ID Lecture 33-34: Sexually Transmitted Infections | Quizlet
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
True or false: The incidence of STIs is increasing.
True
What are the most common STIs?
Chlamydia
Gonorrhea
Genital herpes
Syphilis
Trichomoniasis
When should Doxycycline be used as postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) for STI prevention?
Men who have sex with men
Transgender women
HIV or plan to thave HIV PrEP
What is the treatment recommendation of Doxycycline PEP?
200mg once within 72 hours
What causes Gonorrhea?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
How do females present with Gonorrhea?
Vaginal d/c
dysuria
cervicitis/urethritis
Intermenstrual bleeding
may also be asymptomatic or have minimal s/sx
How do males present with Gonorrhea?
Purulent d/c
dysuria
epididymitis
prostatitis
May also be asymptomatic
What are the complications of Gonorrhea?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Ectopic pregnancy
Infertility
HIV transmission
What is the mechanism of resistance with Gonorrhea?
Penicillinase producing
Tetracycline resistance
Quinolone resistance
decreased susceptibility to azithromycin and cephalosporins
What is the recommended treatment for Gonorrhea?
Ceftriaxone 500mg IM for 1 dose
if >150kg then 1g IM for 1 dose
Alternatives:
Gentamicin
Azithromycin
Cefixime
What should be added to the treatment of Gonorrhea if chlamydia has NOT been ruled out?
Doxycycline 100mg BID x7 days
What is important when treating a patient for an STI?
Treat their recent partners (w/i 4 weeks)
Chlamydia is caused by what?
Chlamydia trachomatis
What is the clinical presentation of chlamydia in males and females?
Asymptomatic
Dysuria
Urinary frequency
Mucopurulent d/c
What is the recommended treatment for Chlamydia?
Doxycycline 100mg PO BID x7 days
Alternatives:
Azithromycin
Levofloxacin
What is the recommended treatment for Chlamydia in pregnancy?
Azithromycin OR Amoxicillin
What are the complications that can arise from Chalmydia?
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Neonatal conjunctivitis
Neonatal pneumonia
What causes Syphilis?
Treponema pallidum
How is Syphilis transmitted?
direct contact with a sore or during pregnancy
What is the progression of syphilis that is left untreated?
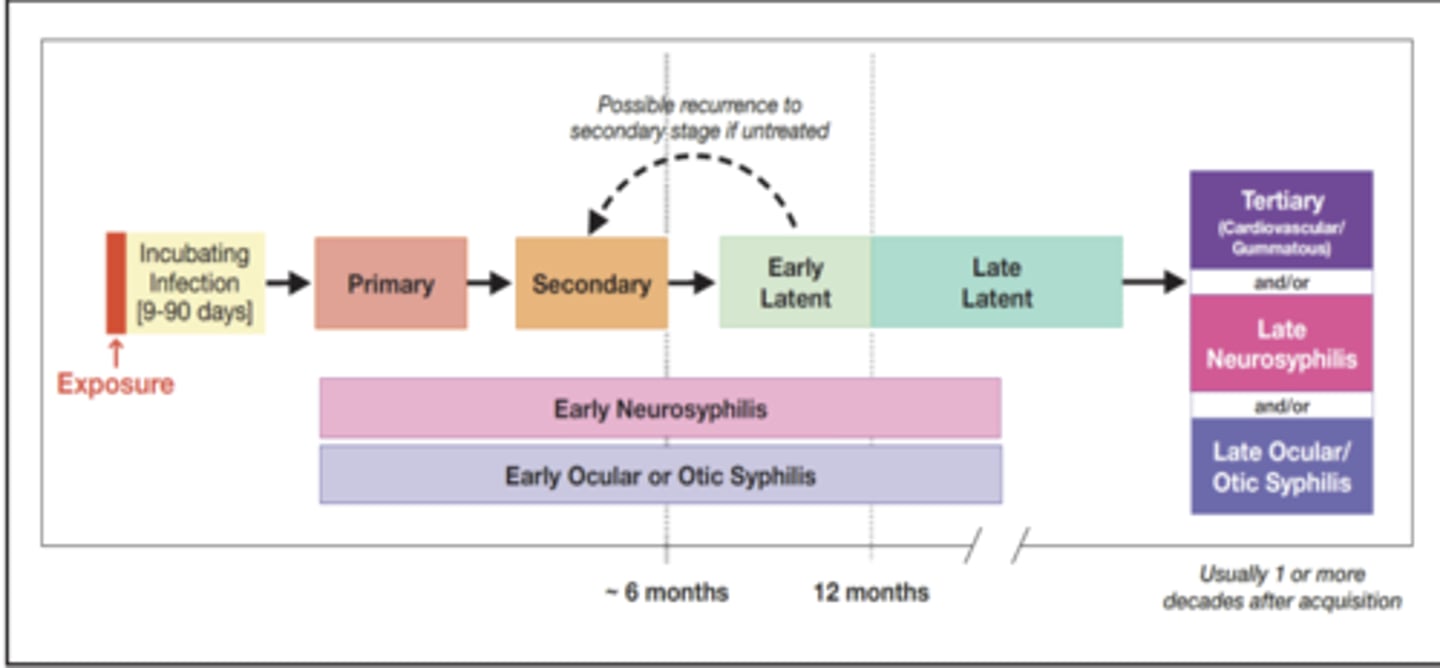
Primary syphilis presentation
Chancre (painless)
Lymphadenopathy
How long does it take for primary syphilis to resolve?
2-6 weeks
What are the infection sites of primary syphilis?
External genitalia
Perianal region
Mouth
Throat
Secondary syphilis
widespread infection that develops 2-8 weeks after initial infection due to hematogenous and lymphatic spread
What is the clinical presentation of secondary syphilis?
Skin lesions (palms and soles)
Rash
Mucocutaneous lesions
Alopecia
Latent syphilis
the third stage of syphilis (early or late), which may last for years, during which symptoms disappear although the person is still infected
Early latent syphilis
infectious due to spontaneous relapses during the 1st year of infection
Late latent syphilis
noninfectious but remains a host - can progress to neurosyphilis or tertiary syphilis
When does tertiary syphilis develop?
10-30 years after initial infection
Tertiary syphilis
the third phase of syphilis, marked by multiple organ damage
How can tertiary syphilis present?
Neurosyphilis
Cardiovascular
Gumma
Gumma syphilis
chronic, destructive lections on the skin, bone, soft tissue, liver, heart, and/or brain
*tertiary*
Cardiovascular syphilis
weakens the aorta
*tertiary*
Neurosyphilis
a variation of syphilis that infects the nervous system
*tertiary*
How is Syphilis diagnosed?
Nontrepomenal tests (screening):
- VDRL
- RPR
If above are positive, then Trepomenal tests for confirmation:
- FTA-Abs
- TPHA
- MHATP
What is the treatment recommendation for late latent or latent syphilis of an unknown duration?
Benzathine Penicillin G 2.4 million units IM weekly for 3 weeks
What is the treatment recommendation for primary, secondary, and early latent syphilis?
Benzathine Penicillin G 2.4 million units IM for 1 dose
What is the treatment recommendation for tertiary syphilis with a normal CSF exam (NOT neurosyphilis)?
Benzathine Penicillin G 2.4 million units IM once weekly for 3 weeks
What is the recommended treatment for neurosyphilis?
Penicillin G 18-24 MU IV for 10-14 days
THEN, follow up with Benzathine Penicillin G 2.4 MU weekly for 1-3 weeks
What is the recommended treatment for neurosyphilis in pregnancy?
Penicillin regimen appropriate for their stage of infection
What is the Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction?
a benign, self-limiting reaction that is common during primary and/or secondary syphilis treatment
*NOT an allergy rxn*
With what STIs should the partners of the infected person also be treated?
Gonorrhea
Chlamydia
Trichomoniasis
What is genital herpes?
HSV 2
How is genital herpes transmitted?
direct contact with lesions or shedding virus from host
What are the treatment options for first clinical episodes of HSV 2?
Acyclovir
Famicyclovir
Valacyclovir
What are the treatment options for recurrent HSV 2 episodes?
Acyclovir
Valacyclovir
Famiciclovir
When should treatment be started for recurrent HSV 2 episodes?
during prodrome phase or within 1 day of symptom onset
When should patients with HSV 2 recieve suppressive therapy?
if they experience 6 or more reactivation episodes per year
What agents are recommended for HSV 2 suppressive therapy?
Acyclovir
Famiciclovir
Valacyclovir
What is the treatment option for HSV 2 in pregnancy?
Acyclovir
What causes Trichomoniasis?
Trichomonas vaginalis
What is the female presentation of trichomoniasis?
Asymptomatic
Vaginal d/c
Vulvar pruritis
Dysuria
Inguinal LA
Strawberry cervic
Gonorrhea co-infection
What is the male presentation of trichomoniasis?
Asymptomatic
Urethral discharge
Pruritis
Dysuria
Gonorrhea co-infection
What is the recommended treatment for females with trichomoniasis?
Metronidazole 500mg PO BID for 7 days
What is the recommended treatment for males with trichomoniasis?
Metronidazole 2g PO for 1 dose
What is recommended for HPV prevention in ages 9-26 y/o?
Gardasil 9 (2-3 dose series)
Monkeypox virus course
Incubation (3-17 days)
Prodrome
Rash (2-4 weeks)
How is monkeypox transmitted?
Contact with mpox rash/scabs
Contact with contaminated objects
Contact with respiratory secretions
Pregnancy
What vaccine is recommended for mpox prevention?
Jynneos vaccine (2 doses)
What are the recommended treatments for mpox?
Antivirals
Skin topicals
Stool softeners
Pain management
Tecoviramat (TPOXX)
treatment that is FDA approved for smallpox but also used in Mpox
Who should recieve TPOXX?
Severe disease
Mpox in anatomic areas that can result in serious sequeale
Immunocompromised
Kids <8 y/o
Pregnant/breastfeeding
Skin conditions
MOA of Tecovirimat
inhibits formation of virions necesary for virus dissemination
ADRs of TPOXX
HA
Nausea
Abdominal pain
What are the treatment options for Mpox besides TPOXX?
Cidofovir
Brincidofovir
VIVIG