DSAT
Math
Given
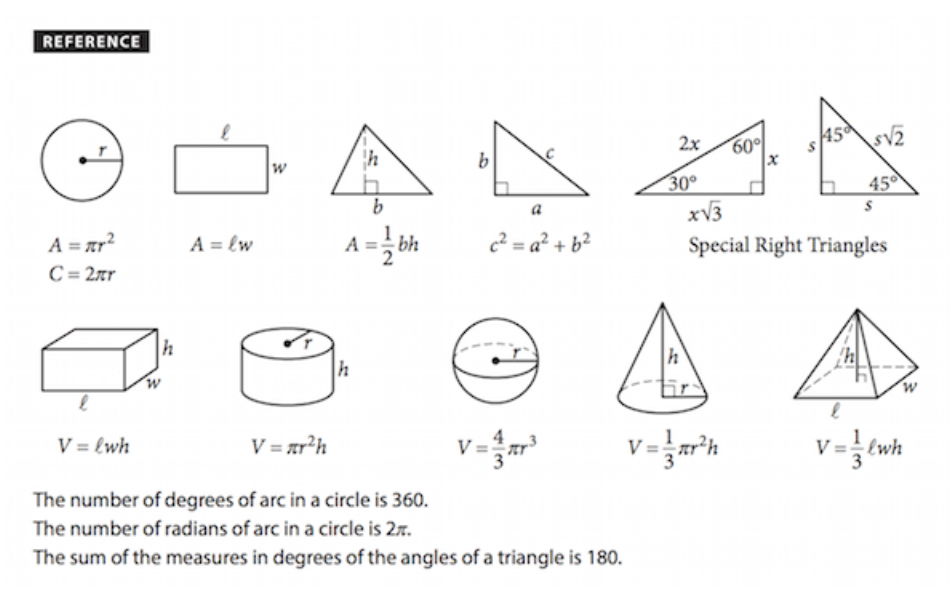
Arithmetic and Algebra
Linear - Slope-Intercept Form of a Line: y=mx+b
m is the slope
b is the y-intercept
same slope, different y-intercept = no solutions (lines are parallel)
different slope, y-intercept is irrelevant = 1 solution (lines intersect)
same slope, same y-intercept = infinitely many solutions (same line)
Slope: m=y2-y2/x2-x1
Midpoint: (x₁ + x₂/2, y₁ + y₂/2)
Vertex Form of a Parabola/ Quadratic: y=a(x-h)²+k
Standard Form: y=ax²+bx+c
a>0 opens upwards
a<0 opens downwards
(h,k) is the vertex
c is the y-intercept
Distance: d=√(x2 - x1)²+(y2 - y1)²
Difference of Squares: a²-b²=(a+b)(a-b)
Quadratic Equation: x = -b ± √b^2 - 4ac / 2a
Discriminant is b²-4ac
b²-4ac>0 = 2 real solutions
b²-4ac = 1 = 1 real solution
b²-4ac<0 = no real solutions
Sum of Solutions: -b/2a
also the x-value at the vertex
also the axis of symmetry
Product of Solutions: c/a
Exponents
Multiplying: (a^n)(a^m)=a^n+m
Dividing: a^n/a^m=a^n-m
To a Power: (a^n)^m=a^n*m
Binomial Product
Difference of Squares: (x-y)(x+y)=x²-y²
Perfect Squares Trinomial
Positive: (x+y)²=x²+2xy+y²
Negative: (x-y)²=x²-2xy-y²
Ratios, Percentages, and Statistics
Simple Interest: A=Prt
P is the principle amount
r is the interest rate
t is time (usually in years)
Average/ Mean: average = sum of terms/ number of terms
Median: middle number
Range: max/min
Standard Deviation: the measure of spread in the data set
higher standard deviation = greater spread
lower standard deviation = smaller spread
Geometry and Trigonometry
Equation of a Circle: (x-h)²+(y-k)²=r²
(h,k) is the center of the circle
r is the radius
Radians:
radians=degrees*(n/180)
degrees=radians*(180/n)
Arc Length: s=r/theta
theta is the radians
Degrees in a Polygon: (n-2)*180
Regular Polygon Interior Angle: (n-2)180/n
SOHCAHTOA:
sin=opp/hyp
cos=adj/hyp
tan=opp/adj
Sine/Cosine Relationship:
sin(x)=cos(90-x)
cos(x)=sin(90-x)
Pythagorean Theorem: a²+b²=c²
c is the hypotenuse
Statistics & Science
Percent: part/100
Percentage Change: (new-old)/old
Probability: desired possibilities/total possibilities
Speed: S=d/T
Density: mass/volume
English
Period = semicolon
Used to separate 2 complete sentences
Comma + it, this, s/he, they (sometimes) = comma splice = WRONG
Colon = single dash = explanation/ list
2 Commas = 2 dashes = 2 parentheses = non-essential clause
Semicolon = period = comma + FANBOYS
Coordinating Conjunctions: FANBOYS - joins 2 independent clauses
For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
Comma + coordinating conjunctions
Subordinating Conjunctions: joins an independent and a dependent clause
After, although, before, because, since, until, when…
Continuers: words that indicate an idea is continuing where it began
ex. Also, and, likewise, moreover…
Cause-and Effect:
ex. Because, consequently, thus, colons, dashes…
Contradictors: words that indicate a sentence is shifting directions/ contrasting
ex. But, in contrast, despite, however…
Comma splices are ALWAYS INCORRECT: caused by 2 constructions
pronoun as subject
adverb at the start of a clause