Tour of the Cell Test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:04 AM on 10/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Theory
-All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
-The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
-Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
-The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
-Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
2
New cards
cytology
the branch of biology that studies the structure and function of cells
3
New cards
biochemistry
study of the metabolism (chemical processes) of organisms and cells
4
New cards
eukaryotic cell size range
10 – 100 um
5
New cards
prokaryotic cell size range
most are 1-5 um, some .1-1 um
6
New cards
What are the organelles present in all cells? Functions?
-plasma membrane: Regulates what goes in and out of the cell
-cytoplasm: Internal space of the cell
-cytosol: Jelly like material in the cytoplasm
-ribosomes and genetic material: protein sythesis
-cytoplasm: Internal space of the cell
-cytosol: Jelly like material in the cytoplasm
-ribosomes and genetic material: protein sythesis
7
New cards
Why is there a limit on how small a cell can be?
Need to be large enough to contain DNA and ribosomes to carry out metabolism for life functions
8
New cards
Why is there a limit on how large a cell can be?
-There are limits to how much material can cross a given area of membrane in a period of time. (Diffusion)
-Want to maximize the size (area) of the membrane compared to the internal space it has to have efficient exchange with environment
-Smaller cells have more efficient exchange because of the large SA to vol ratio.
-When cells increase in size the internal volume increases faster than SA of the membrane
-bigger the cell gets (volume) more nutrients it needs, so needs a good ratio
-If the cell is too large, then the distance materials have to travel within the cell becomes too inefficient (Distance)
-Inadequate to sustain life.
-Want to maximize the size (area) of the membrane compared to the internal space it has to have efficient exchange with environment
-Smaller cells have more efficient exchange because of the large SA to vol ratio.
-When cells increase in size the internal volume increases faster than SA of the membrane
-bigger the cell gets (volume) more nutrients it needs, so needs a good ratio
-If the cell is too large, then the distance materials have to travel within the cell becomes too inefficient (Distance)
-Inadequate to sustain life.
9
New cards
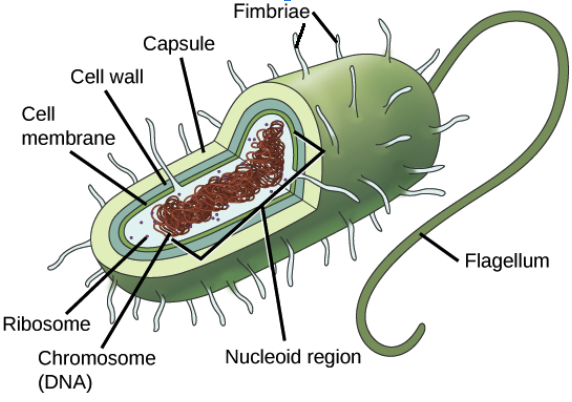
Organelles found in prokaryotic cells and their functions
Cell membrane: Dictates what goes in and out of cell
Cell wall : Prevents lysis
Capsule: slimy coat that protects them against our immune system and antibiotics; Also helps them adhere to surfaces
Cytosol: Jellylike substance in which things are suspended in
Cytoplasm: Space within cell
Ribosomes: Complexes that synthesize proteins
DNA: Stores genetic material that codes for mRNA
Flagella: helps propel them through watery environments
Pili/Fimbriae: extensions that also help bacteria stick to surfaces
Nucleoid Region: Region where DNA is concentrated
Cell wall : Prevents lysis
Capsule: slimy coat that protects them against our immune system and antibiotics; Also helps them adhere to surfaces
Cytosol: Jellylike substance in which things are suspended in
Cytoplasm: Space within cell
Ribosomes: Complexes that synthesize proteins
DNA: Stores genetic material that codes for mRNA
Flagella: helps propel them through watery environments
Pili/Fimbriae: extensions that also help bacteria stick to surfaces
Nucleoid Region: Region where DNA is concentrated
10
New cards
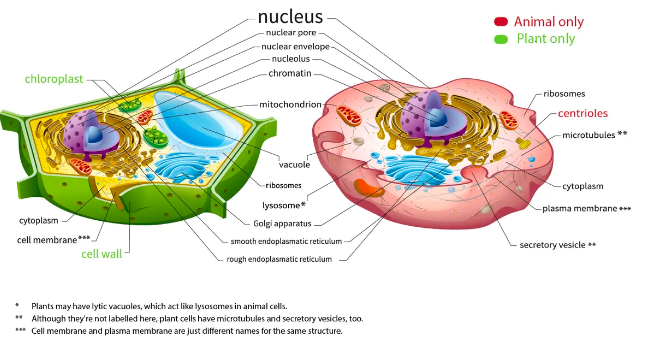
Organelles found in eukaryotic cells and their functions
Nucleus: houses genetic information
Plasma membrane: selectively permeable barrier surrounding the cell
Ribosomes: complexes that make proteins
Golgi Apparatus: active in synthesis, modification, sorting, and secretion of cell products, like proteins
Mitochondria: where CR occurs and most ATP is produced
Peroxisomes: break down and detoxify substances, produces Hydrogen Peroxide and then converts it to water
Cytoskeleton: structural support in cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum: calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism
Plasma membrane: selectively permeable barrier surrounding the cell
Ribosomes: complexes that make proteins
Golgi Apparatus: active in synthesis, modification, sorting, and secretion of cell products, like proteins
Mitochondria: where CR occurs and most ATP is produced
Peroxisomes: break down and detoxify substances, produces Hydrogen Peroxide and then converts it to water
Cytoskeleton: structural support in cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum: calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism
11
New cards
Organelles specific to animal cells
Lysosome, centrioles, flagella
12
New cards
organelles specific to plant cells
chloroplast, central vacuole, cell wall, plasmodesmata
13
New cards
importance of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells
-Allow cell to maintain different local environments for different types incompatible reactions.
-Allows those reactions to happen simultaneously.
-Enzymes built into membranes of organelles that catalyze reactions within organelle.
-Allows those reactions to happen simultaneously.
-Enzymes built into membranes of organelles that catalyze reactions within organelle.
14
New cards
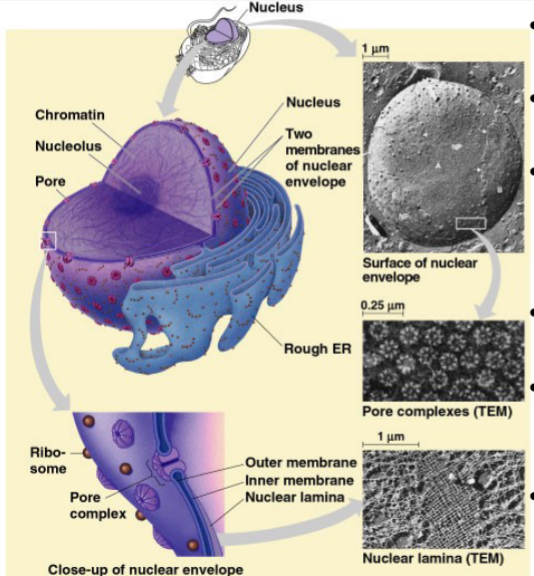
Nuclear envelope
double layered; Encloses the nucleus, separating its contents from the cytoplasm; outer membrane is on outside, inner membrane in inside
15
New cards
Nuclear Pores
Regulates what goes in/out of nucleus (Proteins, RNA, macromolecules)
Connect to either bilayer
Connect to either bilayer
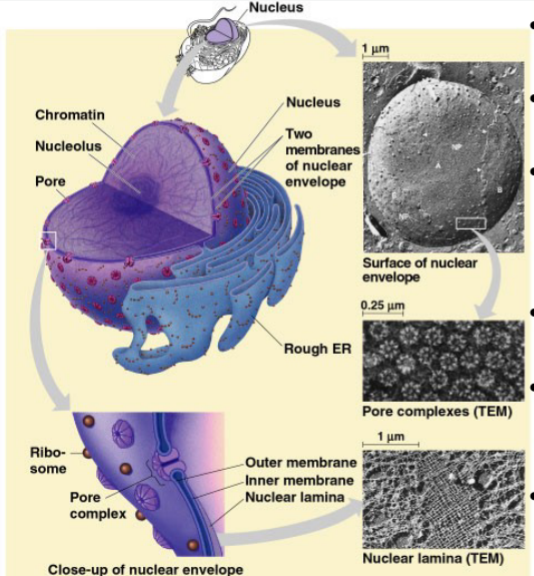
16
New cards
Nuclear Lamina
Netlike array of protein filaments that maintain the shape of the nucleus through mechanically supporting the nuclear envelope
Lines nueclear side of envelope (Except pores)
Lines nueclear side of envelope (Except pores)
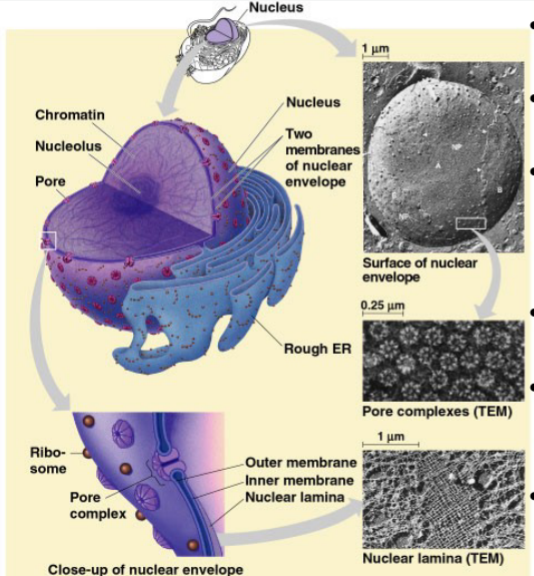
17
New cards
Chromatin
Complex of DNA and proteins making up chromosomes
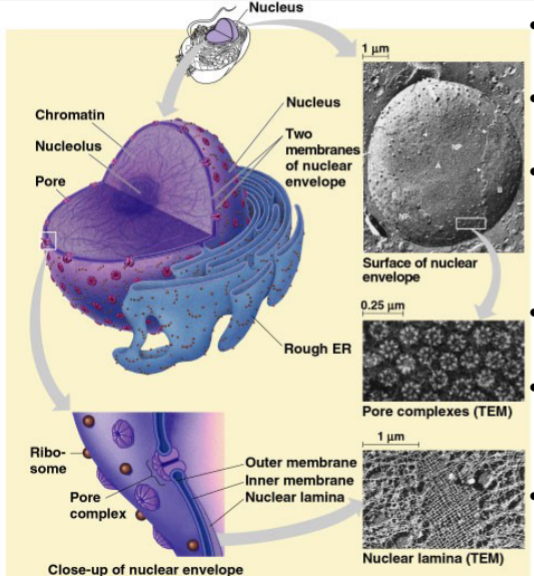
18
New cards
Nucleolus
produces rRNA
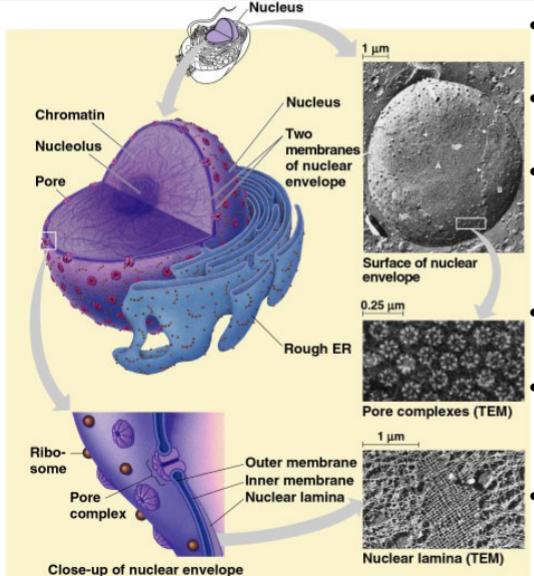
19
New cards
What two macromolecules make up ribosomes?
rRNA and proteins
20
New cards
Ribomes (Function and structure)
-sythesize proteins through translation
-composed of two subunits assembled in cytoplasm (large and small subunits)
-composed of two subunits assembled in cytoplasm (large and small subunits)
21
New cards
Free ribosomes
-Found within the cytosol
-Generally produce proteins that function within the cytosol
-Generally produce proteins that function within the cytosol
22
New cards
Bound ribosomes
-Attached to the Rough ER & nuclear envelope
-Proteins made by bound ribosomes go into cisternal space OR they can be embedded in the ER membrane to then be: secreted from the cell, enzymes in lysosomes or in other vesicles, Embedded in membrane as membrane proteins
-Proteins made by bound ribosomes go into cisternal space OR they can be embedded in the ER membrane to then be: secreted from the cell, enzymes in lysosomes or in other vesicles, Embedded in membrane as membrane proteins
23
New cards
organelles of endomembrane system and their connection
-Nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles/vacuoles, and plasma membrane
-Membranes are all related either through direct physical contact or transfer of vesicles
-Membranes are all related either through direct physical contact or transfer of vesicles
24
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (functions)
-Does not have ribosomes attached to it
-Synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids, steroids (sex hormones), and oils
-Detoxification of drugs and poisons by making them water soluble; Add hydroxyl group to dissolve in water, where it then can be urinated out of the body; The Smooth ER increases in size to keep up with demand (this is called tolerance)
-Attaches receptors to membrane proteins
-Carbohydrate metabolism; breaks down sugars like glycogen through hydrolysis
-Storage of calcium ions; Sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle is modified smooth ER
-Synthesis of lipids, including phospholipids, steroids (sex hormones), and oils
-Detoxification of drugs and poisons by making them water soluble; Add hydroxyl group to dissolve in water, where it then can be urinated out of the body; The Smooth ER increases in size to keep up with demand (this is called tolerance)
-Attaches receptors to membrane proteins
-Carbohydrate metabolism; breaks down sugars like glycogen through hydrolysis
-Storage of calcium ions; Sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle is modified smooth ER
25
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Recticulum
-Has ribosomes attached to it
-Affect secondary and tertiary structure of polypeptide
-Bends polysaccharide into a glycoprotein (protein tagged with a oligosaccharide) for cell-cell recognition
-Polypeptides leave rough ER through transport vesicles and go to Golgi (They will then be secreted, embedded in the plasma membrane, or to be part of the endomembrane system)
-Also considered a membrane factory for the cell (Also produces phospholipids)
-Affect secondary and tertiary structure of polypeptide
-Bends polysaccharide into a glycoprotein (protein tagged with a oligosaccharide) for cell-cell recognition
-Polypeptides leave rough ER through transport vesicles and go to Golgi (They will then be secreted, embedded in the plasma membrane, or to be part of the endomembrane system)
-Also considered a membrane factory for the cell (Also produces phospholipids)
26
New cards
Golgi Apparatus (Function)
-Proteins are Modified, tagged, sorted, stored and sent to destination in cell or secreted from cell.
-Sugar (oligosaccharide) on glycoproteins are altered
-Membrane phospholipids are altered in Golgi too
-Phosphate groups added to proteins tag them for destination.
-Sugar (oligosaccharide) on glycoproteins are altered
-Membrane phospholipids are altered in Golgi too
-Phosphate groups added to proteins tag them for destination.
27
New cards
What cell function is associated with extensive amounts of golgi?
secretion
28
New cards
cis face of Golgi
Site where a transport vesicle will fuse with golgi first
29
New cards
trans face of Golgi
Gives rise to vesicles that pinch off and travel to other sites
30
New cards
lumen
internal compartment or space
31
New cards
lysosome (function)
-Vesicle that pinches off from Golgi, full of hydrolytic enzymes
-Intracellular digestion of food particles, worn-out organelles (autophagy), and non-useful tissues. (finger webbing)
-Intracellular digestion of food particles, worn-out organelles (autophagy), and non-useful tissues. (finger webbing)
32
New cards
What is the pH inside of the lysosome? How is this a protective mechanism for the cell?
-Enzymes work best at pH 5 so proton pumps in lysosome membrane bring in H+ to decrease pH
-if enzymes are released into the cell, lysosomes denature because of neutral pH
-if enzymes are released into the cell, lysosomes denature because of neutral pH
33
New cards
apoptosis
if all lysosomes rupture as a programmed cell death
34
New cards
autolysis
Too much vitamin A ruptures membrane
35
New cards
vesicles
Small membrane bound sac
36
New cards
vacuoles
large membrane bound sac
37
New cards
phagocytosis
Engulfing of smaller organisms or food particles with psuedopods
38
New cards
Describe how lysosomes carry out intracellular digestion.
-Food vacuole formed this way fuse with lysosome whose enzymes digest the food
-Digestion products include simple sugars, AA, other monomers pass through cytosol and become nutrients for cell
-Ex. macrophages, white blood cell engulfs invaders
-Digestion products include simple sugars, AA, other monomers pass through cytosol and become nutrients for cell
-Ex. macrophages, white blood cell engulfs invaders
39
New cards
autophagy
-Hydrolytic enzymes recycle the cells won organic material
damage organelle or small amount of cytosol surround by double membrane
-Lysosome will fuse with outer membrane
-Dismantle enclosed material with enzymes
-Resulting small organic compounds are released to the cytosol for reuse
damage organelle or small amount of cytosol surround by double membrane
-Lysosome will fuse with outer membrane
-Dismantle enclosed material with enzymes
-Resulting small organic compounds are released to the cytosol for reuse
40
New cards
Tay Sachs disease
-Lipid-digesting enzyme is missing or inactive
-Brain becomes impaired by an accumulation of lipids in the cells
-Brain becomes impaired by an accumulation of lipids in the cells
41
New cards
Food vacuole
-Formed by phagocytosis
-deliver nutrients to organelles
-deliver nutrients to organelles
42
New cards
contractile vacuole
-Pump excess water out of the cell, maintains a suitable concentration of ions and molecules inside the cell
-Protects cell from lysing in a hypotonic solution
-Protects cell from lysing in a hypotonic solution
43
New cards
central vacuole
-Stores water, proteins, ions, waste products, pigments, and poisons.
-Helps plant cells grow by absorbing water & elongating the plant cell.
-Doesn't disrupt SA to vol ratio because pushes all organelles to side, so increasing exchange and efficacy
-Helps plant cells grow by absorbing water & elongating the plant cell.
-Doesn't disrupt SA to vol ratio because pushes all organelles to side, so increasing exchange and efficacy
44
New cards
Mitochondria
-Sites of cellular respiration
-Uses oxygen to generate ATP by extracting energy from sugars, fats, and other fuels
- has an inner and outer membrane with many
proteins embedded; creates the Intermembrane space and the Matrix containing DNA and
ribosomes
-can reproduce on their own
-Uses oxygen to generate ATP by extracting energy from sugars, fats, and other fuels
- has an inner and outer membrane with many
proteins embedded; creates the Intermembrane space and the Matrix containing DNA and
ribosomes
-can reproduce on their own
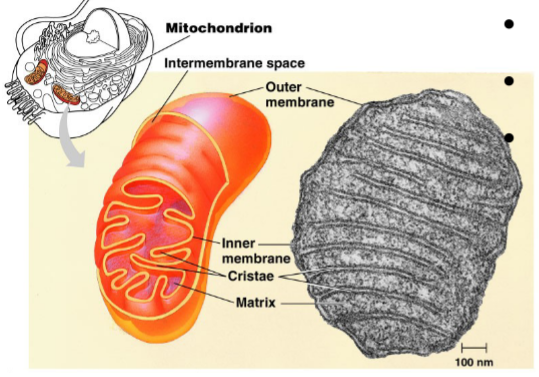
45
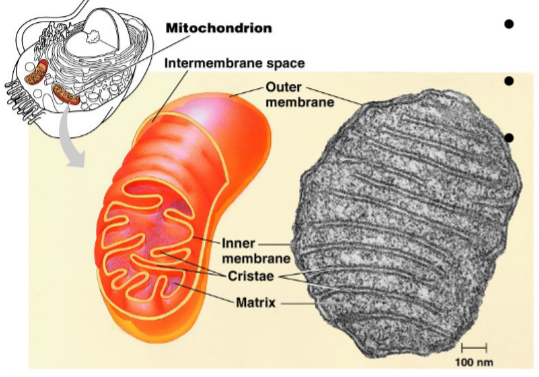
New cards
Christae
bends and folds in mitochondria that increase SA
46
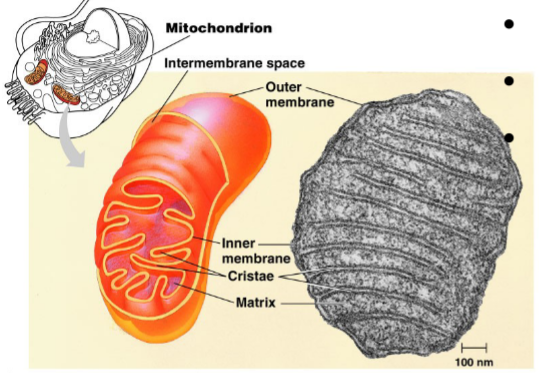
New cards
Matrix
spaces within christae of mitochondria
47
New cards
Chloroplasts
-site of photosynthesis
-Convert solar energy to chemical energy by absorbing sunlight and using it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds such as sugars from carbon dioxide and water
-glucose production
-can reproduce on their own
-Convert solar energy to chemical energy by absorbing sunlight and using it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds such as sugars from carbon dioxide and water
-glucose production
-can reproduce on their own
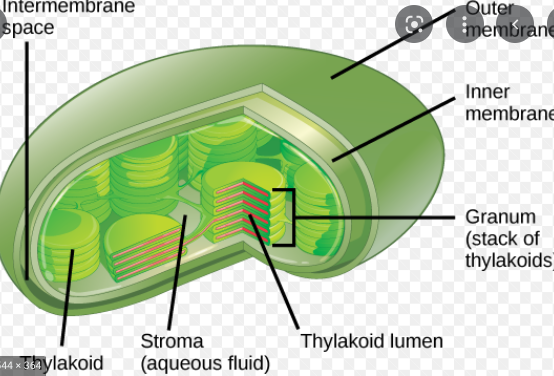
48
New cards
Thylakoids
trap light and contain the thylakoid space
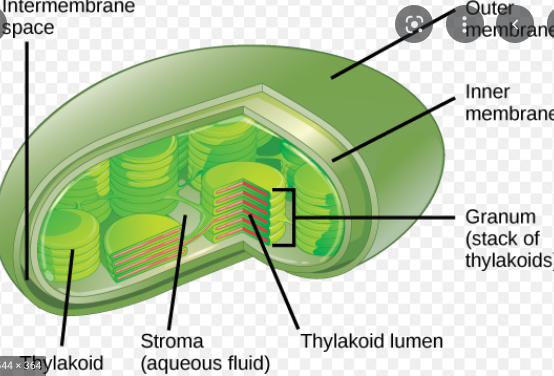
49
New cards
granum
stacks of thylakoids
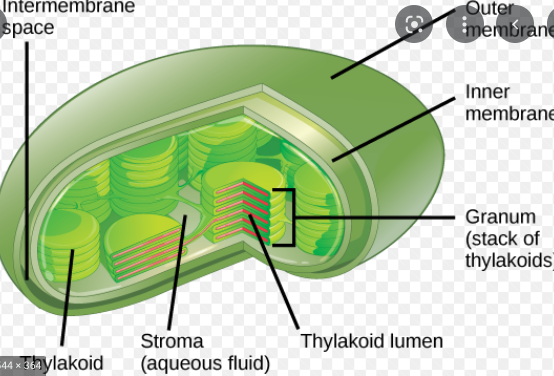
50
New cards
stroma
aqueous fluid within chloroplasts
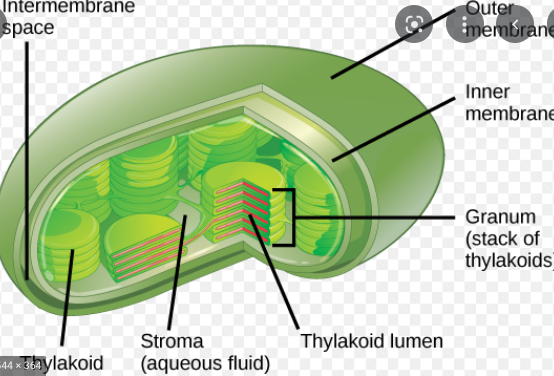
51
New cards
What is the endosymbiont theory stating?
-Prokaryotic cell pinches inward to create some membrane-bound organelles
-Larger prokaryotic cell engulfs a smaller prokaryotic cell through Phagocytosis
-Two cells develops a symbiotic relationship
-Parent gives glucose, smaller gives ATP
-The smaller cell eventually develops into the mitochondria
-Later a photosynthetic prokaryotic cell is engulfed in the same process to create chloroplasts
-Larger prokaryotic cell engulfs a smaller prokaryotic cell through Phagocytosis
-Two cells develops a symbiotic relationship
-Parent gives glucose, smaller gives ATP
-The smaller cell eventually develops into the mitochondria
-Later a photosynthetic prokaryotic cell is engulfed in the same process to create chloroplasts
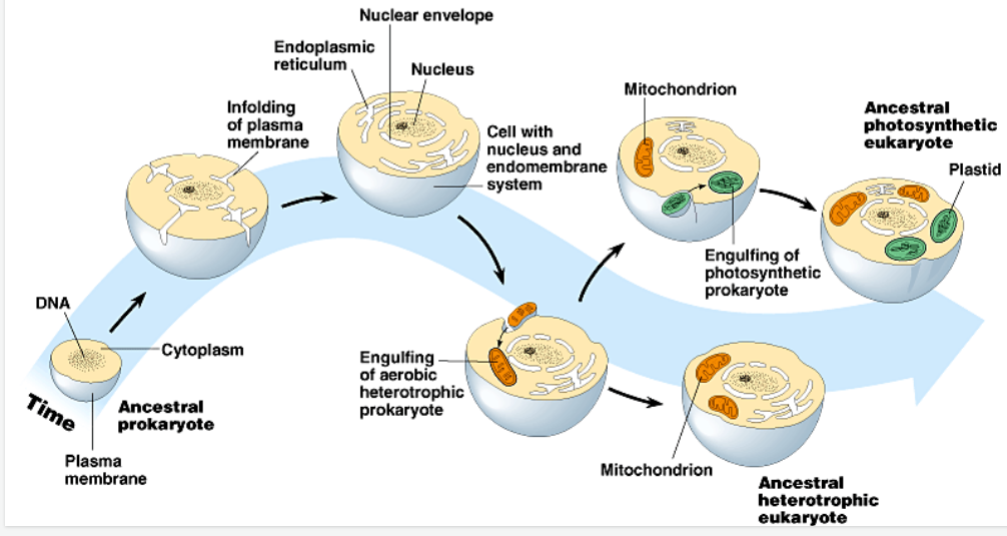
52
New cards
What is the evidence supporting the theory?
-Both mitochondria have 2 membranes surrounding them, suggesting that they were engulfed into a vesicle
-Like prokaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts contain ribosomes, circular DNA attached to inner membranes, and are the same size as prokaryotes; Ribosomes are more similar to prokaryotes than eukaryotes.; Membrane proteins in inner membranes homologous to membrane proteins in modern bacteria
-Mitochondria and chloroplasts are autonomous organelles that grow and reproduce in the cell; Reproduce in similar manner to prokaryotes (binary fission)
-Like prokaryotes, mitochondria and chloroplasts contain ribosomes, circular DNA attached to inner membranes, and are the same size as prokaryotes; Ribosomes are more similar to prokaryotes than eukaryotes.; Membrane proteins in inner membranes homologous to membrane proteins in modern bacteria
-Mitochondria and chloroplasts are autonomous organelles that grow and reproduce in the cell; Reproduce in similar manner to prokaryotes (binary fission)
53
New cards
Lysosome Formation
-In the nucleus, DNA is copied into mRNA through transcription
-mRNA then leaves the nucleus through nuclear pore and travel along cytoskeleton (microtubules) with help from a motor protein
-then goes to a bound ribosome on the Rough ER, where is it translated to form a specific chain of amino acids called a polypeptide chain
-the polypeptide is then inserted into the lumen of the Rough ER where its secondary and tertiary structures are altered, and a oligosaccaride is added to the polypeptide of cell-cell recognition (Becomes glycoprotein)
-it then pinches off into a transport vesicle and travel along the microtubules with help from a motor protein
-it fuses to the cis face of the golgi, dumping its contents, where it is then modified, sorted, and tagged
-it then leaves by pinching off of the trans face of golgi into vesicle
-looks for organelles and food vacuoles to absorb/breakdown through phagocyosis
-mRNA then leaves the nucleus through nuclear pore and travel along cytoskeleton (microtubules) with help from a motor protein
-then goes to a bound ribosome on the Rough ER, where is it translated to form a specific chain of amino acids called a polypeptide chain
-the polypeptide is then inserted into the lumen of the Rough ER where its secondary and tertiary structures are altered, and a oligosaccaride is added to the polypeptide of cell-cell recognition (Becomes glycoprotein)
-it then pinches off into a transport vesicle and travel along the microtubules with help from a motor protein
-it fuses to the cis face of the golgi, dumping its contents, where it is then modified, sorted, and tagged
-it then leaves by pinching off of the trans face of golgi into vesicle
-looks for organelles and food vacuoles to absorb/breakdown through phagocyosis
54
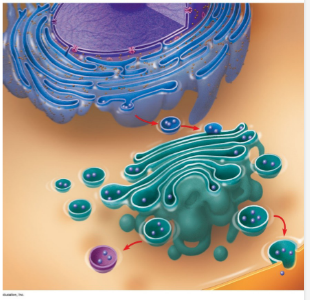
New cards
Journey of a protein from
synthesis to secretion
synthesis to secretion
-In the nucleus, DNA is copied into mRNA through transcription
-mRNA then leaves the nucleus through nuclear pore and travel along cytoskeleton (microtubules) with help from a motor protein
-then goes to a bound ribosome on the Rough ER, where is it translated to form a specific chain of amino acids called a polypeptide chain
-the polypeptide is then inserted into the lumen of the Rough ER where its secondary and tertiary structures are altered, and a oligosaccaride is added to the polypeptide of cell-cell recognition (Becomes glycoprotein)
-it then pinches off into a transport vesicle and travel along the microtubules with help from a motor protein
-it fuses to the cis face of the golgi, dumping its contents, where it is then modified, sorted, and tagged
-it then leaves by pinching off of the trans face of golgi into vesicle
-it then travels along microtubules with help from motor protein
-the vesicle then fuses with the cytoplasmic face of the cell membrane, where protein is released from cell through exocytosis/secretion
-mRNA then leaves the nucleus through nuclear pore and travel along cytoskeleton (microtubules) with help from a motor protein
-then goes to a bound ribosome on the Rough ER, where is it translated to form a specific chain of amino acids called a polypeptide chain
-the polypeptide is then inserted into the lumen of the Rough ER where its secondary and tertiary structures are altered, and a oligosaccaride is added to the polypeptide of cell-cell recognition (Becomes glycoprotein)
-it then pinches off into a transport vesicle and travel along the microtubules with help from a motor protein
-it fuses to the cis face of the golgi, dumping its contents, where it is then modified, sorted, and tagged
-it then leaves by pinching off of the trans face of golgi into vesicle
-it then travels along microtubules with help from motor protein
-the vesicle then fuses with the cytoplasmic face of the cell membrane, where protein is released from cell through exocytosis/secretion
55
New cards
Peroxisomes
-Membranous sac that contains enzymes that transfer a H atom
from a molecule to O2, forming H2O2 (Hydrogen Peroxide) through oxidation
-detoxify substances. (alcohol & formaldehyde)
-breaks FAs down to smaller molecules for CR
-abundant in cells in liver and kidney
from a molecule to O2, forming H2O2 (Hydrogen Peroxide) through oxidation
-detoxify substances. (alcohol & formaldehyde)
-breaks FAs down to smaller molecules for CR
-abundant in cells in liver and kidney
56
New cards
What is the toxin produced by reactions happening in the peroxisome?
-Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
-Catalase breaks hydrogen peroxide down into Water (H2O) and Oxygen (O2) to make it not toxic
-Catalase breaks hydrogen peroxide down into Water (H2O) and Oxygen (O2) to make it not toxic
57
New cards
cytoskeleton
-Mechanical support, shape, movement,
anchorage of organelles and regulation
of biochemistry.
-Dynamic structure, constantly being
broken down & reassembled where
needed.
-Three types of rods: Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments
anchorage of organelles and regulation
of biochemistry.
-Dynamic structure, constantly being
broken down & reassembled where
needed.
-Three types of rods: Microtubules, Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments
58
New cards
Microtubules
-Building blocks: tubulins
-Shape: Hollow Rods
-Function: Maintenance of cell shape, Cell movement (cilia and flagella), Cell division (spindle apparatus), Tracks for motor proteins
-smallest
-Shape: Hollow Rods
-Function: Maintenance of cell shape, Cell movement (cilia and flagella), Cell division (spindle apparatus), Tracks for motor proteins
-smallest
59
New cards
basal bodies
microtubule-based organelles that assemble cilia and flagella, which are critical for motility and sensory functions in all major eukaryotic lineages
60
New cards
microfilaments
-Building blocks: Actin
-Shape: Twisted double chain of actin, linear
-Functions: Tension bearing to support cell shape, Creates changes in cell shape, Muscle contraction, Cytoplasmic streaming (creates a constant flow to allow for movement of vacuoles), Ameboid movement, Mitosis (cleavage furrow)
-biggest
-Shape: Twisted double chain of actin, linear
-Functions: Tension bearing to support cell shape, Creates changes in cell shape, Muscle contraction, Cytoplasmic streaming (creates a constant flow to allow for movement of vacuoles), Ameboid movement, Mitosis (cleavage furrow)
-biggest
61
New cards
intermediate filaments
-building blocks: keratin; fibrous proteins
-shape: fibrous proteins supercoiled into thicker cables
-functions: Supports cell shape through bearing of tension, Creates cages around organelles including nucleus to anchor them in place, Makes up nuclear lamina, Anchor cells together through desmosomes
-medium
-shape: fibrous proteins supercoiled into thicker cables
-functions: Supports cell shape through bearing of tension, Creates cages around organelles including nucleus to anchor them in place, Makes up nuclear lamina, Anchor cells together through desmosomes
-medium
62
New cards
Plasmodesmata
channels through the walls allowing the cytosol of adjacent cells to flow between them (allows transmission of Solutes, water, proteins, RNA)
63
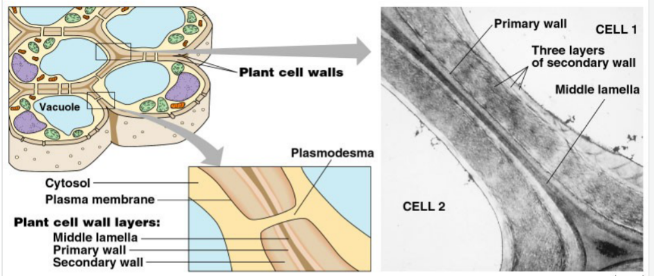
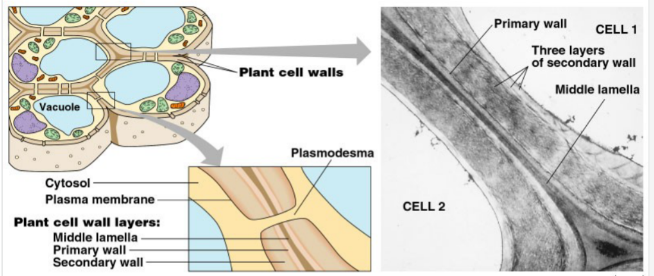
New cards
Cell Wall (funtion and structure)
-provide cell shape & keep from overfilling with water
-Supports plant (wood)
-Middle lamella is “glue” holding adjacent plant cells together
-Primary wall is first wall laid down by young plant.
-Secondary cell walls laid between primary & cell membrane.
-Supports plant (wood)
-Middle lamella is “glue” holding adjacent plant cells together
-Primary wall is first wall laid down by young plant.
-Secondary cell walls laid between primary & cell membrane.
64
New cards
centrosome
Area where microtubules are made and organized (spindle apparatus); contain centrioles in animals cells
65
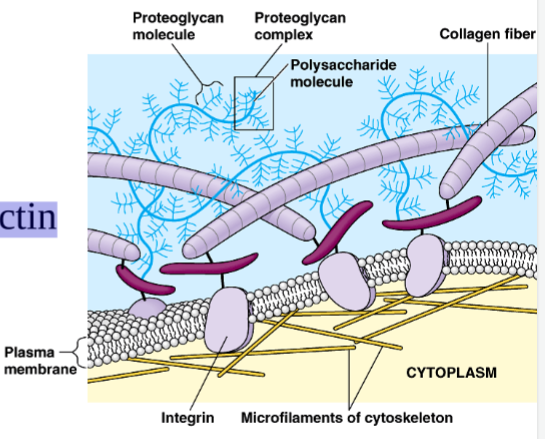
New cards
extracellular matrix (Be able to label)
-On outer surface of animal
cells
-Secreted by cell
-Attached to cell by fibronectin
proteins
-Give membrane stability
-Transmits signals into cell
cells
-Secreted by cell
-Attached to cell by fibronectin
proteins
-Give membrane stability
-Transmits signals into cell
66
New cards
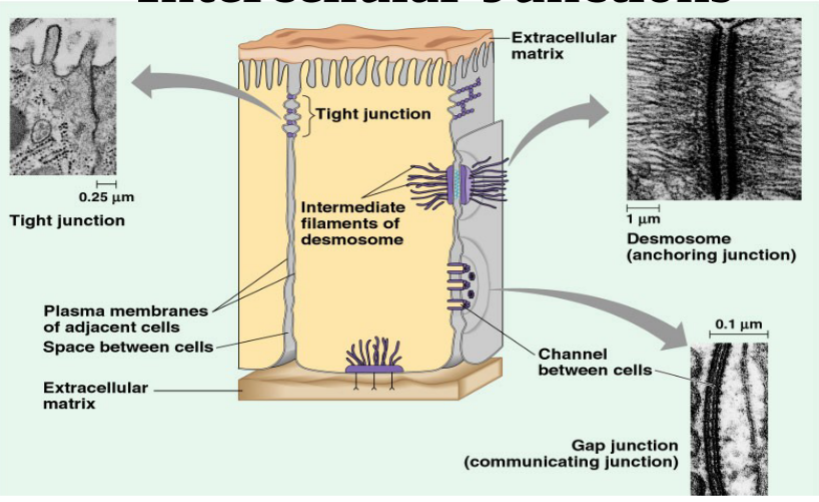
tight junction
impermeable barrier, cell membranes of
neighboring cells are fused. (cells lining alimentary and cells with microvilli in digestive system)
neighboring cells are fused. (cells lining alimentary and cells with microvilli in digestive system)
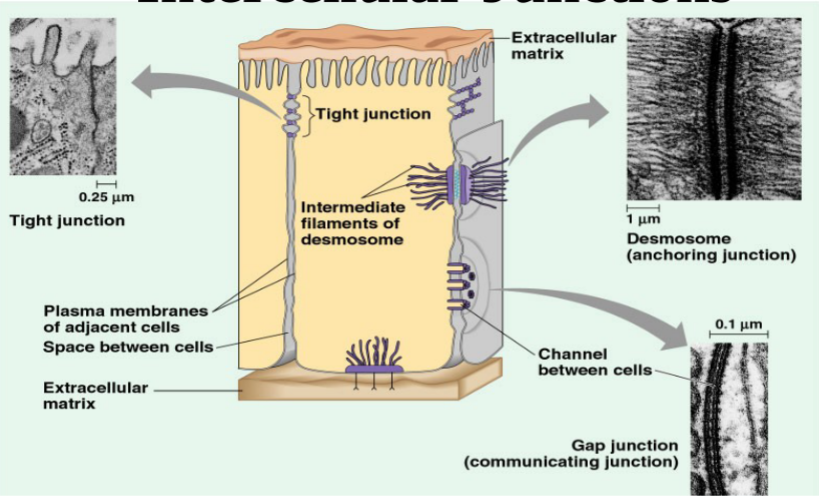
67
New cards
desmosomes
anchor cells together (skin cells & uterine cells)
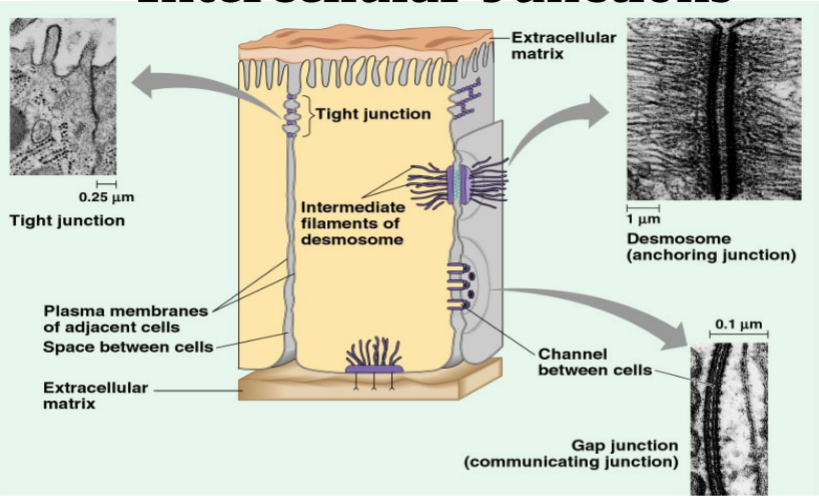
68
New cards
gap junctions
pores connecting adjacent cells (heart cells)