TAE020: Sustainable Energy
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Energy Problem
High carbon emissions
Oil
Expanding global demand (1-2% increase per year)
Factors
Slow progress for fossil fuel alternatives
Changing limitations
Policy
Late response (yesterday was to act, act now)
Global Energy Use/Development
Consumption increased 2.5 times from 1970 to 2015 about 2% per year until 2013, and around 1.0 % from 2014-2016.
Most growth occurred up to 2000 in the developed countries and after 2000 in the developing countries.
Non-OECD (82% population) consumes energy at a rate of:
52 MBtu per capita
(compared to whopping 184 MBtu in OECD countries)
Energy per capita increased by __% in non-OECD countries, while it dropped by __% in the US and 8% in all other OECD countries
58, 15
Core indicators of human welfare/standards of living/education/income are reflected in the use of:
high-quality energy
Energy Use in the USA
The energy intensity of the economy improved by 27%, and per capita consumption dropped by 15%.
Electricity consumption increased significantly from 2000-2007
Petroleum consumption has decreased since 2006, and
reliance significantly (25-60%) on imports.
Agri-food sector currently consumes __ percent of the total energy demand globally,
30
Around _-_% of total final energy consumption is used directly in the agriculture sector, about _._% of total US primary energy consumption.
3-5, 1.9
Greenhouse Effect
Specific molecules transmit short-wavelength solar radiation but block irradiated long-wavelength
Equilibrium surface temperature increases
All energy establishing equilibrium is from the sun
Geothermal only accounts 0.1% of earth’s total heat
Equilibrium w/o atmosphere is __oC
-19
Solar power absorbed by the planet: Formula
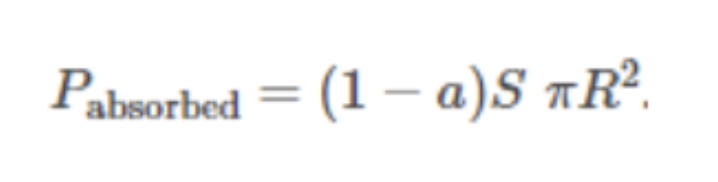
Solar power radiated from the planet: Formula
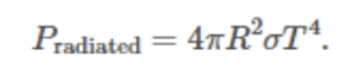
Global energy balance from the above two sources & sinks:
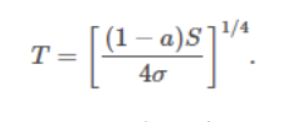
The earth's surface temperature will be higher (+__°C) than predicted by the simple model, which excludes the atmosphere (-__°C).
11, 19
The atmosphere traps heat, causing the greenhouse effect and increasing the earth's average temperature by more than __°C
30 (degrees)
Climate Change (Carbon Emissions)
Combustion of fossil fuels produces CO2
This CO2 adds to GHG → equilibrium raised
Evidence of Global Warming
Reduction in Arctic sea ice: The area has decreased by about 9 % in the past decade, and the thickness has decreased by 15 – 40 % over the past 30 years.
I.e. migration routes, geographic ranges
Increased sea levels
Predicted Temperature Changes for the Next Century
Global temperature increases of 2 to 8 C ° above the preindustrial level can be expected by 2100
Carbon Sequestration
Capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide. It is one method of reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere with the goal of reducing global climate change.
Climate Change Scientific Consensus/Initiatives
Reduce energy consumption to mitigate enviro. effects
Major industrialized countries: binding 6-8% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions relative to 1990
IPCC
Paris Agreement/Accord
Kyoto Protocol
UNFCCC
100% Solution: Hypothetical Roadmap
Transition energy infrastructures to clean, renewable (Wind, Water, and Solar) (WWS) using existing technologies for 80% of all electricity, transportation, heating/cooling, industry, and agriculture/forestry/fishing by 2030 and 100% by 2050.
Energy
The ability/capacity to work
Work (W)
The product of force (F) and the distance (d) over which it acts
Force
Newton’s Law
F = ma
Work done against a gravitational field to lift an object to a height (h) is:
W = mgh
Power
The rate at which the work is done
Energy
The product of power (P) times time over utilization (t)
Kinetic Energy
Associated with the movement of an object
Two Types of Kinetic Energy
Translational motion (E = 1/2(m)(v)2)
Rotational motion (E = 1/2(l)(w)2)
Potential Energy
Most commonly associated with the energy of an object in a gravitational field given by:
E = mgh
Thermal Energy
Kinetic energy associated with the microscopic movement of molecules
E = 3/2(nRT)
A quantity of energy supplied Q supplied to material of mass and specific heat will increase the temperature by delta T.
Delta T = Q/mC
Chemical Energy
Energy associated with chemical bonds between atoms
Exothermic and endothermic reactions
Energy released in combustion reactions →
Nuclear Energy
Energy associated with bonds between neutrons and protons in the nucleus
Much greater than chemical energy
Energy release during an exothermic nuclear reaction → changes in total mass of system
Electrical Energy
Energy associated with flow of electreons in a conductor
Current (I) in conductor will experience voltage drop
Ohm’s law
V = IR
Energy of the electric and magnetic fields associated with electromagnetic waves (such as light).
Waves have a wavelength (λ) related to the frequency (f) and the velocity (c, speed of light).
Laws of Thermodynamics
0: Two systems both in thermodynamic equilibrium with a third system are in equilibrium
1: Energy is conserved
2: A closed system will move towards equilibrium
3: It is impossible to attain absolute zero temperature
Zeroth Law Thermodynamics
Implies that the thermodynamic state of system can be defined by a single parameter, the temperature
PV = nRT
Ideal Gas Law: linear relationship between temp and pressure
First Law Thermodynamics
When energy is applied through heat:
Internal energy of the gas increases if piston of tube is fixed
Energy is used to lift piston if piston moves
Second Law Thermodynamics
Heat naturally flows from hot to cold
Analogous to gravitational potential energy: object in a gravitational field only works if it moves from point of high potential to low
Total Energy in a system is calculated simply as:
= useful energy delivered + wasted energy
Energy efficiency (Ƞ) =
Useful energy delivered/energy input
Overall efficiency of a system =
product of all individual efficiencies
Efficiency
reducing the amount of energy input needed to meet our energy output needs
Conservation
reducing energy output needs or waste, e.g., through behavior/lifestyle changes
Types of Efficiency
Conversion efficiency
Functional/system efficiency
Heating your home
Specific Heat
Energy to raise a unit of mass by one degree
Heat Capacity
Ability of a substance to store heat