17. Biological Membrane - Active Transport
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Which of the following is/are a highly specific mechanism(s) of cell transport? Select ALL possible answers.
Select all that apply
A)
Active transport of ions and medium size polar molecules
B)
Receptor mediated endocytosis
C)
Simple diffusion
D)
Facilitated diffusion
E)
Osmosis
A)
Active transport of ions and medium size polar molecules
B)
Receptor mediated endocytosis
D)
Facilitated diffusion
proteins involved in active transport are specific to the molecules that they let in, same with facilitated diffusion
Which of the following cells can perform phagocytosis? Choose all that apply.
Select all that apply
A)
Bacteria
B)
White blood cells
C)
Plant cells
D)
Fungal cells
E)
Skin cells
F)
Amoeba
B)
White blood cells
F)
Amoeba
Ion channel proteins are always ____________________________
A)
glycoproteins with oligosaccharide attached
B)
lipoproteins with lipid attached
C)
soluble proteins in the cytoplasm
D)
integral membrane proteins
E)
peripheral membrane proteins
D)
integral membrane proteins
Transmembrane proteins are integral protein that can form a channel for ions to go through the membrane.
Animal viruses infect specific host cells and do not cross host range. This is because viruses are recognized and allowed inside cells through _______________________
A)
Phagocytosis
B)
Pinocytosis
C)
Receptor mediated endocytosis
D)
Facilitated diffusion
E)
Exocytosis.
C)
Receptor mediated endocytosis
Receptor proteins on cells are recognized and bound by proteins on viruses which trigger the endocytosis of the virus. Receptor is specific to the viral protein
Refer to the ECG chart segment shown above and choose the point that represents the depolarized state that results in the action potential.
A) P
B)Q
C)R
D)S
E)T
C) R
R represents the most positive membrane potential and leads to the action of reversal to make the membrane potential negative.
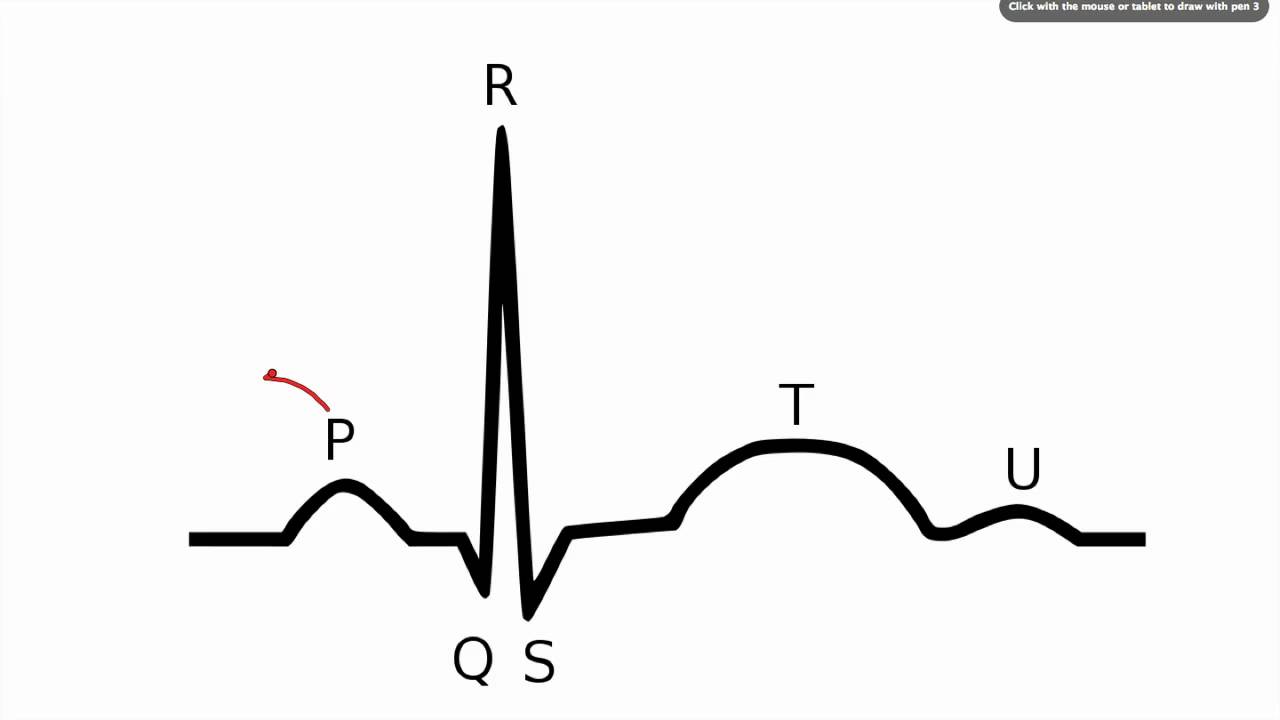
Refer to the ECG chart segment shown above and answer the following question. Which proteins will be responsible for the depolarization from Q to R?
A)
Na+-K+ pump moving 2 K+ in and 3 Na+ out
B)
H+ pump transporting protons inside
C)
ATP synthase pumping ATP outside
D)
Voltage gated K+ channel pumping K+ outside
E)
Voltage gated Na+ channel pumping Na+ inside
E)
Voltage gated Na+ channel pumping Na+ inside
When the cell's membrane potential reaches +30 mV, what should happen to restore the membrane potential to become -70 mV?
A)
Allow K+ to leave cell and Na+ to come in
B)
Transport Cl- to outside
C)
Transport both Na+ and K+ inside
D)
Transport K+ to outside
D)
Transport K+ to outside
When cations such as K+ leave cell the inside become more negative and reaches -60mV
A high level of LDL (Low-density lipoprotein) – cholesterol found in blood (serum) is a major risk factor for heart disease. Such high cholesterol may be due to diet or genetic make-up. Which of the following may be the reason for a vegan (no animal or dairy products) to have high levels of serum LDL cholesterols?
A)
Synthesis of cholesterol by liver
B)
Lack of membrane receptors to take up cholesterol
C)
Consumption of cholesterol in the vegan diet
D)
A and B
E)
A and C
D)
A and B
Cholesterol is not present in plants and hence vegan diet will not have any dietary cholesterol.
What is the form of energy being used in the active transport of protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion?
A)
ATP synthase making ATP
B)
Voltage gated ion channels
C)
Electron flow through the membrane proteins
D)
Citric acid cycle
E)
Break down of ATP into ADP and Pi
C)
Electron flow through the membrane proteins
List the sequence of cell transport mechanisms that transports a simple sugar, complex carbohydrate, and minerals/ions from the intestine into the epithelial cells lining the small intestine.
rough ER to vesicle to golgi to vesicle to cell membrane for exocytosis