Lecture 16: cell transport
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
cell membrane
Made up of phospholipids in a phospholipid bilayer
role of cell membrane
Keep internal and external environment separate
Control what enters and exits
Remain fluid to allow all parts to move around
parts of the cell membrane
phospholipids
proteins
cholesterols
glycolipids / glycoproteins
cholesterol in the cell membrane
keeps cell membrane fluid
glycolipids / glycoproteins in the cell membrane
proteins and lipids with sugars attached, helps identify the cell as being part of you
phospholipid bilayer
selectively permeable —> only lets certain things enter or exit the cell
proteins in the cell membrane
can help select objects move in and out the cell
solvent
the substance things are dissolved into (like water)
solute
substance being dissolved (like NaCl)
solution
solvent + solute
diffusion
Spontaneous movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to low concentration
osmosis
Passive diffusion of water from a high water concentration to a low water concentration
DOES NOT MOVE THE SOLUTE
movements that do not require energy
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion (channels)
movements that require energy
facilitated active transport (using pumps)
molecules that cannot cross the membrane
ions (have charge)
larger molecules (sugars, amino acids, nucleic acids)
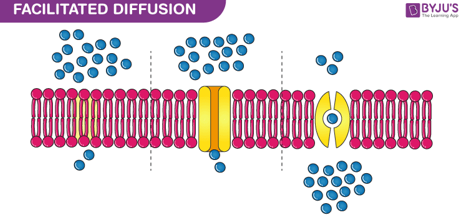
facilitated diffusion
uses channel proteins allow a specific molecule through
facilitated = done by proteins
pumps during active transport
use ATP to move material up its concentration gradient
vescicles
a smaller phospholipid bilayer used for transportation within the cell
when the cell can’t rely on facilitated diffusion or active transport
exocytosis
Releasing a large amount of material outside the cell by fusing a vesicle with the cell membrane to release material
e.g. LDL and HDL excreted by liver cells into the bloodstream
endocytosis
when the cell takes in a large amount of substances by engulfing them with the cell membrane, forming a vesicle
e.g. immune system engulfing a bacteria for destruction
molecules that can pass the membrane without assistance
water (osmosis), small fat molecules, small gas molecules (oxygen, CO2)