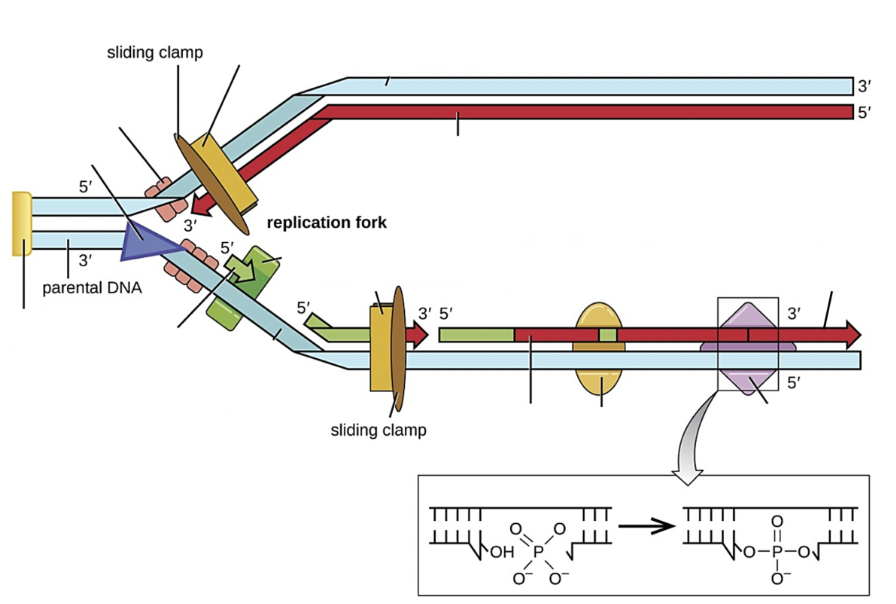
Select all the structure(s) on the image that are RNA primase
green block
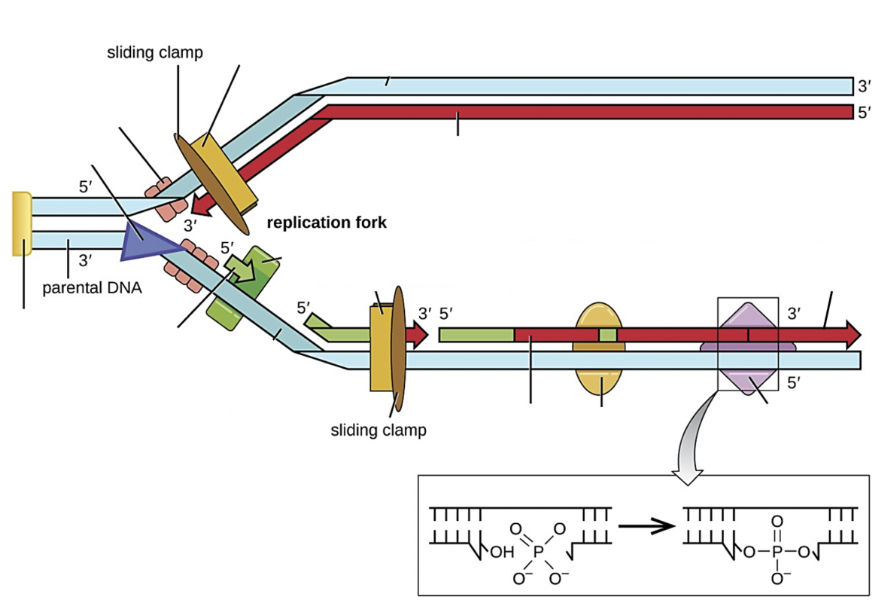
Select all the structure(s) on the image that are Okazaki fragments
shorter red lines on bottom strand
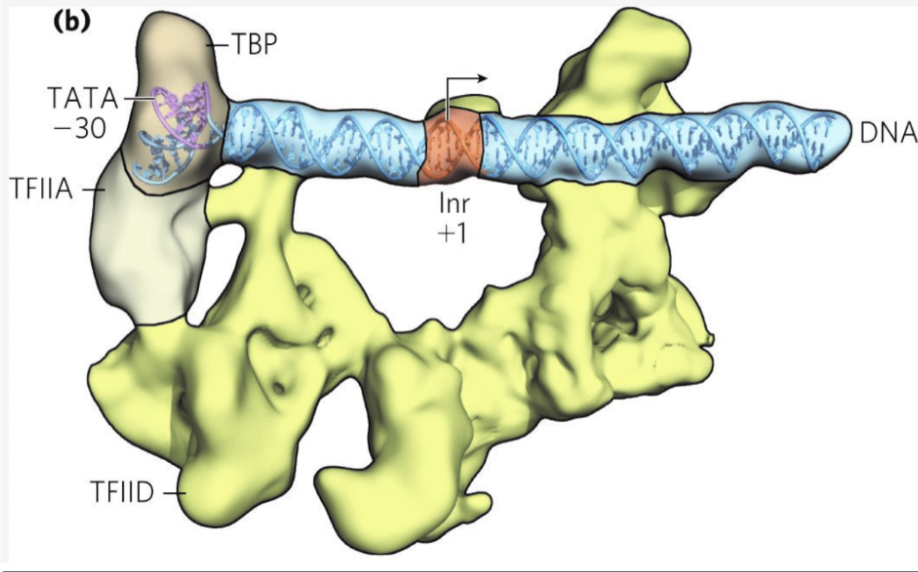
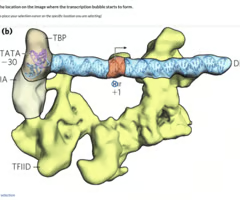
select the location on the image where the transcription bubble starts to form
check anywhere near the lnr+1 box
Which one of the following reactions correctly represents the Watson-Crick base pairing of RNA during transcription?
(NMP)n + NTP --> (NMP)n+1 + PPi

The promoter sequence in RNA is found to extend between:
none of these are correct

What do you think the role of NusA is with RNA polymerase (RNAP)
all are correct EXCEPT facilitates the formation of transcription bubble ( so it induced, fine tunes, becomes, and promotes)
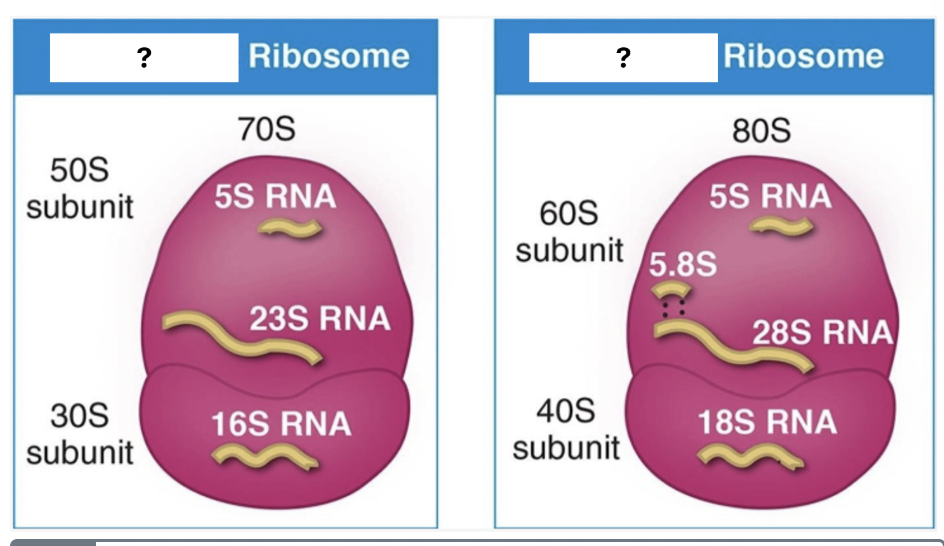
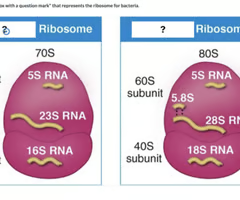
Select the “white box with a question mark” that represents the ribosome for bacteria.
70S ribosome (LEFT)
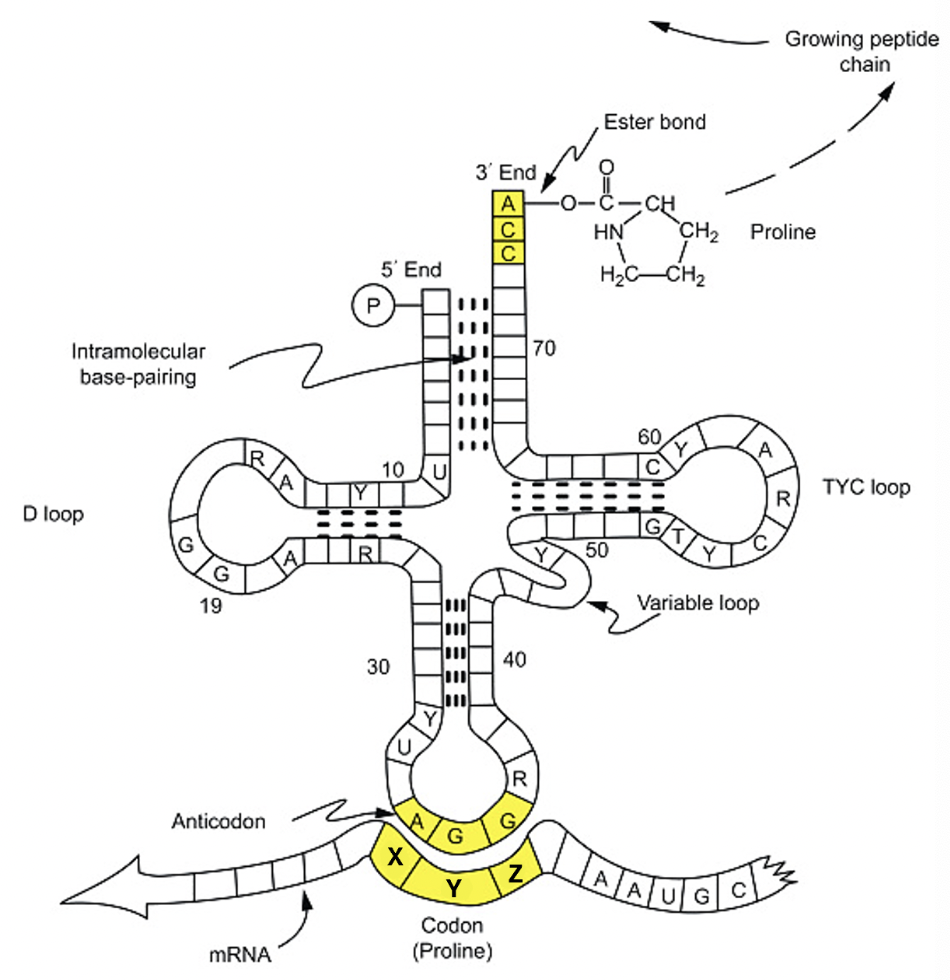
Analyze the image below and determine what the sequence of the codon should be
X: 3’-U
Y: C
Z: C-5’
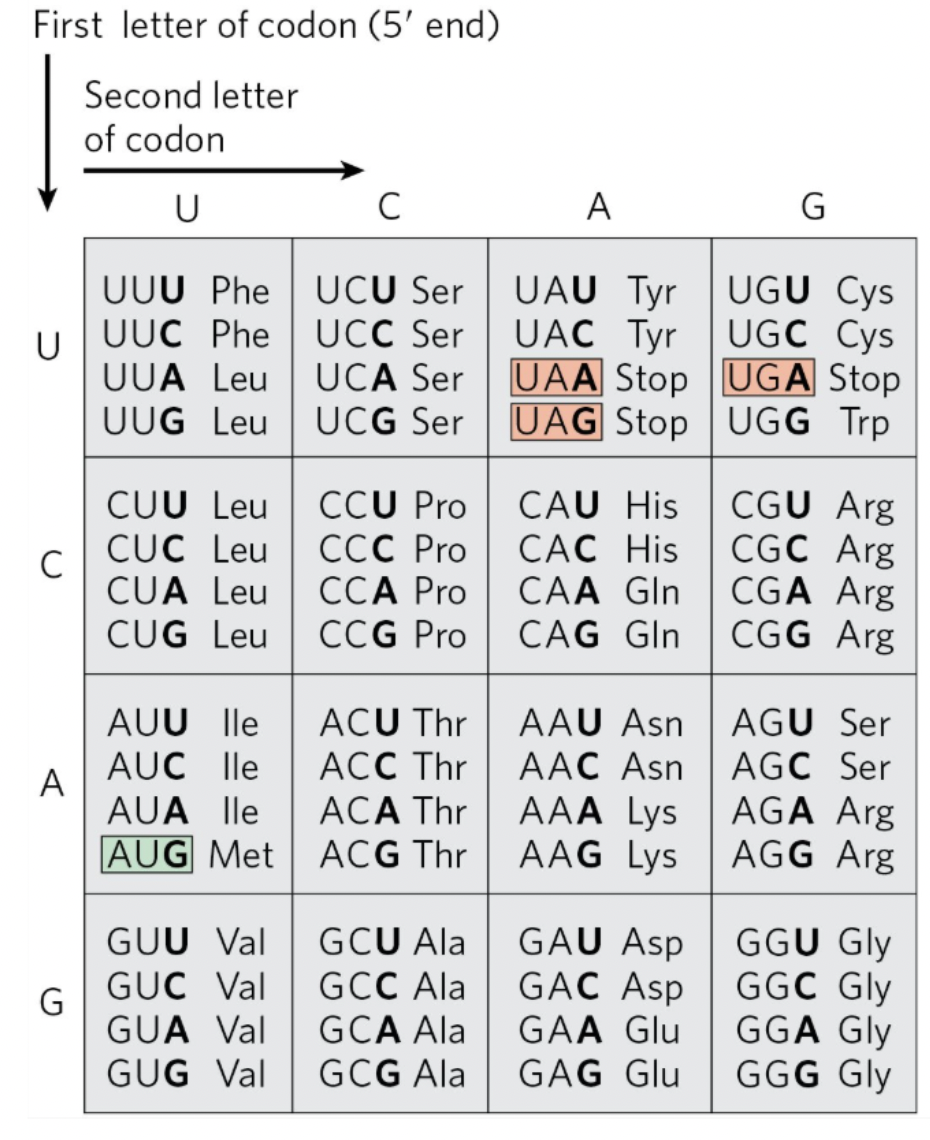
Determine what the codon, anticodon, and amino acid are for this sequence of DNA (the bottom strand in the 5’ —> 3’ direction is the coding strand)
3’-ATG-5’
5’-TAC-3’
Codon: 5’-UAC-3’
Anticodon: 3’-AUG-5’
Amino Acid: Tyr
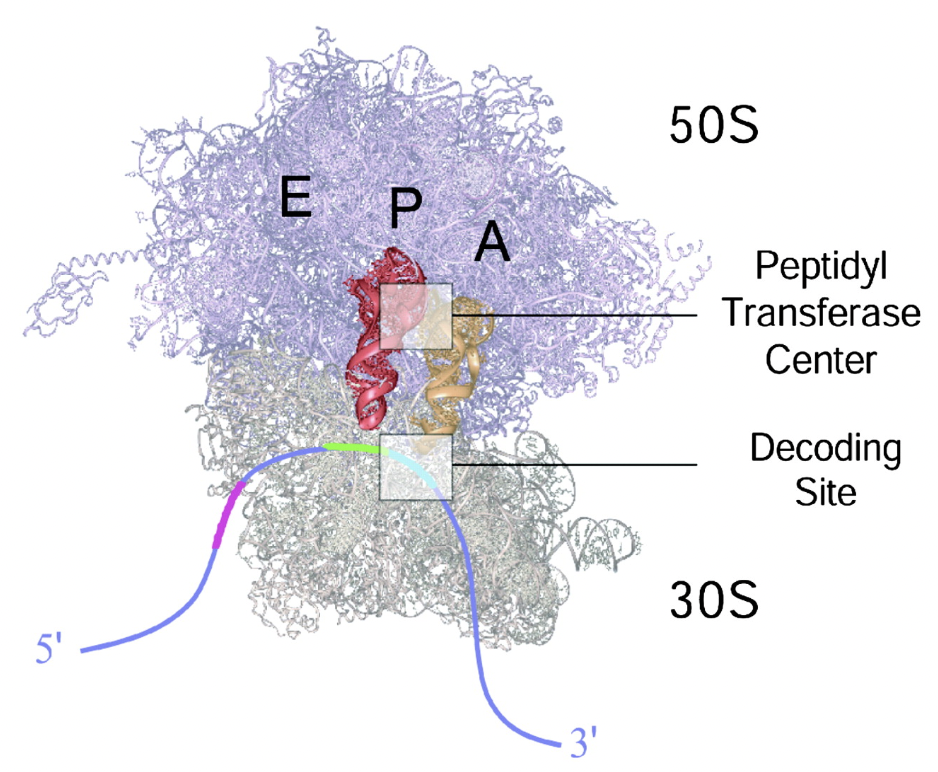
Select the location in the image where the peptide chain is held and grows
Anywhere on or near the P (on top of the red)
The presence of fMet specifically directs the initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria, ensuring that protein synthesis begins with this modified methionine residue
True