AP Bio Unit 1-4 Midterm
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
CHNOPS - which of these elements are in carbs? lipids? proteins? Nucleic acids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Sulfur
Carbs and Lipids are CHO
Sulfur is only in proteins
Nucleic acids have Nitrogen and Phosphate
Structure of a water molecule; why is it polar?
H20; Because Oxygen wants electrons
Effects of hydrogen bonding in water
Causes ice to float on top of the water; makes it a solvent
As a solvent, what kinds of things can water carry? Why does it matter in bio?
Anything that has a charge - other ions; polar molecules, not nonpolar molecules
Water can dissolve lots of things
Types of substances water can disslove; Why?
Anything that has a charge can get dissolved
Relationship between acid/bases and pH values, H+/OH- concentration
Solutions have pH values less than 7, indicating higher H+ concentration. Basic solutions have pH values greater than 7, indicating higher OH- concentration.
Covalent, Ionic, Hydrogfen bonds, Vanderwaals forces - what are they? Where are they found?
Covalent is a shared bond - Find it in proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, all types of molecules
Ionic takes electrons and makes something more negative and attract the positive - found in chemicals but not in an organic being
Hydrogen bonds - Hydrogen bonds are intermolecular forces of attraction between a partially positive hydrogen atom (H⁺) and a partially negative electronegative atom (like O, N, or F) in another molecule.
Vanderwaals forces are found in flies walking up walls supports their weight
Hydrolosis
Pulling apart a water molecule
Dehydration synthesis
Take out the water moleceule cause the other 2 molecules to come close
Why carbon?
It can bond with almost anything, very versatile element
-OH
Hydroxyl
-COOH
Carboxyl
C=O
Carbonyl
-NH2
Amino
Why do functional groups matter?
They have different properties; giving the molecule different properties
Carboxyl
Amino acid will always have at least one of these, gives them their acid
Amino
In an Amino acid, the amino part
Carbohydrate Structure
CHO on the sides of a carbon chain
Monomer
A monomer is a small, basic unit that can join together with other monomers to form a larger molecule called a polymer.
Fatty acid Structure
A long chain of carbons surrounded by hydrogens
Saturated Fatty Acid
No double bonds; completely surrounded by hydrogens
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Has some missing hydrogens, causing double bonds
Primary Structure
Long chain of amino acids; peptide bonds
Secondary Structure
Protein begins to fold
Tertiary Structure
Then folds into a ball
Quaternary Structure
The arrangement of multiple protein subunits into a functional, three-dimensional structure is known as quaternary structure. It stabilizes the protein and contributes to its overall function. Examples include hemoglobin, which consists of four subunits, and DNA polymerase, which has multiple subunits working together.
Peptide bonds
Bonds between amino acids
Denaturations
Denaturation is the process of altering the structure of a protein.
Heat, pH changes, or exposure to chemicals can cause it.
Denaturation disrupts the protein's secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures.
It can lead to loss of protein function.
What are enantiomers?
Mirror image molecules
Prokaryotic
Prokaryotes don’t have a nucleus, their DNA is in a loop, have their own ribosomes
Eukaryotic
membrane boud organelles, has a nucleus
Nucleus
Center of a cell where the DNA is held
Nucleolus
Structure within the nucleus of a cell responsible for producing ribosomes. Contains DNA, RNA, and proteins. Plays a crucial role in protein synthesis.
Plasma membrane
A thin barrier surrounding cells, made up of phospholipids and proteins. It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, maintaining cell integrity and regulating cell processes.
Nuclear membrane
A double-layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell. It separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores.
endoplasmic reticulum
Plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, folding, and transport, as well as lipid metabolism. The rough ER is studded with ribosomes and involved in protein synthesis, while the smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification.
ribosomes
They are found floating around and on the Endoplasmic reticulum making it “rough”
golgi apparatus
Organelle responsible for packaging and modifying proteins in eukaryotic cells. Plays a crucial role in intracellular transport and secretion of proteins.
vesicles/vacuoles
Pipes that connect one part of the system to another
lysosomes
Waste management, break down waste and recycle it
cell wall
Phospholipid bulayer that protects the cell
Endomembrane system
Manufacture and export proteins outside the cell
Compartmentalization
When an organelle can do 2 things at once
Cell fractionation
Helps to examine a cell, breaks up a cell into it’s organelles in a centrifuge
Characteristics that makes chlorplasts and ribosomes unique
They all have their own ribosomes and DNA; ties to endosymbiote theory
Chloroplasts
Where photosynthesis is preformed in a plant cell
Plasmodesmata
Passageways that connect a plant to the rest of it
Gap junctions
How animal cells transfer data between cells
SA-V ratio
SA divided by Volume
V= LxWxH
SA=LxW
or 6*A
Osmosis
Process by which water molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration across a selectively permeable membrane.
Hypertonic
When the water moves out of the cell; solution has more salt
Hypotonic
Water moves in; water solution has less salt
Isotonic
Neutral; reaches equilibrium
Why aquaporins are needed
Aquaporins are proteins that allow water through the cell membrane
Diffusion vs active transport
Process that moves molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration. No energy required. Helps maintain equilibrium.
Process that moves molecules against the concentration gradient. Requires energy. Helps maintain concentration differences.
ATP; why do we need it in active transport
A high-energy molecule used in active transport. It provides the energy needed to move molecules against their concentration gradient, from low to high concentration. This process is crucial for maintaining cell homeostasis and carrying out essential functions such as nutrient uptake and waste removal.
Ligands and receptors
the molecule that fits into the receptor and releases a cell signal
Autocrine
Cell signaling mechanism where a cell secretes signaling molecules that bind to its own receptors
Paracrine
Signals that are recieved when they’re touching
Synaptic signaling
Signaling in nerves; over a short jump
Endocrine; long distance signaling
A hormone that goes through the whole body; only things with receptors will take it; hormones
How one hormone can cause multiple responses
Depends on the cell it hits, can do different things to different cells
Benefits of signaling pathways
1) It can be regulate
2) It can amplify it
Reception, Transduction, Response
The signaling chain and pattern
Phosphorylation Cascade
Chain of ATP donating Phosphates to activate proteins
Second messenger
Things like CAMP; something released through the cell that triggers the rest of the process
G-protein scenario
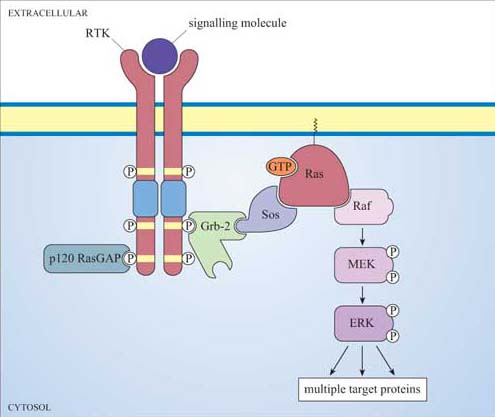
Ion-gated ligand scenario
Gate that opens and closes when a ligand is recepted
growth factors
Triggers mitosis in a cell
Mitosis and it’s purpose
Division and creates identical copies of a cell; cell reproduction
How are chromosomes formed?
Formed from Chromatin
Chromatin
Pieces of DNA
Histones
Proteins that help package DNA into a compact form called chromatin.
Role of spindle fibers in mitosis
They pull apart the chromosomes to copy the DNA
PMAT
Prophase- Chromosomes get copied
Metaphase- Cells align together in the middle; nucleus dissolves
Anaphase- Spindle fibers attach to the chromatin
Telaphase- 2 Nuclie
Cyclins - CDKs
Regulatory proteins that control the progression of the cell cycle.
Cancer - unregulated cell cycle
Abnormal cell growth caused by a disrupted cell cycle.
Density-dependent inhibition, attachment
When cells grow too big they stop; or when they are touching another
Rules of Thermodynamics
1) Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted.
2) The entropy of an isolated system always increases.
3) As temperature approaches absolute zero, entropy approaches a minimum value."
Enzymes
Proteins that breakdown things in your body; catalyze chemical reactions
Gibbs free engery
Measure of a system's ability to do work or drive a chemical reaction. Determines spontaneity and equilibrium of a process.
Endergonic
A type of chemical reaction that requires an input of energy to proceed. It has a positive change in free energy and is not spontaneous.
Exergonic
A chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of ATP. It occurs when the products have less energy than the reactants.
Spontaneous reactions
Reactions that occur naturally without the need for external energy input. They tend to proceed in a forward direction, releasing energy and increasing entropy. Examples include combustion, dissolution of salts in water, and some chemical reactions.
Potential energy in living things
Substrate-enzyme concentration curve
effect of temperature, PH on enzyme activity
Oxidation
Reduction
Glycolosis - Steps, inpouts, outputs, and location
Pyruvate Oxidation and krebs cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Role of Oxygen
Oxidative phosphorylation vs Substrate level
Proton motive force
Chemiosmosis
Light Dependent reactions
Calvin Cycle
Chloroplast structure
Pigments; Color absorptions