Unit 1 Terms/Concepts
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
cartography
the study and practice of making and using maps
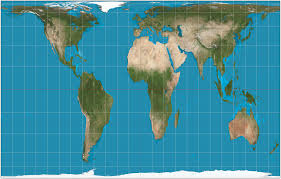
mercator projection
a map projection that fairly accurately shows shape and direction, but distorts distance and size of land masses
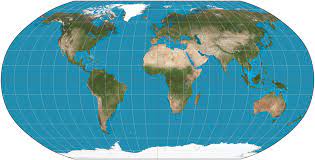
robinson projection
shows the entire earth and distorts both shape and size slightly to make the two-dimensional representation look the most like the three-dimensional reality of the earth
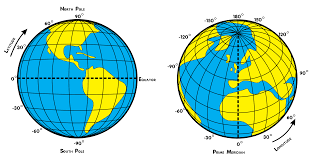
geographic grid
the internationally-recognized system of latitude and longitude used to locate positions on Earth's surface
latitude
an angular measurement north or south of the equator
parallel
imaginary line extending around the Earth parallel to the equator (describes latitude)
equator
an imaginary line around the middle of Earth
longitude
vertical lines that measure east or west of the meridian in Greenwich, England
meridian
an arc drawn on a map between the North and South poles (describes longitude)
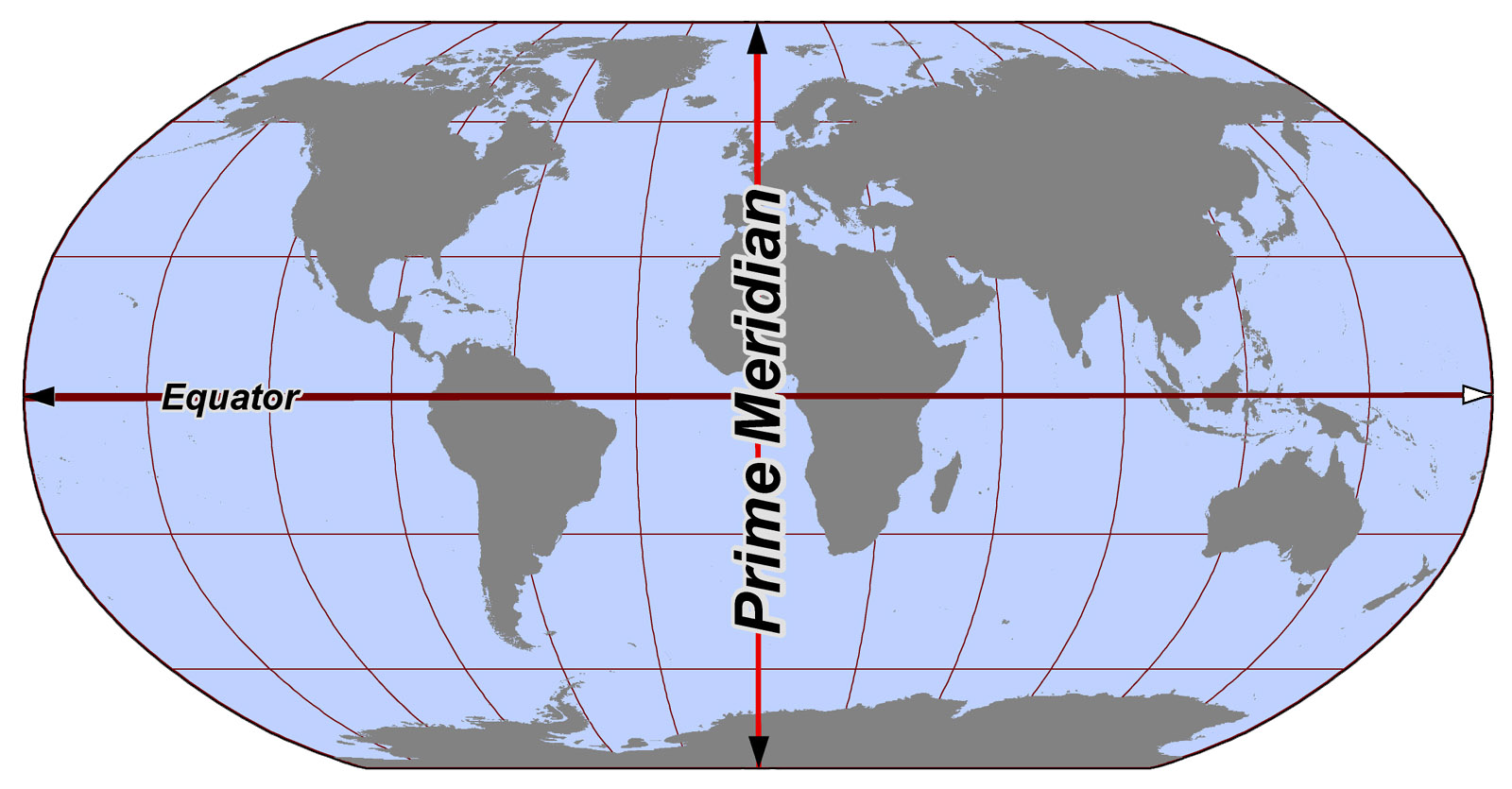
prime meridian
the line of 0° longitude, the starting point for measuring distance both east and west around Earth (opposite the int. date line)
international date line
a boundary from which each calendar day starts (opposite the prime meridian)
greenwich mean time
the name for mean solar time of the longitude (0°) of the Royal Greenwich Observatory in England
absolute location (coordinates)
its exact place on Earth, often given in terms of latitude and longitude
global positioning system
used to determine an individual's exact location on Earth through satellite navigation
geographic information systems
a computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth's surface
lithosphere
the solid, outer part of Earth
plate tectonics
the movement of geologic plates causes mountain building, volcanoes, and earthquakes
land formations
mountains/hills, valleys/canyons, plateaus, plains/flatlands, islands/peninsulas
hydrosphere
the water which covers 70% of the Earth’s surface
water cycle
describes where water is on Earth and how it moves
saltwater
97% of hydrosphere, made up of oceans, bays, seas, and harbors
freshwater
3% of hydrosphere, made up of rivers, streams, lakes, and ponds
atmosphere
the layer(s) of gases surrounding the Earth
climate
average weather conditions in a given region (tropical, dry, warm mid-latitude, cold mid-latitude, polar)
climate zones
results from the climate conditions of an area: temperature, humidity, amount and type of precipitation, and seasonality (tropical, dry, warm mid-latitude, cold mid-latitude, polar)
biosphere
the sum of all living organisms on Earth
microorganisms
first and most basic forms of life
vegetation
>300,000 species of plants on Earth (forests, jungles, grasslands, tundras)
ecosystem
a network of interconnected lifeforms
environmental determinism
the doctrine that human growth, development and activities are controlled by the physical environment
possibilism
the theory that the physical environment may set limits on human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to the physical environment and choose a course of action from many alternatives
toponym
the accepted name given to a place
site
the set of physical traits which define a place
situation
the position of a place relative to other places
formal region
an area clearly defined by distinct, measurable and predominant characteristics
functional region
an area defined in some way by its connection or proximity to a specific node (focal point)
node
an area organized around a focal point
vernacular region
an area believed to exist as part of a specific cultural identity
space
the physical gap or interval between two objects
distribution
the way something is spread out or arranged over a geographic area
density
the number of things—which could be people, animals, plants, or objects—in a certain area
concentration
measures how evenly or unevenly distributed the people, animals, or objects are
clustered concentration
when objects in an area are close together
dispersed concentration
when objects in an area are relatively far apart
landscape analysis
a process of studying and describing a landscape, generally with the goal of assessing the impact of humans on that space
pattern
the arrangement of objects on earth's surface in relationship to one another
distance decay
the weakening of connection due to increased physical space between people/places
space-time compression
a reduction in the time it takes to establish connections between people/places
sustainability
the use of Earth's resources in ways that ensure their availability in the future