Chemistry - 5 Chemical Changes - 5.7 Neutralisation and the pH Scale & 5.8 Strong and Weak Acids
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Alkali
a soluble hydroxide
Base
substance that can neutralise acids
Acid
any compound that forms H⁺ ions in solution
Neutral
neither acidic nor alkaline
Dissolving sodium hydroxide in water
sodium hydroxide (water→) sodium ions(aq) + hydroxide ions(aq)
Indicators [4]:
- litmus paper
- universal indicator
- phenolphthalein
- methyl orange
Litmus paper [3]
acid: red
neutral: no change
basic: blue
Universal indicator
an indicator with a different colour for each pH value.
Phenolphthalein [3]
acid: colourless
neutral: colourless
basic: pink
Methyl orange [3]
acid: red-orange
neutral: yellow
basic: yellow
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14

Neutral solution + universal indicator
green
Acidic solution + universal indicator
red - yellow
Basic solution + universal indicator
blue - purple
pH meter
a device used to measure the pH of a solution

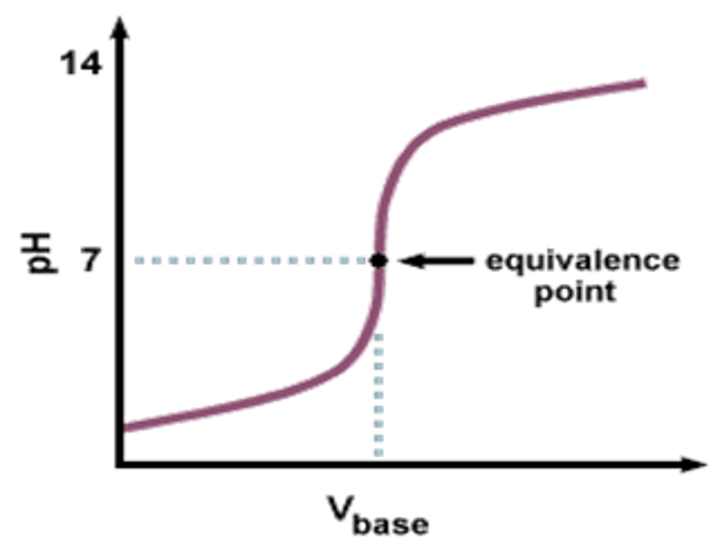
Equivalence point
the point in a titration where the number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of moles of hydroxide ions (middle of vertical drop)
Ionise
the reaction of a molecular substance with a solvent to form ions in solution.
Acids are classed as strong or weak depending on how they...
ionise in water
In aqueous solutions, acid molecules...
ionise and release H⁺ ions
Strong acids ... in aqueous solutions
fully ionise
How can we tell if an acid is weak?
it is a reversible reaction
Weak acids ... in aqueous solutions
partially ionise
Carbonic acid
H₂CO₃
Ethanoic acid
CH₃COOH
Citric acid
C₆H₈O₇
As the pH scale decreases by one unit...
the concentration of hydrogen ions increases by ten times
Concentration of acid
number of moles of acid molecules per unit of volume
Concentration vs. strength
concentration is the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solution while strength refers to the solute's tendency to form ions in water
Ethanoic acid dissolving in water
CH₃COOH ⇌ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺