MCAT (NON-ENZYMATIC PROTEIN FUNCTION AND PROTEIN ANALYSIS)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Collagen
Triherical fiber (3-alpha helices woven together to a secondary helix) Makes up most of extracellular matrix of connective tissue. Strength + flexibility
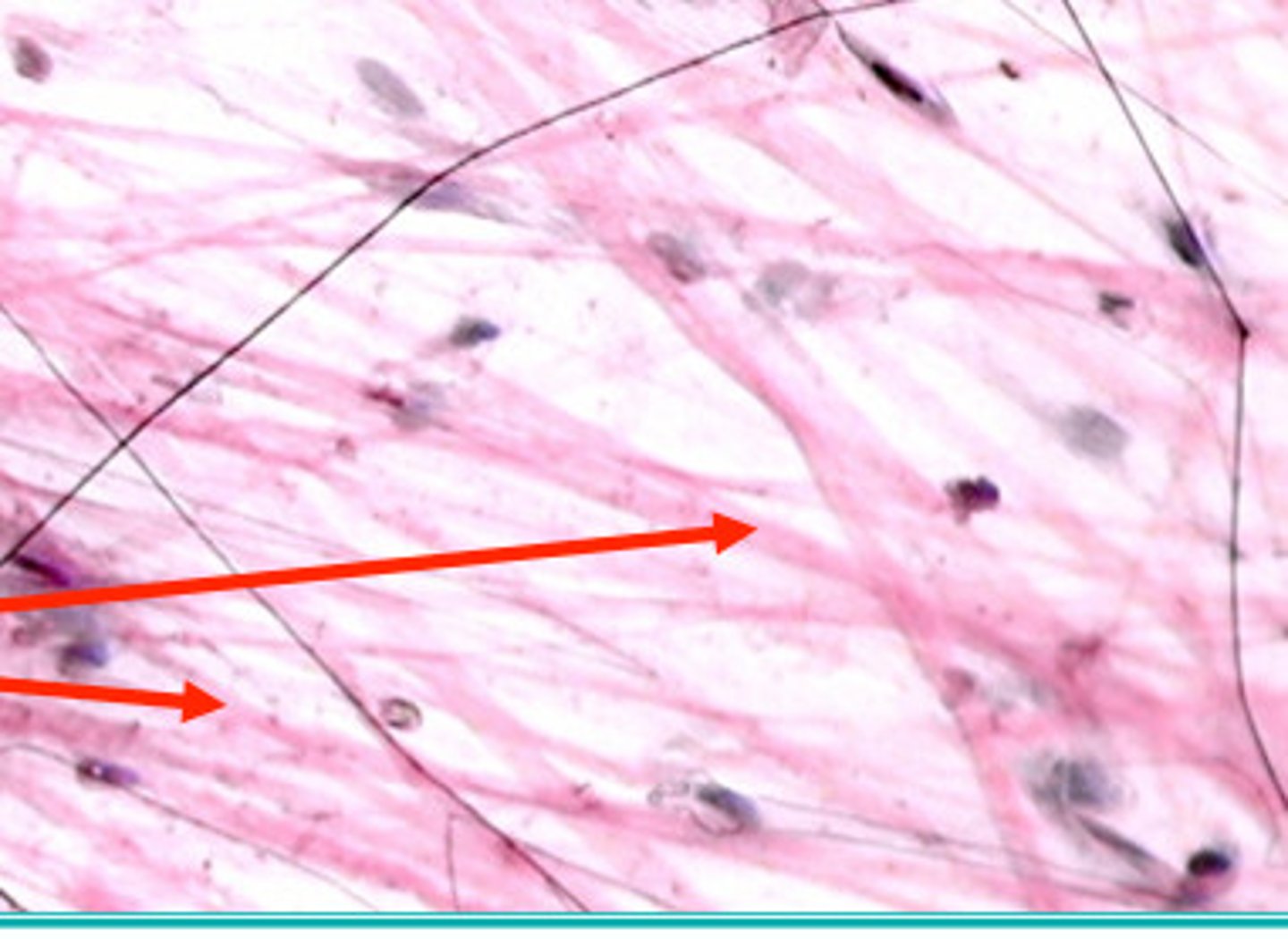
Elastin
Extracellular of connective tissue. Stretch and recoils back into shape
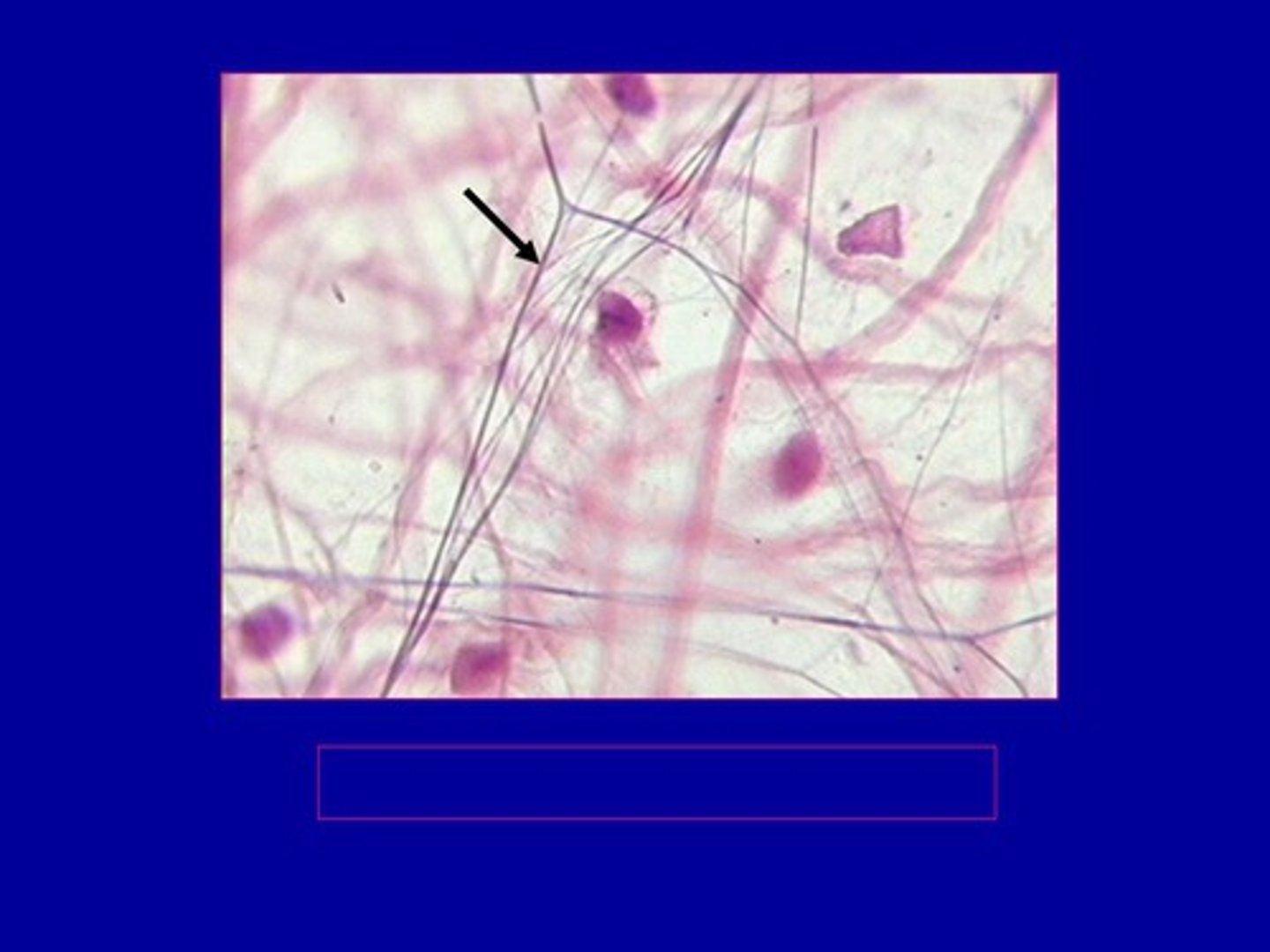
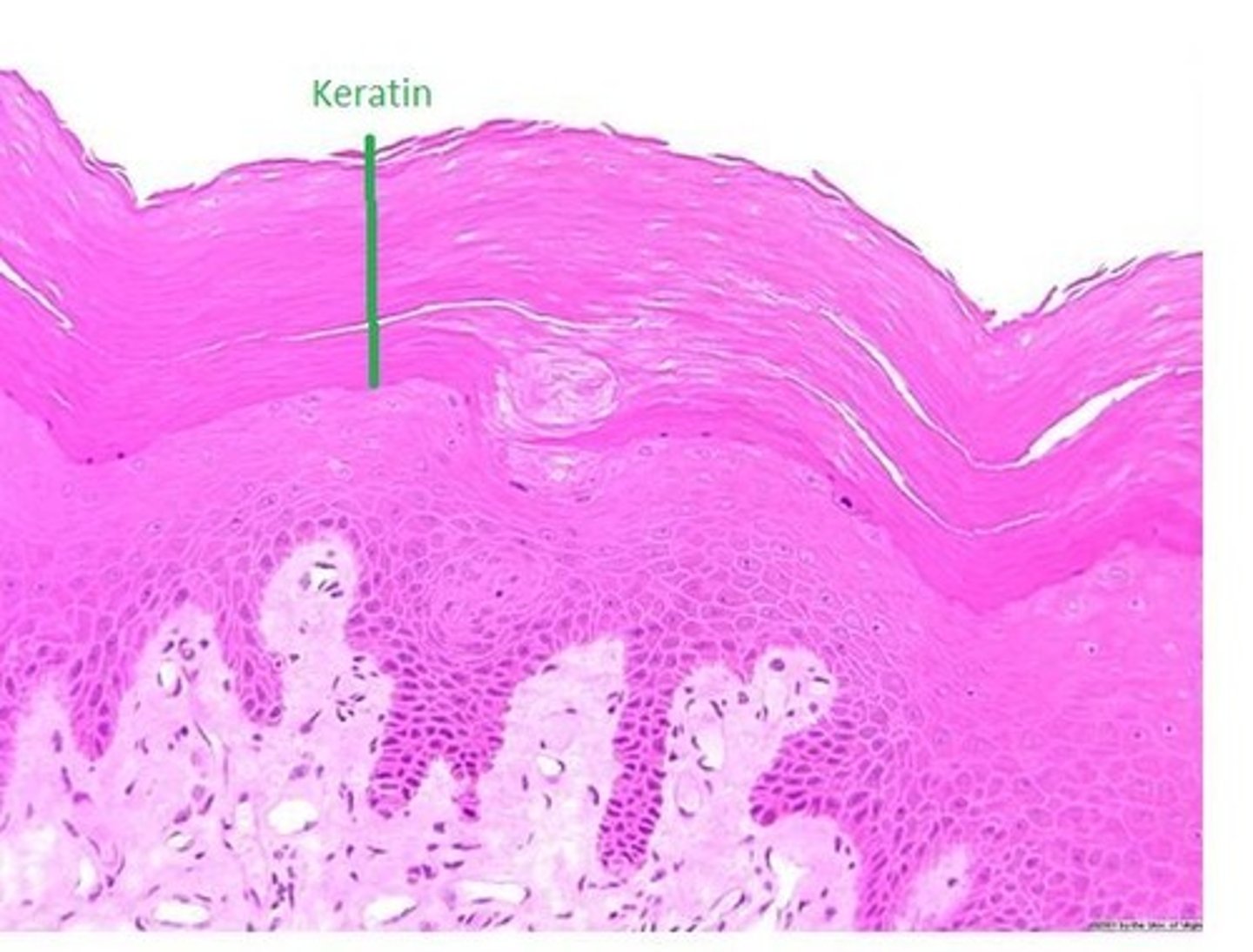
Keratins
I.F proteins found in epithelial cells. Makes up hair and nails. Contribute to the mechanical integrity of the cell and functions as a regulatory protein.
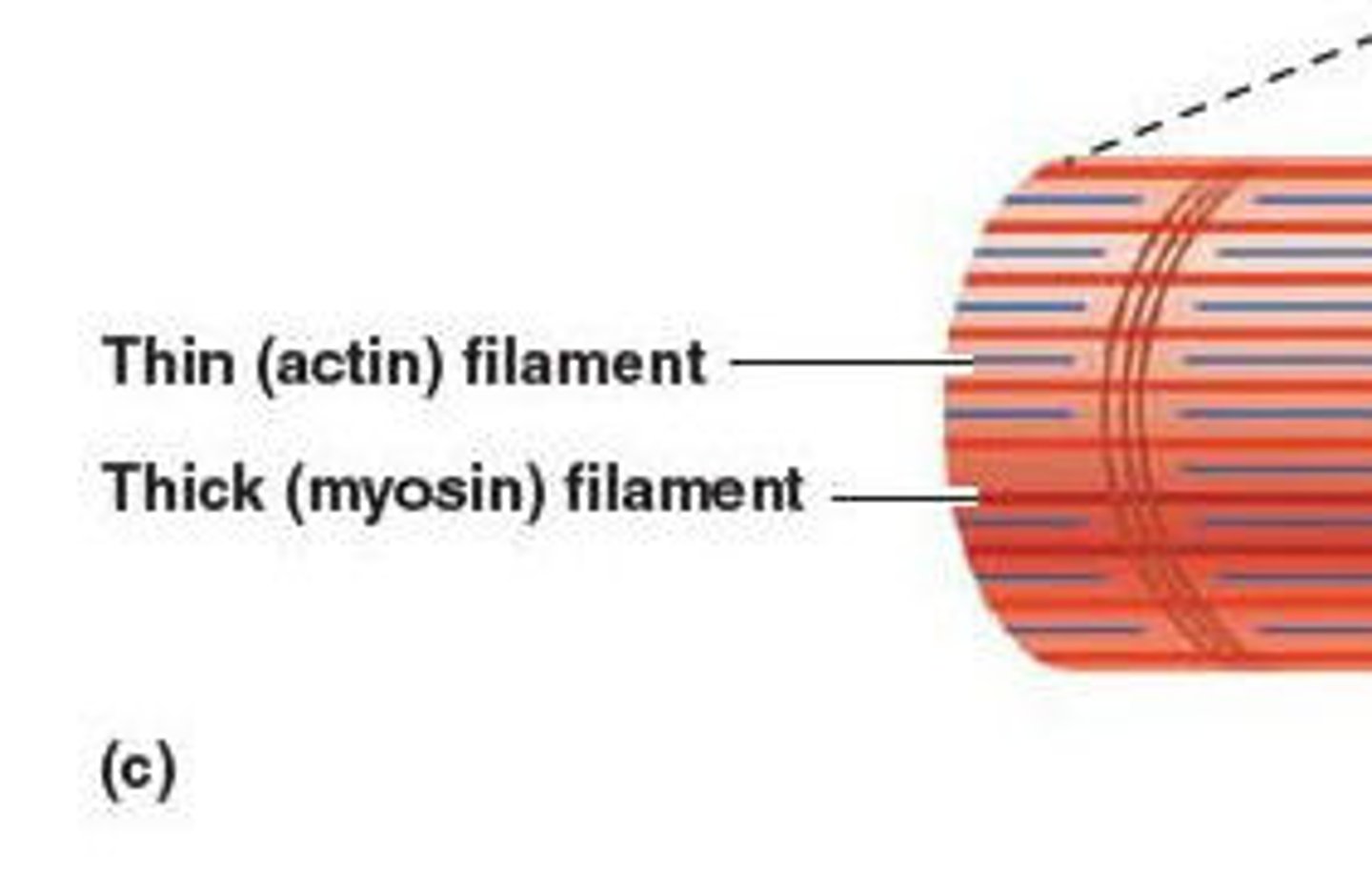
Actin
Makes up microfilaments and the thin filaments in myofibrils. + and - side, this polarity allows motor proteins to travel like a one-way street along actin filaments
Tubulin
Make up microtubules. Has polarity. -end adjacent to nucleus and + periphery of a cell
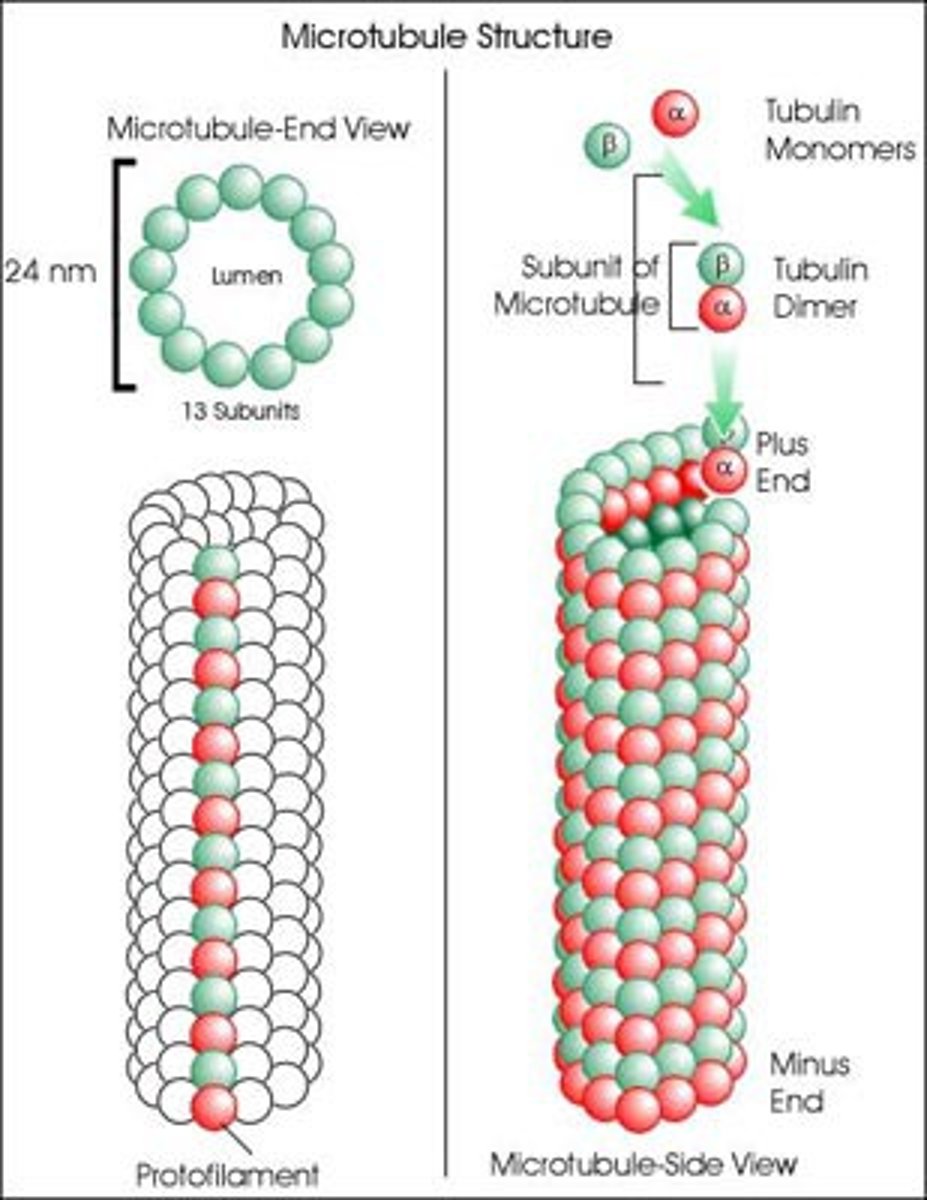
Myosin
acts with actin, involved in cellular transport .It functions as a motor that drives filament sliding
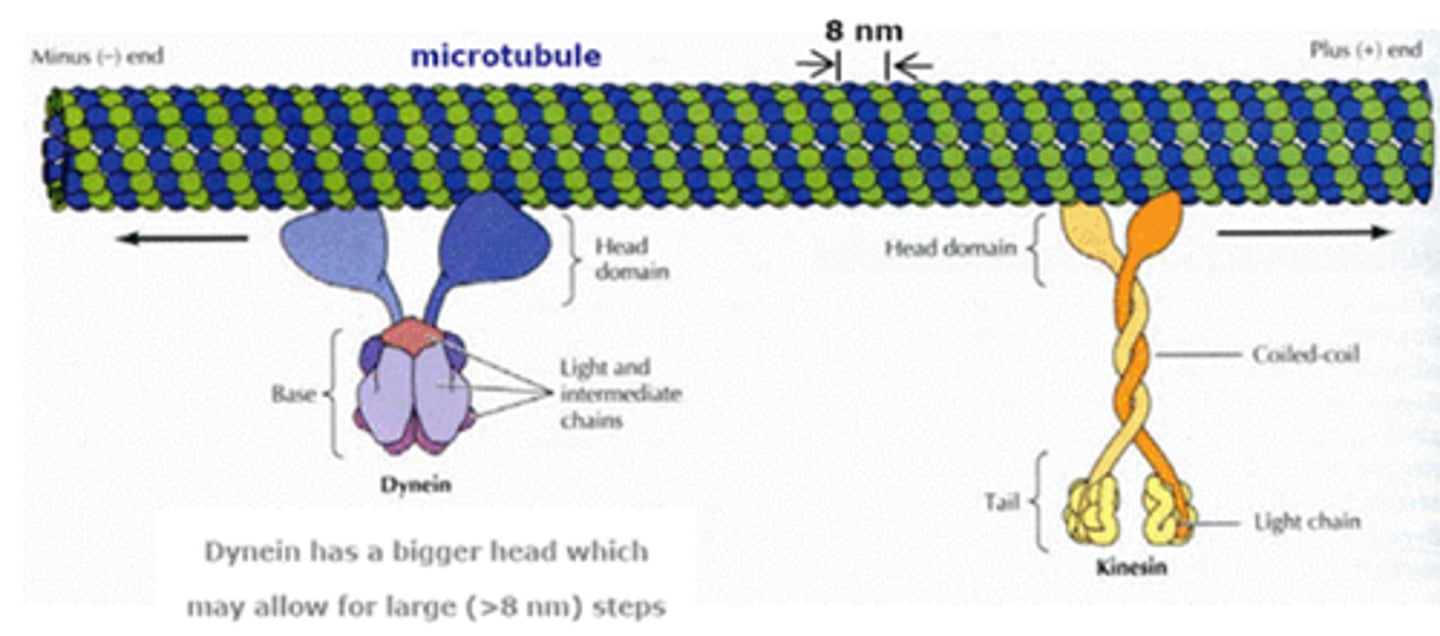
Kinesin and Dyneins
Associated with microtubules. Kinesins align chromosoms in metaphase and depolymerizing microtubules during anaphase.
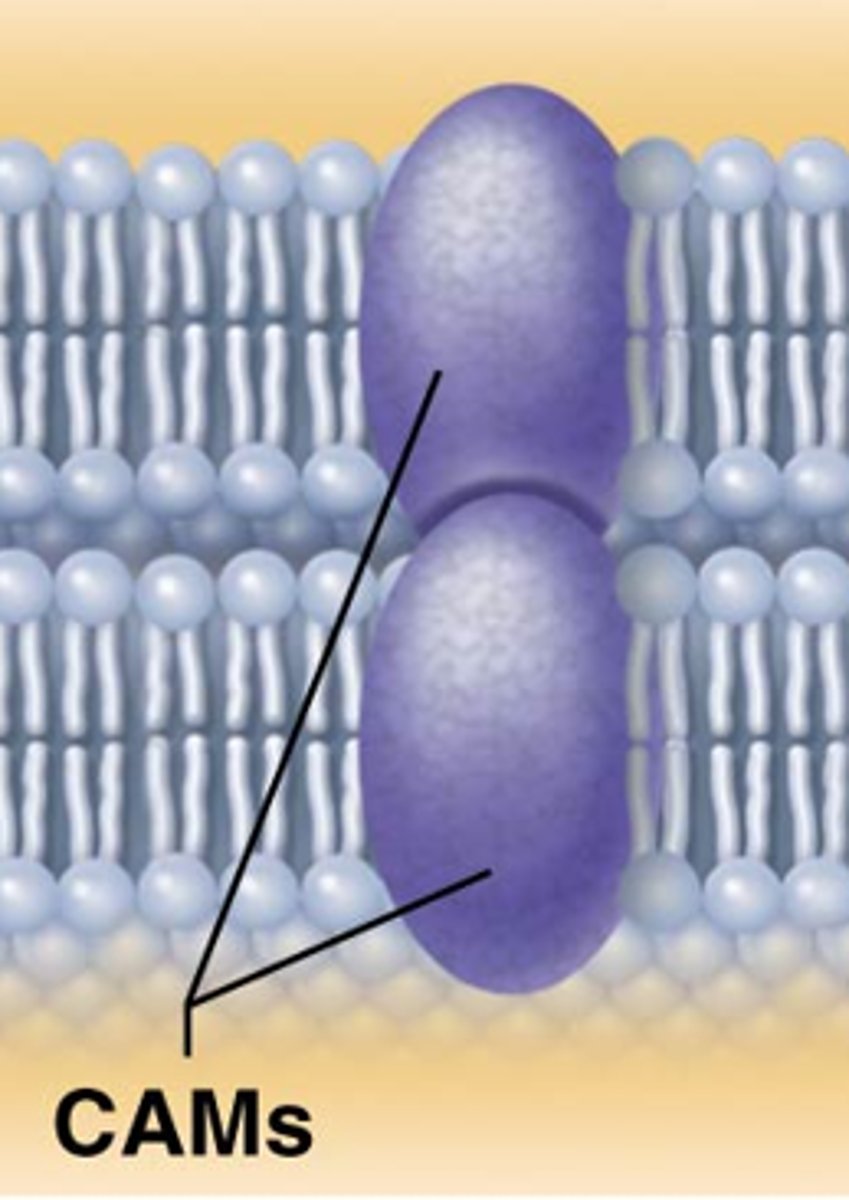
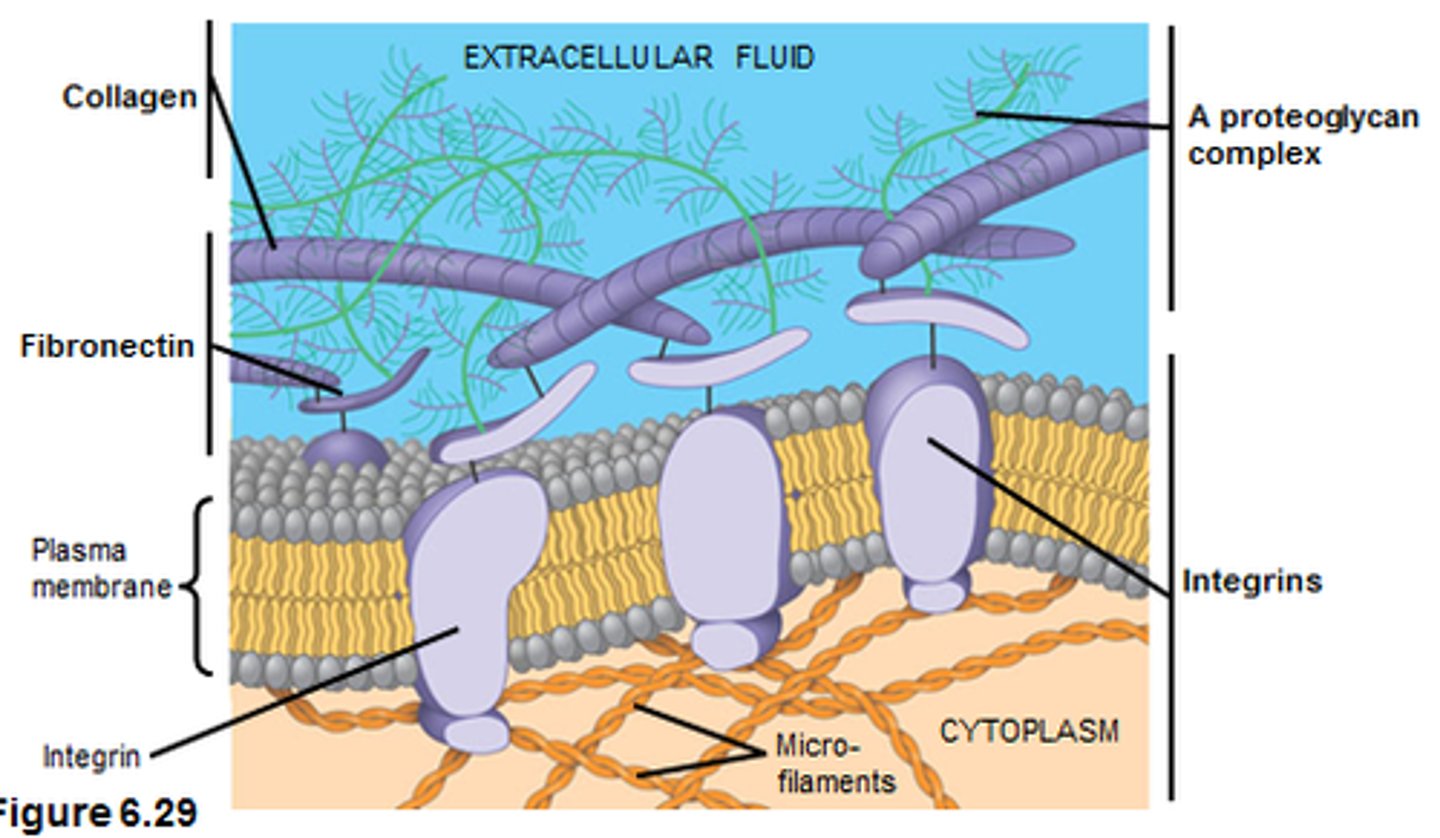
Cell Adhesion Molecules
Found on the surface of most cells, aid in the binding of cells to the extracellular matrix of other cells.
Cadherins
group of glycoproteins, mediate calccium dependent cell adhesion. Hold similar cell types together
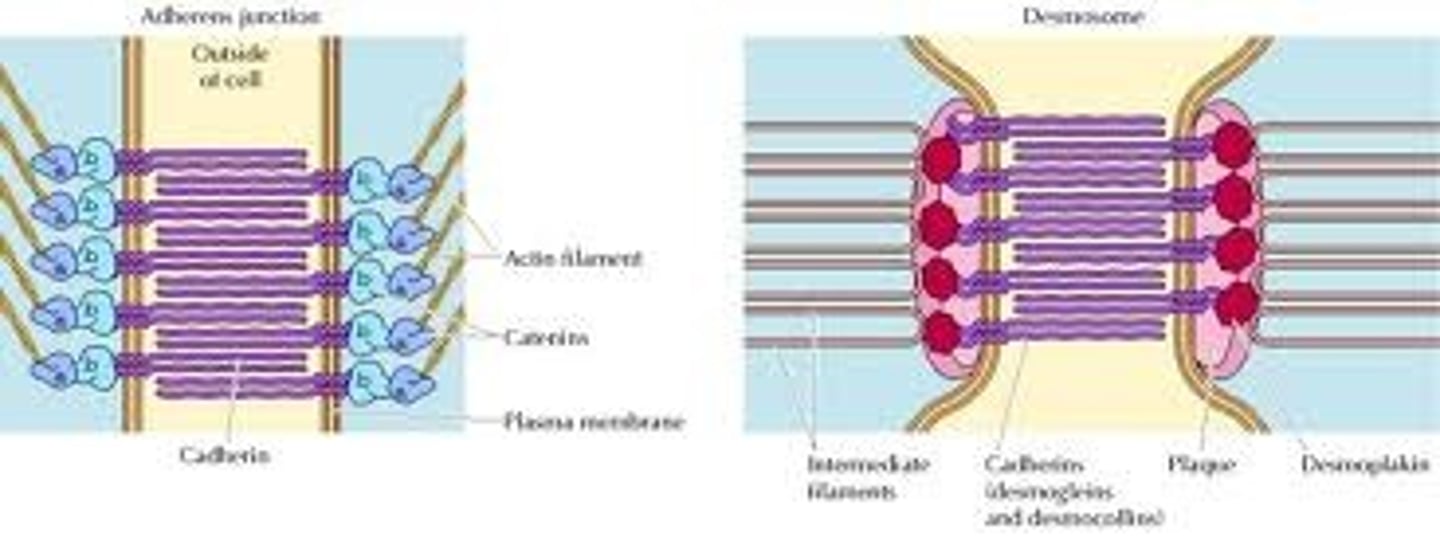
Integrins
Have 2 membranes spanning chains alpha and beta important in cellular signaling, can impact cell function by promoting cell division, apoptosis etc
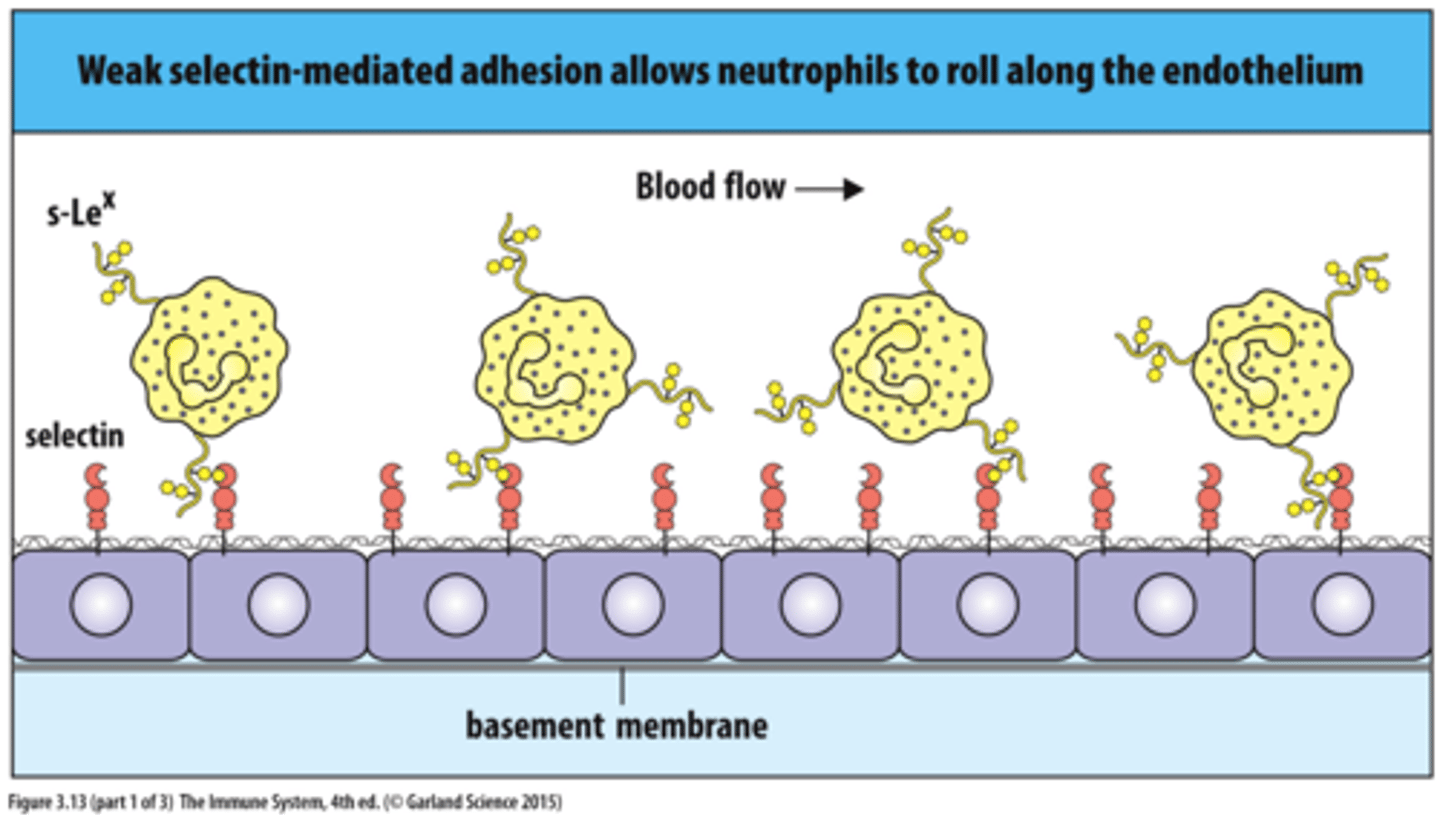
Selectins
Allows cells to adhere to carbohydrates on the surface of other cells and are most commonly used in the immune system
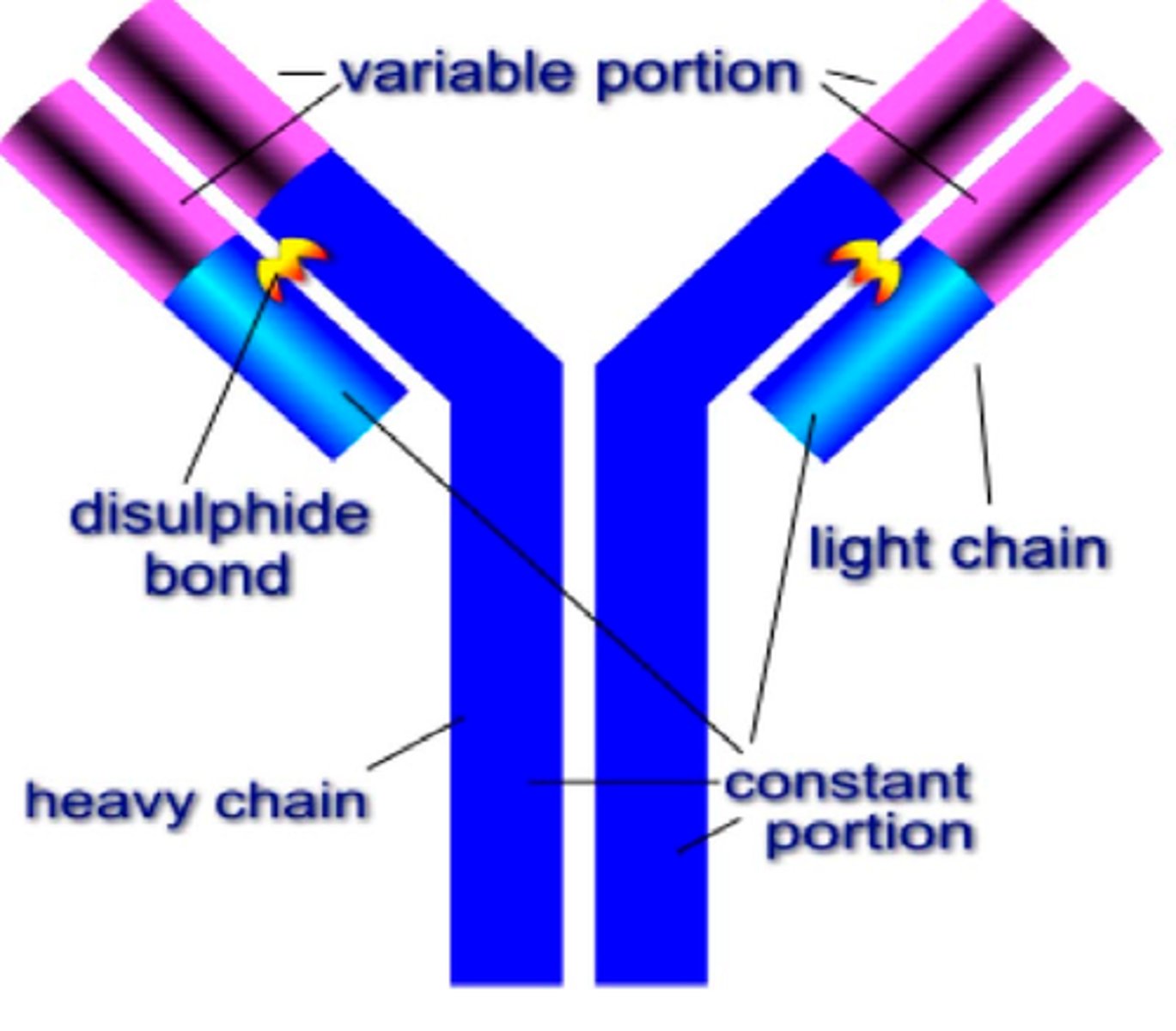
Antibodies
Used in the immune system to target a specific antigen, which may be a protein on the surfaces of a pathogen or a toxin.
Ion Channels
used to regulate ion flow into and out of the cell
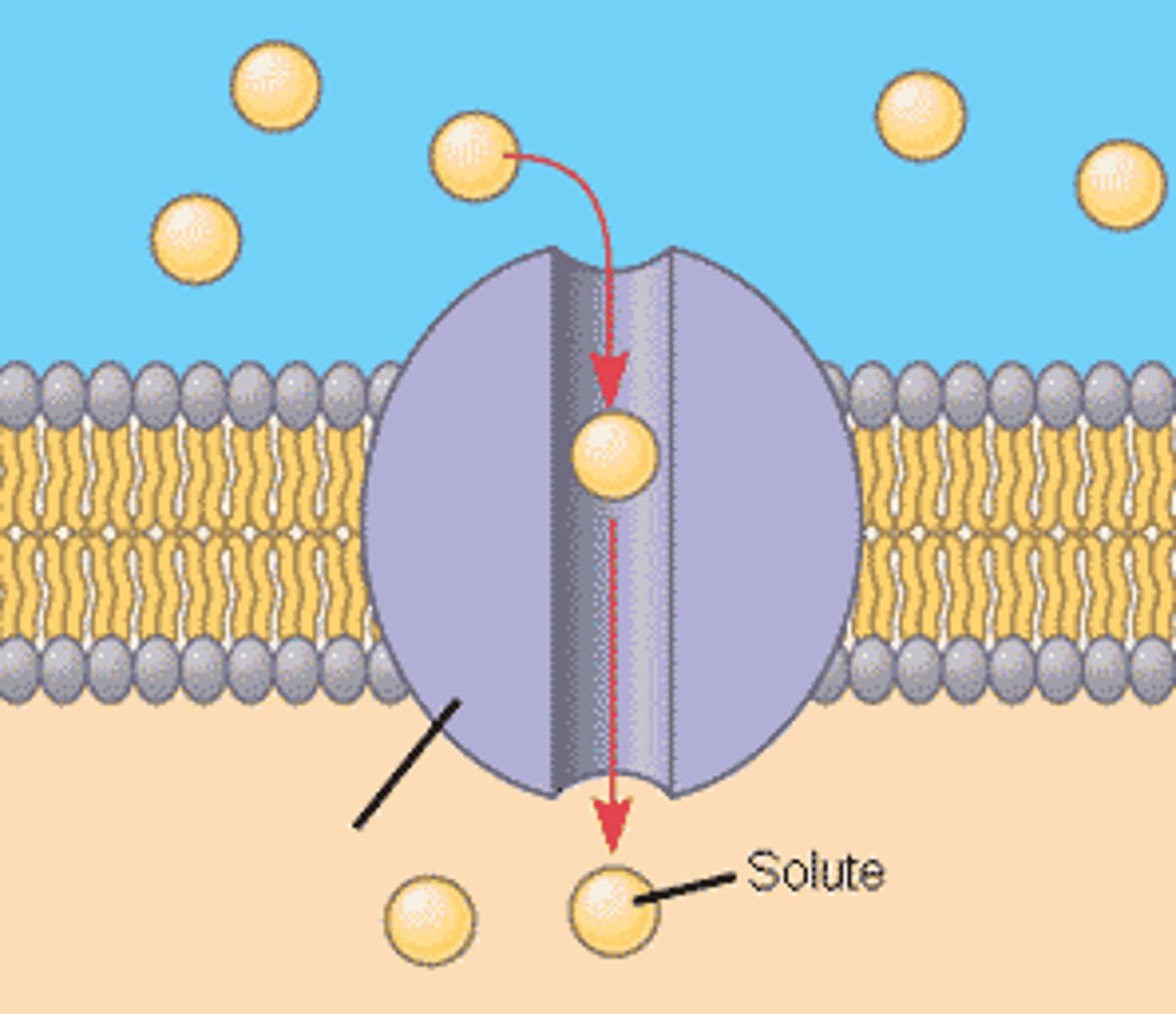
ungated channel
always open
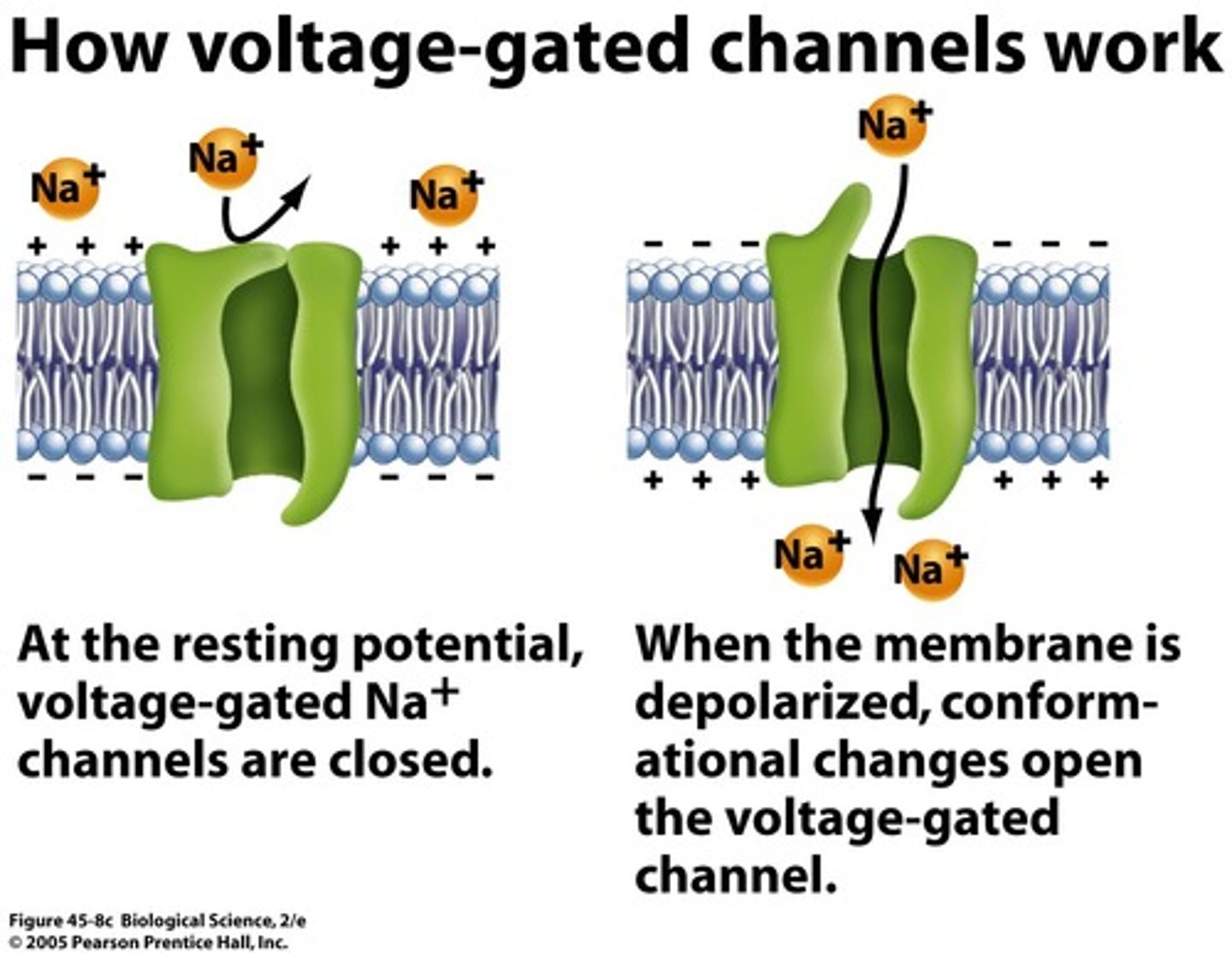
voltage gated channel
open within a range of membrane channels
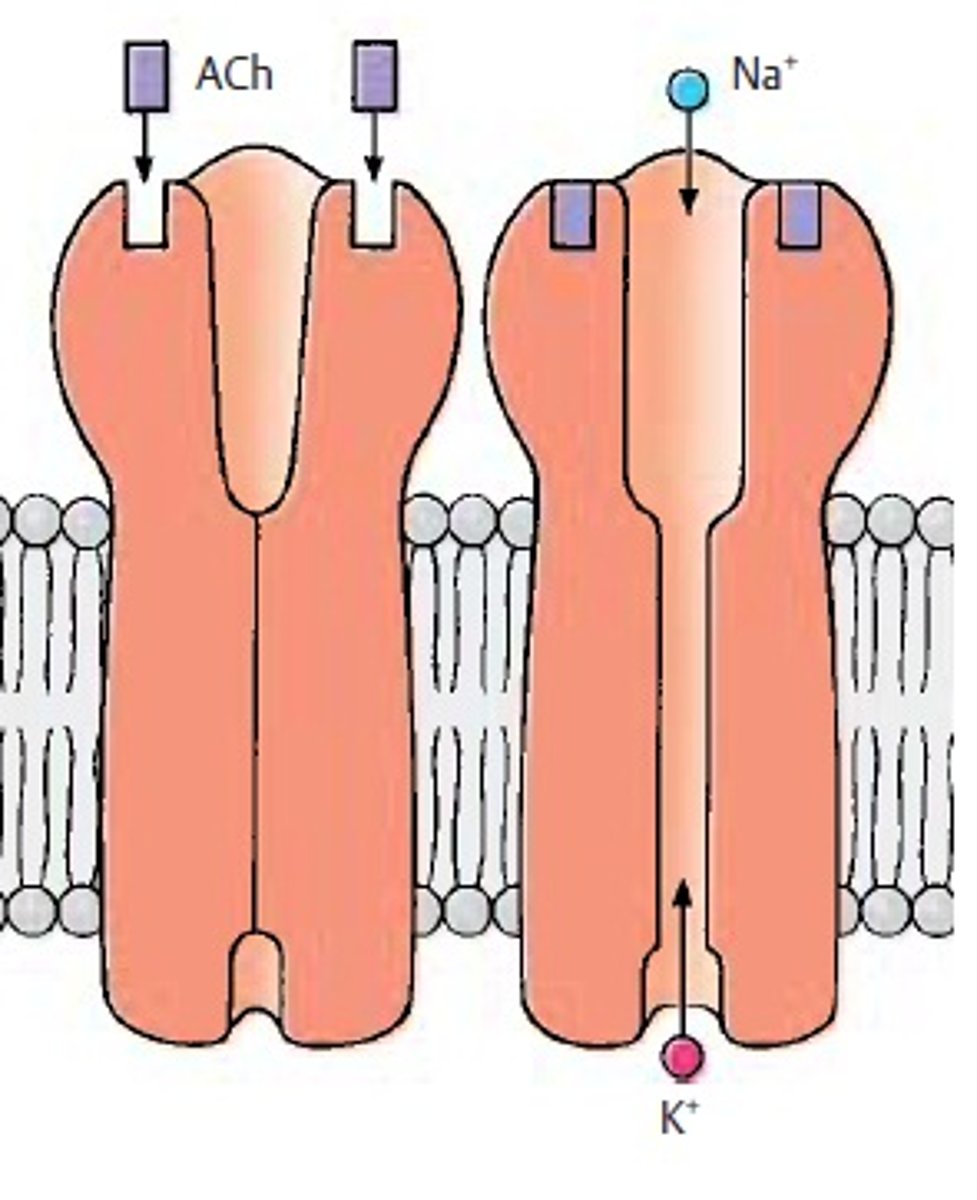
Ligand gated channel
Open in presence of a specific binding substance, usually a hormone or neurotransmitter
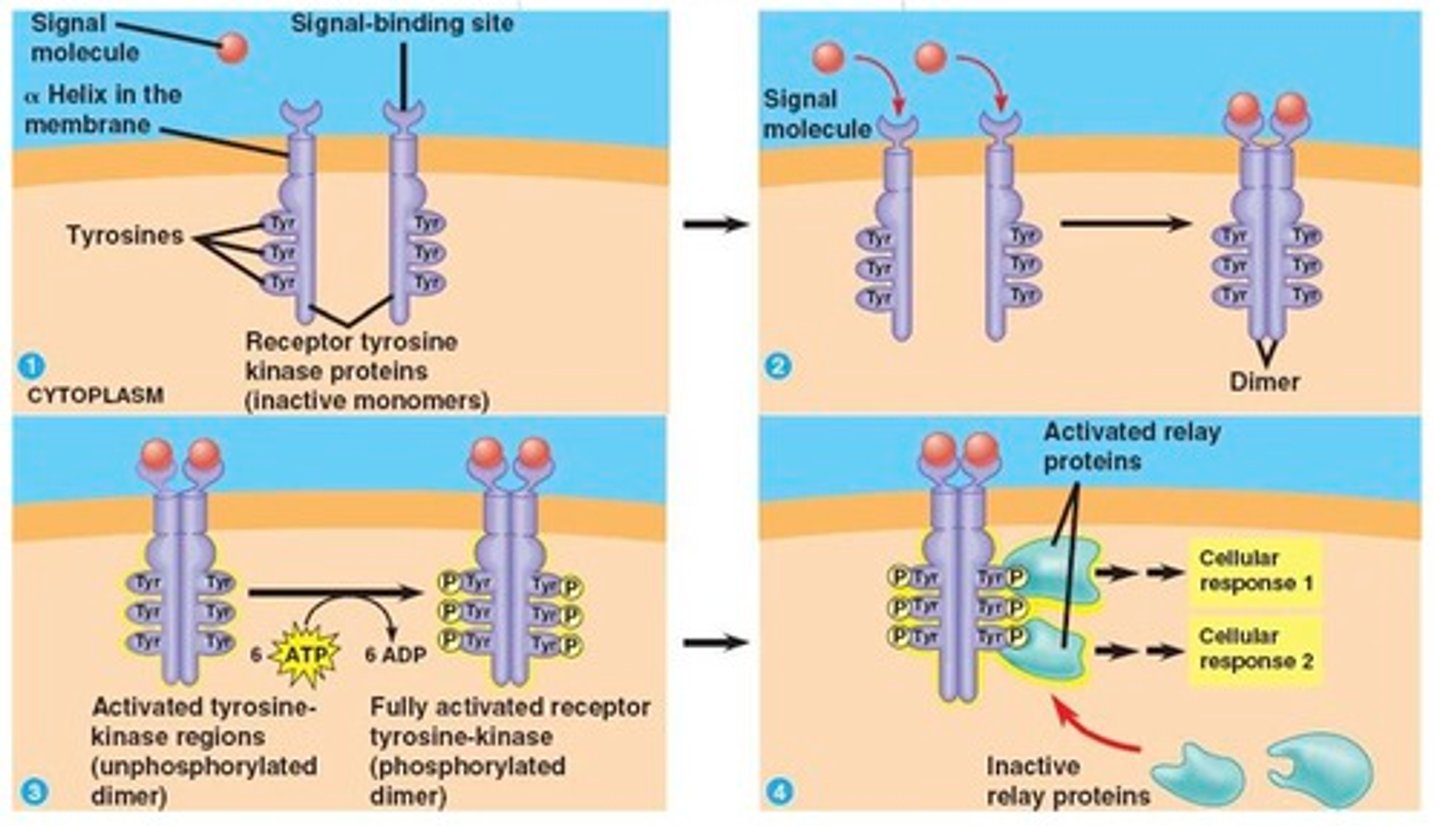
Enzyme-linked receptor
Participate in cell signalling through extracellular ligand binding and initiation of second messenger cascades
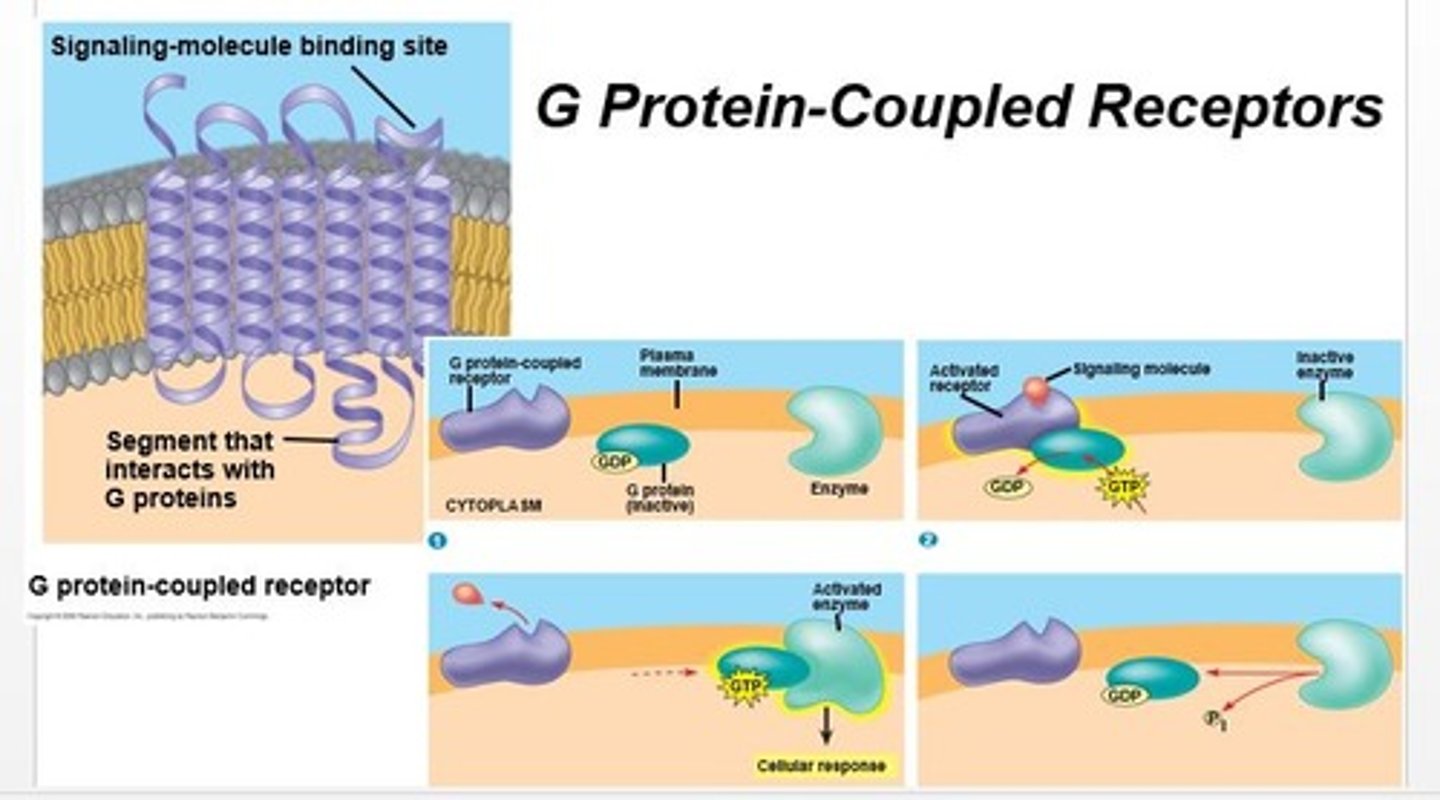
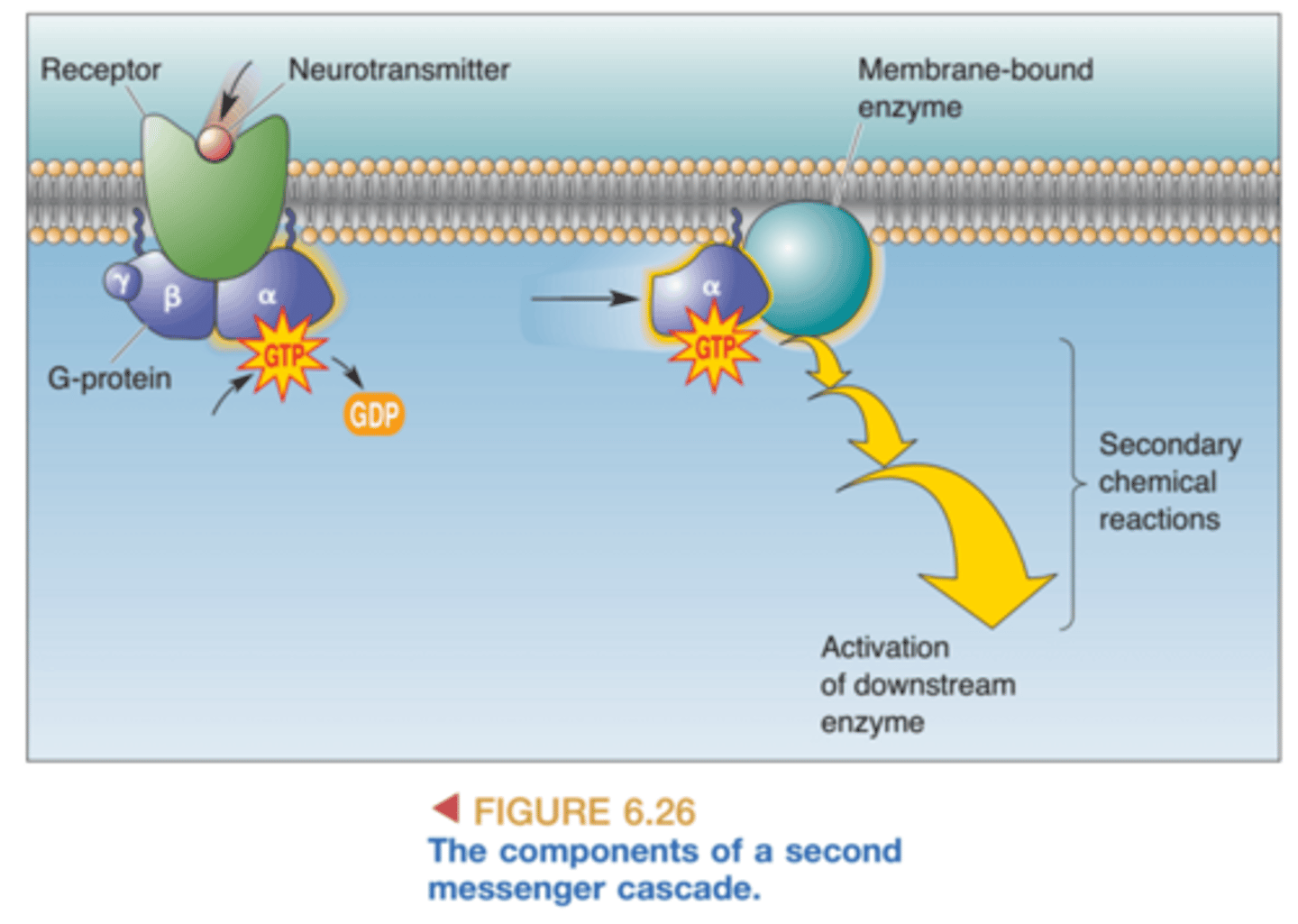
G protein coupled receptors
Have a membrane bound protein with a trimeric g protein. Initiating second messenger cascades
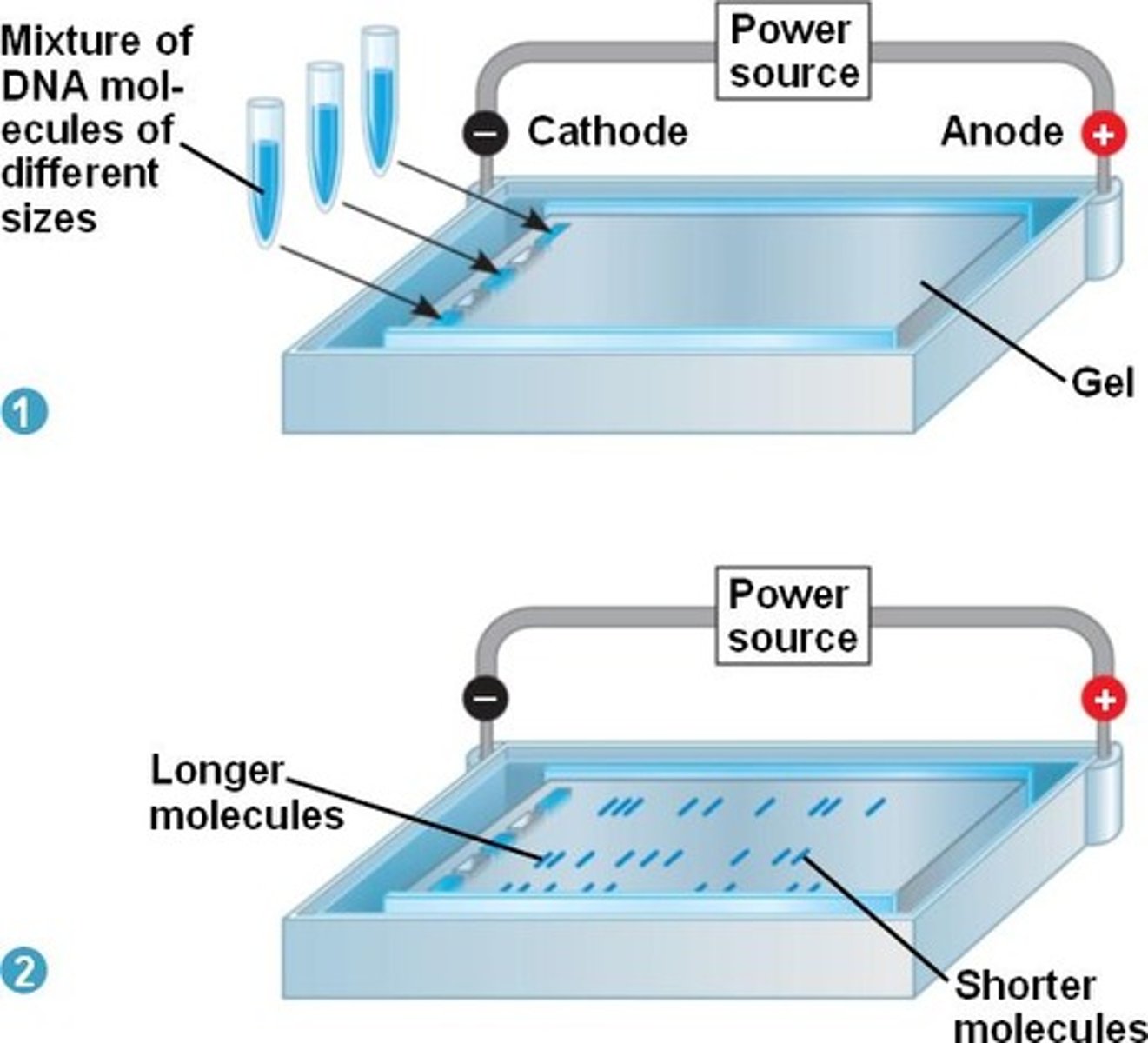
Electrophoresis
Uses a gel matrix to observe the migration of proteins in response to an electric field.
Native PAGE
Maintains the protein's shape, but results are difficult to compare because the mass to charge ratio differs for each protein

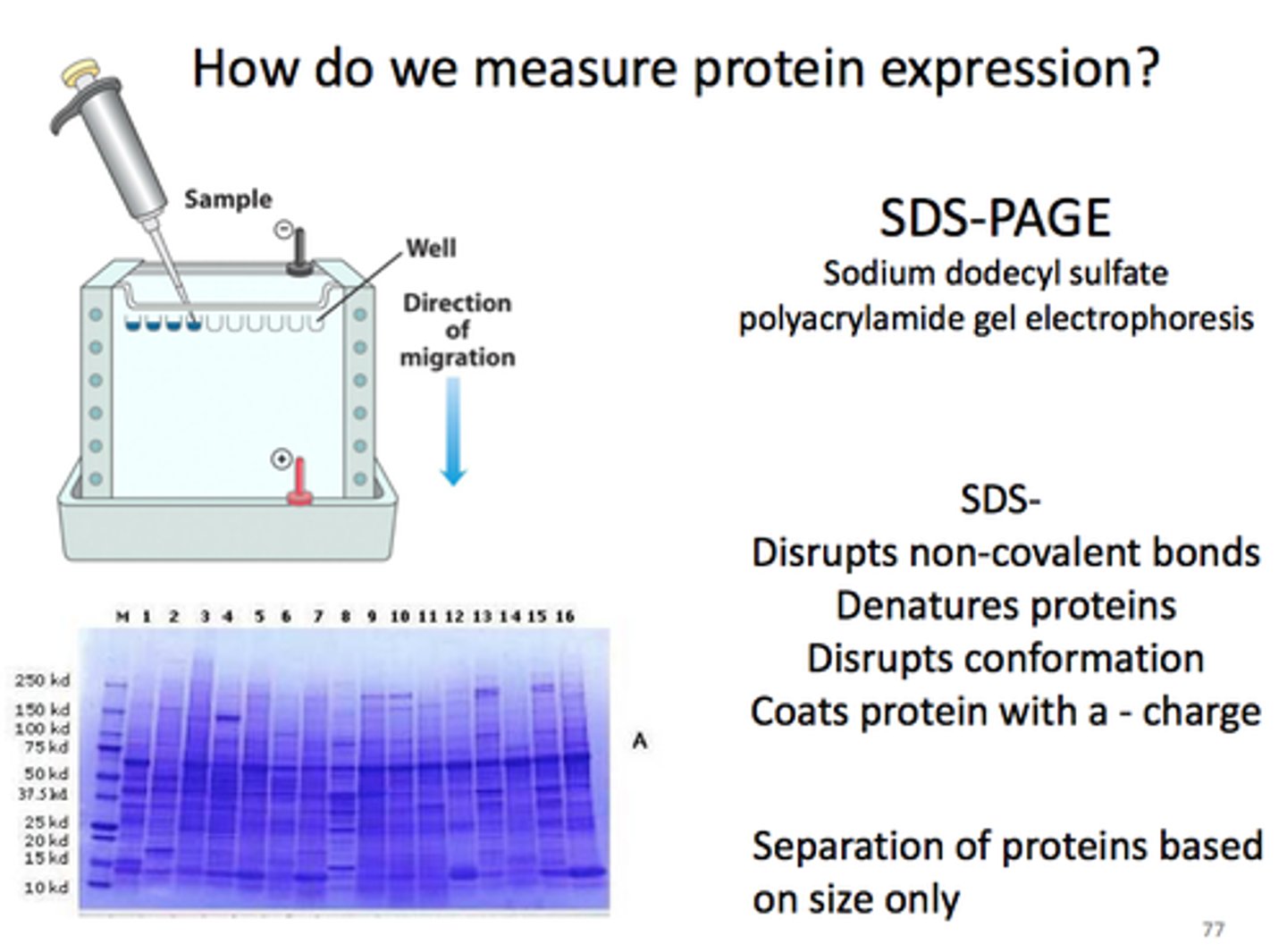
SDS PAGE
Denatures the proteins and masks the native charge so that comparison of size is more accurate, but the functional protein cannot be recaptured from the gel
Isoelectric focusing
Seperates proteins by their isoelectric point; the protein migrates toward an electrode until it reaches a region of the gel where pH=pI of the protein
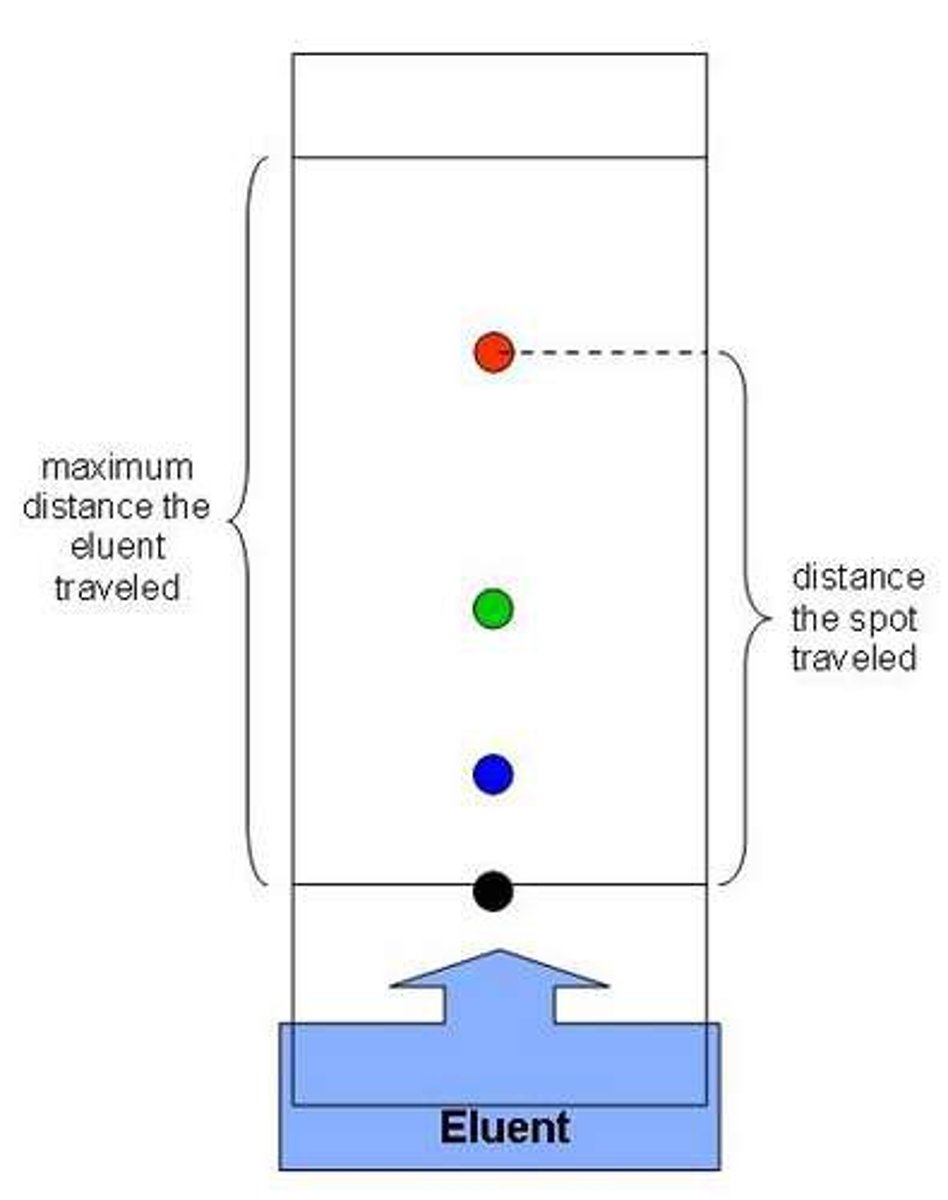
Chromatography
Separates protein mixtures on the basis of their affinity for a stationary phase or mobile phase
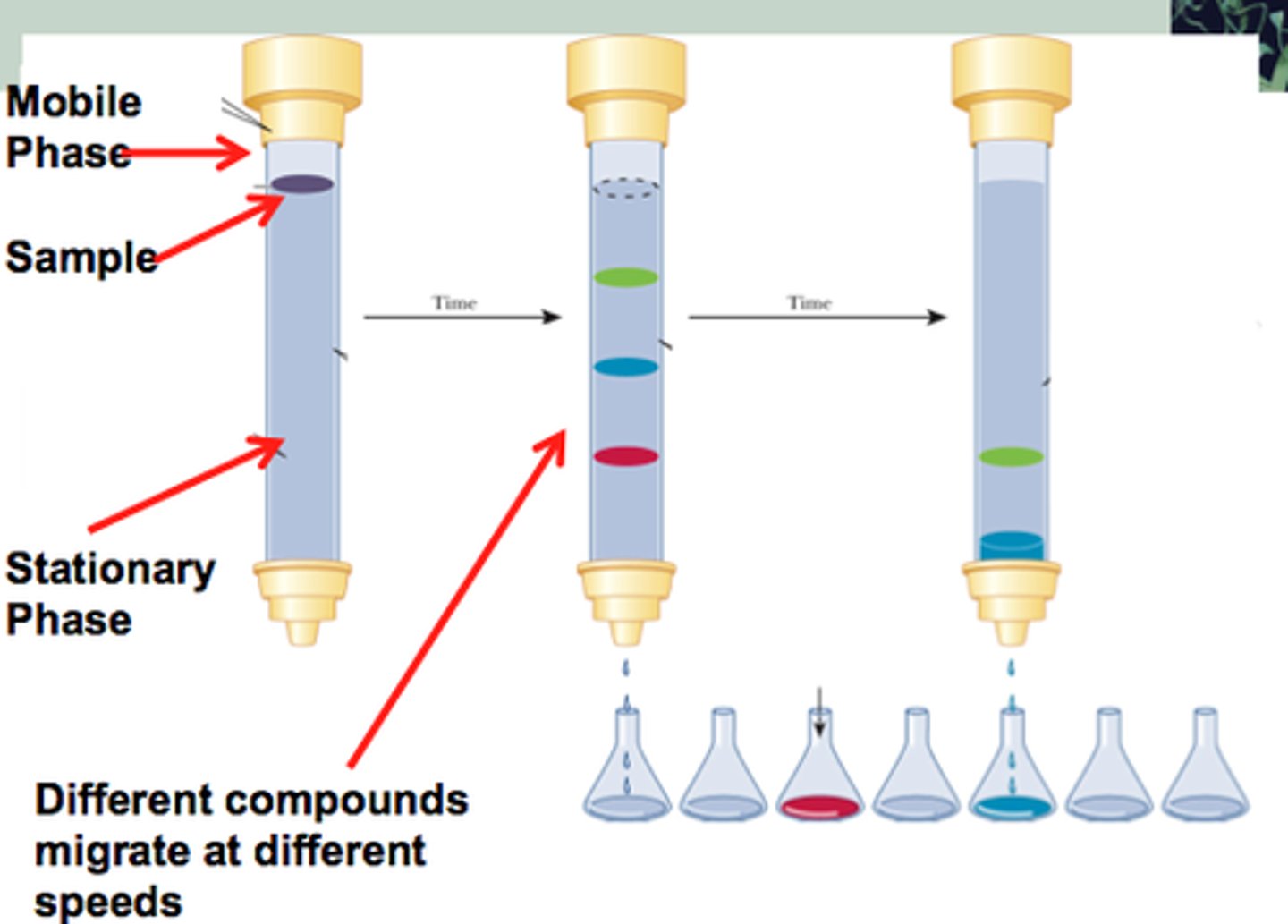
Column chromatography
Uses beads of a polar compund, like silica or alumina, with a nonpolar solvent
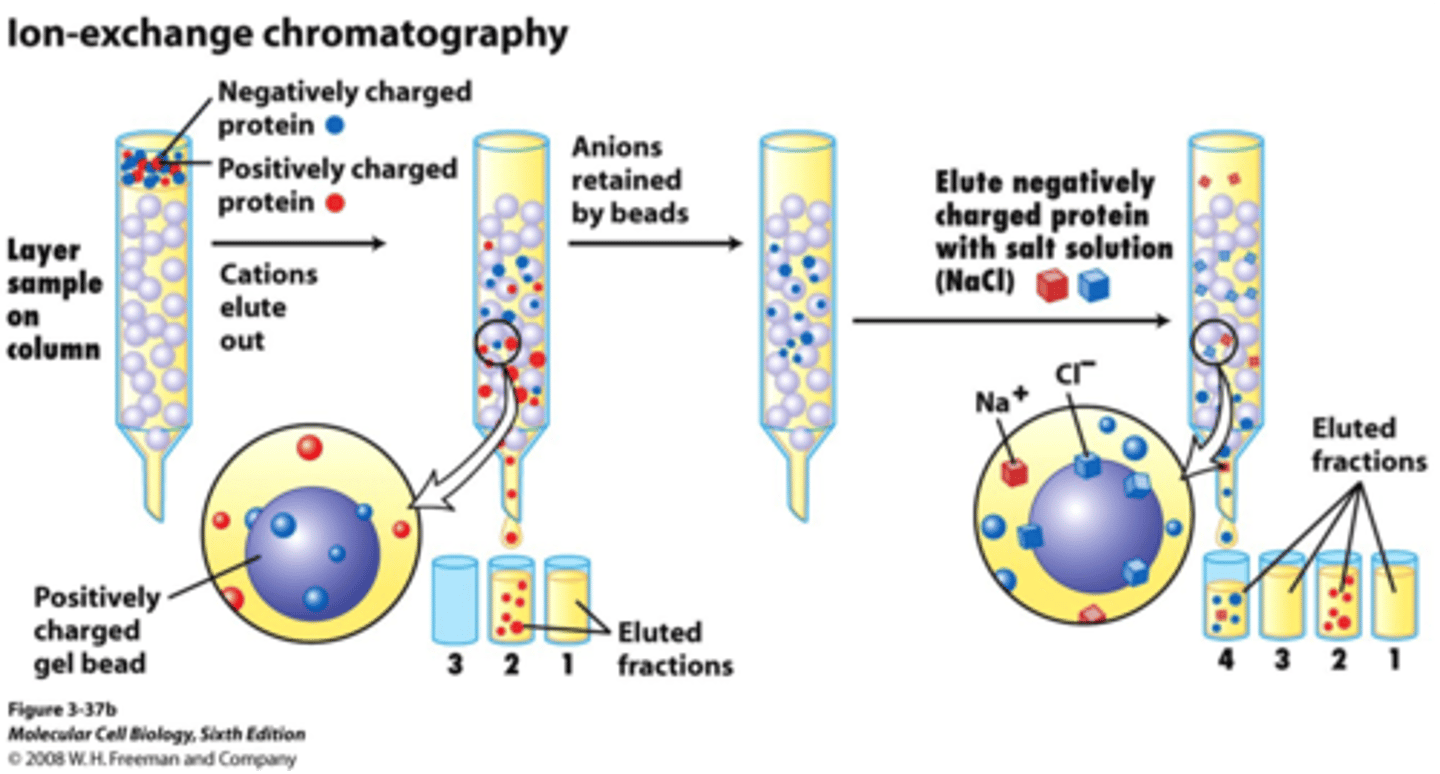
Ion-exchange chromatography
Uses a charged column and a variably saline eluent
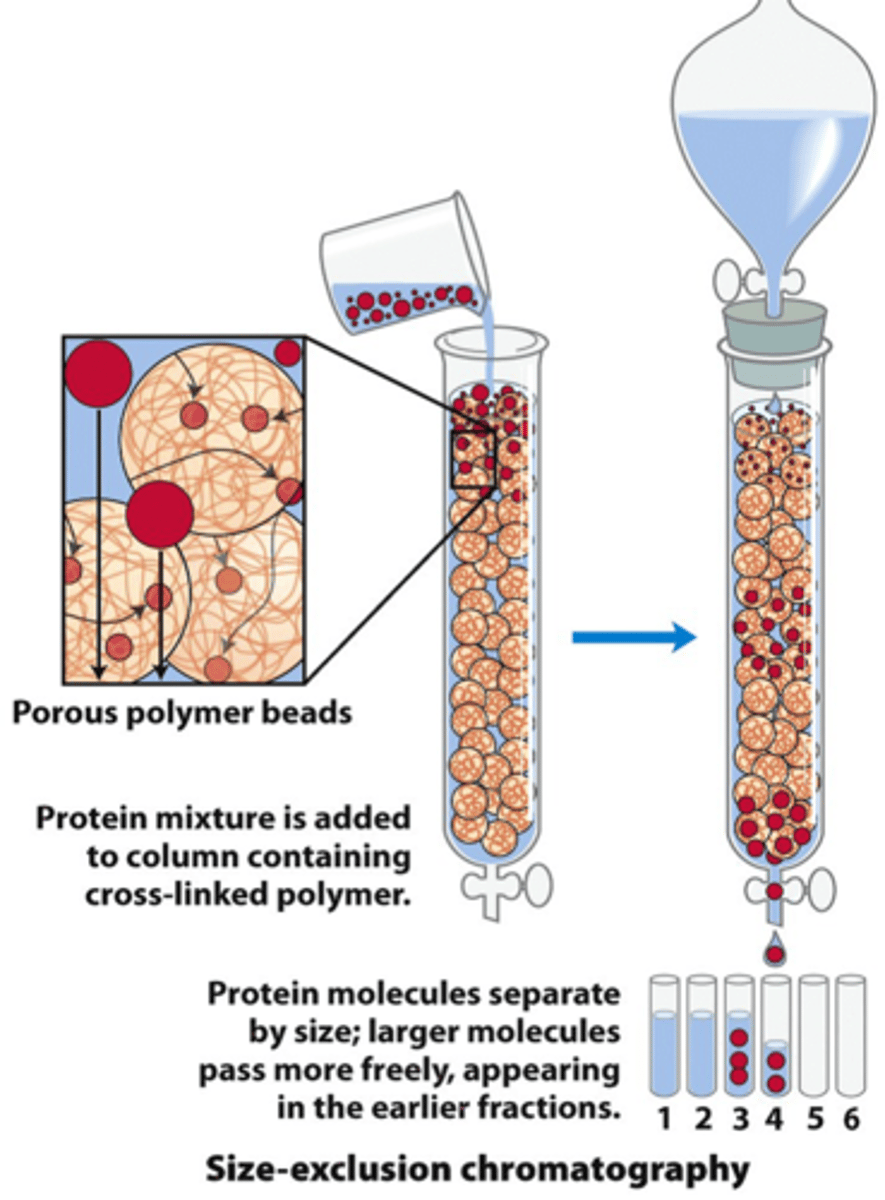
Size-exclusion chromatography
relies on porous beads. Larger molecules elute first because they are not trapped in the small pores
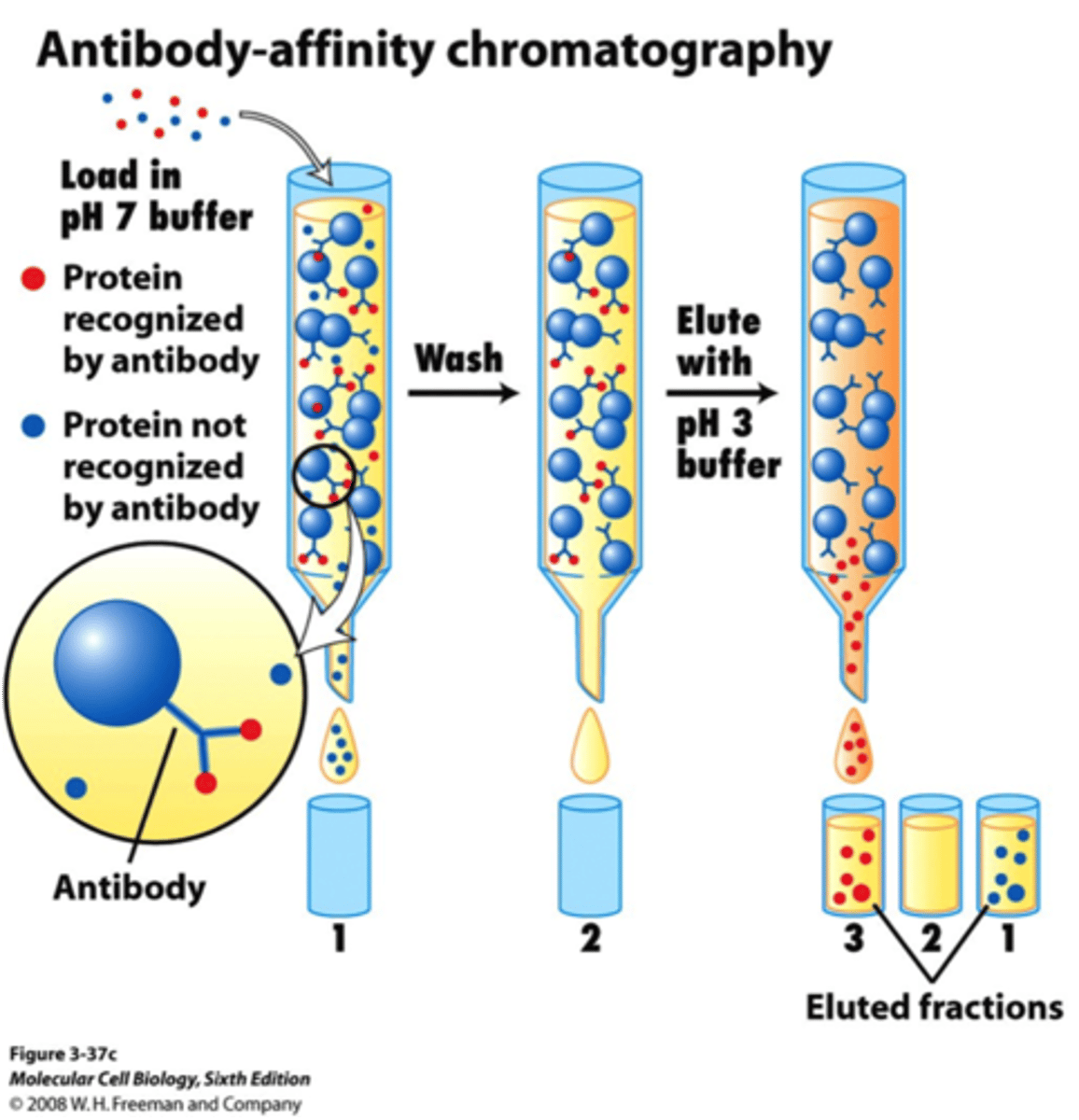
Affinity chromatography
Uses a bound receptor or ligand and an eluent with free ligand or receptor for the protein of interest
How is protein structure determined
X ray crystallography or NMR
Edman degradation
How amino acid sequencing is degraded
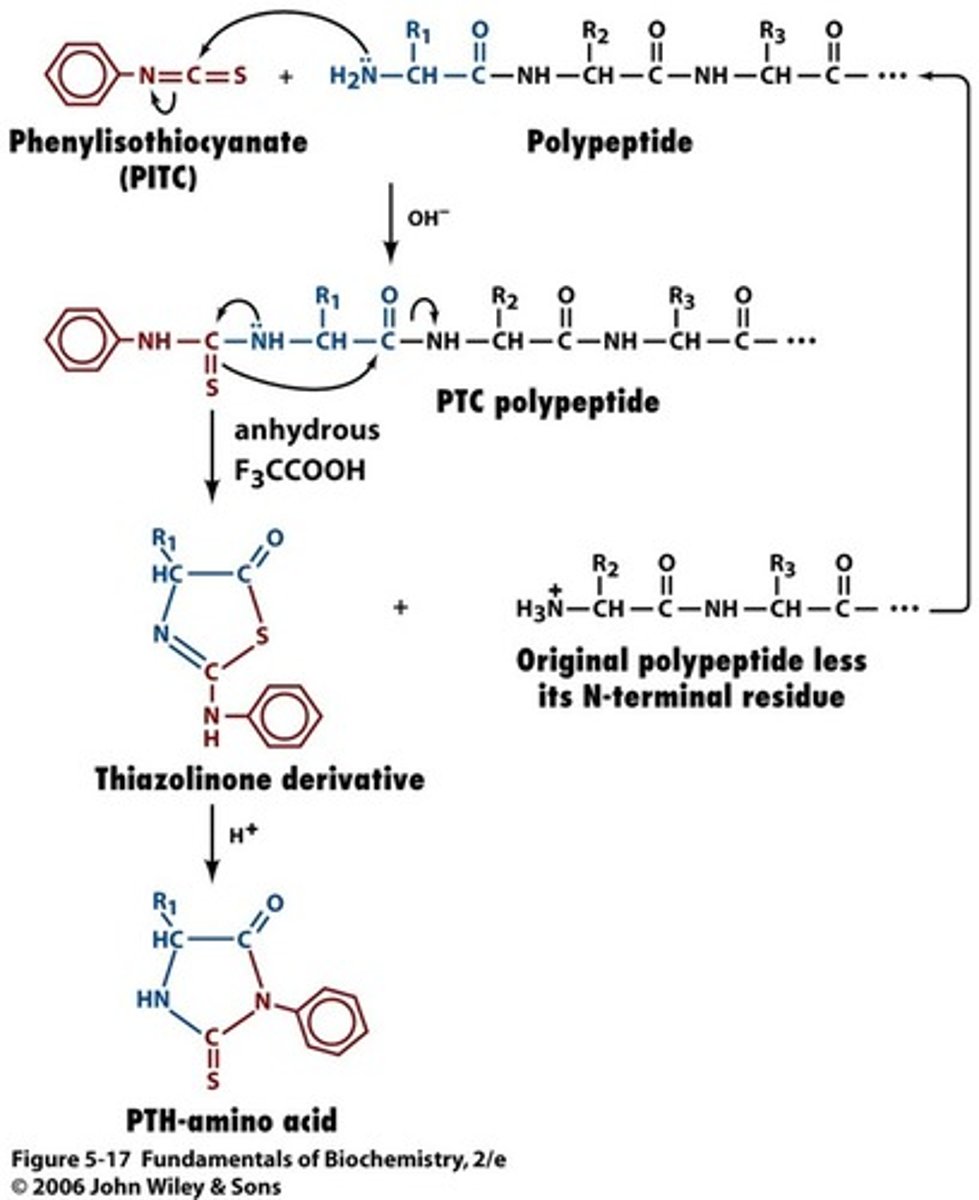
BCA assay, Lowry reagent assay, Bradford protein assay
Each test for protein. The Bradford protein assay, which uses a color change from brown-green to blue is most common
What is the function sodium dodecyl sulfate in SDS-PAGE
SDS solubilizes proteins to give them uniformly negative charges, so the separation is based purely on size
Which is not involved in cell migration
Dynein
flagella
actin
centrioles
centrioles
Which of the following is most likely to be found extracellular
Tubulin
Myosin
Collagen
Actin
Collagen
Hormones are found in low concentrations. What type of receptors are hormones most likely to act on
GPCRs and Enzyme linked receptors. For a ligand low in concentration we expect it to have a second messenger cascade.
Second messenger cascades
Amplify signals because enzymes can catalyze a reaction more than once while they are active and often activate other enzymes.
Which of the following is not attributed to antibodies
antibodies bind to more than one distinct antigen/ only binds 1
Ion channel responsible for maintaining resting membrane potential
Ungated
List the timeric g protein subunits
alpha beta gamma
Best for seperating large quantities of proteins
Size-exclusion chromatography
which amino acid contributes significantly to the pI of a
lysine and arginine
difference between gel in isoelectric focusing and traditional electropheresis
Isoelectric focusing uses a gel with a pH gradient that encourages a variable charge.
Which protein properties allow UV spec to be used as a determining concentration?
Proteins have aromatic groups in certain groups in certain amino acids
A protein collected through affinity chromatography displays no activity even though it is found to have a high concentration using the Bradford protein assay. What explains this
The active site is occupied by free ligand.
What property of protein-digesting enzyme allows for a sequence to be determined without fully degrading the protein
Selectivity