Systems Path Section 6 - Lung injuries
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
collapsed lung
atelectasis
lung collapse due to airway obstruction and resorption of air in alveoli
resorption atelectasis
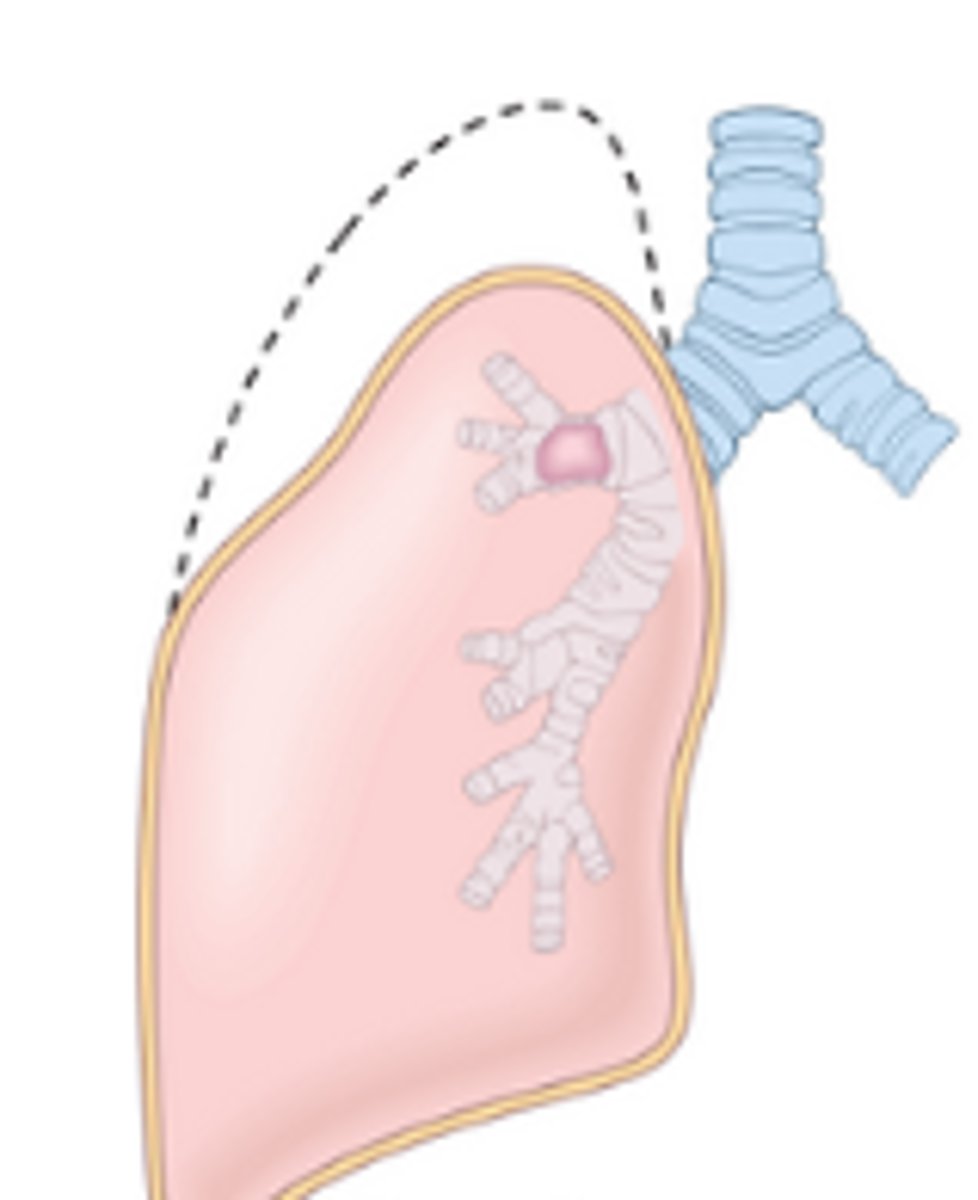
Features of resorption atelectasis
dyspnea and cyanosis
risks associated with resorption atelectasis
CF, chronic bronchitis, tumor, foreign body
form of lung collapse where pleural space fills with fluid/air and compresses lungs causing collapse
compression (passive) atelectasis
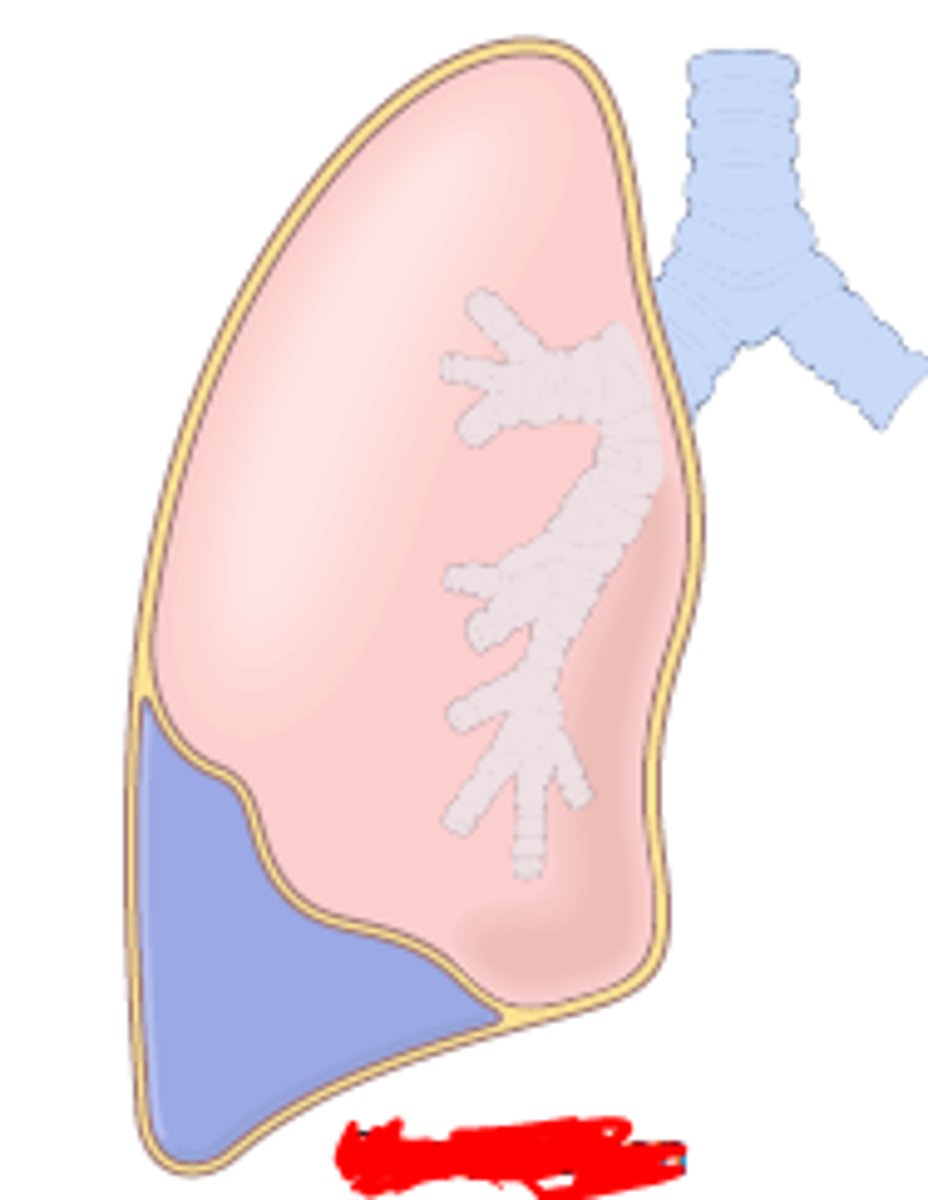
features of compression atelectasis
dyspnea and cyanosis
risks for developing compression atelectasis?
heart failure and trauma
form of lung collapse due to decreased lung expansion; chronic inflammation leads to fibrosis
contraction atelectasis
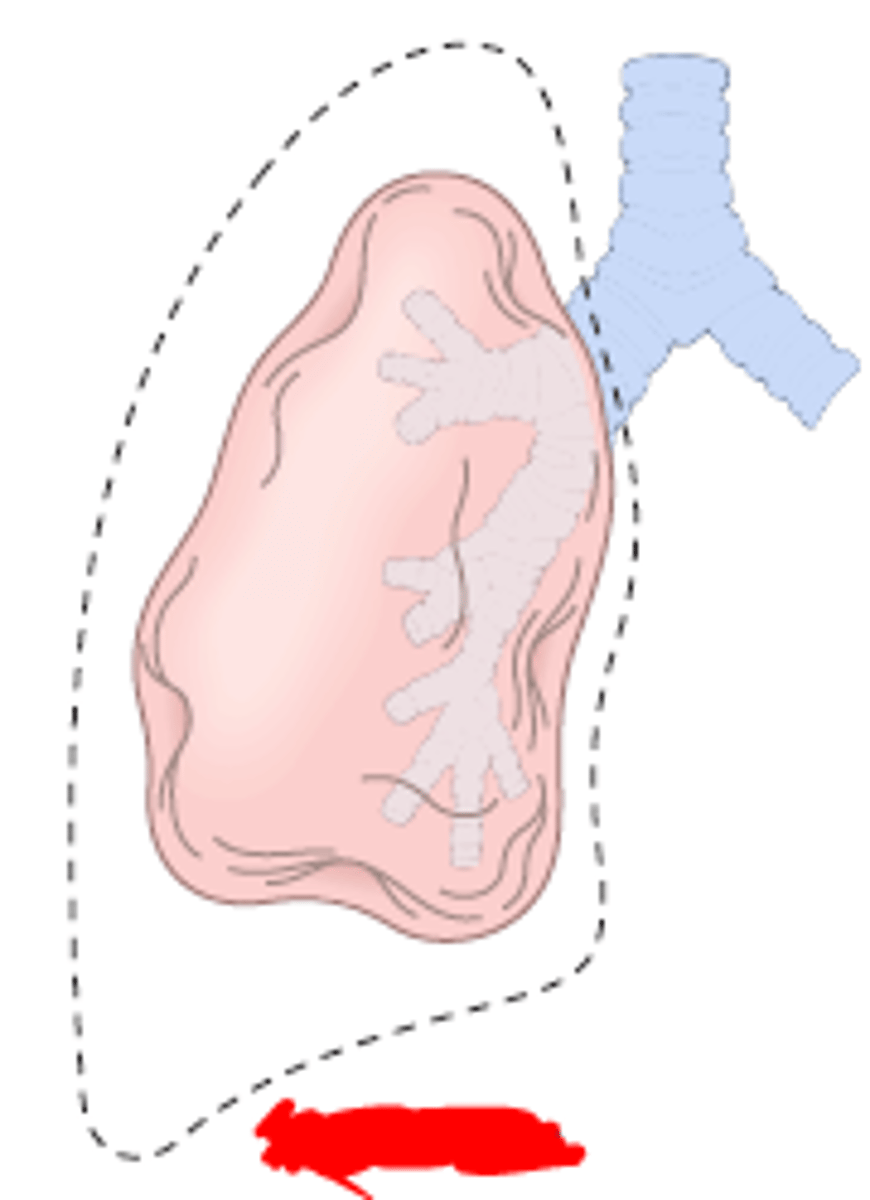
risk associated with developing contraction atelectasis
history of pulmonary fibrosis
features of contraction atelectasis
dyspnea and cyanosis ; poor prognosis
severe lung injury that leads to alveolar damage and massive inflammation characterized by severe dyspnea, cyanosis, and hyaline membranes
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
why may someone develop ARDS?
history of pneumonia or trauma
signs/symptoms of ARDS
diffuse alveolar damage, bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, acute dyspnea, hypoxemia, organ failure
acute/subacute respiratory illness defined by e-cig / vaping use, pulmonary infiltrates, or absence of other lung disease
vaping associated lung injury (VALI)
viral causes of common cold
rhinovirus, coronavirus, RSV, influenza
bacterial causes of common cold
group A b-hemolytic strep or H. influenzae
locations of acute respiratory infections
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, epiglottis
widespread viral infection called the "kissing disease" characterized by pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, exudative pharyngitis, and splenomegaly
EBV (mono)
Cause of acute laryngitis
inhalation of irritating agent
acute laryngitis symptoms
pharyngitis, hoarseness, cough, dysphagia
alternative forms of laryngitis
tuberculosis, diphtheritic
hallmark of diphtheria
"dirty gray" pseudomembranes
Diphtheria causative agent
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
self-limited viral URTI caused by parainfluenza (MC) or RSV
laryngotracheobronchitis (Croup)
hallmarks of croup
prominent stridor, "seal-like" bark
croup increases risk for
secondary bacterial infection (staph MC, strep, H. influenzae)
small, round nodules on vocal cords
vocal cord polyp
raspberry-like growth on vocal cords
laryngeal papilloma
who are carcinomas of larynx MC in?
>40 years, males
what are carcinomas of larynx caused by?
smoking, alcohol, irradiation, asbestos
malignancy of larynx, early sign = hoarseness
laryngeal carcinoma
MC laryngeal carcinoma (60-70% of cases)
glottic
20-40% of laryngeal cancers
supraglottic
very rare laryngeal carcinoma
subglottic