lesson 3 skeleton of trunk
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
how many cervical vertebrae do we have
7
how many thoracic vertebrae
12
how many lumbar vertebrae
5
how many sacral vertebra
5
how many coccygeal vertebrae
3-4
how is the vertebra column liked
by discs and ligaments (provides stability and allows movement)
how does the size increase and why
increases caudally
(gets bigger as you go down he spine)
they have to support more weight
the vertebrae move a little what does this mean
add up to give the spine its full range of motion
role of first 2 cervical vertebra
c1 atlas and c2 axis
support
move
and position the head
what does the vertebral column protect
nervous system
contains spinal cord
what are the 2 types of curvatures
primary
secondary
primary curvature direction
concave ventrally
primary curvature regions
thoracic and sacral
when is the primary curvature developed
from embryo
(we are born with these)
purpose of the primary curvature
original foetal position
secondary curvature direction
concave dorsally
region of secondary curvature
cervical and lumbar
when is the secondary curvature developed
after birth
purpose of secondary curvature
weight-baring and posture
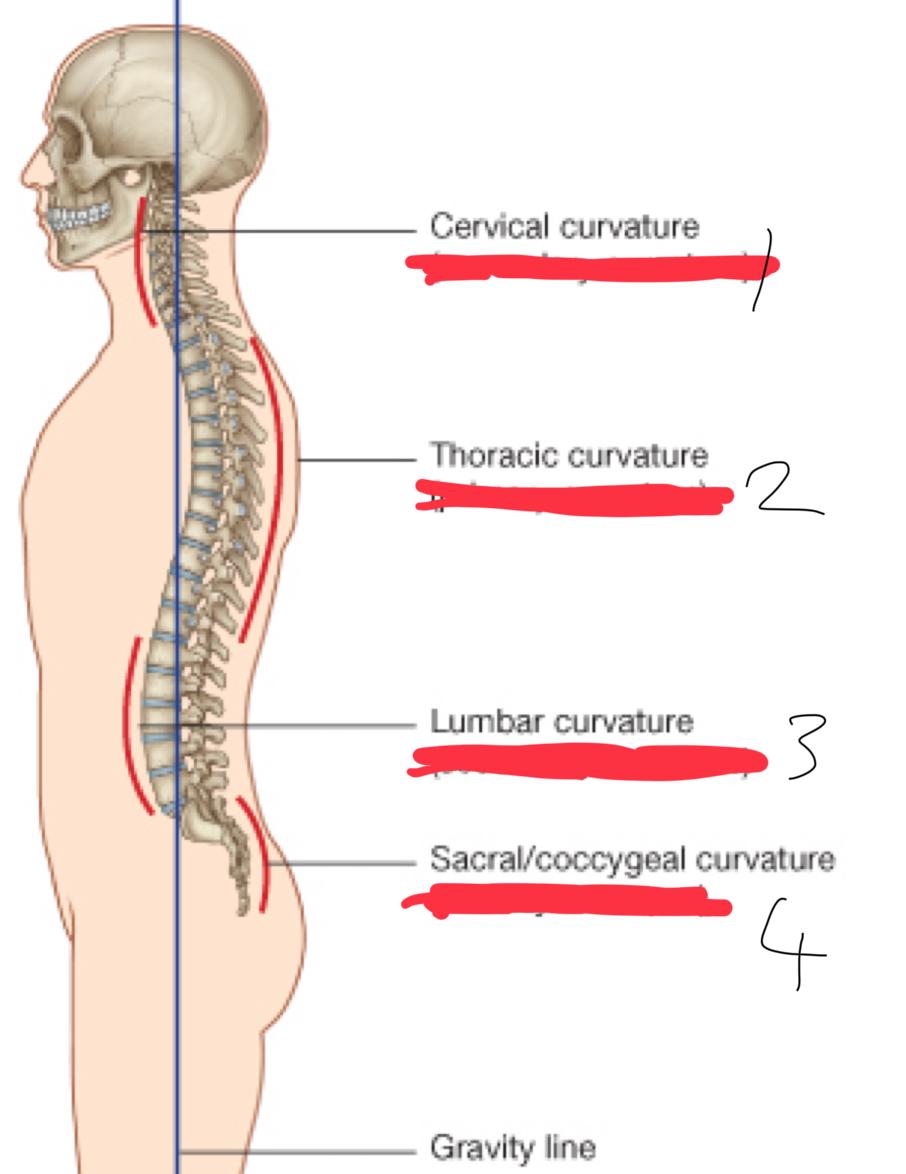
1,2,3,4?
secondary
primary
secondary
primary
vertebral column flashcards
done
what numbers are the cervical vertebra
1-7
what shape are the cervical vertebra body from above
square
what is the shape of the vertebral canal of cervical vertebra
triangle
c1 atlas is known as the ….. bone
YES
(movement to nod yes)
what is a major feature or lack of feature that atlas has
NO vertebral body
what does having no vertebral body mean
no vertebral discs between atlas and axis
c1 articulates with the head allowing yes no movement -why?
the Atlanto-occipital joints
PRIMARY FUNCTION OF C1
the Atlanto-occipital joints are why you van nod your head “yes”
this is a primary joint of flexion and extension
c2 axis is called the …. bone
NO
(shake head)
the c2 axis acts as a what for c1 atlas
as the pivot around which the atlas and head rotate
the most important feature is the Axis C2
the Dens (odontoid process)
how is the dens held in place (held in the facet for dens)
transverse ligament of the atlas
(posterior to it )
what does the dens act as
a pivot
how does the dens allow the atlas and head attached to rotate and why
side to side (no movement) because of the Atlanto-axial joints
C1(atlas) + skull =
YES Atlanto-occipital joint
C1(atlas) + C2 (axis) =
NO Atlanto-Axial Joints
what are the 3 primary movements made by the cervical vertebra
flexion-extension (yes moment)
axial rotation (no movement)
lateral bending (side bending)
flexion and extension what is it
flexion - bending head forward
extension- bending head backwards
flexion and extension is caused by
c1-skull , atlanto-occipital joint
axial rotation what is this
turning head left or right
how does axial rotation happen
Atlanto-axial joint (c1-c2)
lateral flexion what is it
tilting your ear towards your shoulder
how does lateral flexion happen
the movement from typical vertebra c2-c7
how many thoracic vertebrae T?-T?
T1-T12
how are all the thoracic vertebrae characterised
articulation with ribs
what do all thoracic vertebra have
superior and inferior costal facets
transverse facet on transverse process
what shape is the thoracic vertebral body
heart shaped
what shape is the thoracic vertebral canal
circular
how many lumbar L?-L?
L1-L5
what is the lumbar body shape
large and cylindrical
what do lumbar vertebrae NOT have
transverse facets
what shape is the lumbar foramen
triangular and larger than the thoracic vertebrae
how many fused sacral vertebra —
s1-s5
what is the shape of fused sacral vertebrae
triangular and curved
how doescfused sacral vertebra articulate with L5
cranially / superiorly
how does fused sacral vertebra articulate with coccyx
caudally / inferiorly
how does fused sacral vertebra articulate with the pelvis bone
laterally
how many anterior and posterior foramina in fused sacral vertebra
4-5
why are there 4-5 foramina in the fused sacral vertebra
the passage of s1-s4 spinal nerves
how many coccygeal vertebra —
3-4
2 features of coccygeal vertebrae
small
no vertebral arches so no vertebral canal
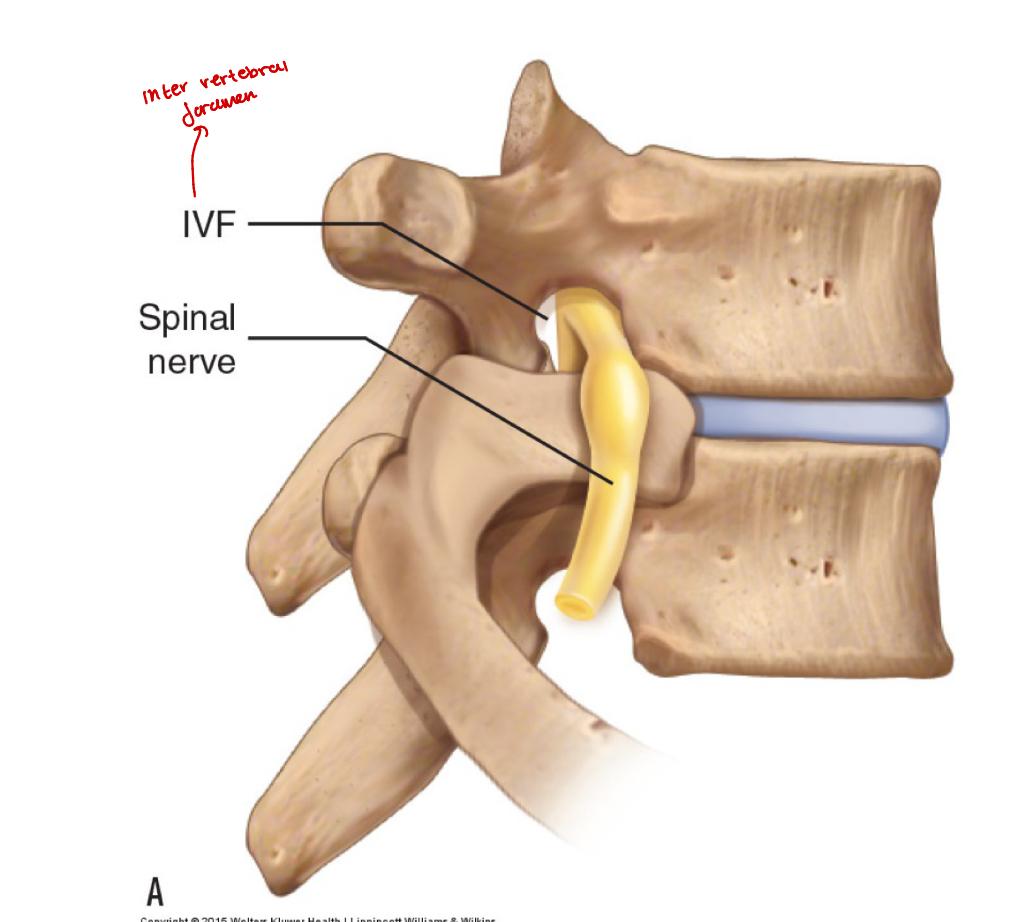
what is the intervertebral foramen
area where the spinal nerve and blood vessels pass in and out the vertebral canal
where is the intervertebral foramen found
formed between adjacent vertebral arches
what are the joints between vertebrae
Zygapophysial joints
Symphysis
uncovertebral joints (cervical vertebrae)
what are Zygapophysial joints
synovial joints
between superior and inferior articular processes on adjacent vertebrae
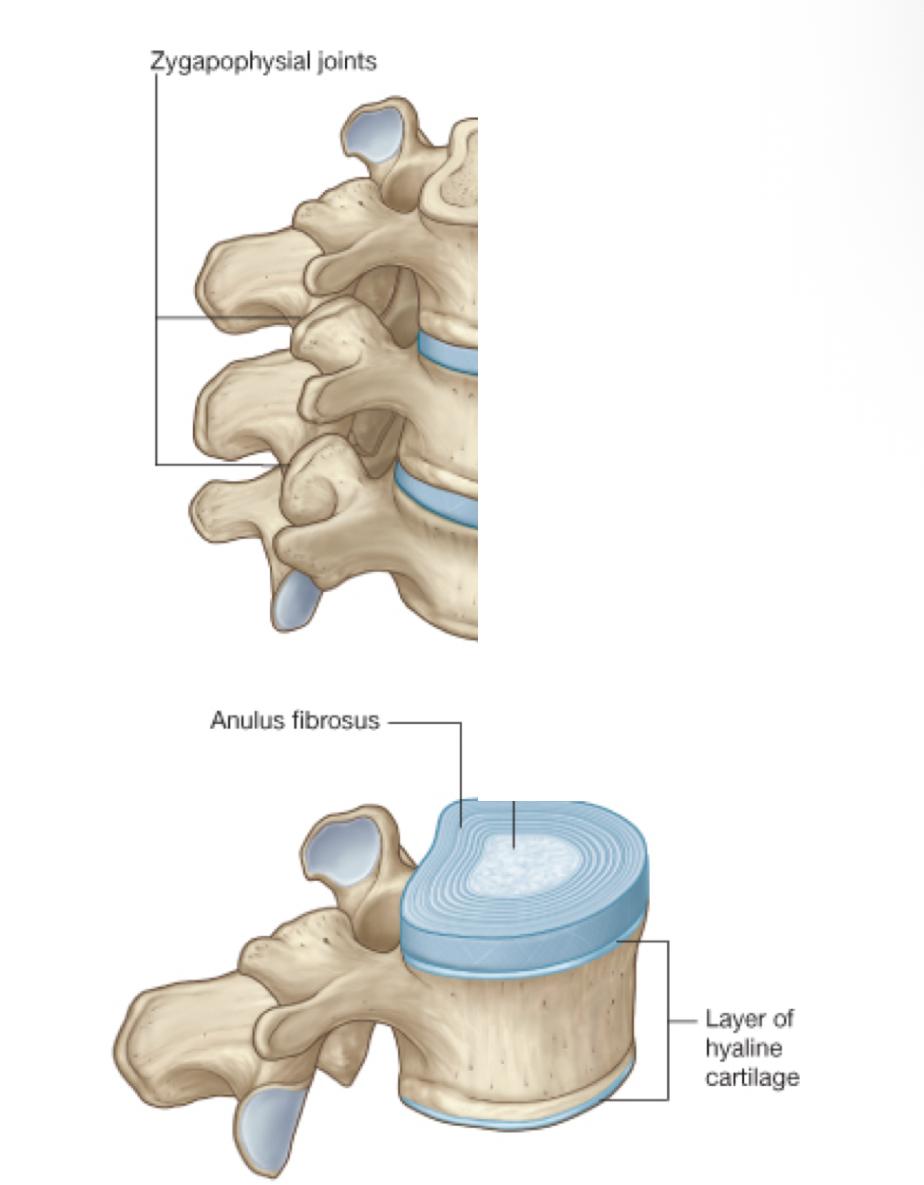
where is the symphysis located
between adjacent vertebral bodies
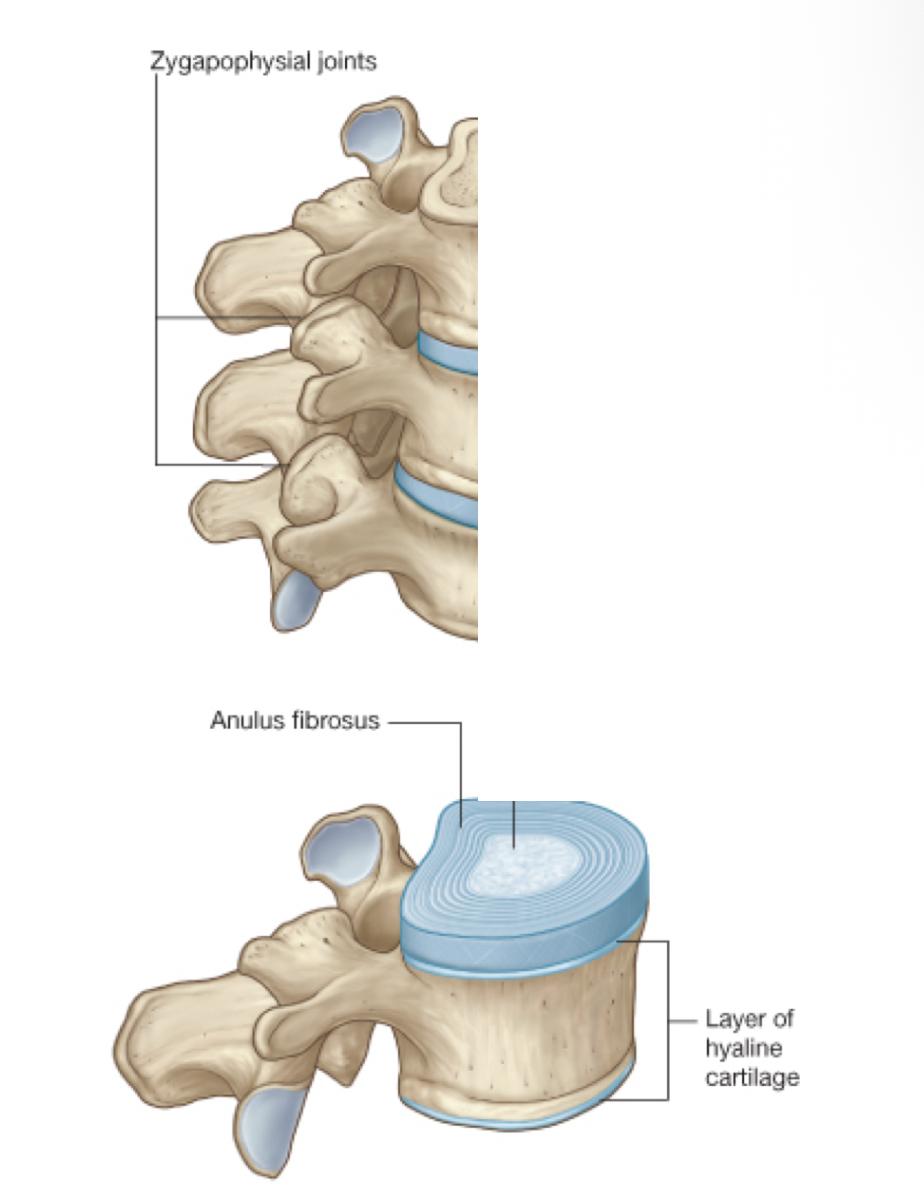
how is the symphysis joints formed
a layer of hyaline cartilage on each vertebral body and an intervertebral disc
what are uncovertebral joints
small synovial joints found only in the cervical vertebra C3-C7
where specifically is the uncovertebral joints in the cervical spine
uncinate process
where is the intervertebral disc found
between the vertebral bodies from C2 - the sacrum, the disc is a symphysis (a cartilaginous joint)
what are the 2 main parts of the intervertebral disc
Nucleus pulposus (core)
Anulus Fibrosus (wall)
nucleus pulposus
gelatinous
absorbs compression forces between vertebrae
anulus fibrosus
collagen
arranged in a lamellar configuration
limits rotation between vertebrae
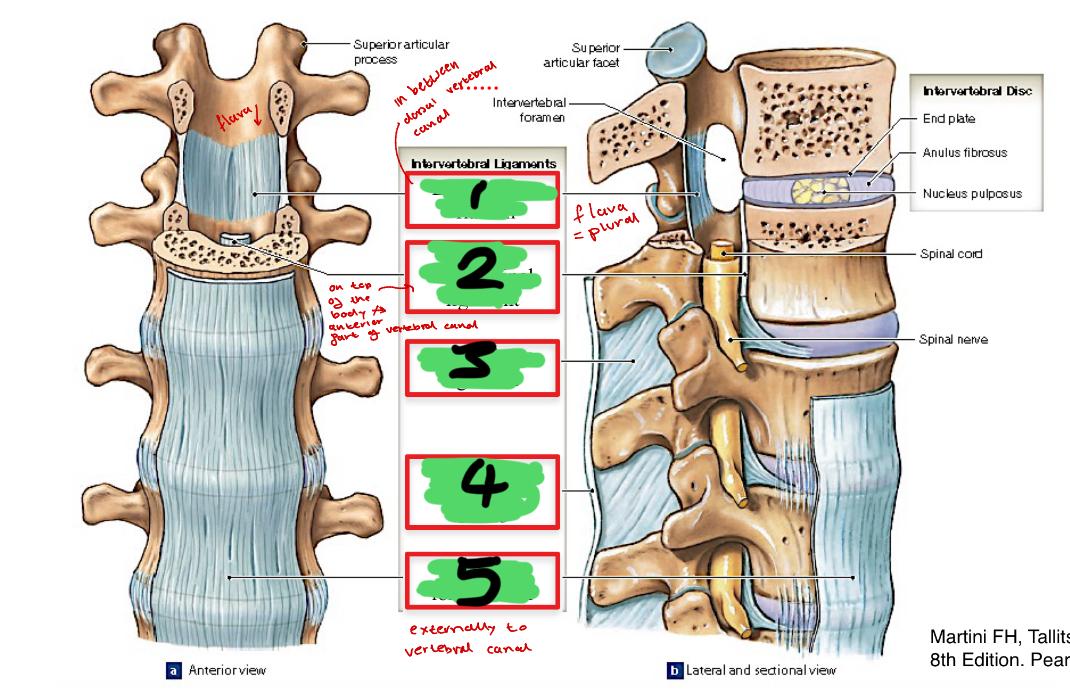
1
ligamentum flavum
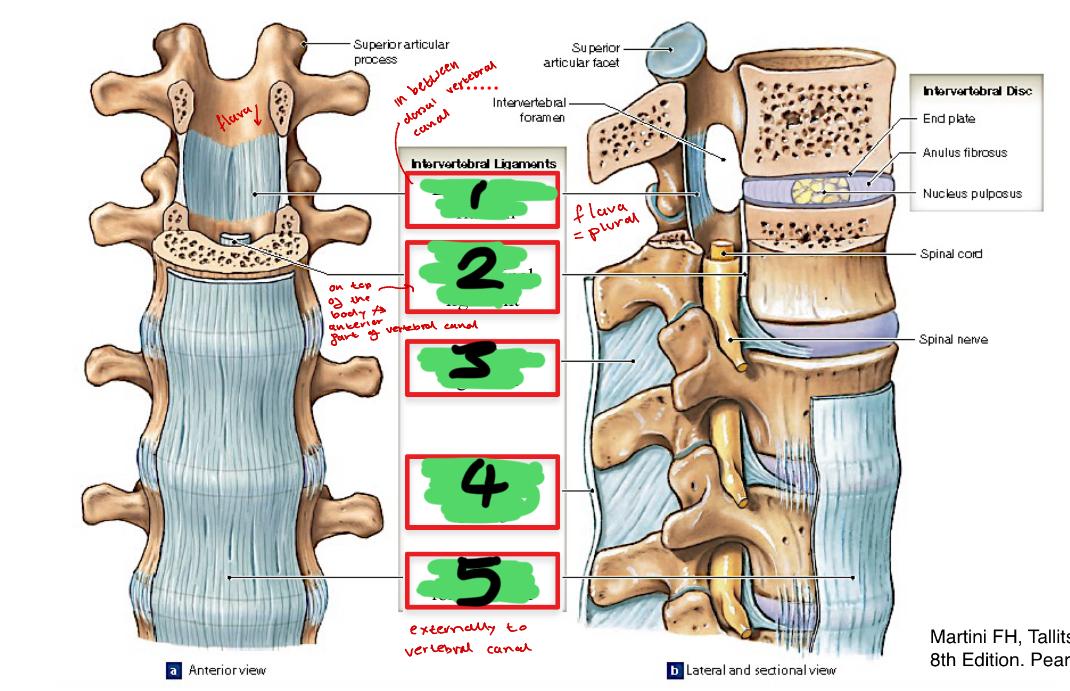
2
posterior longitudinal ligament
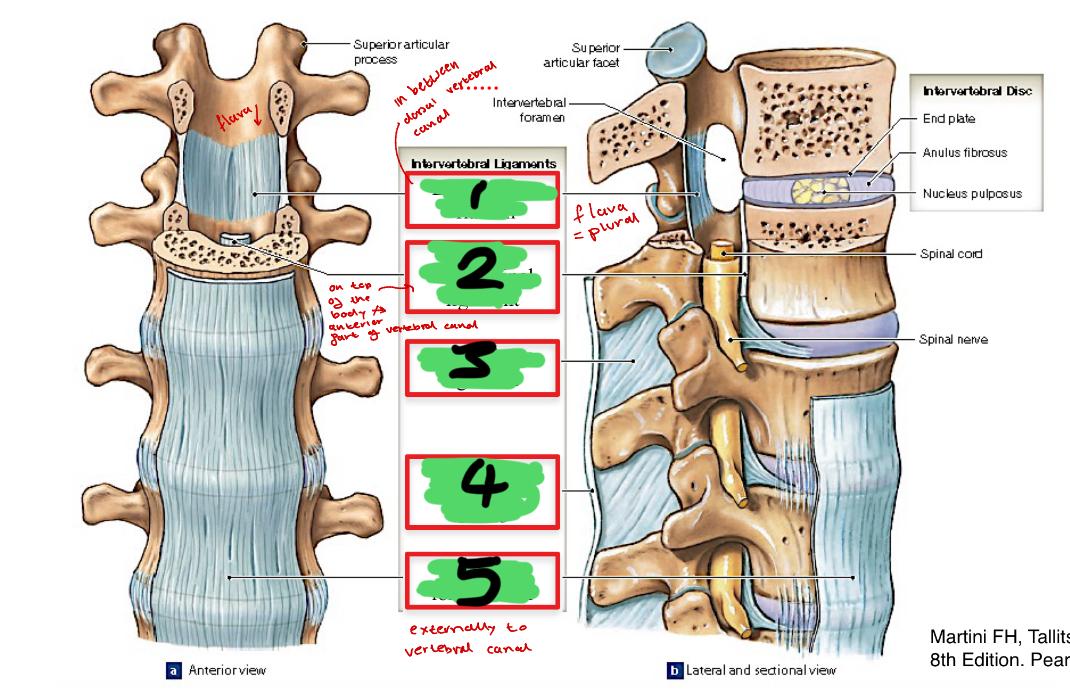
3
interspinous ligament
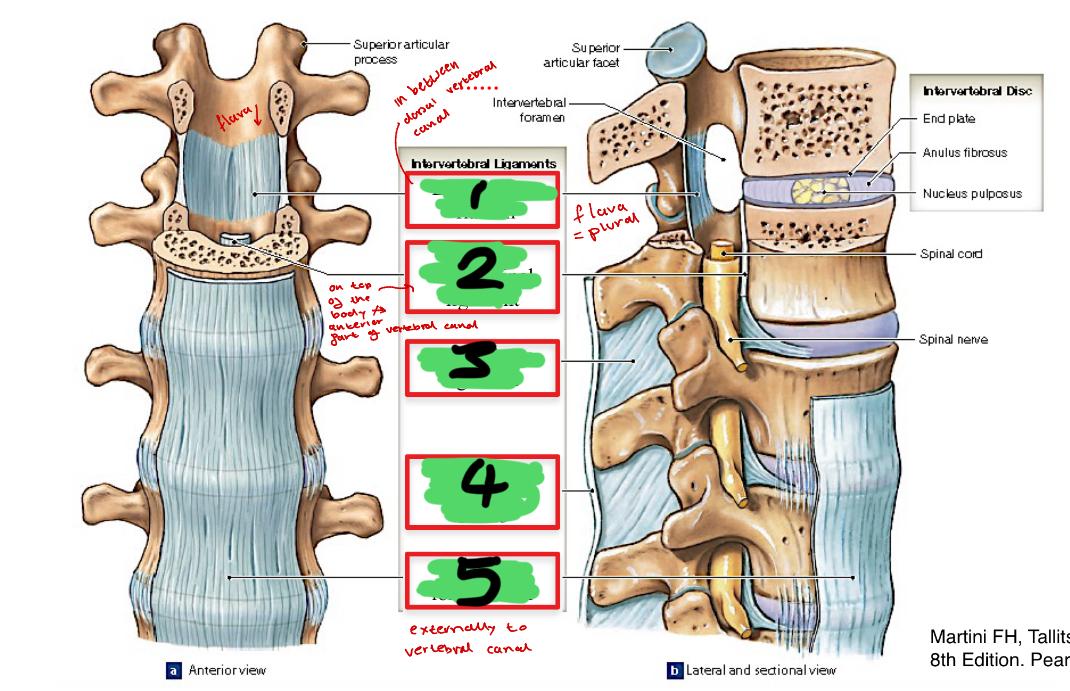
4
supraspinous ligament C7-L3
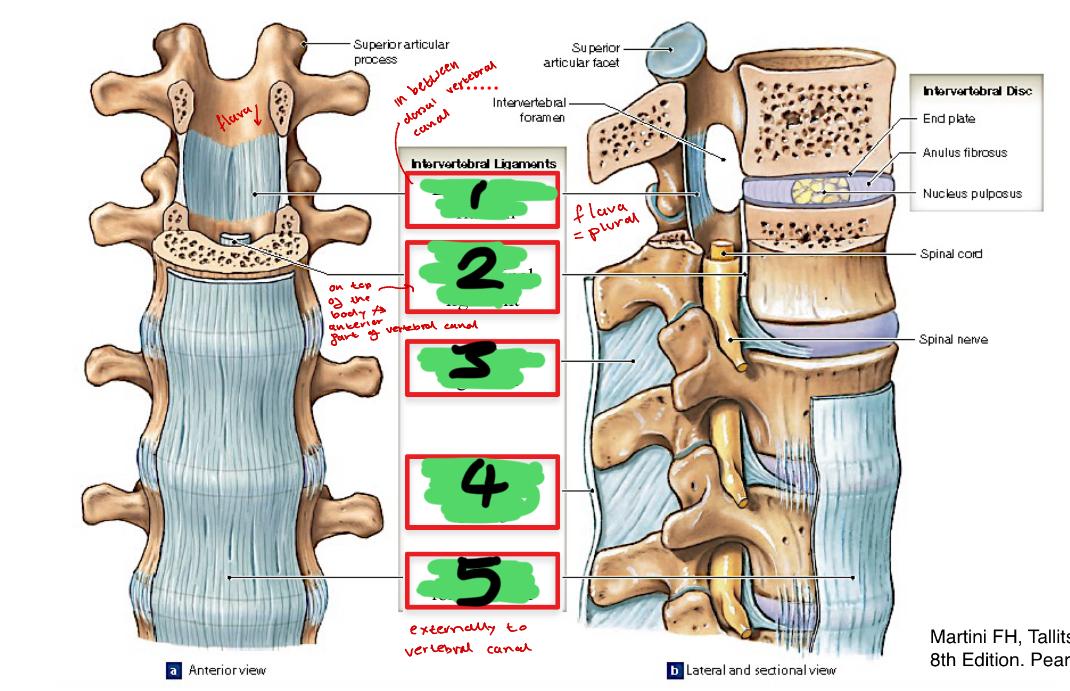
5
anterior longitudinal
anterior longitudinal ligament is attached
cranially to the anterior base of the cranium
attached to the ventral surface of the sacrum
(base of the skull runs all the way down attaching to the anterior surface of the sacrum)
function of anterior longitudinal ligament
reinforcement and maintenance of the joints
posterior longitudinal ligaments location
lines the ventral surface of the vertebral canal
attached to the posterior part of both vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs
function of posterior longitudinal ligament
reinforcement and maintenance of the joints
where is the supraspinous ligament
connect sand passes along the spinous process from C7 - sacrum
function of supraspinous ligament
reinforcement and maintenance of the joints
ligamentum nuchae
triangular sheet like ligament that lies in the midline of the back of your neck
ligamentum nuchae location
attaches superiorly to the external occipital protuberance and foramen magnum to the spinous process of C7
function of ligamentum nuchae
supports head
resits flexion
facilitates the return to the atomical position
reinforcement and maintenance of the joints
ligamentum flavum
on each side attached to the laminae of adjacent vertebrae
ligamentum flavum function
reinforcement and maintenance of the joints
interspinous ligament location
pass between adjacent spinous processes
function of interspinous ligament
reinforcement and maintenance of the joints
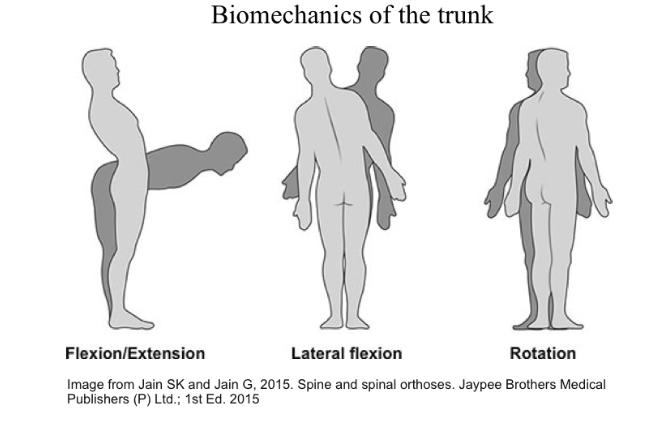
what are the biomechanics of the trunk
flexion/extension
lateral flexion
rotation
whats the difference between superficial and intermediate groups compared to deep
superficial and intermediate - extrinsic because the originated embryologically from locations OTHER THAN the back
deep - are intrinsic because they develop IN the back
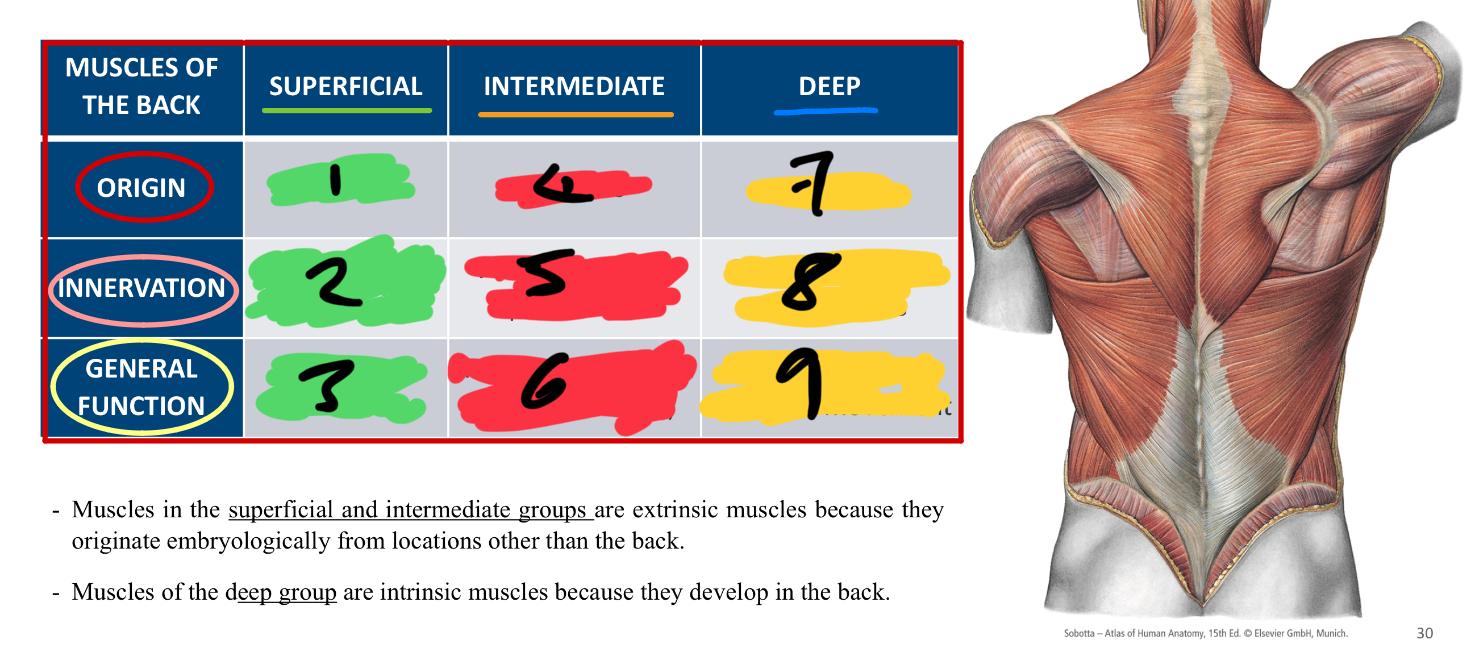
1,2 3
extrinsic
anterior rami of spinal nerves
upper limb movement
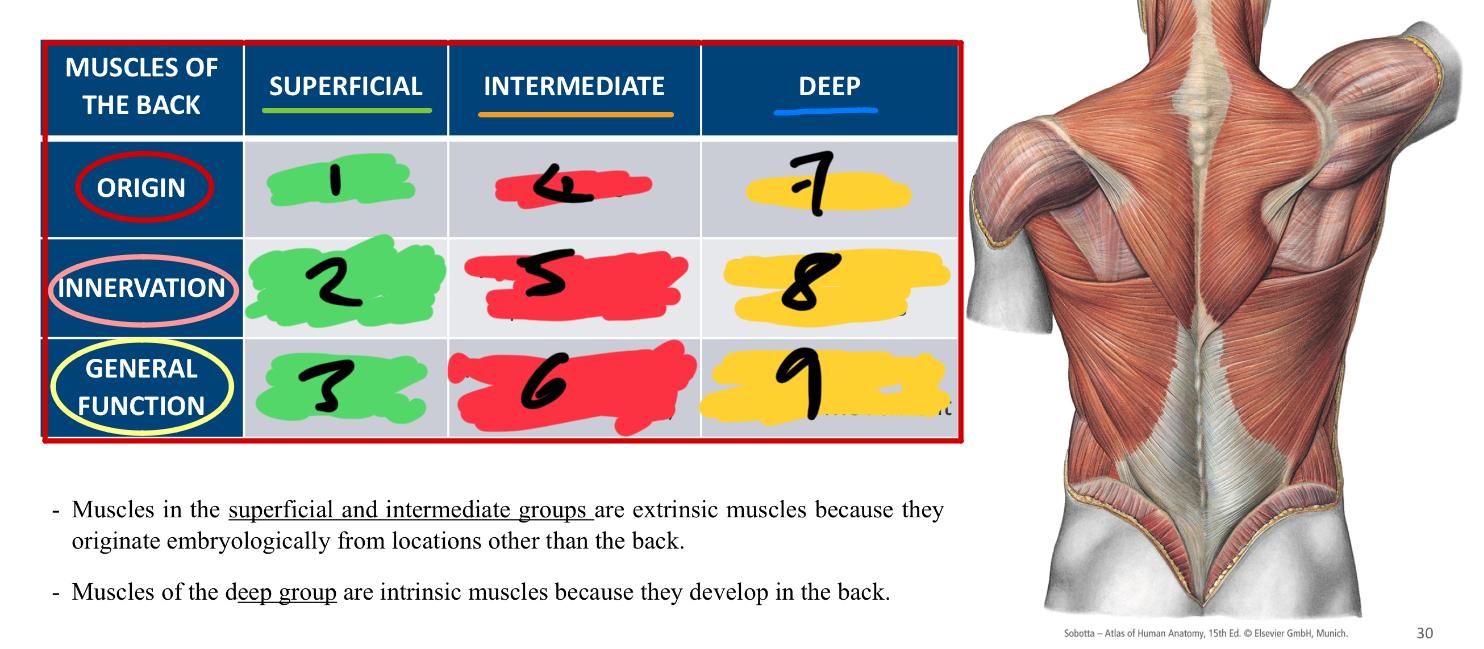
4,5,6
extrinsic
anterior rami of spinal nerve
respiratory function (attached to ribs)
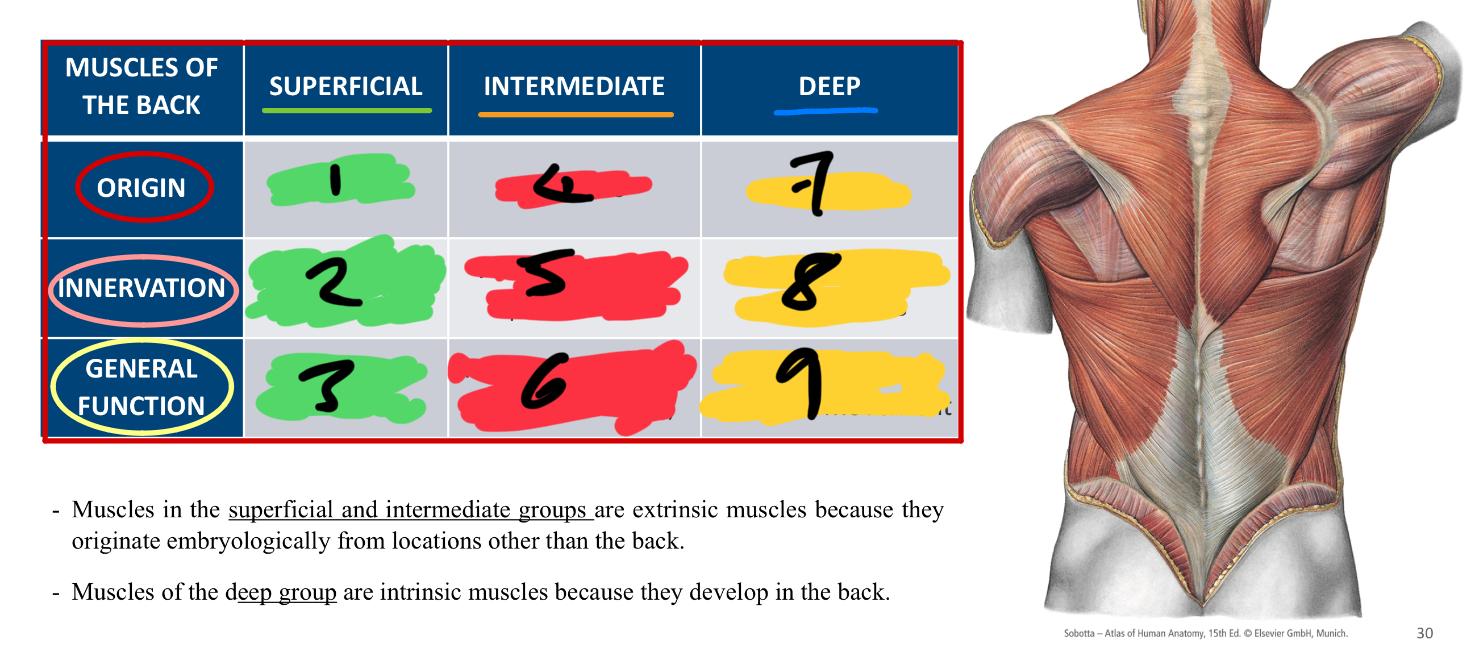
7,8,9
intrinsic
posterior rami of spinal nerves
vertebral column and head movement
what are the extrinsic superficial muscles
trapezius
latissimus dorsi
romboid major
Romboid minor
levator scapulae
general characteristics of extrinsic superficial muscles
immediately deep to the skin and superficial fascia
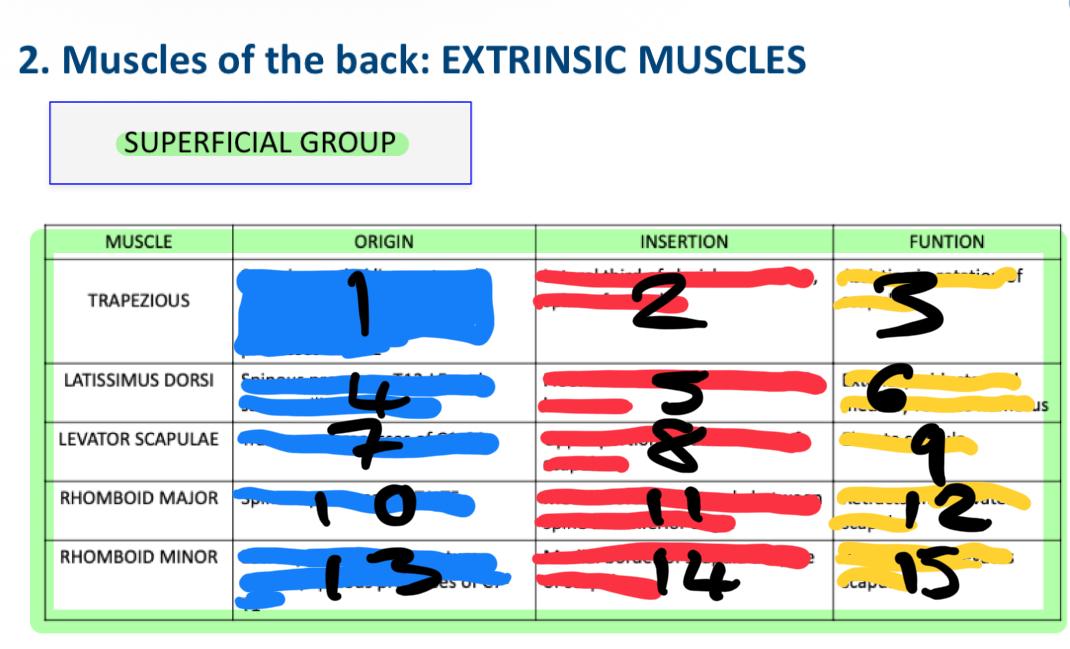
1
skull and spine (neck to midback
C7-T12