3. Fatigue failure
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Definition of fatigue failure
Failure of material under cyclical load (load that varies over time)
Stress level fatigue occur
can occur below yield stress
Dangers of fatigue stress
no warning →no deformation, necking
sudden, catastrophic fracture
4 Methods where crack appear
manufacturing defects
fatigue processes
corrosion
creep
Types of fatigue failure (in terms of cycle and presence of cracks)
Cycle:
Low cycle fatigue
low no. of cycle
occur above σy
High cycle fatigue
million cycles to fail
occur below σy
Crack:
1. Crack-free
Pre-existing cracks - non destructive testing method used to spot cracks)
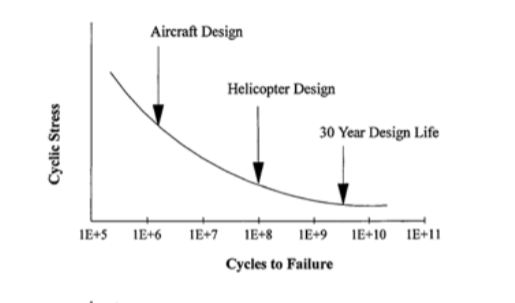
High cycle load cyclic stress-no. of cycle relationship (Stress-number (SN) curve)
for crack-free specimen
for any cyclic load, follow SN curve of σm (mean stress)

Benefit for SN curve
material comparison
early design estimate
high cycle fatigue regime
Limitations of SN curve
remaining life of cracked component
crack growth behaviour
high scatter in experiemental data
long test required
most of lifetime used to initate defect
IGNORES CRACK SIZE
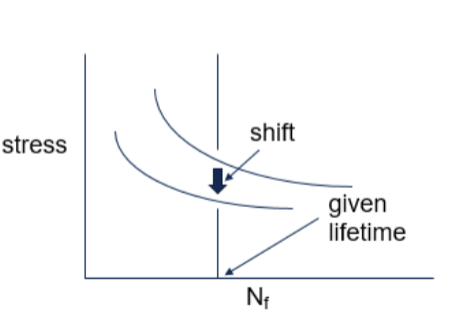
Method to solve limitation of SN curve
find one curve for certain stress value
shift curve up and down for different stress
estimate but useful
**
Calculation of fatigue life (by number of cycle)
Ni: crack initiation
Np: crack propagation
depends on crack size & stress intensity range
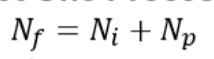
Definition of Paris Law
rate of fatigue crack growth
relate crack growth to range of stress intensity factor
occur AFTER crack propagation

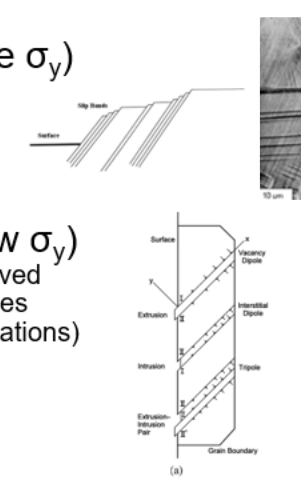
Methods to form defect(crack initiation) (Low vs high cycle)
Low:
plasticity causes slip steps on surface
act as stress concetrator to start fatigue
High:
no gross plasticity but homogeneties in atomic level raise local stress and initiate fatigue
Design method to reduce fatigue
reduce section stress (raise cross-section)
remove stress concentrators(add fillers, welding)
Environmental method to cope with fatigue
consider corrosion-fatigue relationship
Surface treatment to cope with fatigue
locally harden surface as crack usually initates there
case hardening, work hardening, shot peening (locally inducing elastic compressive stresses)
3 ways material is used to cope with fatigue
remove porosity ( at source or via hot working)
employ 2 phases (to deflect crack path)
employ composites(blunt crack as it propagates)
Maintenance method to cope with fatigue
employ non-destructive method(NDE) to detect cracking
repair, remove replace or review