Endocrine System - Epinephrine Pathway
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Epinephrine
Adrenaline. Hormone produced by the adrenal glands that activates our fight or flight. Increases heart rate, blood pressure, etc. Hydrophilic so it has a membrane bound receptor and relay molecules in the cytoplasm. Cellular response to this includes turning enzymes on and off. Focusing on response pathway to blood glucose drop specifically.
Know how to label these
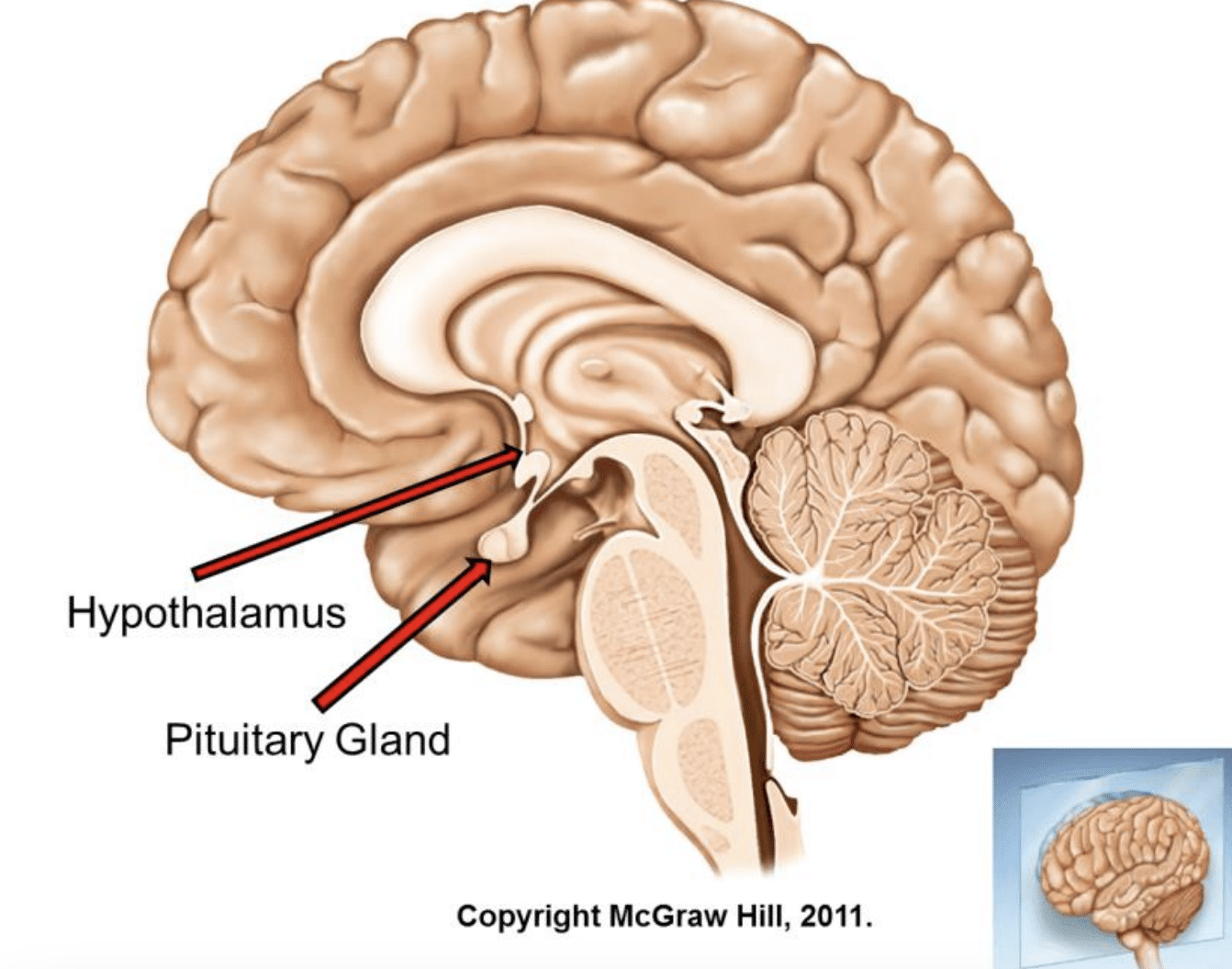
Hypothalamus
Links nervous system to endocrine system via anterior pituitary. Upon stressor, will either stimulate sympathetic nervous system pathway or release CRF.
Stressor
Stimulus that triggers a fight or flight stress response (adrenal hormone release). ex. tiger growl, blood glucose drop
Adrenal glands
Sit above kidneys, produce hormones including epinephrine
Adrenal medulla
Inner part of adrenal glands, secretes stress hormones like epinephrine upon signal from sympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Preps the body for fight or flight. Releases epinephrine from the adrenal medulla
SNS pathway from hypothalamus
Hypothalamus → sympathetic nervous system → adrenal medulla releases epinephrine into bloodstream → blood glucose drop response → enzyme led inhibition of glycogen synthesis and promotion of glycogen breakdown
Adrenal cortex
Outer part of adrenal glands, secretes stress hormones (ex. cortisol) upon signal from ACTH
Trophic hormone
Stimulates production of other hormones. Produced in the anterior pituitary. CRF and ACTH are these
Corticotrophin Release Factor (CRF)
Tropic hormone released by the hypothalamus. Stimulates the release of ACTH from the anterior pituitary gland
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)
Tropic hormone triggered by CRF and released by the anterior pituitary. Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release stress hormones
Production of ACTH and CRF in the anterior pituitary
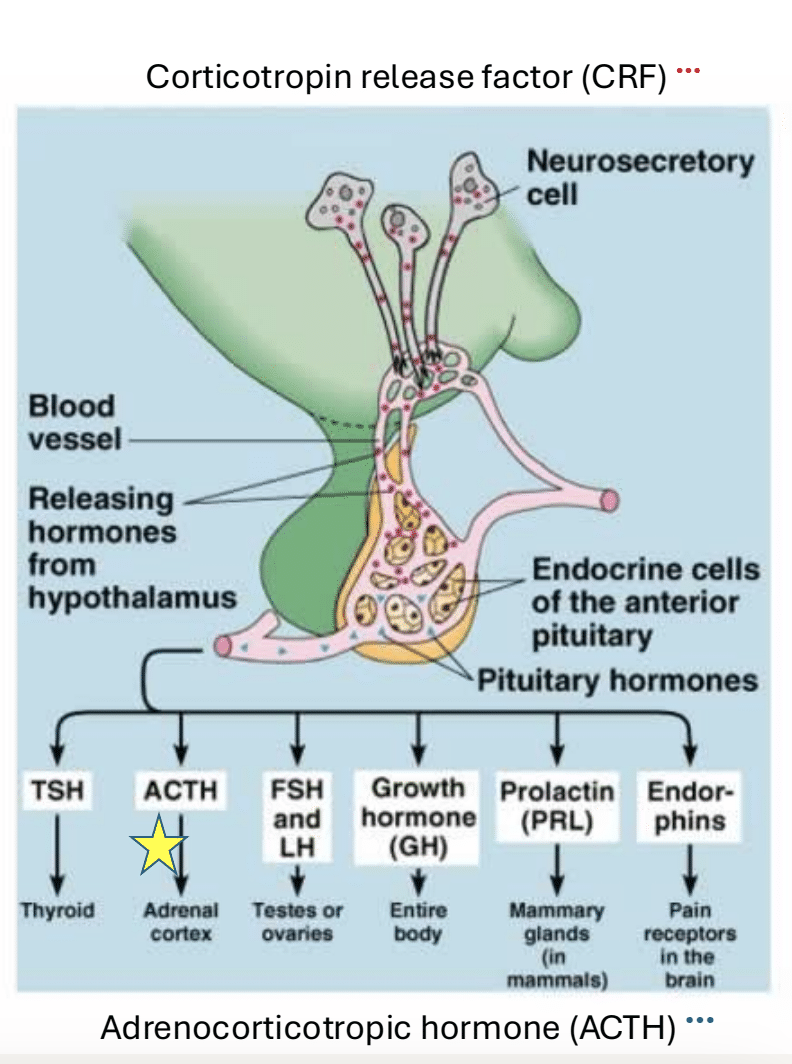
CRF pathway from hypothalamus
Hypothalamus → CRF released → anterior pituitary secretes ACTH → adrenal medulla releases epinephrine → initiates stress response and increases blood glucose levels
Glycogen synthesis inhibition and glycogen breakdown promotion. Makes glucose molecules available for use
Endocrine response to epinephrine in event of blood glucose drop
Liver
Glycogen synthesis and breakdown occur in the
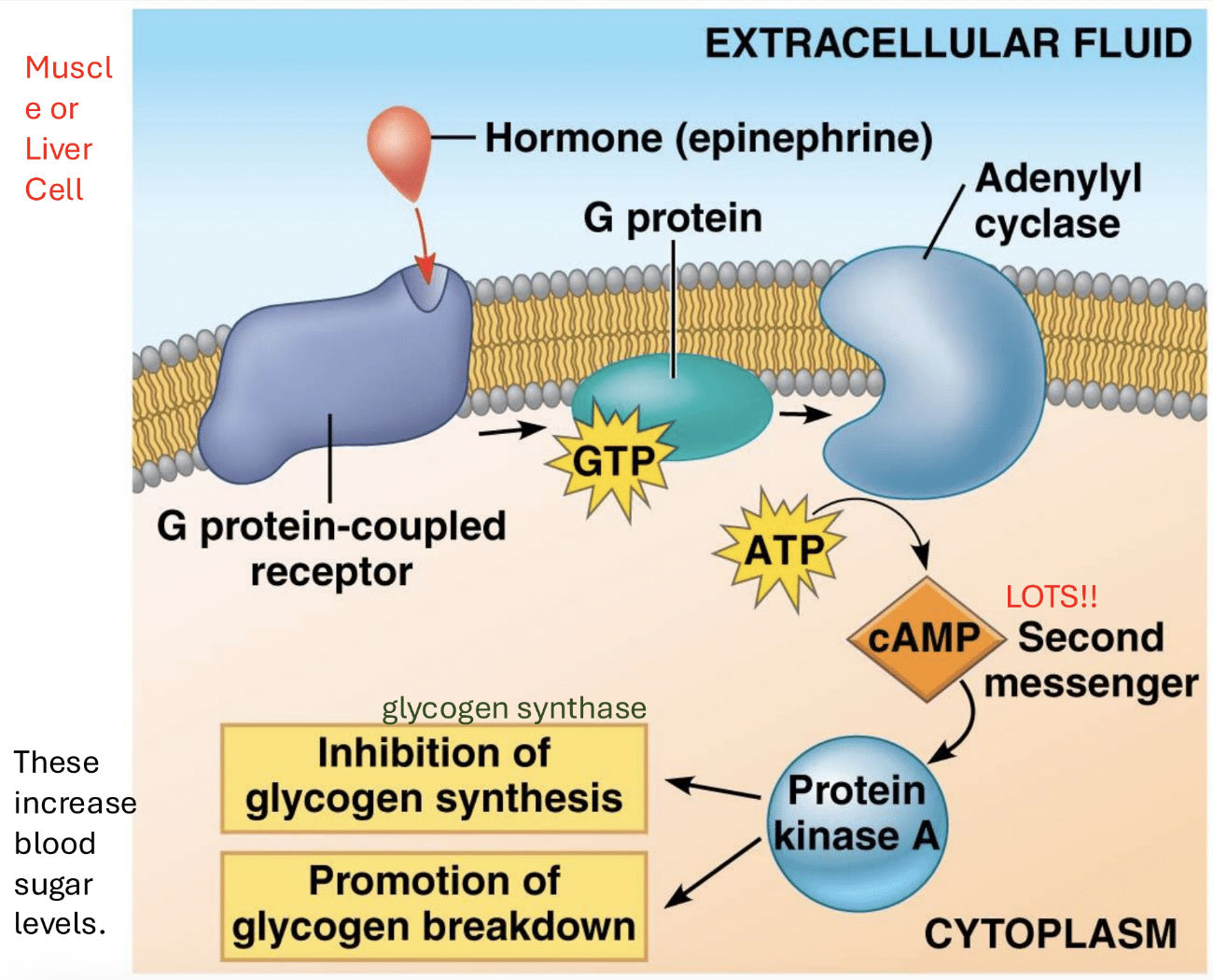
Reception in plasma membrane, transduction by relay molecules in cytoplasm, response (ex. turn enzymes on and off)
General signal transduction pathway
Enzymes
All chemical reactions in biological systems are catalyzed by
Liver
Pathway response to blood glucose drop occurs in the
Hormone (epinephrine), G protein coupled receptor, G protein, GDP and GTP, Adenylyl cyclase, ATP, cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen synthase, glycogen synthesis inhibition, glycogen breakdown promotion
Parts included in epinephrine response
Use glucose to make glycogen
Goal is to turn off enzymes that
Hydrolyze (adding water to break down) glycogen for release into blood
Goal is to turn on enzymes that
Phosphorylation
Adding a phosphate group to a protein to result in a functional change. Requires ATP. An example of cellular work and a cellular response to a signal.
G protein coupled receptor
Activates upon receiving signaling molecule/first messenger (epinephrine) and binds to G protein
G protein
Upon receptor binding, changes shape and drops GDP. Can now bind GTP, which changes its shape again. Uncouples from membrane and can now bind adenylyl cyclase
Adenylyl cyclase
Upon binding to G protein/GTP, catalyzes phosphorylation of 4 ATP to 4 cAMP
cAMP
Second messenger in the signaling pathway. Converted from ATP through phosphorylation by adenylyl cyclase. Activates protein kinase A.
Protein kinase
Modifies other proteins by adding phosphate groups to them
Protein kinase A
Has 2 regulatory subunits and 2 catalytic. Activated when cAMP binds to its regulatory binding sites. Releases its 2 catalytic subunits.
PKA catalytic subunits
Influence glycogen synthesis and breakdown. One adds phosphates to glycogen synthase to inactivate it (this uses ATP). The other adds a phosphate to phosphorylase kinase and activates it.
Glycogen synthase
Inactivated/inhibited by PKA catalytic subunit phosphorylation. Stops synthesis of glucose into glycogen
Phosphorylase kinase
Activated by PKA catalytic subunit phosphorylation. Phosphorylizes glycogen phosphorylase to activate it
Glycogen phosphorylase
Activated by phosphorylation from phosphorylase kinase. Catalyzes breakdown of glycogen into glucose. Glucose released into bloodstream to raise blood glucose levels
Glycogen synthesis inhibition, glycogen breakdown promotion
Inhibition of glycogen synthase and activation of glycogen phosphorylase. PKA-mediated phosphorylation
Process as graphic
raise blood glucose level, vasodilation, vasoconstriction
Other functions of epinephrine depending on receptor type or intracellular protein type