i love lucas
5.0(2)Studied by 7 people
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Last updated 5:13 PM on 12/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
Atoms
an atoms is the basic particle from which elements are made
2
New cards
structure of an atom
positively charged nucleus (center) , negatively charged out cloud, orbitals w/ electrons.
3
New cards
Atomic Mass
the amount of protons + neutrons.
4
New cards
atomic number
the number of protons in a nucleus
5
New cards
valence electrons
the electrons w/ the highest energy ( the ones on the outside orbital)
6
New cards
chemical bonds
the force of attraction that holds atoms together as a result of the reagargenment of electrons between them.
7
New cards
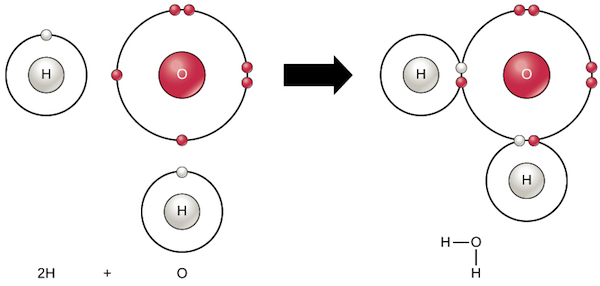
ions
is an atom or a group of atoms that have an electric charge (ex: Br-1)
8
New cards
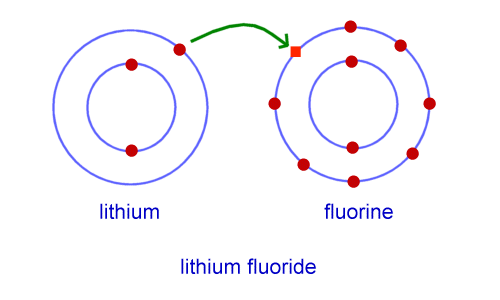
ionic bond
is the attraction between two oppositely charged ions
9
New cards
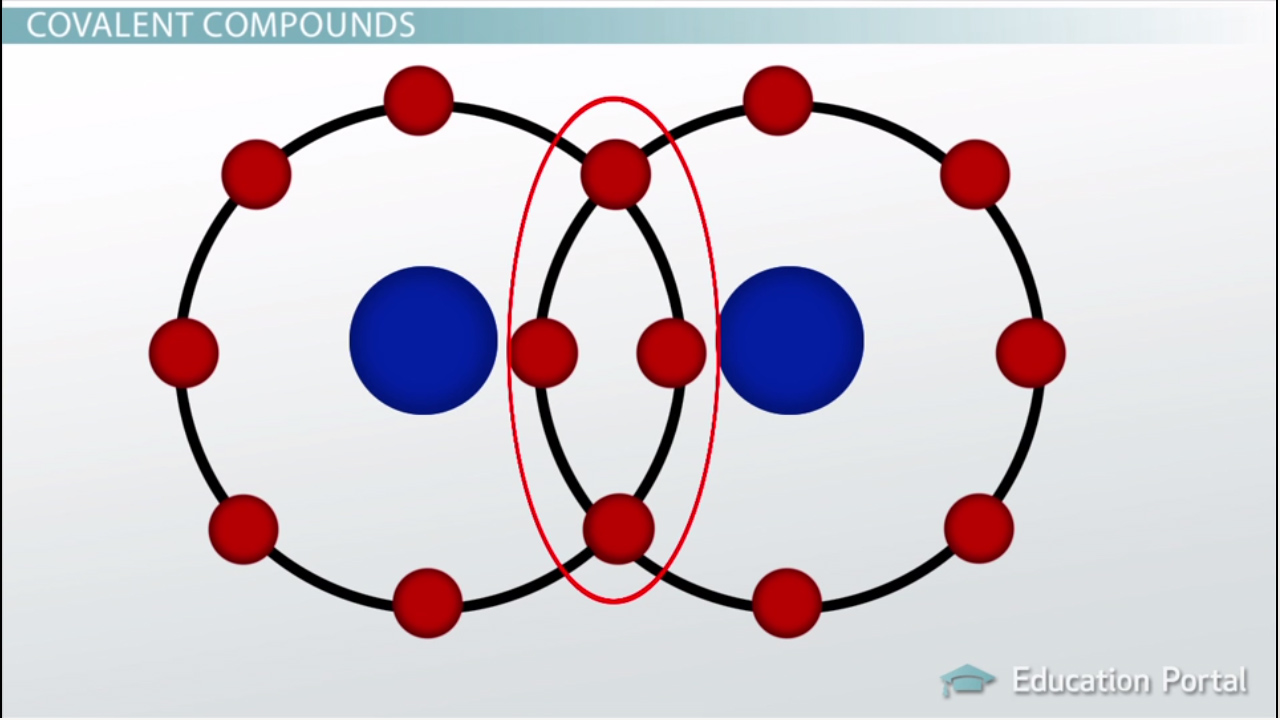
covalent bond
a bond formed when 2 atoms share electrons
10
New cards
polar bond
a covalent bond when the electrons are not being equally shared
11
New cards
nonpolar bond
a covalent bond when the electrons are being shared equally
12
New cards
metallic bond
an attraction between a positive metal ion and surrounding electrons
13
New cards
element
a substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances by chemical or physical means.
14
New cards
molecule
a group of 2 or more atoms held together by chemical bond (s)
15
New cards
chemical formula
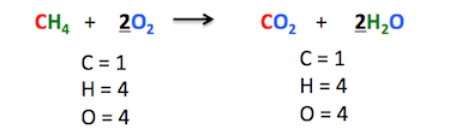
16
New cards
Heterogeneous mixtures
you can usually see the different parts and can easily be separated (ex: salad)
17
New cards
homogeneous mixtures
evenly mixed, you can't see the different parts and it is hard to seperate (ex:soy sauce)
18
New cards
physical change
alters the form or appearance of the matter but doesnt turn the substance in the matter into a different substance.
19
New cards
chemical change
a change in matter that produces one or more new substances.
20
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
,atter cannot be created or destroyed in any chemical or physical change.
21
New cards
isotopes
atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons [(no charge) ex : uranium-235 and uranium-238 atom ]
22
New cards
reactants
substances that undergo a chemical change
23
New cards
products
the new substances formed from the reactant
24
New cards
exothermic change
energy is released
25
New cards
endothermic change
energy is absorbed
26
New cards
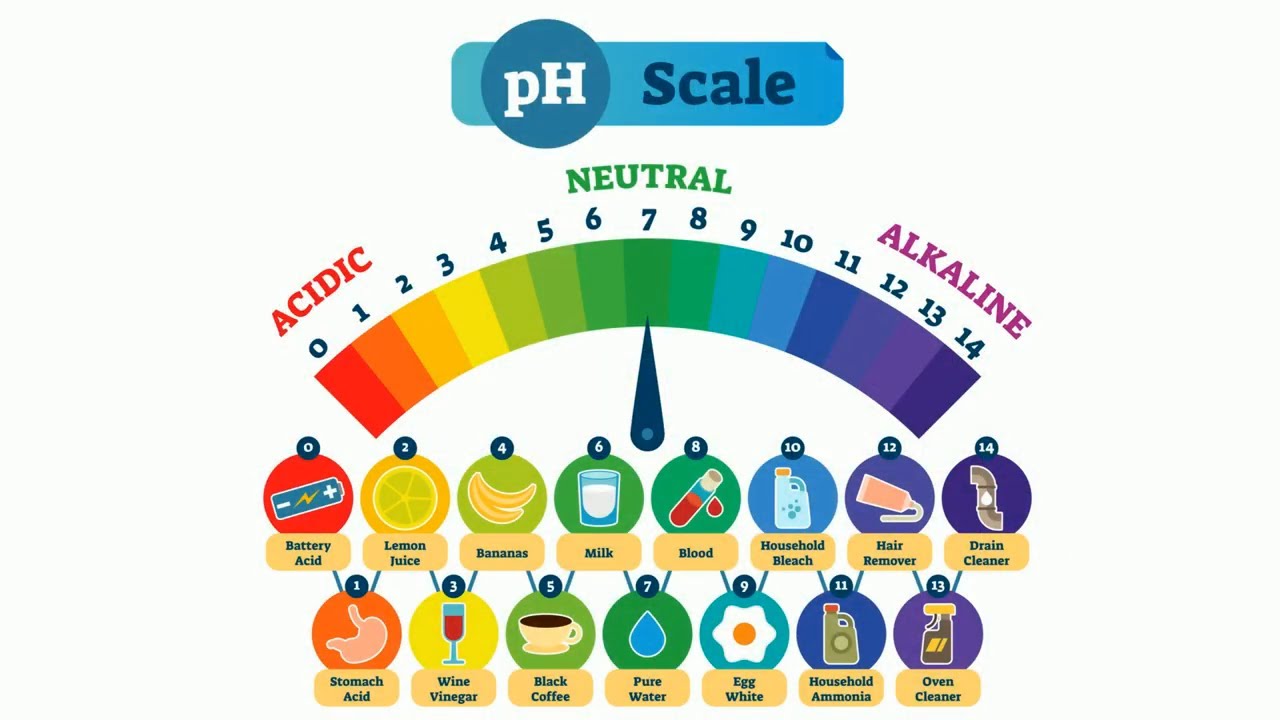
pH scale
range of 0-14 indcates concentration of H+ ions in a solution
bases produce 0H- in water (more than seven)
acids produce H+ ions in water (less than seven)
even amounts of OH- and H+ = water = neutral
bases produce 0H- in water (more than seven)
acids produce H+ ions in water (less than seven)
even amounts of OH- and H+ = water = neutral