MCAT Amino Acids
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
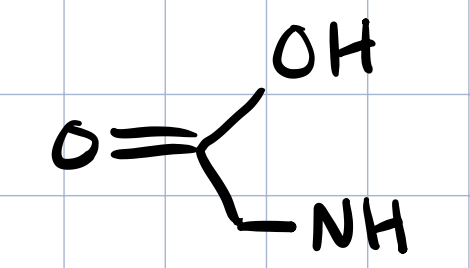
glycine
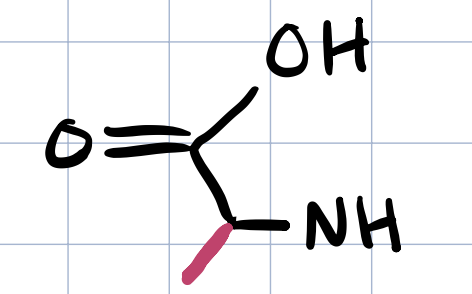
alanine
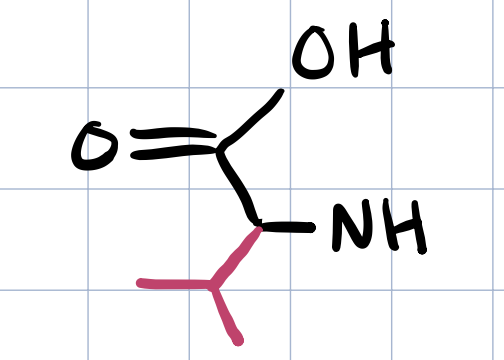
valine

leucine
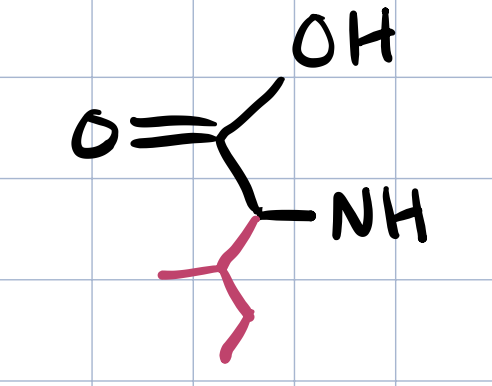
isoleucine
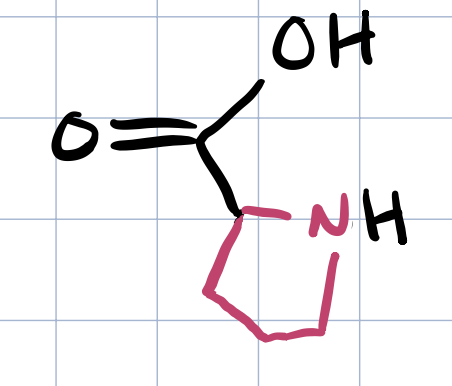
proline
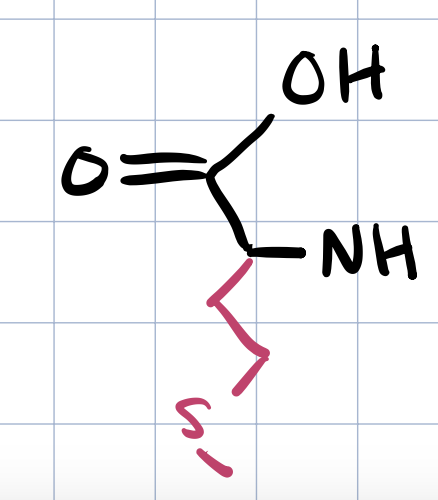
methionine
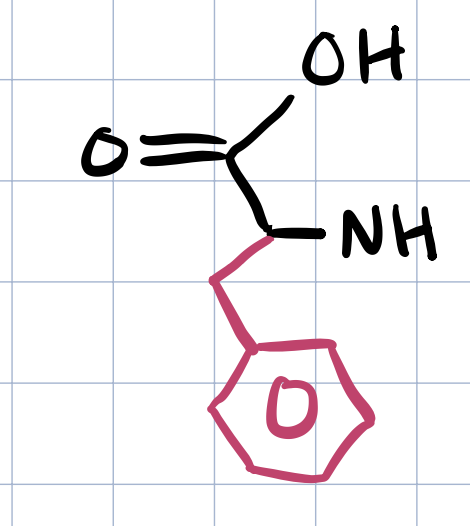
phenylalanine
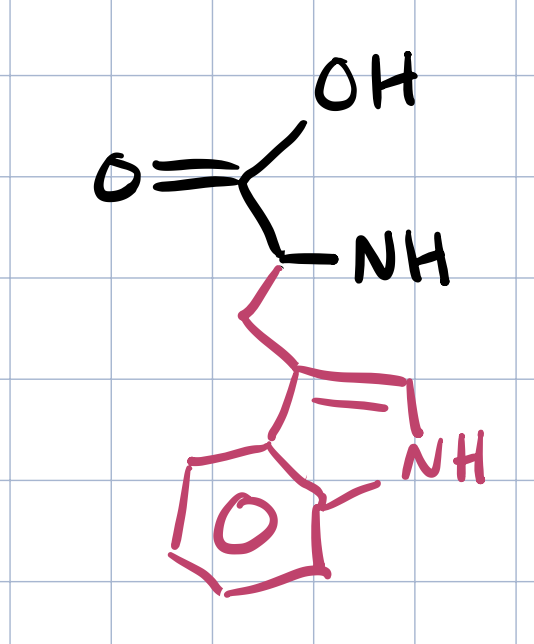
tryptophan
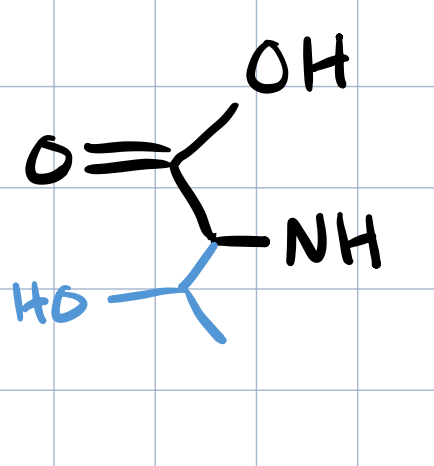
serine
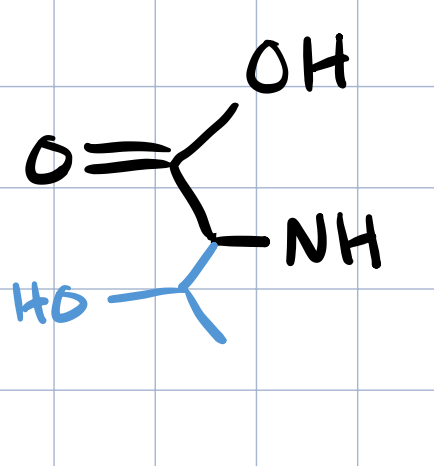
threonine
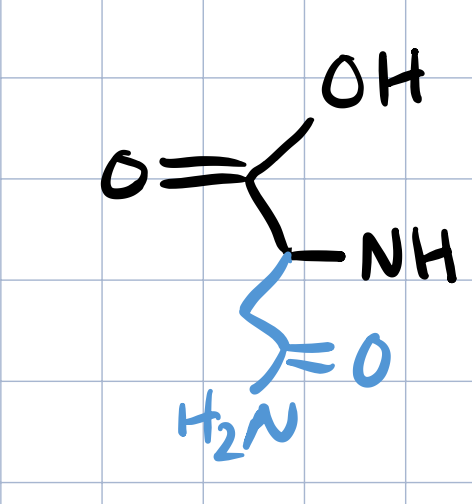
asparagine
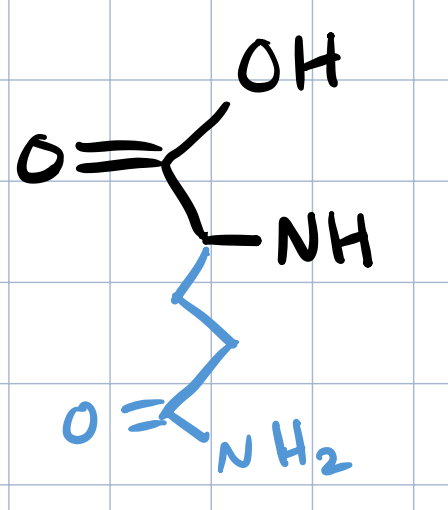
glutamine
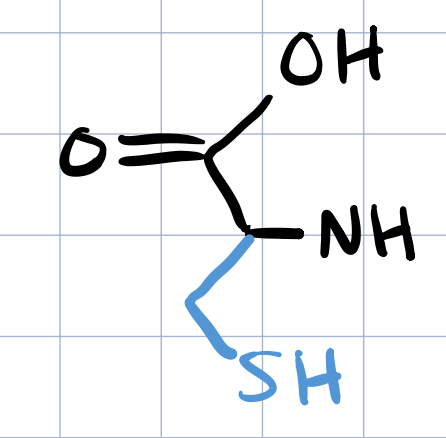
cysteine
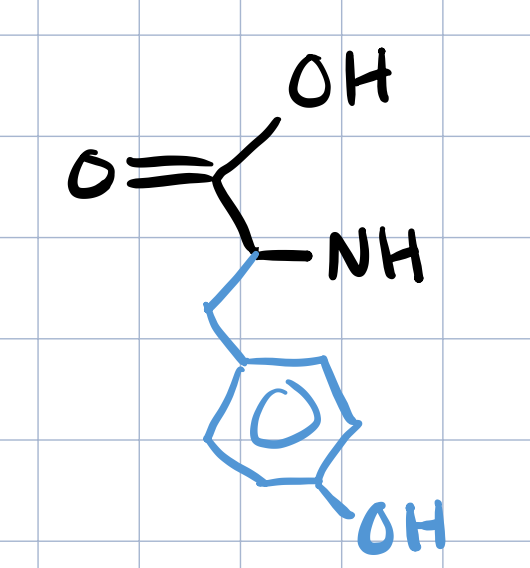
tyrosine
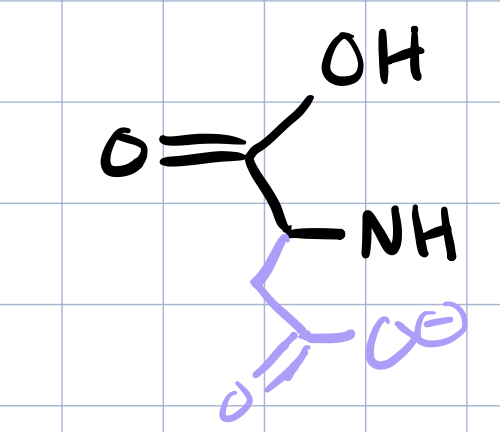
aspartic acid
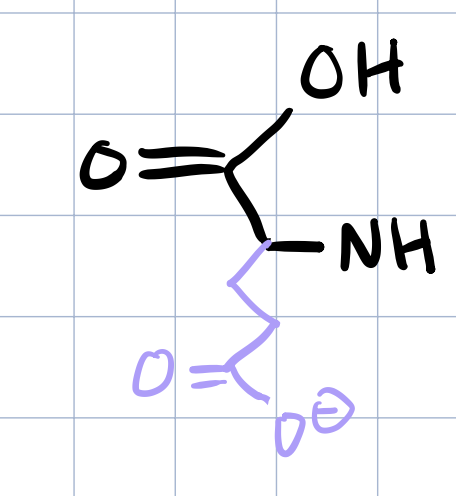
glutamic acid
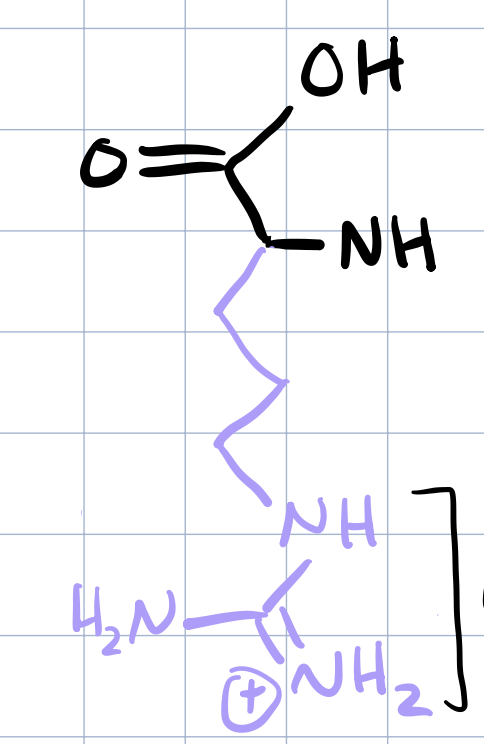
arginine
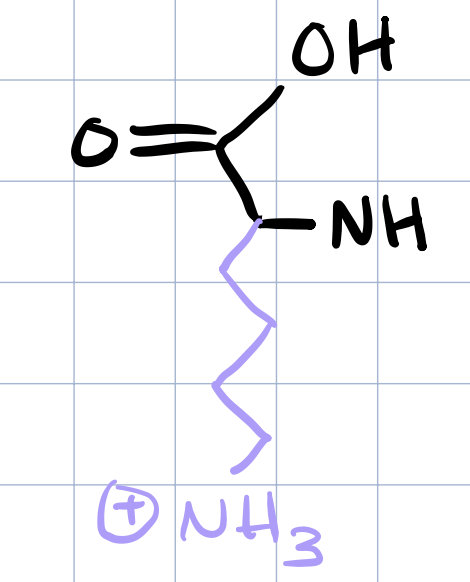
lysine
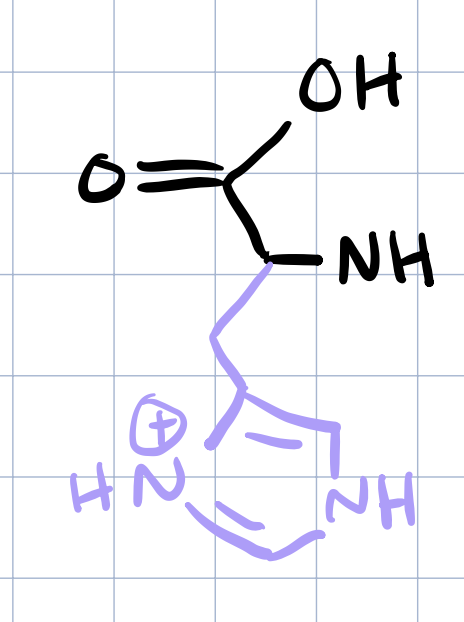
histidine
what are the nonpolar amino acids with aliphatic (hydrocarbon) side chains
glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine
what are the nonpolar AAs with unique side chains
proline, methionine
what are the nonpolar AAs with aromatic side chains
phenylalanine, tryptophan
what are the polar uncharged AAs
serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, cysteine, tyrosine
what are the polar NEGATIVE/ACIDIC AAs
aspartic acid, glutamic acid
what are the polar POSITIVE/BASIC AAs
arginine, lysine, histidine
what is the only achiral AA
glycine
what mutation in hemoglobin causes sickle cell
glu to val
what is the difference between leucine and isoleucine
leucine has an isbutyl group, isoleucine has a sec-butyl group with 3iary carbon closer to alpha carbon
what makes proline special
only AA with a cyclic component linking back to amine N, causes kinks in 2ary structure and is common in turns of beta sheets
is the sulfur in methionine able to donate H bonds
no
what is the precursor for serotonin and melatonin
tryptophan
does tryptophan form many H bonds?
no b/c of the ring structures
what amino acids are target by phosphrylation
serine, threonine, tyrosine, histidine (IN PROKARYOTES)
can cysteine form H bonds
yes - it’s just not very polar
what kind of bonds can cysteine form with itself
covalent disulfide bonds-2 cysteines make a cystine, 3ary structure
which amino acid is an excitatory NT in CNS
glutamic acid
what is the most basic AA
arginine b/c charge becomes resonance stabilized when an H is picked up
what AA is involved in methylation and acetylation
lysine
which form of histidine is dominant in physiological conditions
DEprotonated form, is a buffer that can act as a weak acid or base
three and one letter code for glycine
GLY, G
three and one letter code for ALANINE
ALA, A
three and one letter code for VALINE
VAL, V
three and one letter code for LEUCINE
LEU, L
three and one letter code for ISOLEUCINE
ILE, I
three and one letter code for PROLINE
PRO, P
three and one letter code for METHIONINE
MET, M
three and one letter code for PHENYLALANINE
PHE, F
three and one letter code for TRYPTOPHAN
TRP, W
three and one letter code for SERINE
SER, S
three and one letter code for THREONINE
THR, T
three and one letter code for ASPARAGINE
ASN, N
three and one letter code for GLUTAMINE
GLN, Q
three and one letter code for CYSTEINE
CYS, C
three and one letter code for TYROSINE
TYR, Y
three and one letter code for ASPARTIC ACID
ASP, D
three and one letter code for GLUTAMIC ACID
GLU, E
three and one letter code for ARGININE
ARG, R
three and one letter code for LYSINE
LYS, K
three and one letter code for HISTIDINE
HIS, H