unit 1 quiz #3 - condensation, hydrolysis, and carbohydrates
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Condensation Definition
Synthesis reaction
When 2 or more molecules combine due to REMOVING water molecules at the site of the linkage
Removing water forms a bond to make it overall bigger
Condensation Biological Importance
Allow formation of biological polymer → starch, proteins, fat, and nucleic acids
Hydrolysis Definition
Catabolic reaction
Where a water molecule is used to break a covalent bond to split (lyse) a larger molecule into subunits
Water is ADDED to make the large molecule into smaller components
Hydrolysis Biological Importance
In digestion → break down nutrients
Breaks down polymers into monomers
4 Different Types of Carbohydrate Structures
Monosaccharides (single subunit)
Disaccharides (2 subunits)
Oligosaccharides (a few subunits)
Polysaccharides (hundreds to thousands of subunits)
examples/includes: sugars, satrches, cellulose, chitin
contains: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (H2O)
Carbohydrates Function
Immediate energy sources, energy storage, and structural materials
About Sugars
Provide energy immediately
Simplest carbohydrates
Simple sugars are monosaccharides, with 3-7 carbon atoms
Most important sugars for humans are involved in energy conversions and have 5 (pentose) or 6 (hexose) carbons
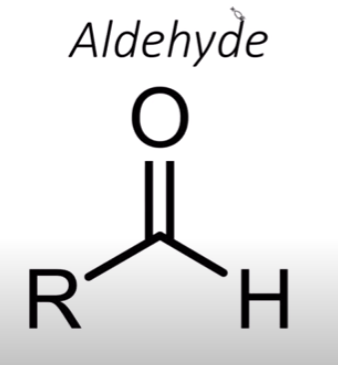
Aldehyde
An aldehyde has a double-bonded oxygen attached to a carbon that has a hydrogen next to it
think alde-H-yde because there’s an "H" on the carbon
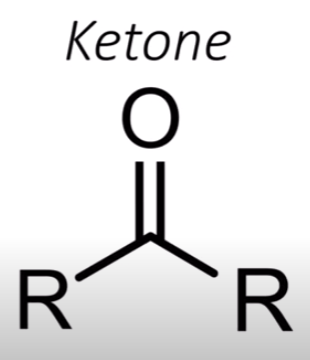
Ketone
Have a double-bonded oxygen with carbons on both sides, so there’s no hydrogen directly attached to that carbon
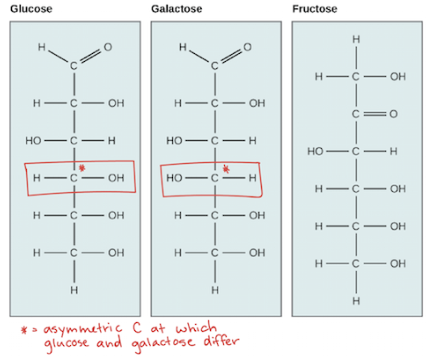
Three Hexose Sugars
Aldehyde - glucose and galactose
Ketone - Fructose
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked together
Formed by condensation reactions
Disaccharides: Glucose + Glucose
= Maltose + Water
Disaccharides: Glucose + Fructose
= Sucrose + Water
Disaccharides: Glucose + Galactose
= Lactose + Water