10b Coagulation Disorders
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HTHSCI 2H03
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
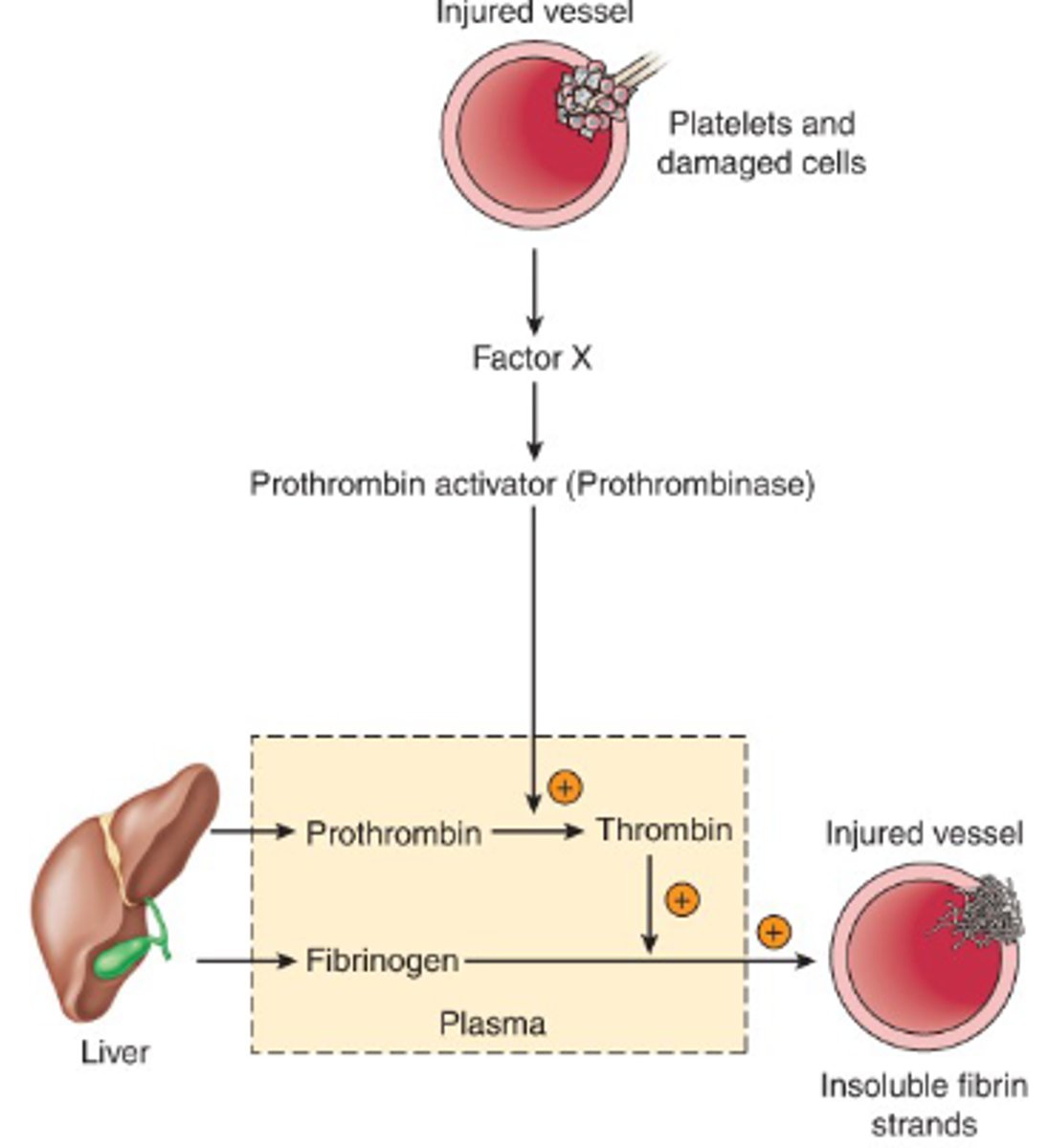
What happens when there is damage to a vessel?
- injury
- spasm
- platelets cover hole
- fibrin provides scaffolding for clot
How does the body get rid of a clot?
- 24-48 hr after clot
- release Tissue Plasminogen Activator (t-PA)
- converts plasminogen --> plasmin
- plasmin digest fibrin, destroys clot
Blood clots are formed through the action of which 2 processes?
1. coagulation cascade
2. activation of platelets
What are thrombolytic disorders?
- formation of non-therapeutic clots
- ex AF
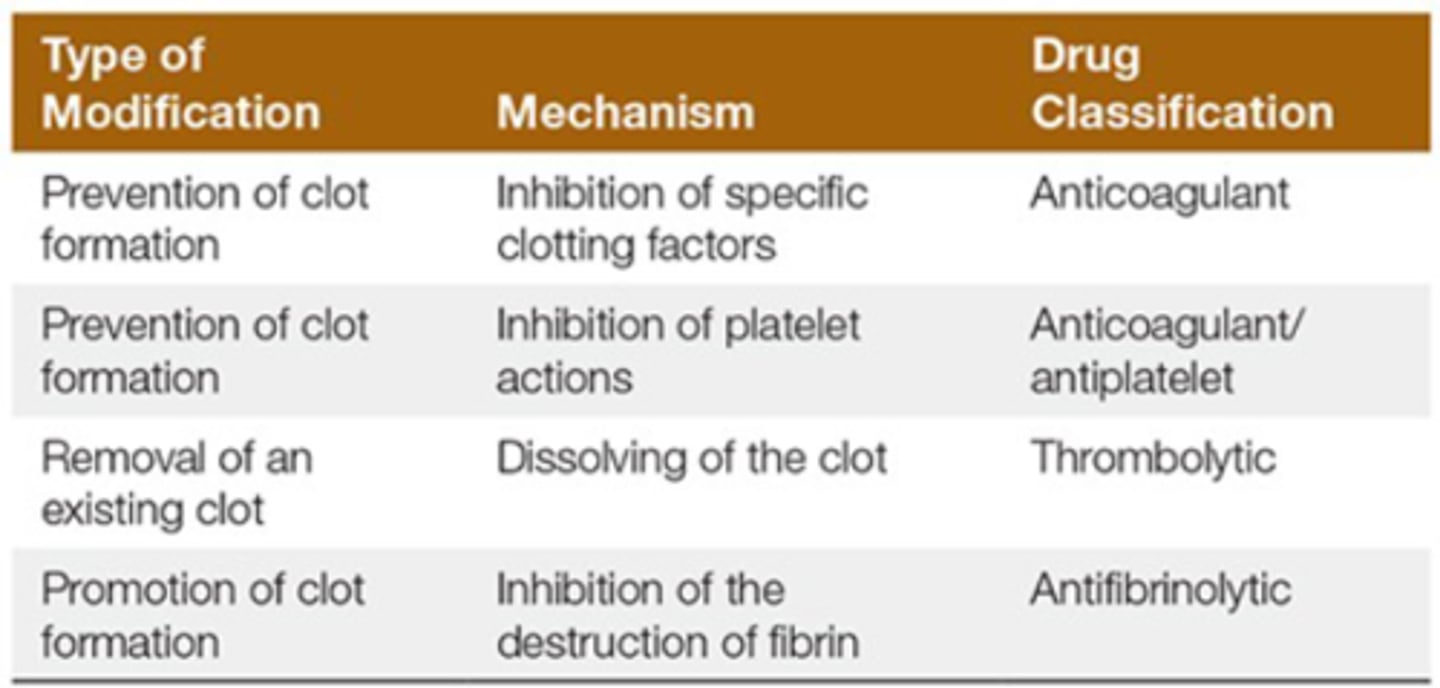
How can you prevent clot formation? mechanism and drug class?
1. Inhibition of clotting factors
a) anticoagulant
2. Inhibition of platelet actions
a) anticoagulant/antiplatelet
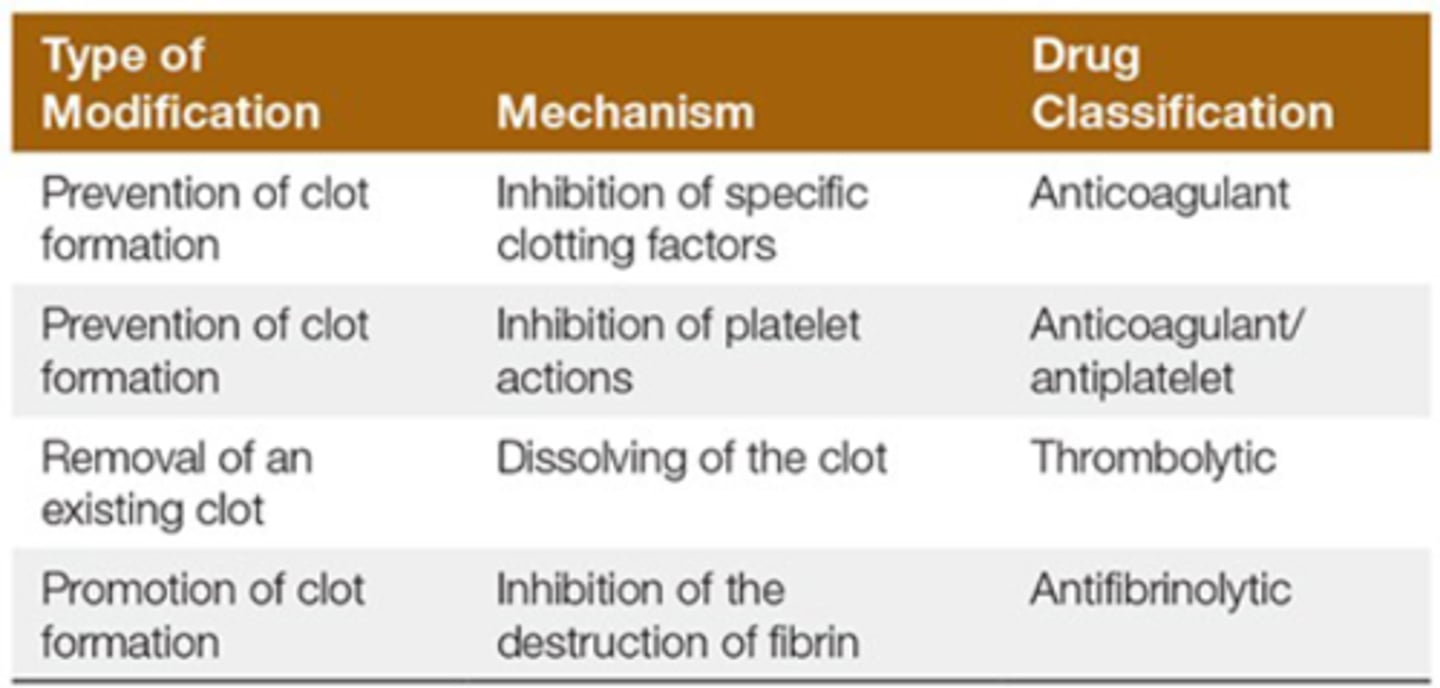
How can you remove a existing clot? mechanism and drug class?
- dissolve clot
- thrombolytic
What are the 5 types of anti-coagulant drugs?
1. Heparin
2. Warfarin
3. Low Molecular Weight Heparins (LMWH)
4. Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
4. Direct Xa Inhibitors
What is the MOA of heparin?
- enhances ability of antithrombin III to inactivate
- Thrombin --> no conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
- Xa --> inhibits intrinsic and extrinsic clotting pathways
Why is heparin only used in hospital?
- blocks thrombin and Xa
- higher risk
- more monitoring
What is the MOA of LMWHs?
- same as heparin
- mostly Xa
- therefore can be used in the community
What is the MOA of warfarin?
- inhibits epoxide reductase
- decrease body's ability to recycle VitK
- needed for synthesis of active clotting factors
How does it take for warfarin to start working? Why is this significant?
- 3 days
- overlap with heparin therapy for 3 days before discharge
- very high risk for bleeding
What are 2 signs of internal bleeding?
- low RBC
- low BP
What is MOA direct thrombin inhibitors?
directly and reversibly binds to and inhibits thrombin
What is antidote for direct thrombin inhibitors?
- Praxbind
- direct thrombin inhibitors would rather bind to praxbind distracting it from thrombin
What is the MOA of direct Xa inhibitors?
- Bind factor Xa--> prevent conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
- no effect on platelets
What is the antidote for direct Xa inhibitors?
- Andexxa
- direct Xa inhibitors would rather bind to andexxa distracting it from factor Xa
Which drug class has begun to replace warfarin and some LMWHs? Why?
- Direct Xa Inhibitors
- orally administered
- predictable
- less monitoring
- fewer drug interactions
How is bleeding monitored?
1. International Normalized Ration (INR): prothrombin levels
2. Prothrombin Time: time required for clotting to occur
What are the three types of antiplatelets drugs? Which is rarely used?
1. Irreversible cyclooxygenase inhibitors (ASA)
2. ADP Rc Antagonists
3. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Rc Antagonists *IV only, rarely used
What is the MOA of ASA?
- irreversibly blocks COX1/2 enzymes
- inhibits synthesis pf prostaglandins (thromboxane A2)
Who is ASA beneficial for? Who is to not?
Beneficial: established CVD
No Benefit: no evidence of CVD --> increased risk of bleeding
What is the MOA of ADP Rc antagonists?
- irreversibly changes molecular conformation of ADP Rc on platelets
- platelets no longer receive chemical signal to aggregate
- inhibits thrombus formation
What is the MOA of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibitors?
- normally glycoprotein IIb/IIIa is a Rc found on platelets
- activation causes binding to fibrinogen and aggregation
- antagonist prevents this
What is the route of admin for these?
- IV only
- in cath lab
What drug classes dissolves thrombus'?
Thrombolytic drugs
What is the MOA of thrombolytic drugs>
- converts plasminogen to plasmin
- promotes fibrinolysis
- dissolve fibrin
What is a risk of thrombolytic drugs?
- dissolves all clots
- therapeutic or not
- high risk with traumas
Which thrombolytic drug is no longer used, why?
Streptase
- caused allergic reaction
- one time use
What was developed instead?
Tissues Plasminogen Activator
- identical endo tPA that dissolves clots
- specific to fibrin bound plasminogen (no systemic effects)
What are antifibrinolytic drugs used ofr?
- facilitae blood clotting
- shorten bleeding time
- p/o bleeding
What is the MOA of antifibrinolytics?
- enzyme inhibitor
- inactivates plasmin
- prevents dissolution of fibrin