Chapter 13: Alkenes
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Alkenes are .............. hydrocarbons with a .......... ...........bond
unsaturated, double covalent C=C
formula for an alkene
CnH2n
Alkenes contain a .......... bond and a ........ bond between 2 Cs
sigma, pie
sigma bond/σ bond
-a ........ ..........bond
- electrons move .............. ..... ......... between atoms
-involves overlap of 2 .............
-1 ............... is given from each .......... atom
-single covalent, C-C
-directly in line
-orbitals
-electron, bonding
pi bond/ π bond:
- and sigma bond together form a ......... .......... bond
- ........... move above and below the ............. of the atom
-involve overlap of 1 .... orbital on each ..........
-Each carbon contributes 1 ...... to the pair that's ......... in the pi bond
-double covalent C=C
-electrons, plane
-p, carbon
- electron, shared
π bond + σ bond forms..
a double bond between 2 Cs
single bonds are
sigma bonds
The shape around each C in an alkene is ............. .............. (bond angle .....)
trigonal planar, 120 degrees
π bond vs σ bond (where they are)
-π bond in a double bond
- σ bond in single and double bonds
π bond vs σ bond (where electrons move)
-π bond: above and below plane of atom
- σ bond: directly in line between atoms
alkanes vs alkenes:
-type of bonds involved...
-shape...
-bond angle...
-formula
-alkanes: sigma, alkenes: pi and sigma bonds
-alkanes: tetrahedral, alkenes: trigonal planar
-alkanes: 109.5 degrees, alkenes: 120 degrees
-alkanes: CnH2n+2, alkenes: CnH2n
In alkenes, the atoms around the .......... ....... bond can't move as there's no ........ ................. around it
double C, free rotation
stereoisomers: isomers with same ............. ............. but different ............... of atoms in space
-structural formula, arrangement
2 types of stereoisomers
E and Z
E/Z isomers:
-only occur in molecules with ......... bond
-groups attached to the Cs in C=C are in ............. positions
because of ...... electrons ............... & ............. the plane of the ..... bond
C=C
-fixed, pi, above, below, sigma
Z in E/Z stands for ................., so groups are on ............ sides of the molecule
zusammen, same
A molecule has an E/Z isomer if it has both:
-a ............ ............. bond
-.............. groups attached to each ..... of the C=C bond
-C=C double bond
-different, carbon
to decide if something is an E or Z isomer, find the highest priority atom:
-highest priority atoms have a ............. atomic number
higher
H H
\ /
C=C
/ \
CH3 CH3
name this molecule: (E or Z isomer and why)
Z-but-2-ene
as CH3 groups on same sides of the molecule
H CH3
\ /
C = C
/ \
CH3 H
name this molecule: (E or Z isomer and why)
E-but-2-ene
as CH3 groups on different sides of molecule
H CH3
\ /
C = C
/ \
Cl OH
-highest priority groups are ...
-this molecule is called..
-Cl and O
-Z-1-chloro, 2-hydroxy prop-1-ene
H3C CH2CH2Cl
\ /
C = C
/ \
H CH2CH2OH
name this molecule:
Z-3-chloro ethyl 1-hydroxy pent-3-ene
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Nomenclature:
-system used to name ..... ............ based on priority of groups attached to ........
-Higher ......... ......... is priority
-E/Z isomers, C=C
-atomic number
cis/trans isomers:
-special case of ...... isomers
-one attached group on each C of the C=C must be a .....
-E/Z
-hydrogen
Cis isomers: H atoms on ............. side
-always ......... isomers
same, z
Trans isomers: H atoms on ............. side
-always ....... isomers
-opposite/different, E
CH3 CH3
\ /
C = C
/ \
H H
name this cis/trans isomer
cis but-2-ene
CH3 H
\ /
C = C
/ \
H CH3
name this cis/trans isomer
trans but-2-ene
alkenes are ......... reactive than alkanes, due to the presence of a ..... bond
-more, pi
Reactivity of alkenes:
-the presence of a pi bond makes them ........... reactive than alkenes because the pi e- ........... & ........... the plane are more ............ than e- in the sigma bond
-therefore, pi bonds break .......... easily than sigma bonds
-more, above, below, exposed
-more
Alkenes are involves in ......... reactions ( as it ........ the C=C bond)
addition, breaks
bond enthalpy for σ > π
because...
more energy needed to break a sigma bond than a pi bond
which is more reactive, alkenes or alkanes? and why?
alkenes
e- in pi bond above and below plane of atom are more exposed than e- in sigma bonds
Alkene + hydrogen (with ......... catalyst) -->
(nickel catalyst) --> alkane
alkene + halogen-->
(this is used as a test for ........ e.g. bromine water)
haloalkane, unsaturation
alkene + hydrogen halides --> ........
what happens if the alkene is unsymmetrical?)
haloalkane
(2 possible products if alkene unsymmetrical)
alkene + steam --> (with conc. ........... catalyst)
if alkene unsymmetrical: 2 possible .........
alcohol (H2SO4 catalyst)
-products
electrophile
atom/group of atoms that's attracted to an electron rich centre & accepts an electron pair
electrophilic addition:
-........... take part in addition reactions
-........ reactants, ............ product
-electrophilic addition is a .............
-the high density of ..... e- attracts .........
-alkenes
-2,1
-mechanism
-pi, electrophiles
draw mechanism for ethene + HBr
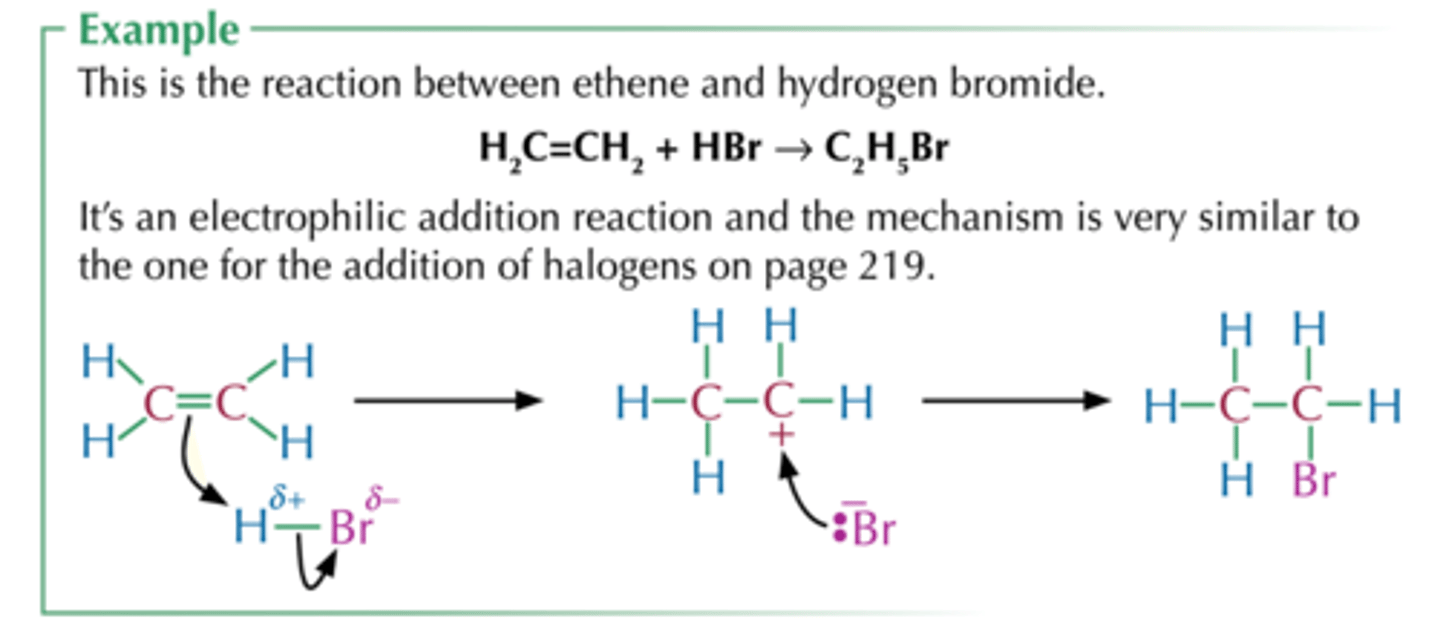
ethene + HBr
-the bond breaks h........ly
-the intermediate is a c......
-this mechanism is called ......... ........
-HBr already has a d....... because Br is more ........ than H
-the electrophile is ...
-heterolytically
-carbocation
-electrophilic addition
-dipole, electronegative
-Hδ+ in HBr
draw mechanism for ethene + Br2
with 2 dots on Br-
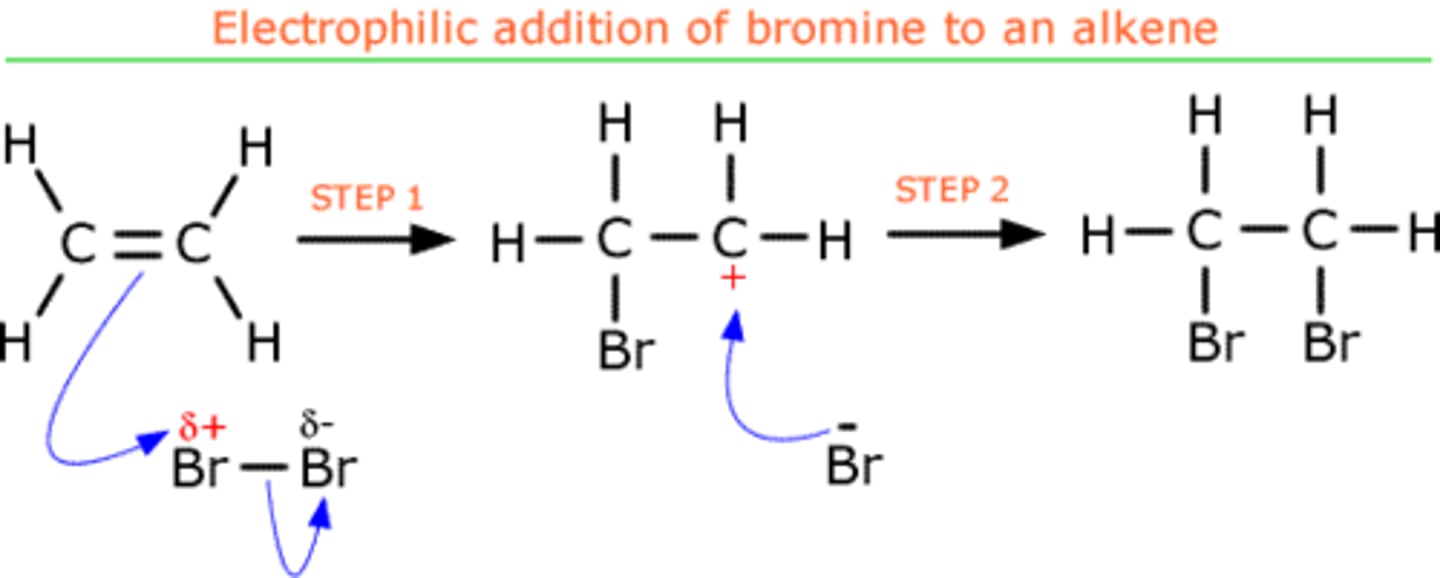
-bromine isn't ........., but can react with alkenes because the ..... bond electrons repel electrons on one ......
-this is an i......... .........
polar, pi, Br, induced dipole
when propane reacts with HBr, why is 2-bromopropane formed more than 1-bromo propane?
2-bromo propane has a slightly more stable intermediate
-Cs surrounding the carbocation funnel e- to it
-therefore it's the major reaction
Markovnikoff's Rule
the H in a hydrogen halide attaches itself to the C of the alkene with the most Hs and least Cs
Electrophilic addition occurs in 2 steps:
step 1 called c.........
-a ............ intermediate is formed (fyi these can be primary or secondary)
carbonation, carbocation
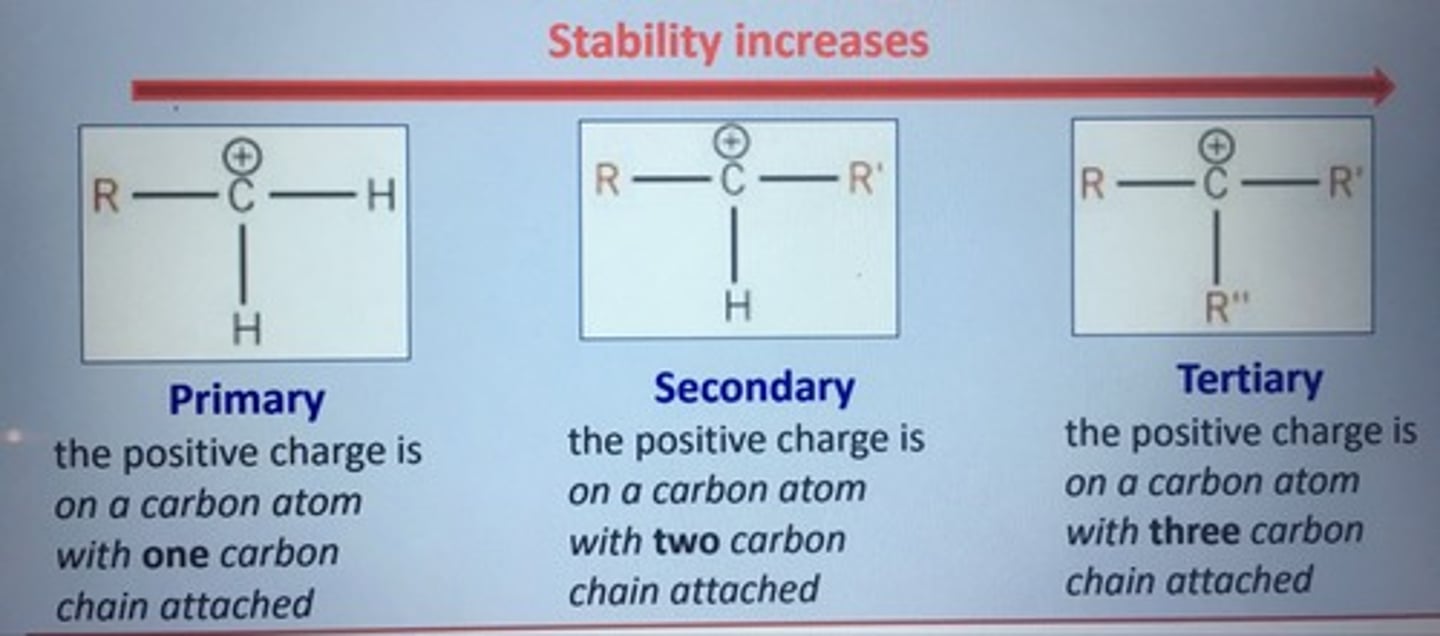
carbocations:
-become more stable, the more .......... groups are joined to the ..... ion
-the more stable route produces the ....... product
alkly, carbon, major
draw primary, secondary & tertiary carbocations
(using R group)
addition polymerisation:
-u........ alkene m........ join to form long s....... c..... aka p..........
unsaturated monomers, saturated chains, polymers
industrial polymerisation conditions:
-high ....
-high .....
-a ........
temp, pressure, catalyst
polymers have high m......... m...
molecular mass
repeat unit is
the specific arrangement of atoms in the polymer molecule that repeats
repeat unit is always drawn with ...
square brackets, n after bracket
A B
I I
n[ C=C ] -->
I I
D E
draw polymer repeat unit
A B
I I
-[- C-C-]-
I I
D E n
waste polymers can be: (3)
-r.......
-used as f........
-used as f.... to...
recycled, feedstock, fuel, generate energy
environmental concerns:
-many alkene based polymers aren't .........
biodegradable
polymers are used because they're:
-c..... & available
-lack of r........... (makes them suitable to store food)
cheap, reactivity
recycling polymers:
-reduced ...... impact by conserving f........ f..... f..... & decreasing l..... w........
environmental, finite, fossil, fuels, land waste
recycling polymers:
-polymers must be sorted by t.....
-they're ch.., w.....,d.. & m......(verbs)
type, chopped, washed, dried, melted
PVC recycling:
-is h......... due to high c....... content & range of a........
hazardous, Chlorine, additives
PVC recycling:
-PVC isn't suitable for l......
-when burnt it releases h.......... c......... which is a c... g.....
landfill, hydrogen chloride, corrosive gas
PVC recycling:
-s......... are used to d.......... PVC & high-g..... PVS is recovered by p........
solvents, dissolve, grade, precipitation
Waste polymers as fuel:
-polymers derived from p........... or natural g...... have high stored e..... value
petroleum, gas, energy
Waste polymers as fuel:
-polymers can be i....... making heat/s...... to drive t...... producing e.............
incinerated, steam, turbines, electricity
feedstock recycling:
-describes c........./t........ processes that reclaim m........, gases & oils from waste polymers
chemical, thermal, monomers
feedstock recycling can handle un......... polymers
washed/sorted
bioplastics:
-produced from plant s.....
-offer a r......... alternative to o....-based products
starch, renewable, oil
biodegradable polymers:
-broken down by m....... into biological compounds
microorganisms
compostable polymers:
-de..... and leave no visible/toxic r.......
degrade, residue
photodegradable polymers
Contain bonds that are weakened by absorbing light to start the degradation