DNA Structure, replication, Transcription and translation
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
DNA Replication
the process of making identical copies of DNA before cell division

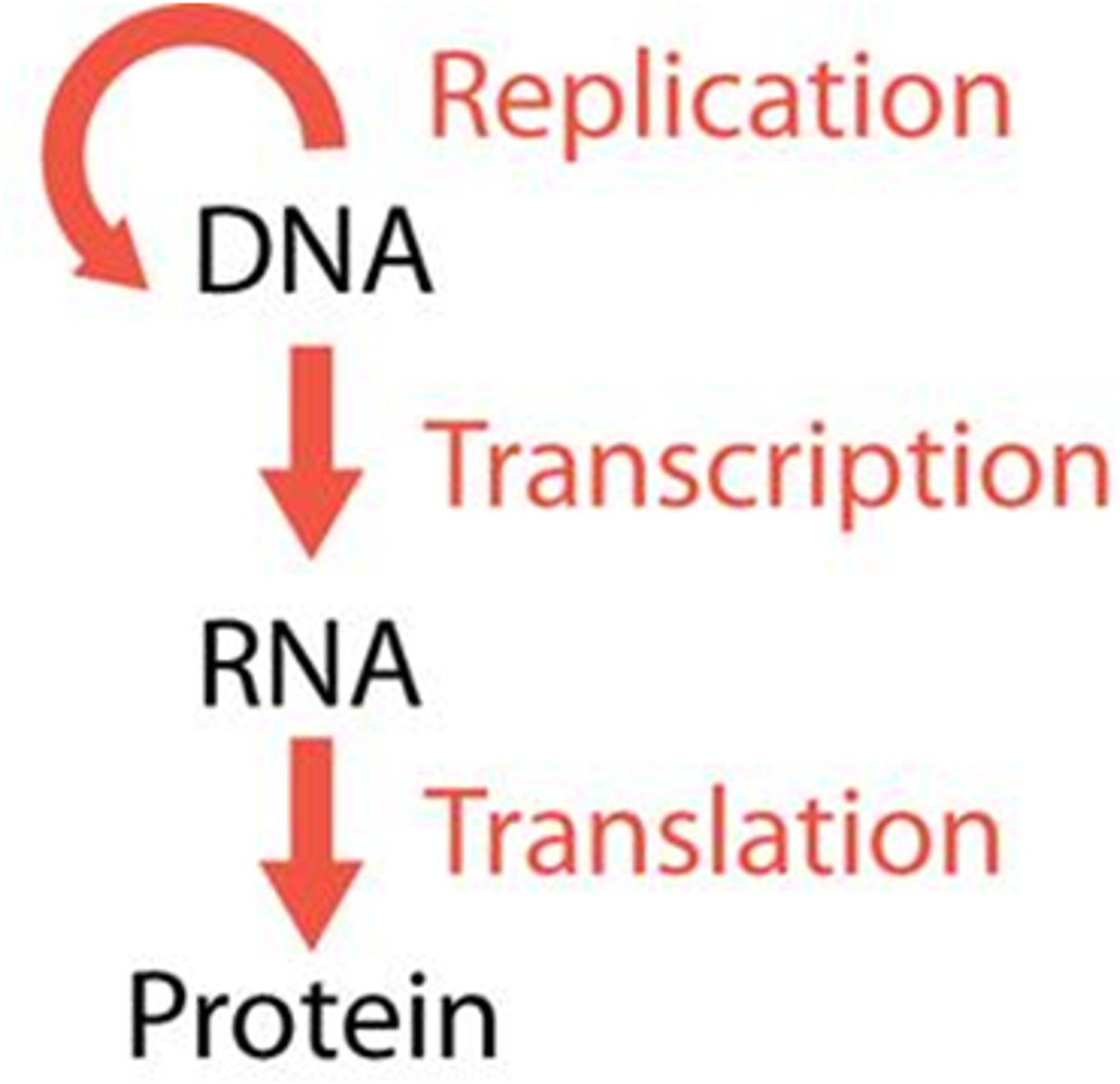
central dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
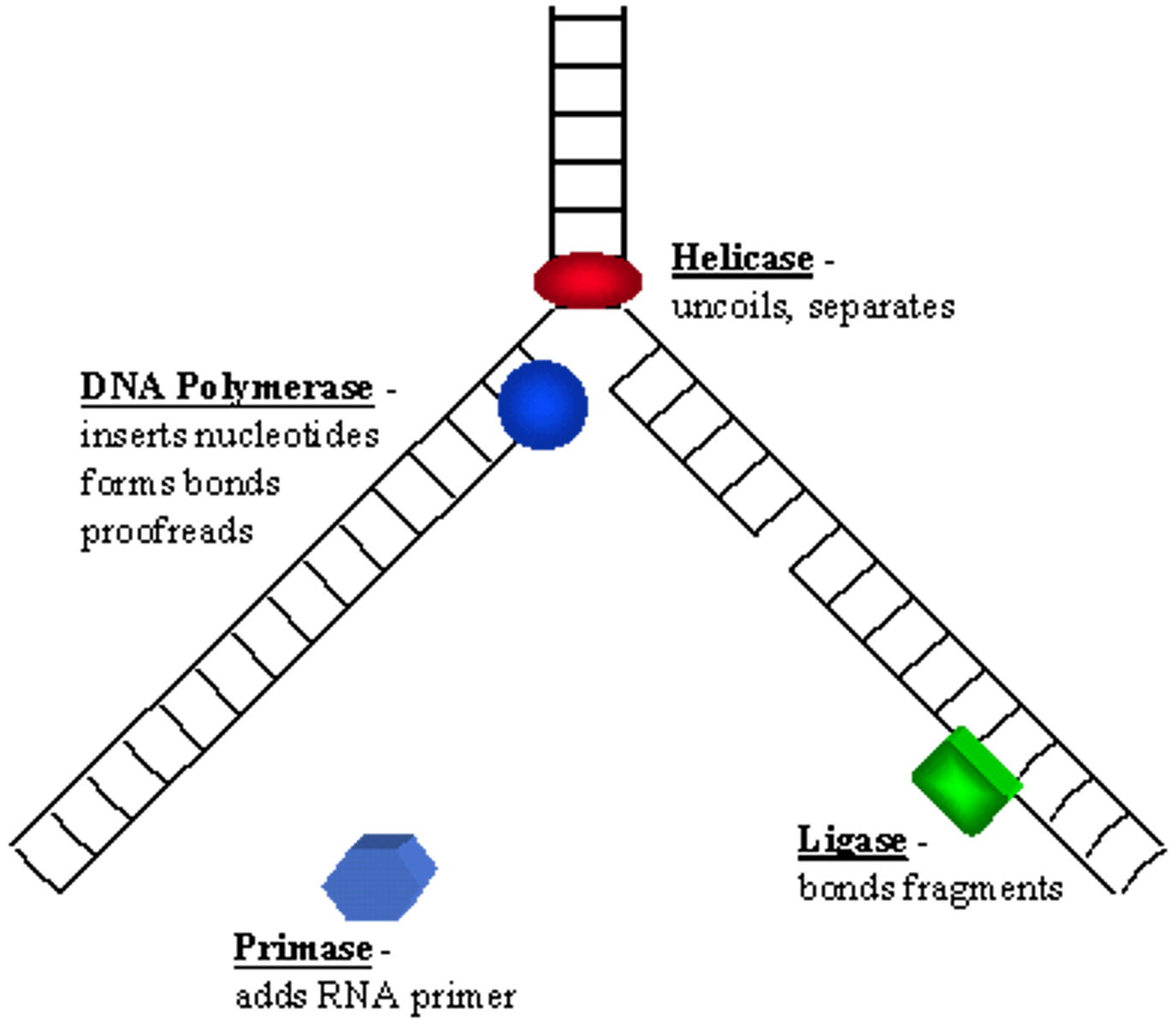
DNA helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the double helix of DNA and separates the DNA strands in preparation for DNA replication.
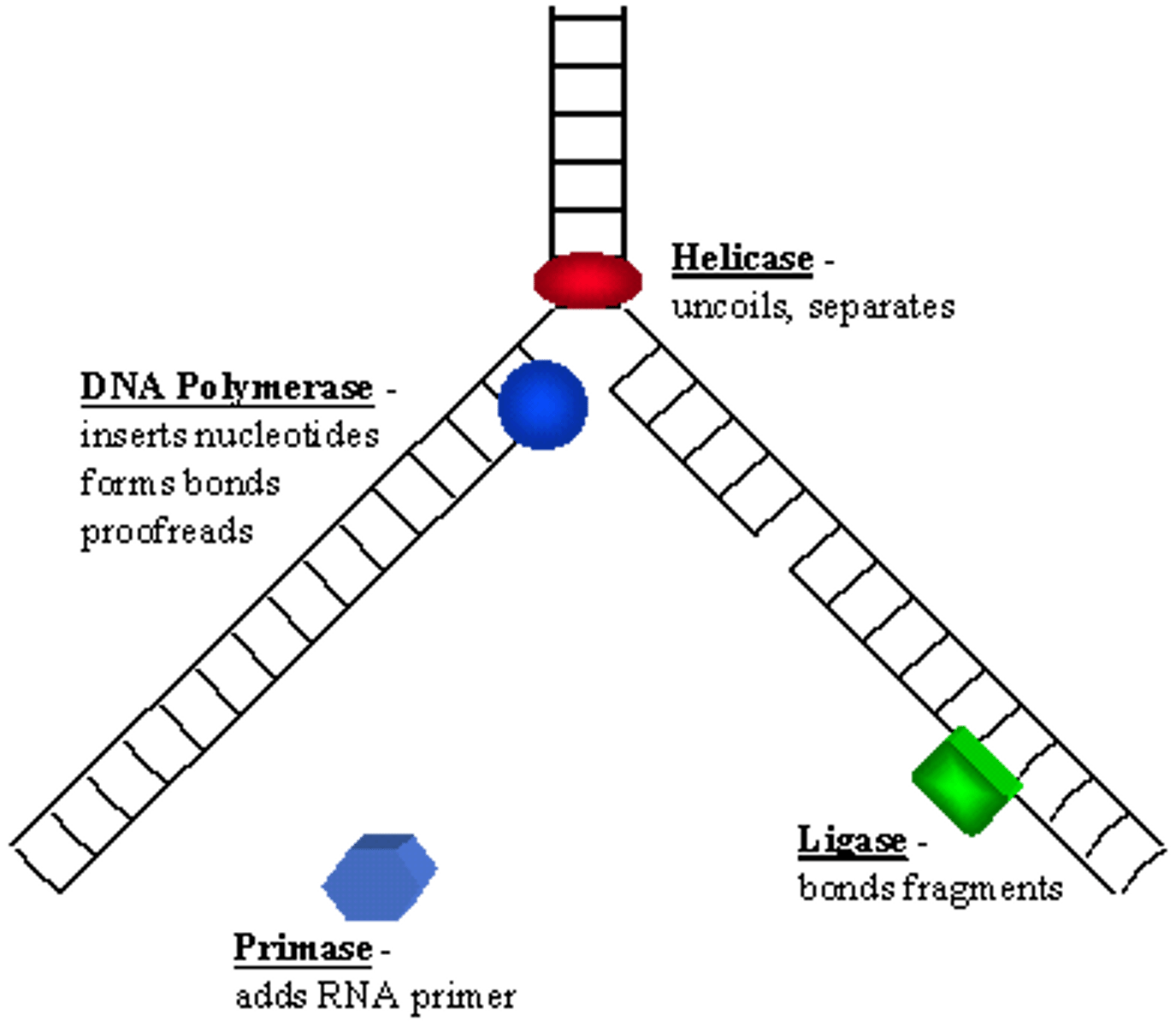
DNA Polymerase
"Proof reads", to fix mistakes in DNA, Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
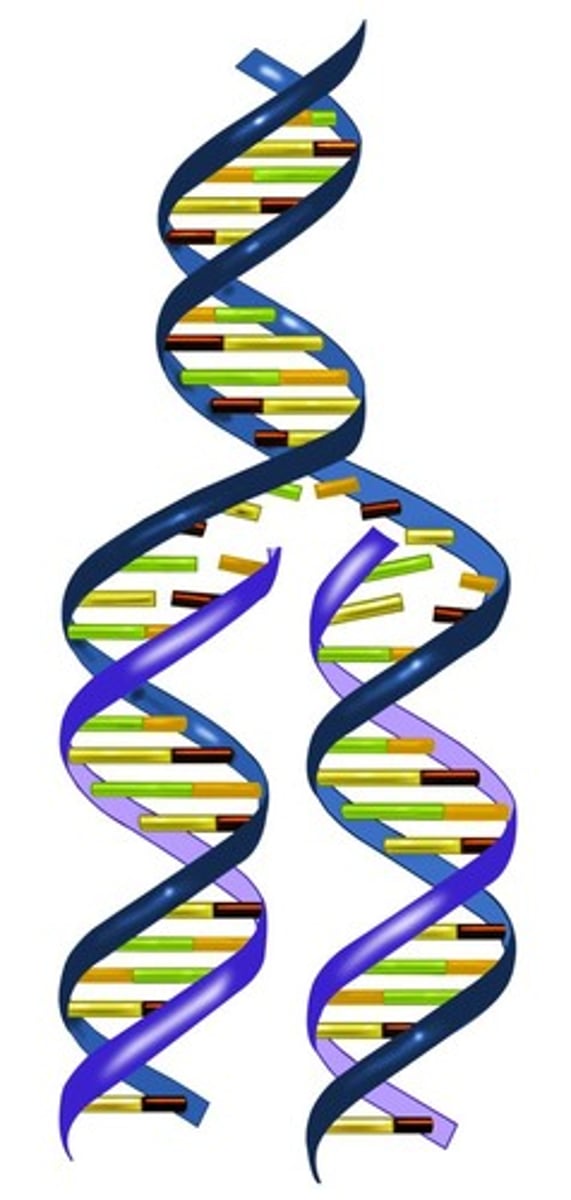
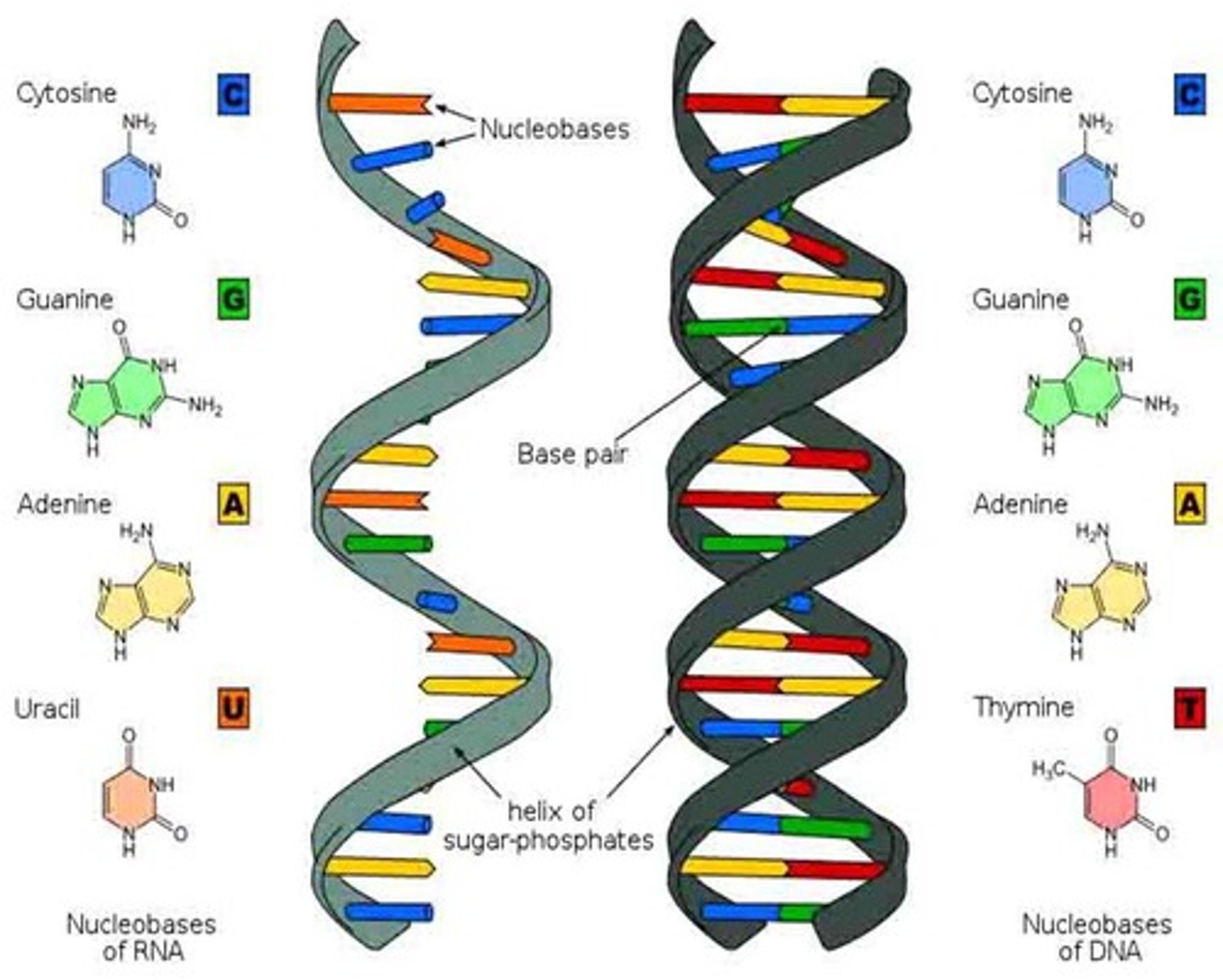
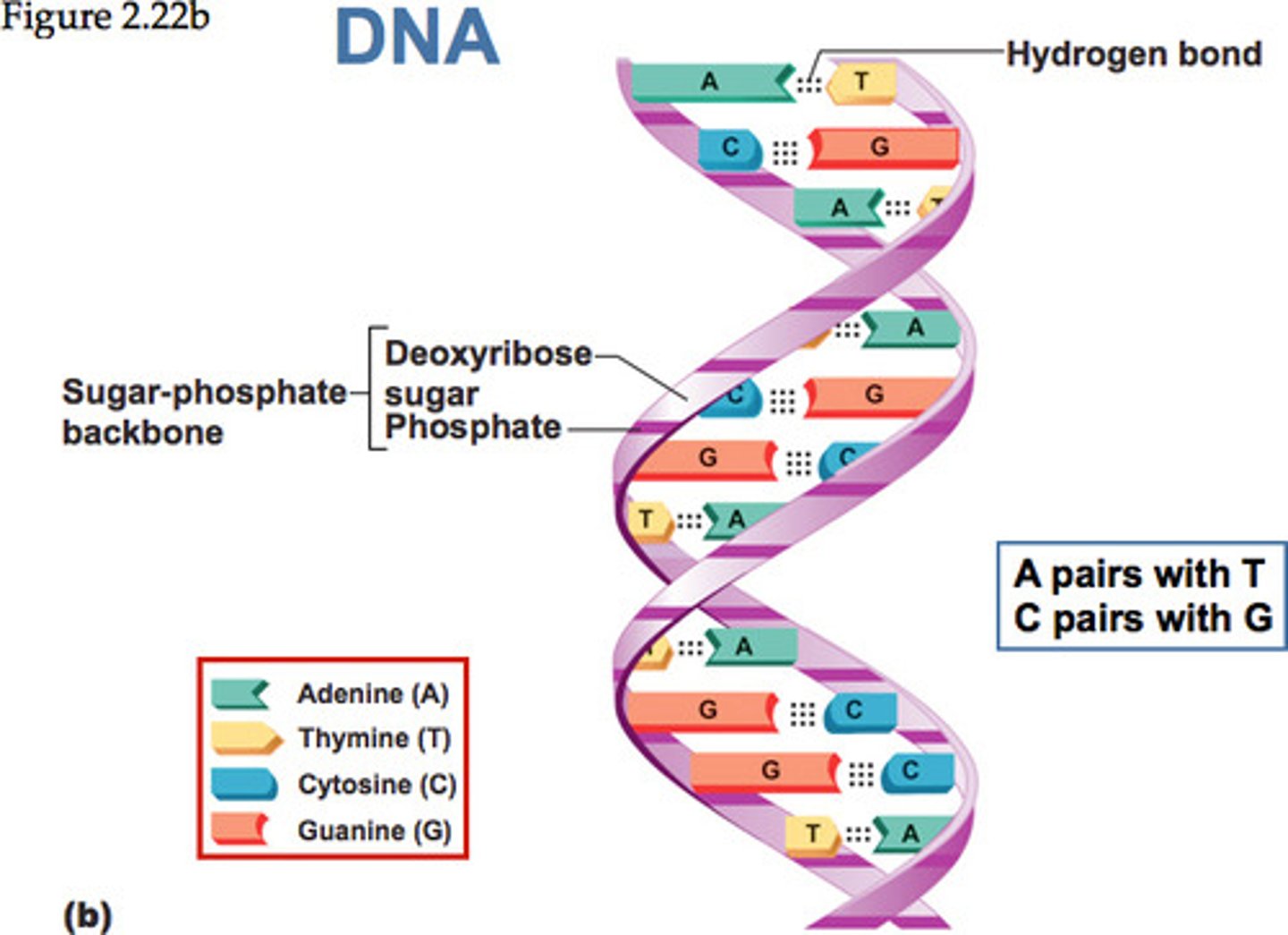
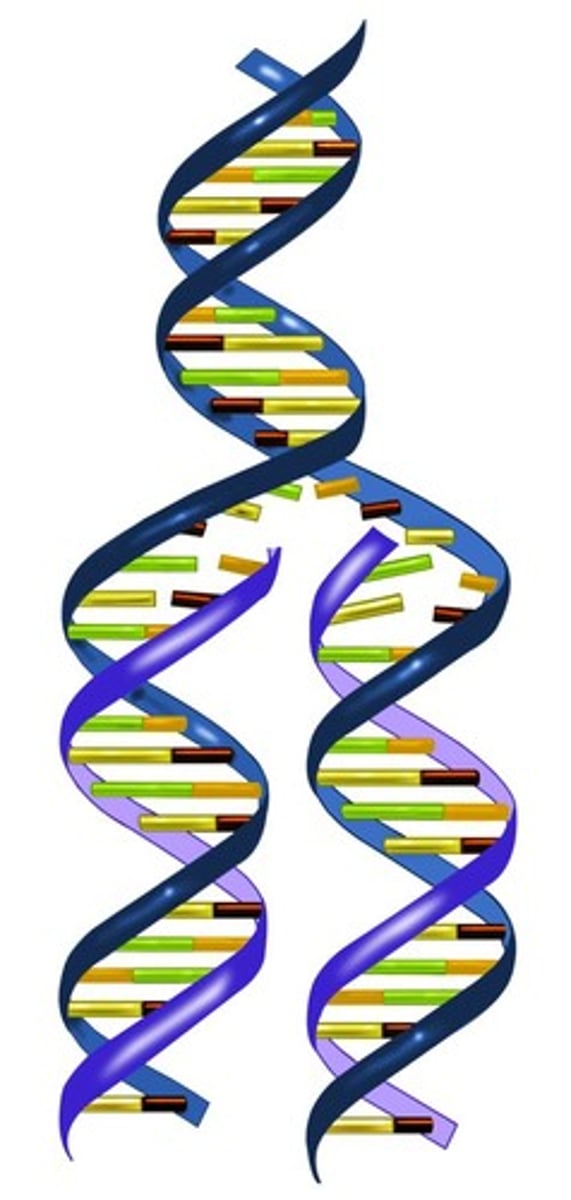
double helix
The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent polynucleotide strands wound into a spiral shape.
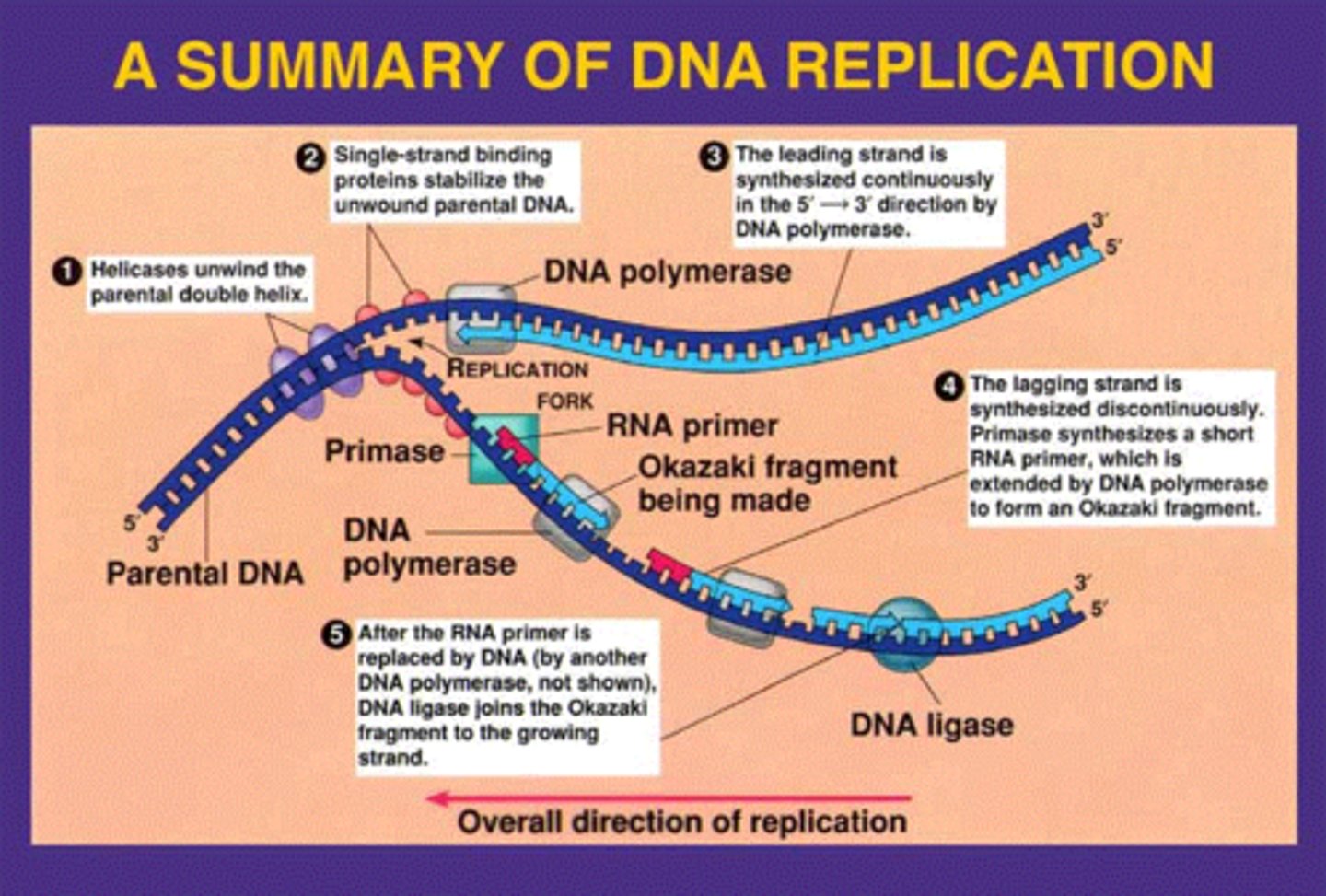
stages of replication
Initiation (RNA primer, then DNA polymerase attaches) + Elongation (DNA polymerase adds bases)
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.
RNA primer
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication
DNA helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix during DNA replication
Leading strand
the new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' --> 3' direction
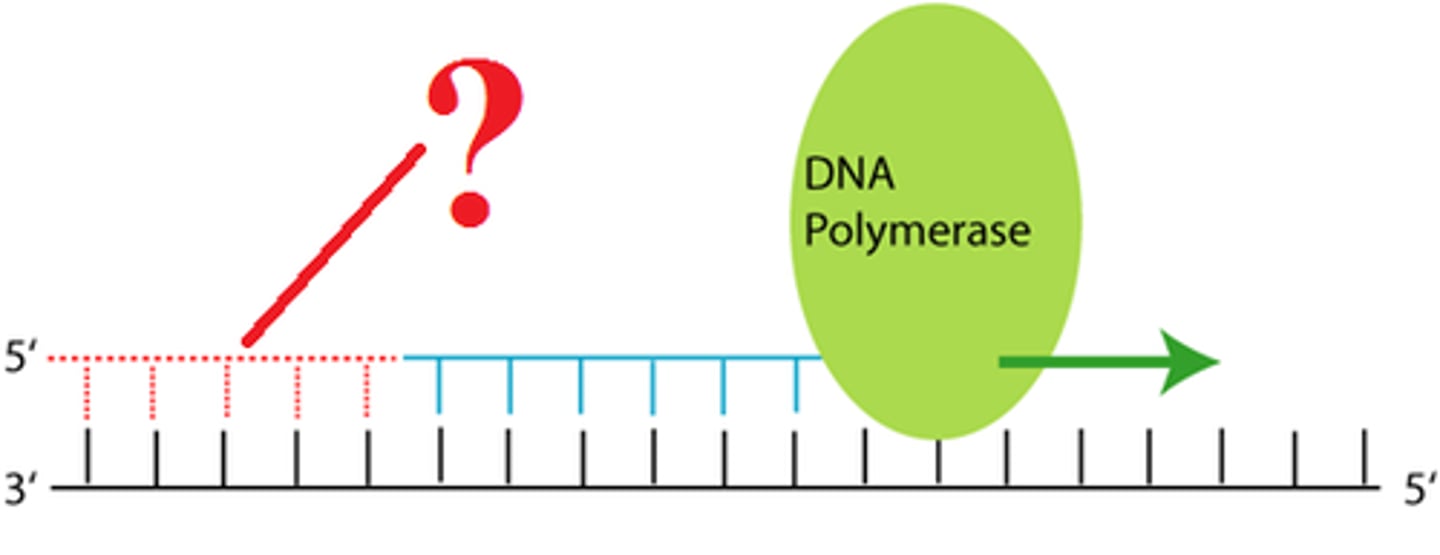
Lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates in a direction away from the replication fork.
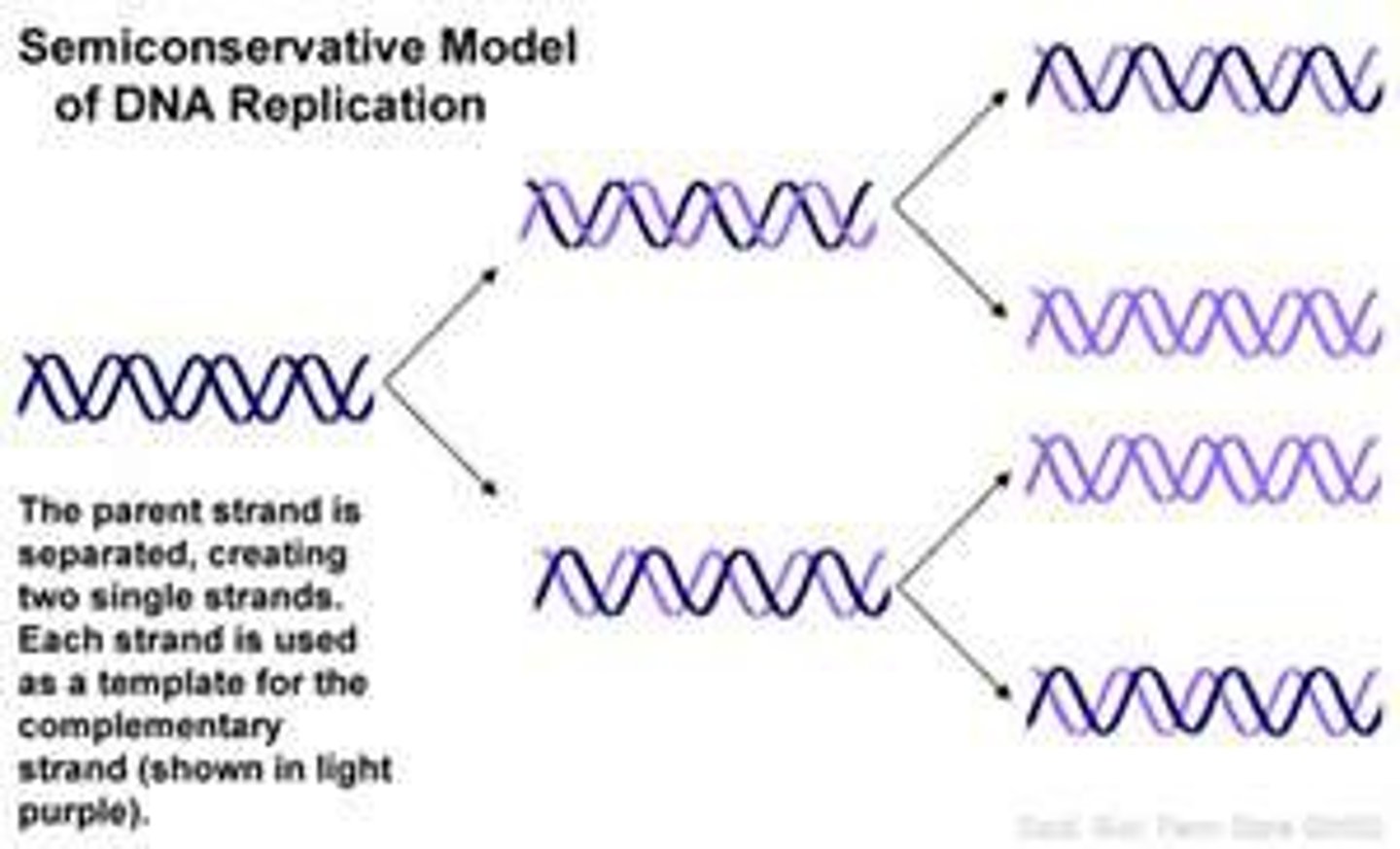
semi conservative
Each half of an original DNA molecule serves as a template for a new strand, and the two new DNA molecules each have one old and one new strand.
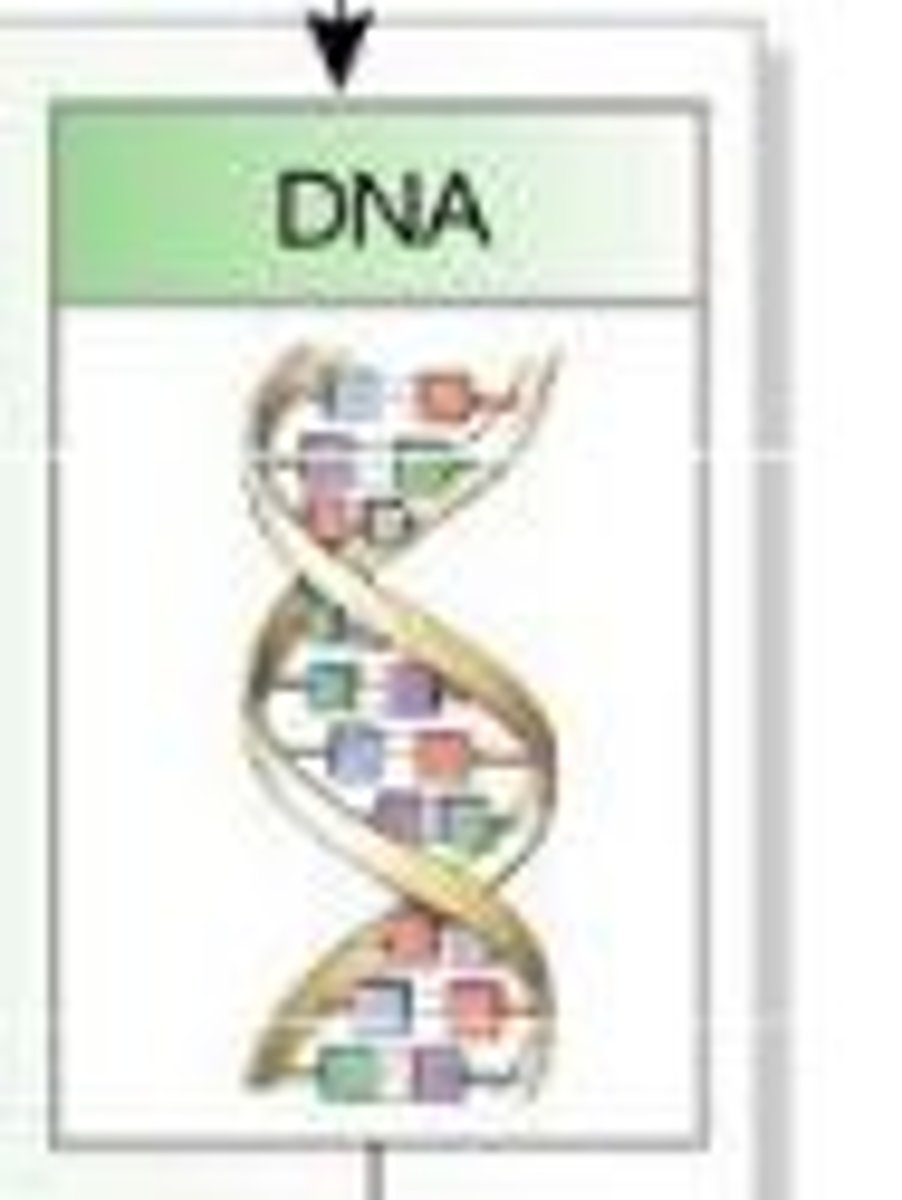
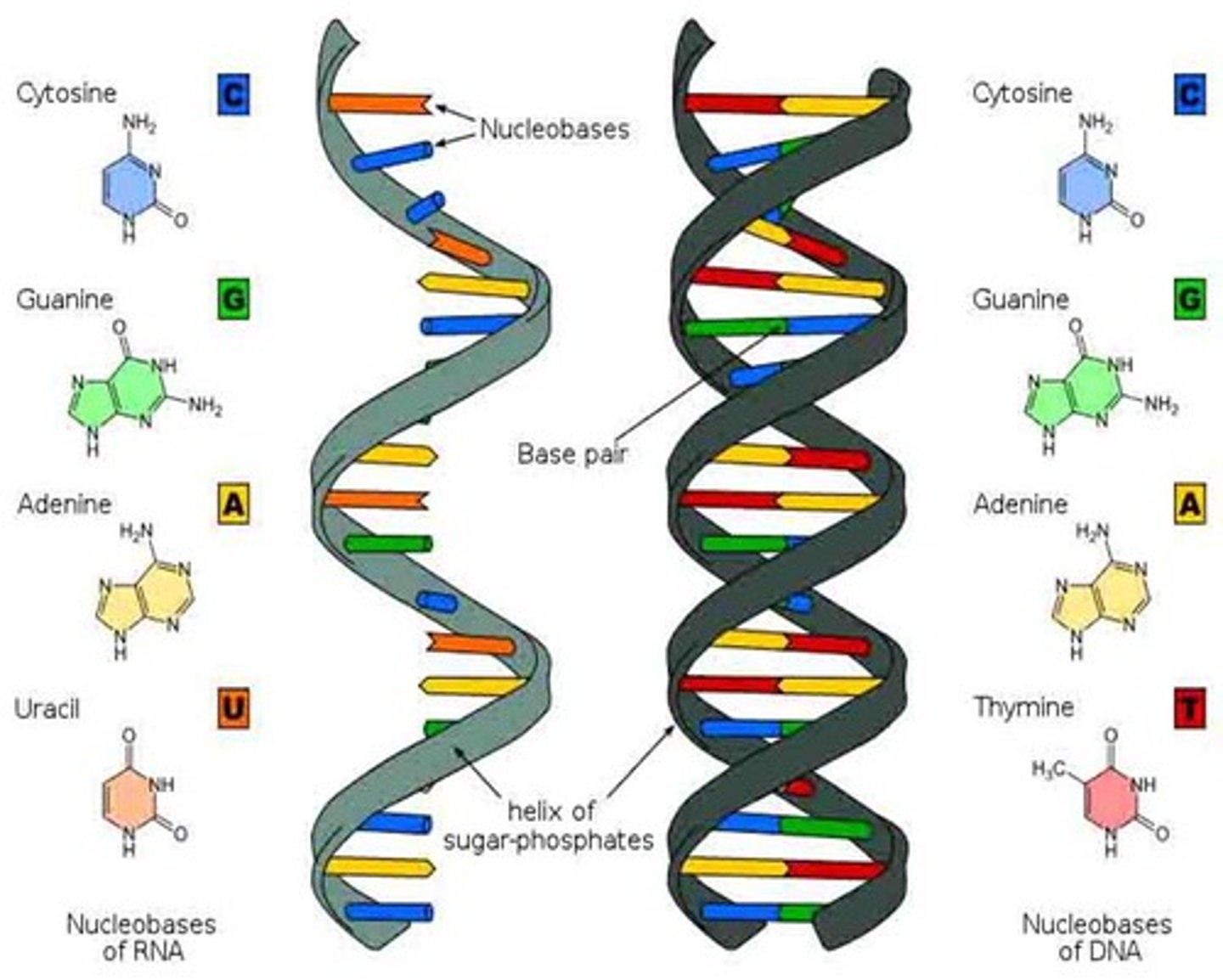
deoxyribonucleic acid
A nucleic acid molecule, usually a double stranded helix, in which each polynucleotide strand consists of nucleotide monomers with a deoxyribose sugar and the nitrogenous bases A T C G; capable of being replicated and determining the inherited structure of cell's proteins.
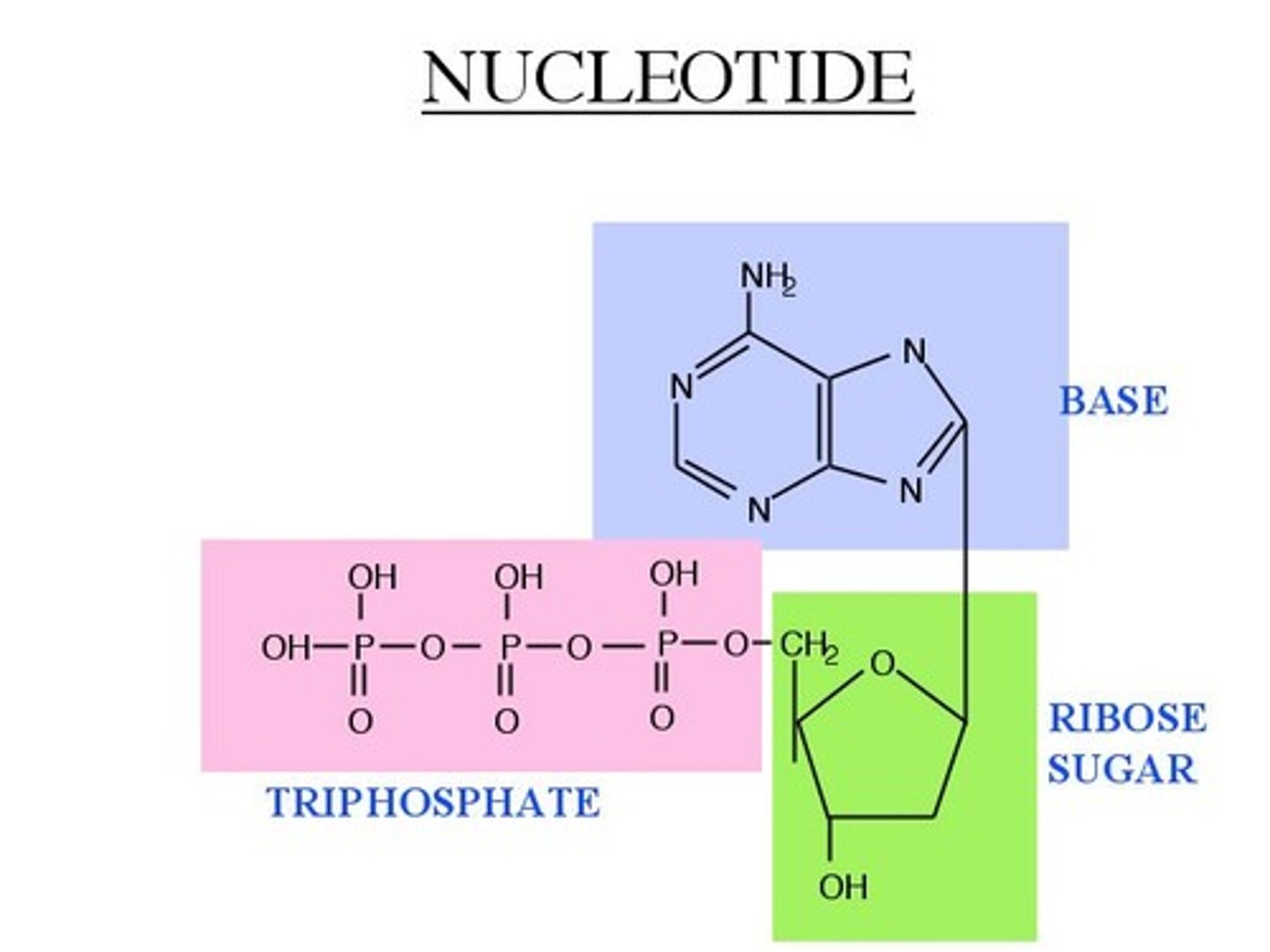
nucleotide
long chain of polymers; A subunit of nucleic acids formed from a simple sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
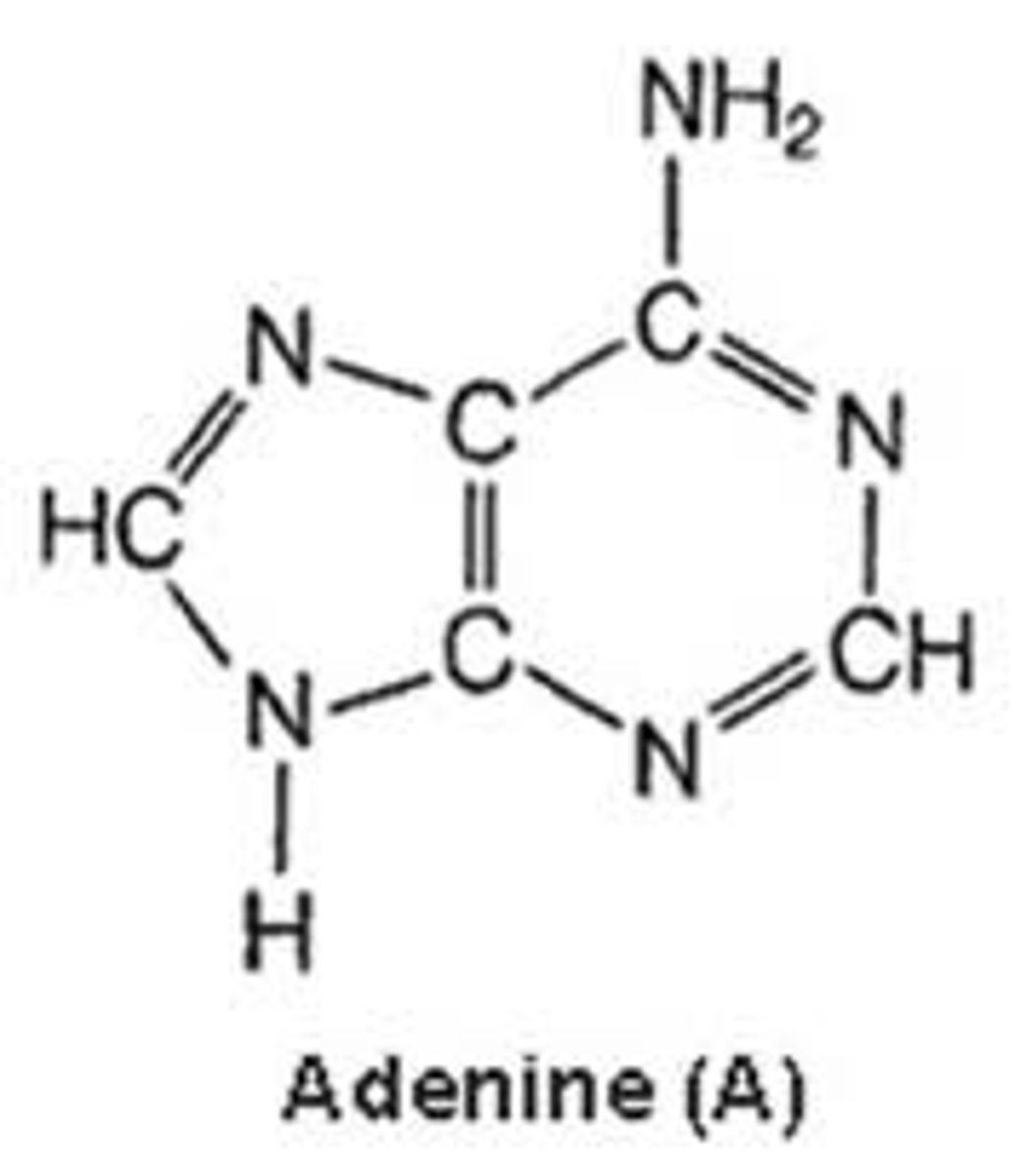
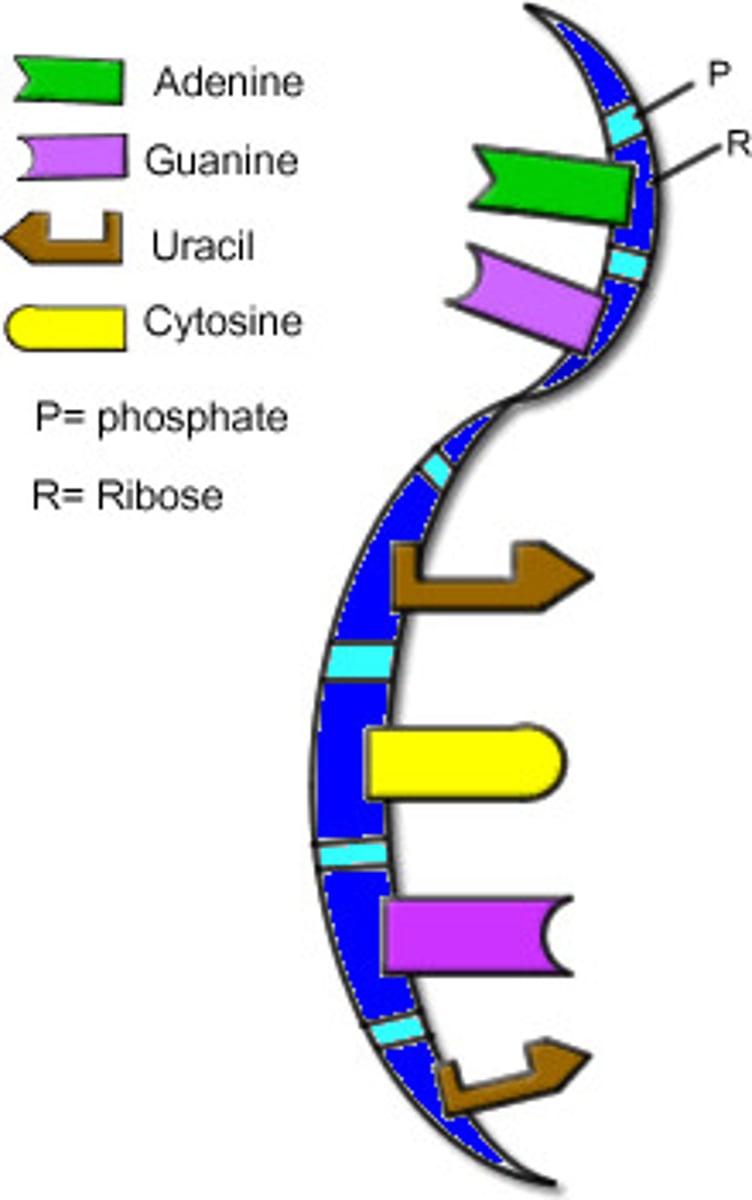
adenine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA. It pairs with thymine in DNA and with uracil in RNA
guanine
A nitrogenous base found in both DNA and RNA; pairs only with cytosine.
thymine
A nitrogenous base that pairs with adenine. Found only in DNA.
cytosine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA; pairs with guanine
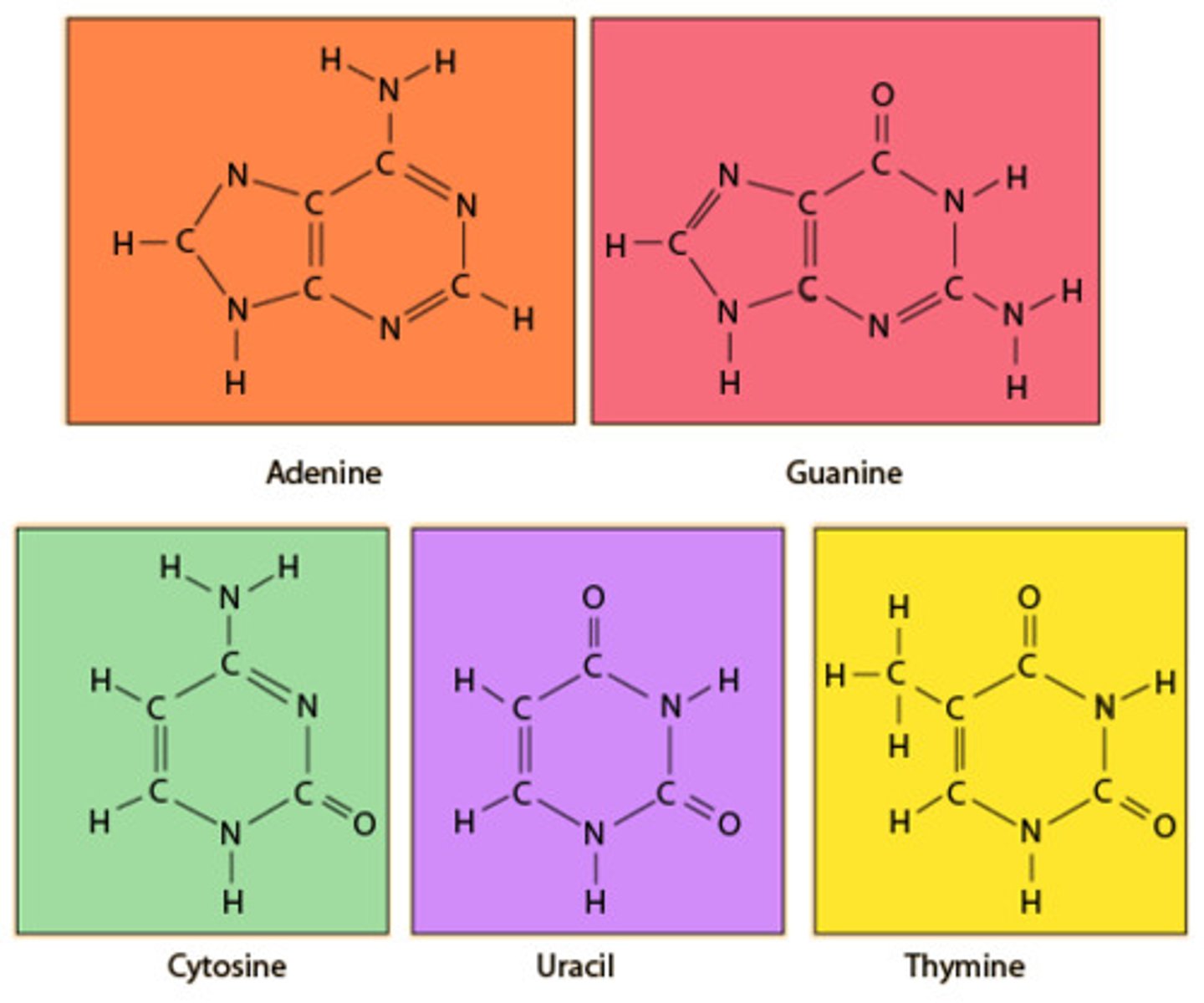
purine
A class of nucleotides that includes adenine and guanine.
- double ring
replication
The process whereby DNA makes a copy of itself before cell division

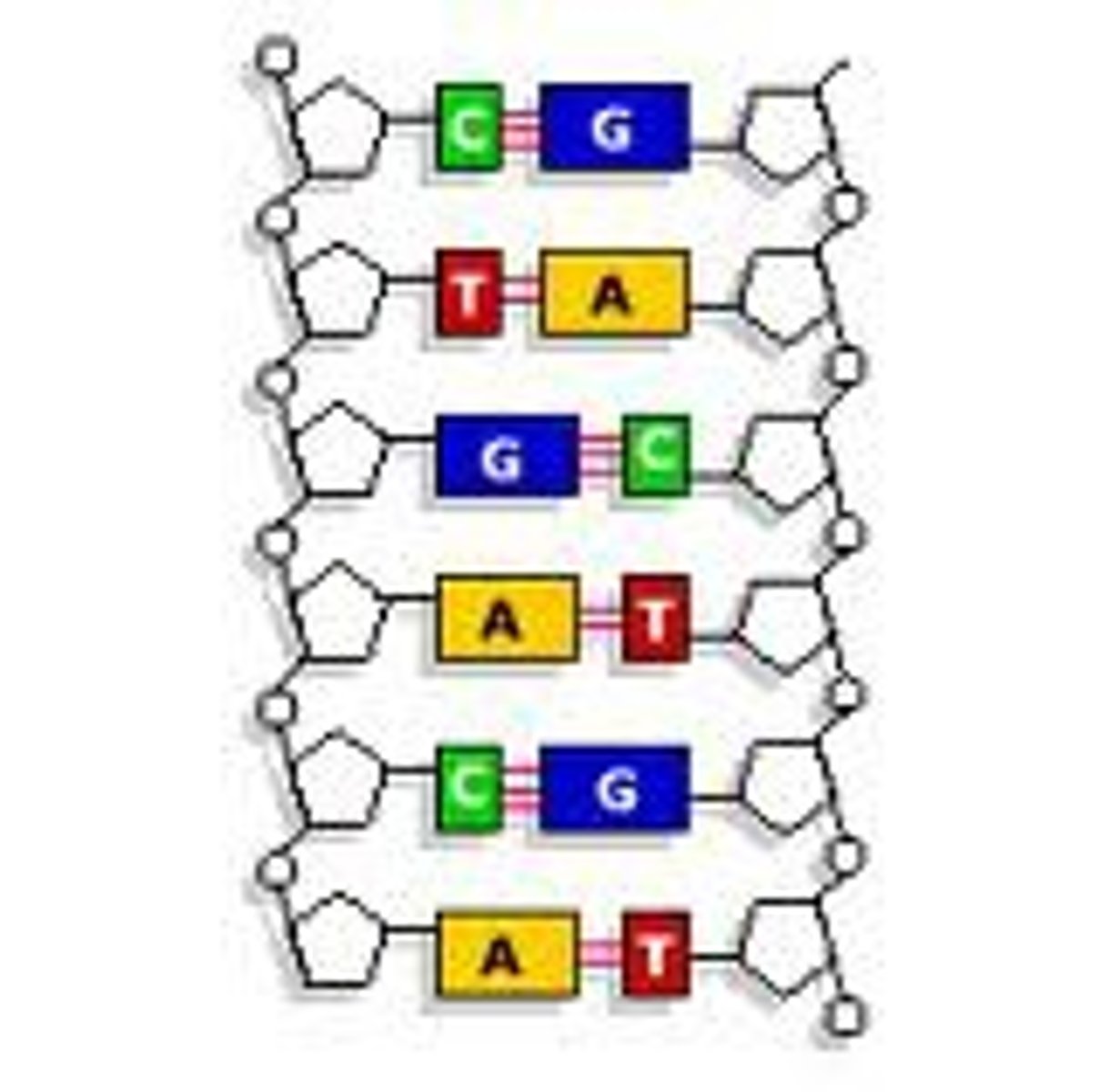
complementary
Capable of precisely base-pairing with one another by matching G with C and A with T.
base pairs
Any of the pairs formed between complimentary bases in the two nucleotide chains of DNA, such as A-T and C-G (DNA); A-U and C-G (RNA)
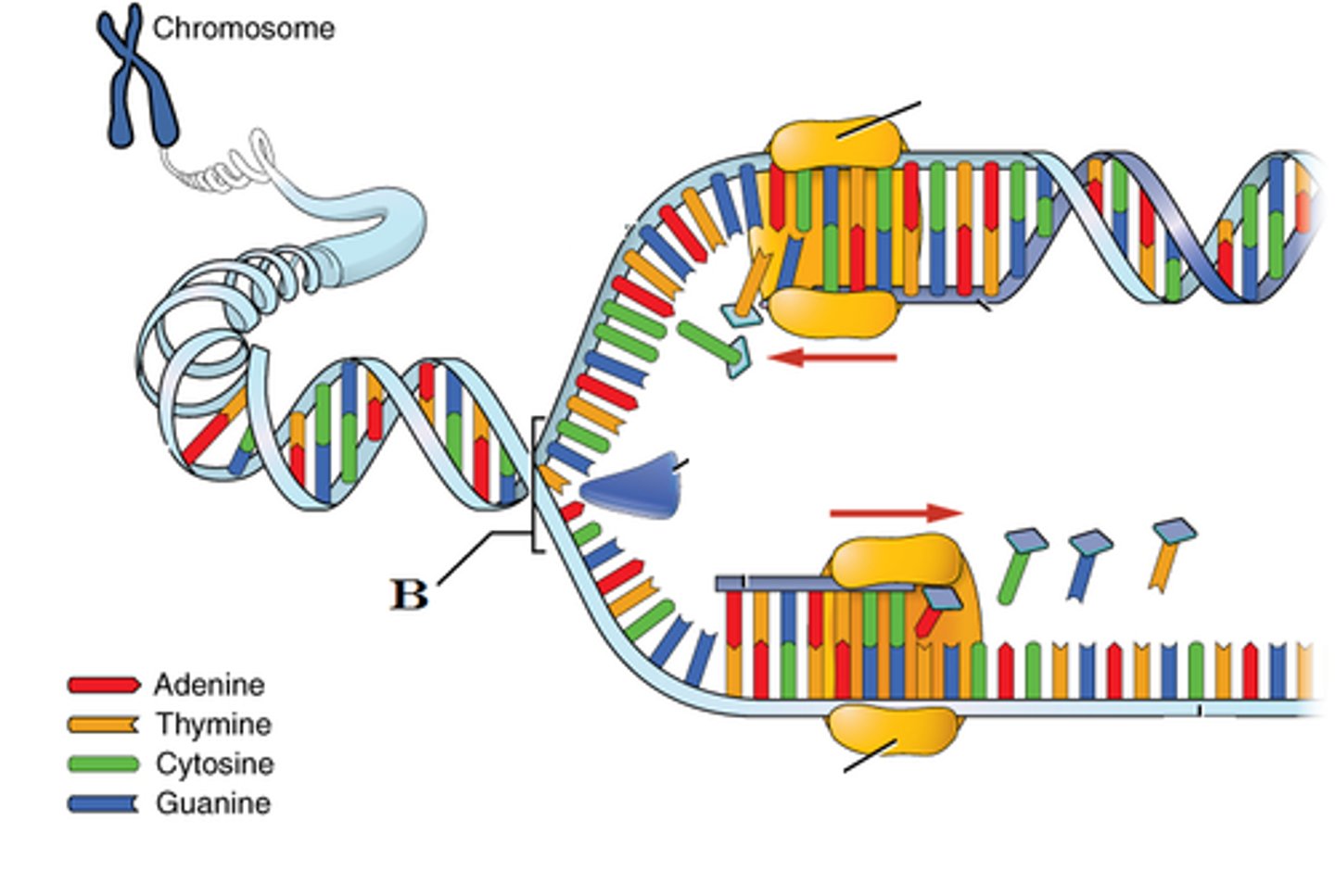
replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing.
- Point where DNA is separated and replication begins
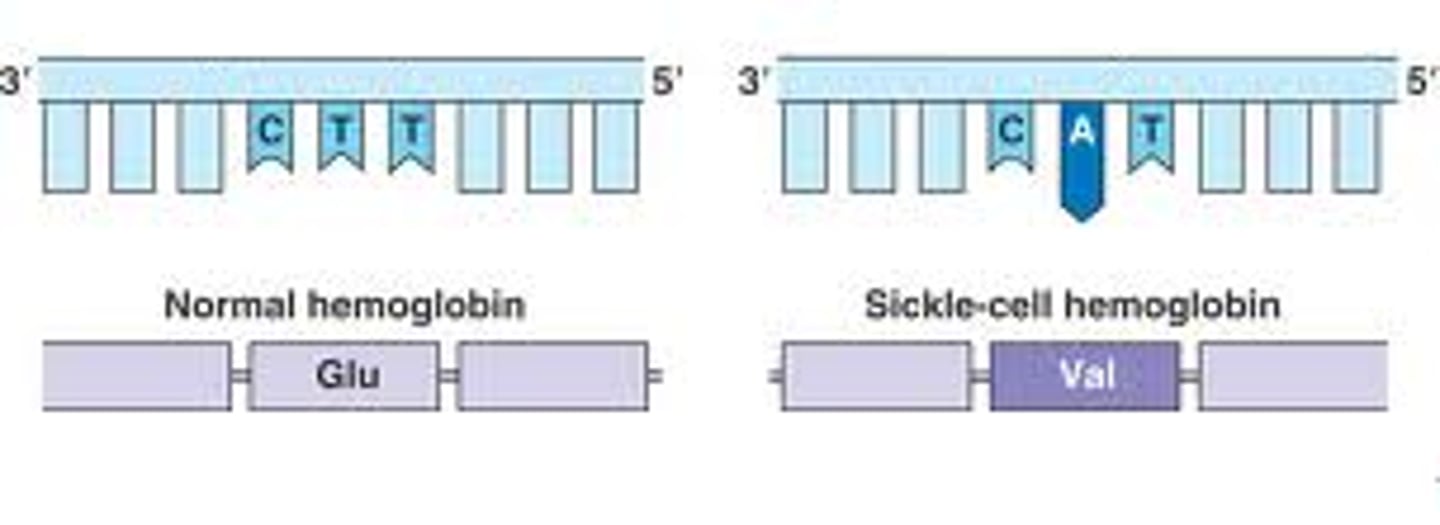
Mutation
- An error during replication
- any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA
- wrong nucleotide is added, changes the gene sequence, one error per billion nucleotides
Nitrogenous Base
Flags, two different groups (Pyrimidines and Purines)
Double Helix
Two twisted strands of DNA
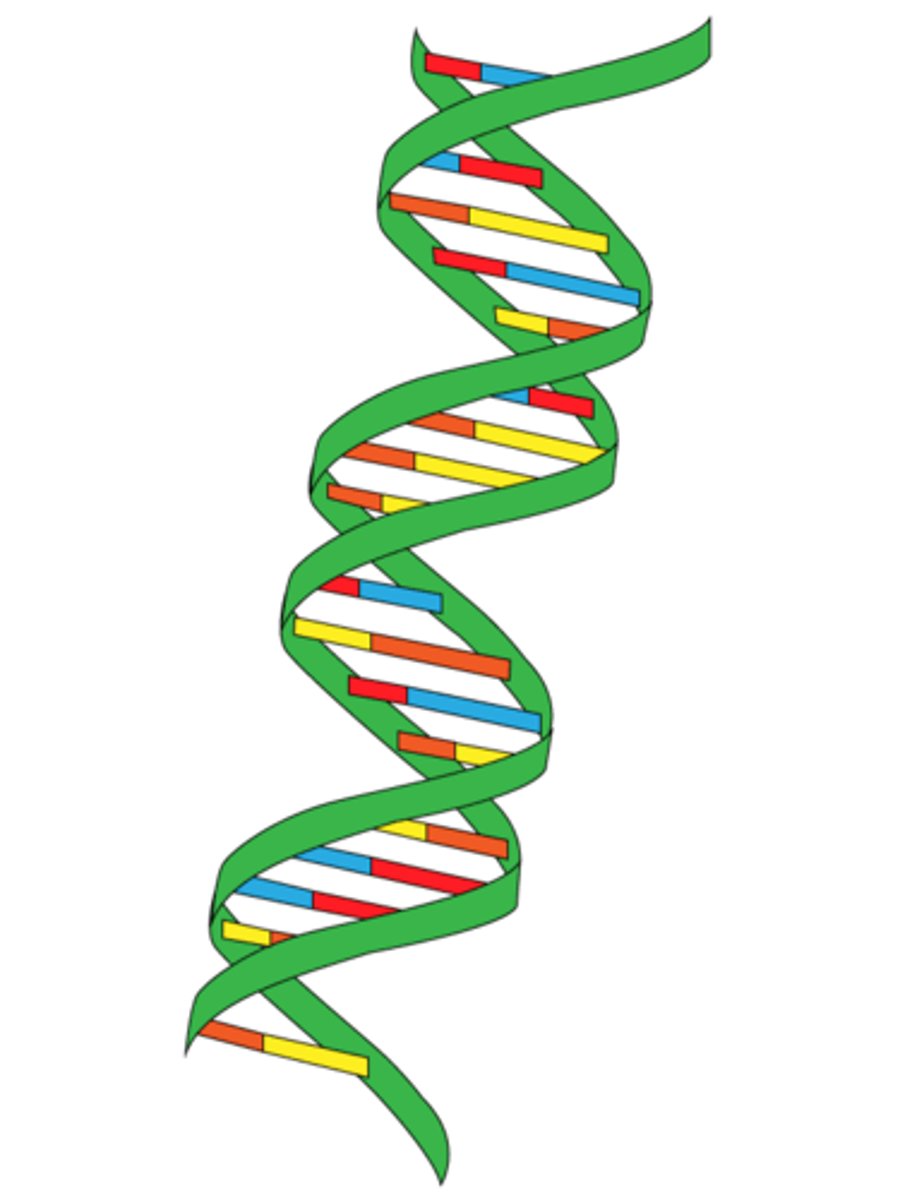
Polyneucleotides
long chain of nucleotides
- assembled in the 5 prime to 3 prime direction (covalent bonds)
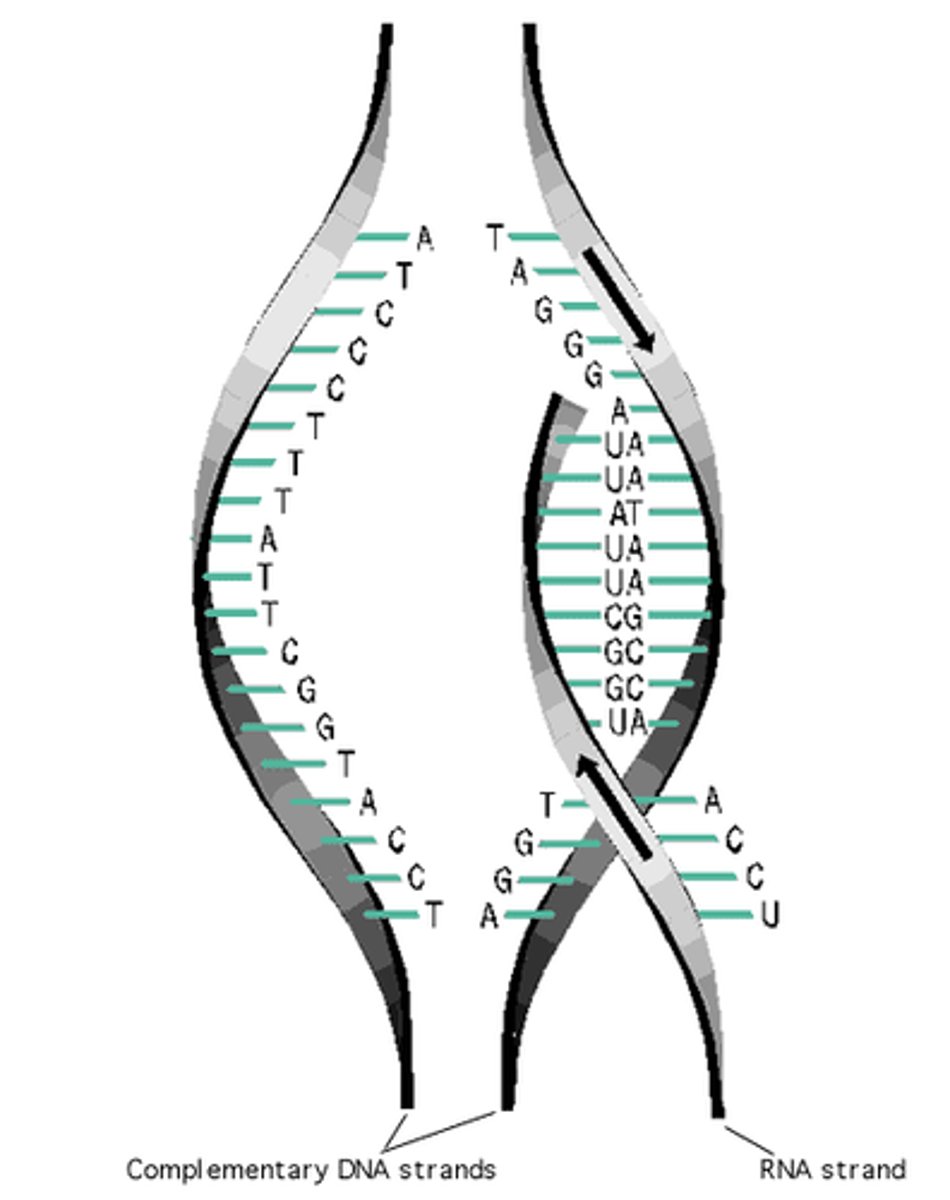
Transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
DNA to mRNA
Construction of mRNA from a DNA molecule
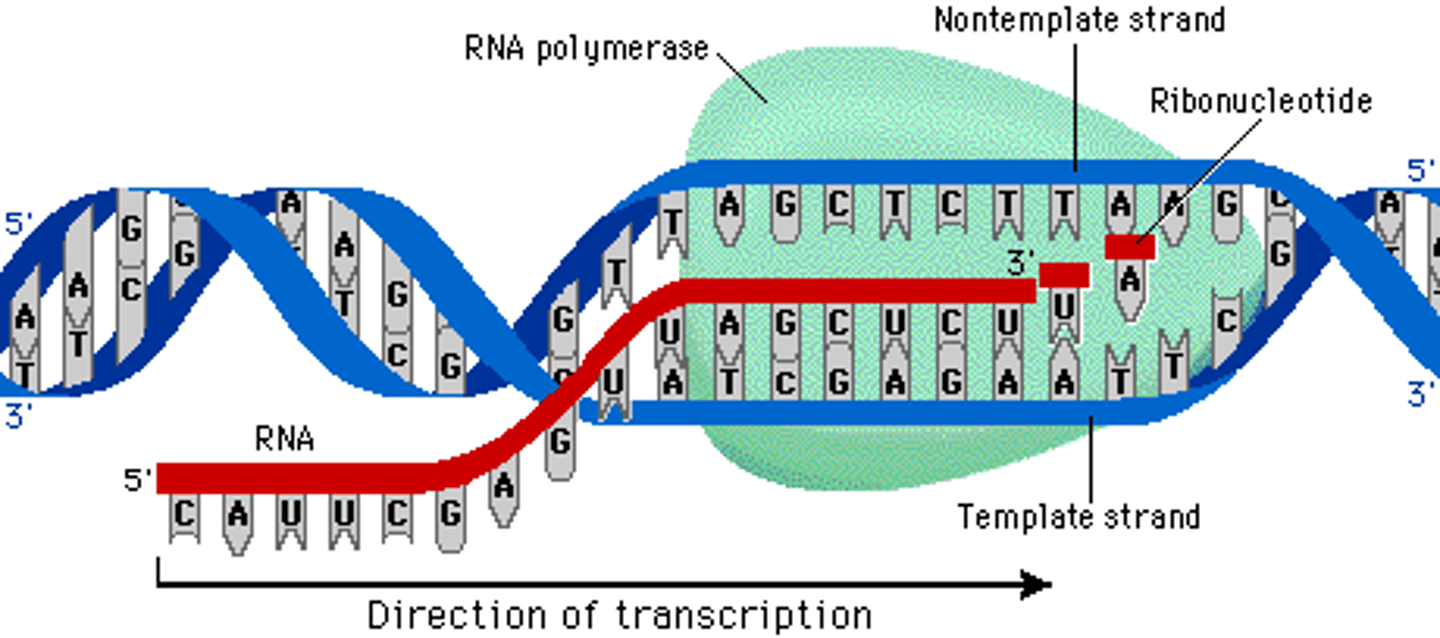
RNA polymerase
Enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands during transcription
An enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription, using a DNA strand as a template.
mRNA
A type of RNA, synthesized from DNA, that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein; also called messenger RNA.
Stages in Transcription
initiation, elongation, termination
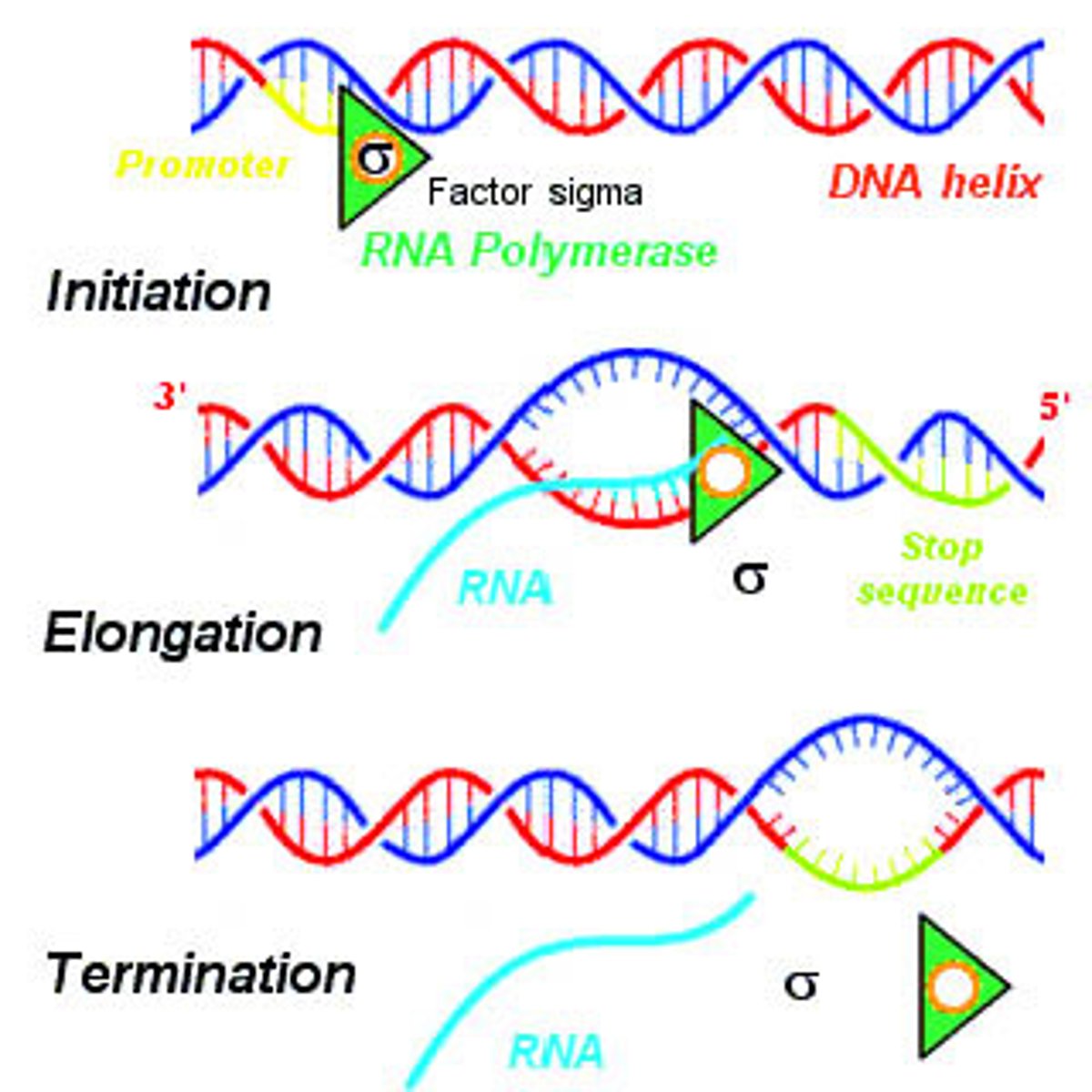
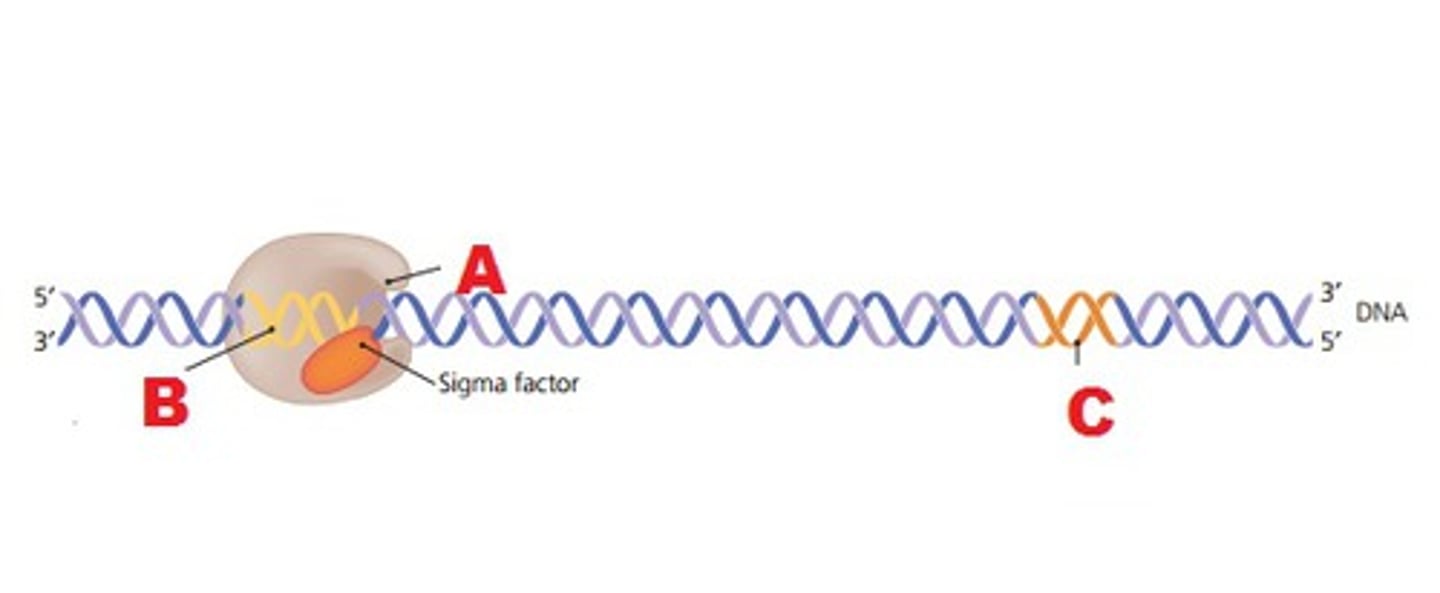
Initiation in transcription
Attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter
RNA polymerase binds to a promoter start (start!)
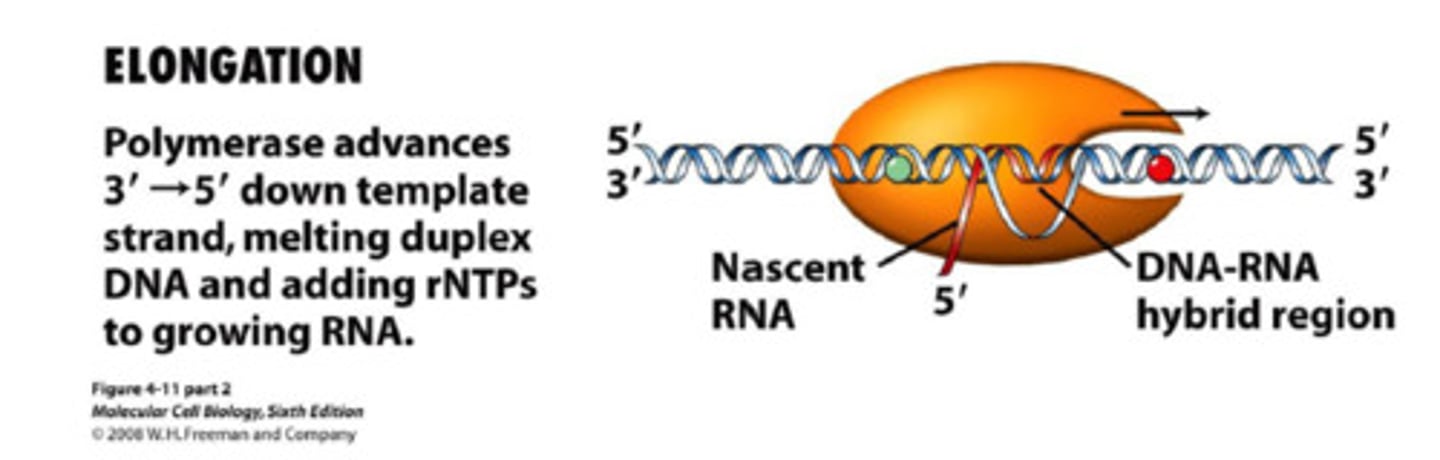
elongation In transcription
RNA nucleotides are added to the chain
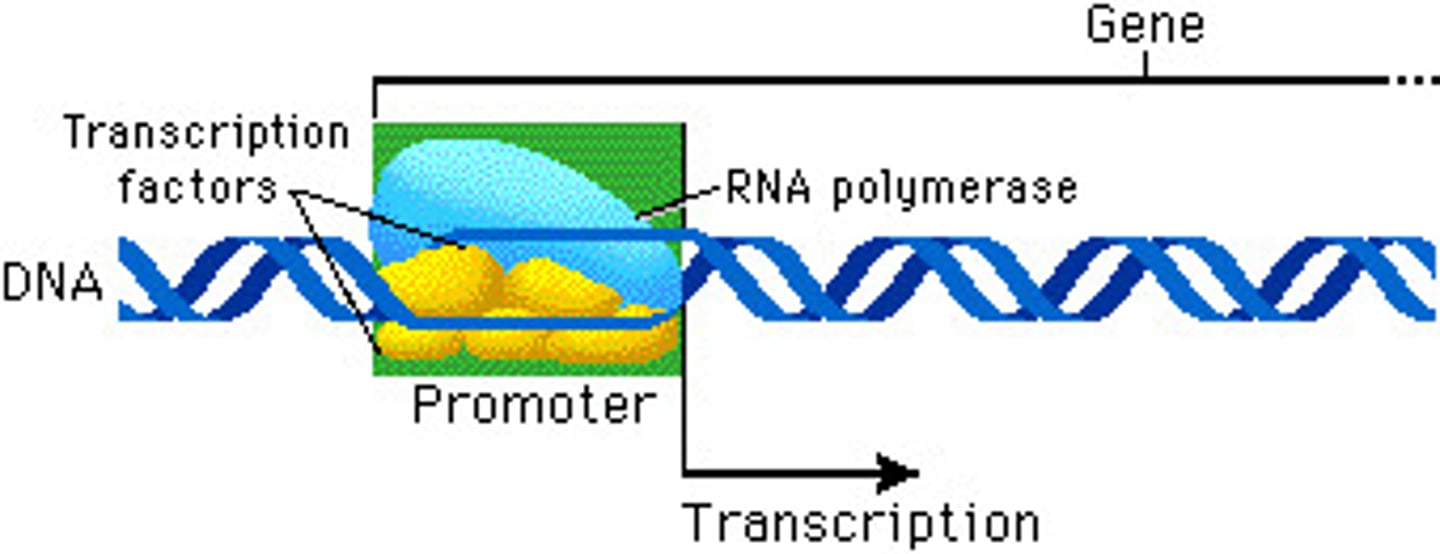
promoter
A specific nucleotide sequence in DNA that binds RNA polymerase and indicates where to start transcribing RNA.
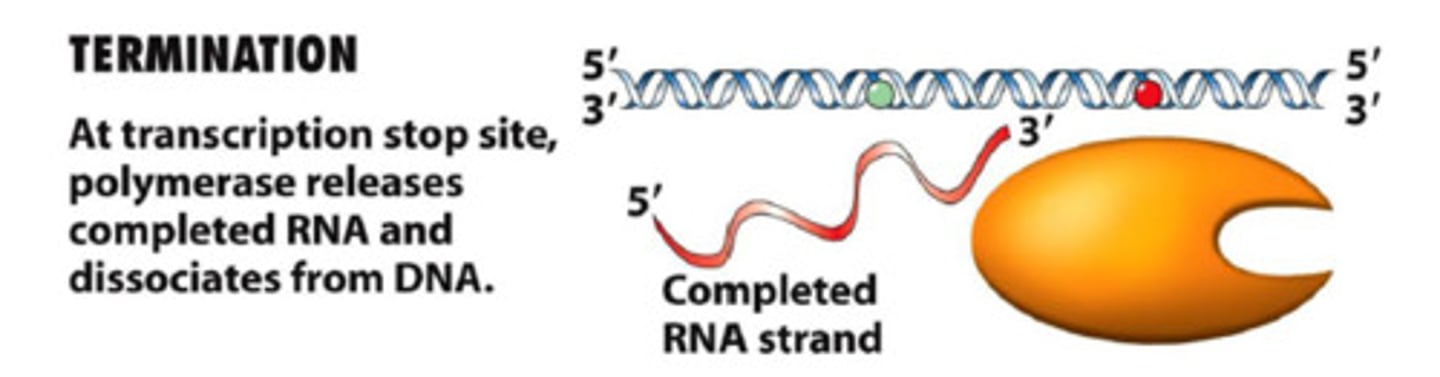
Termination in transcription
RNA polymerase reaches a terminator sequence (Stop codon) and detaches from the template
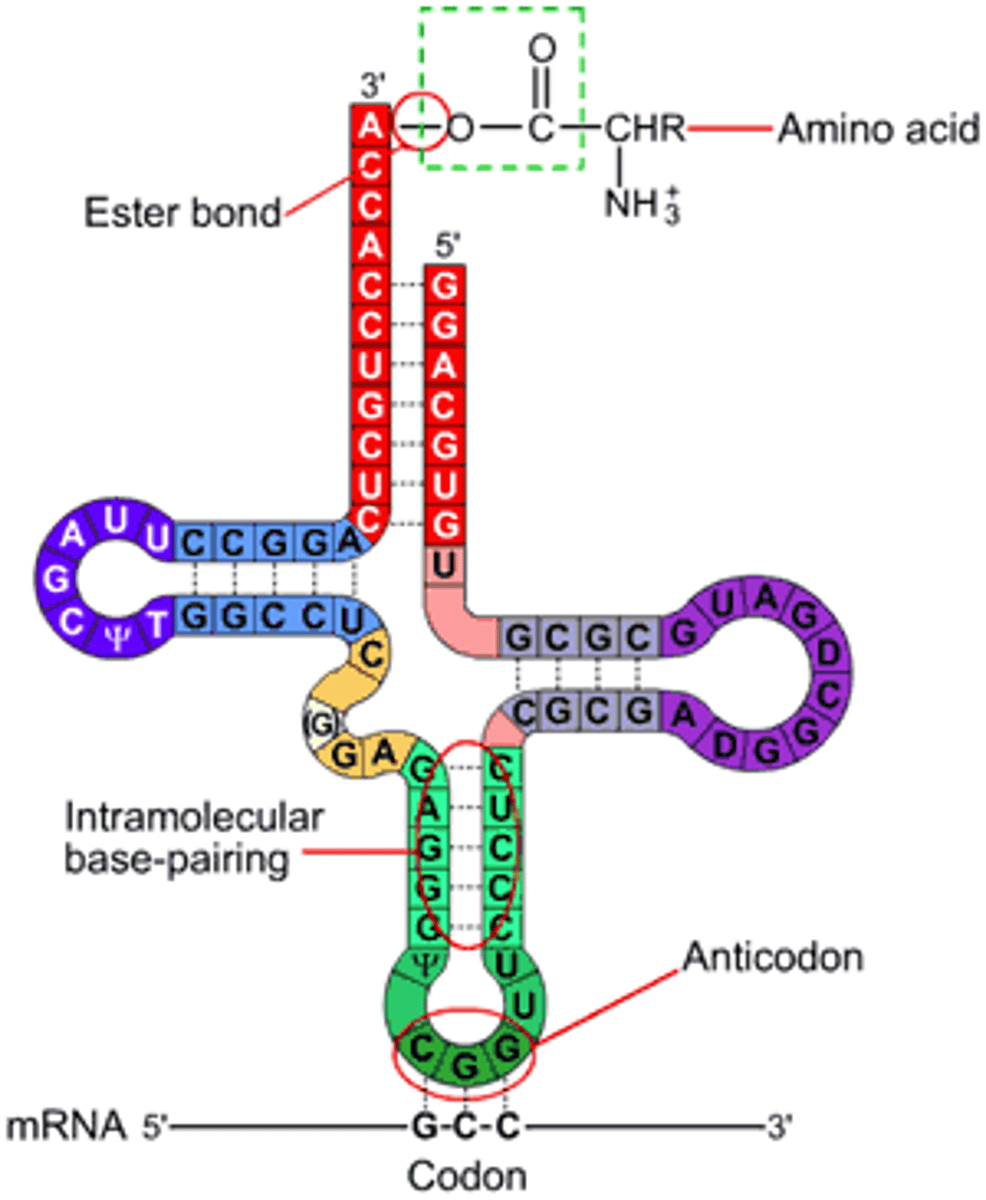
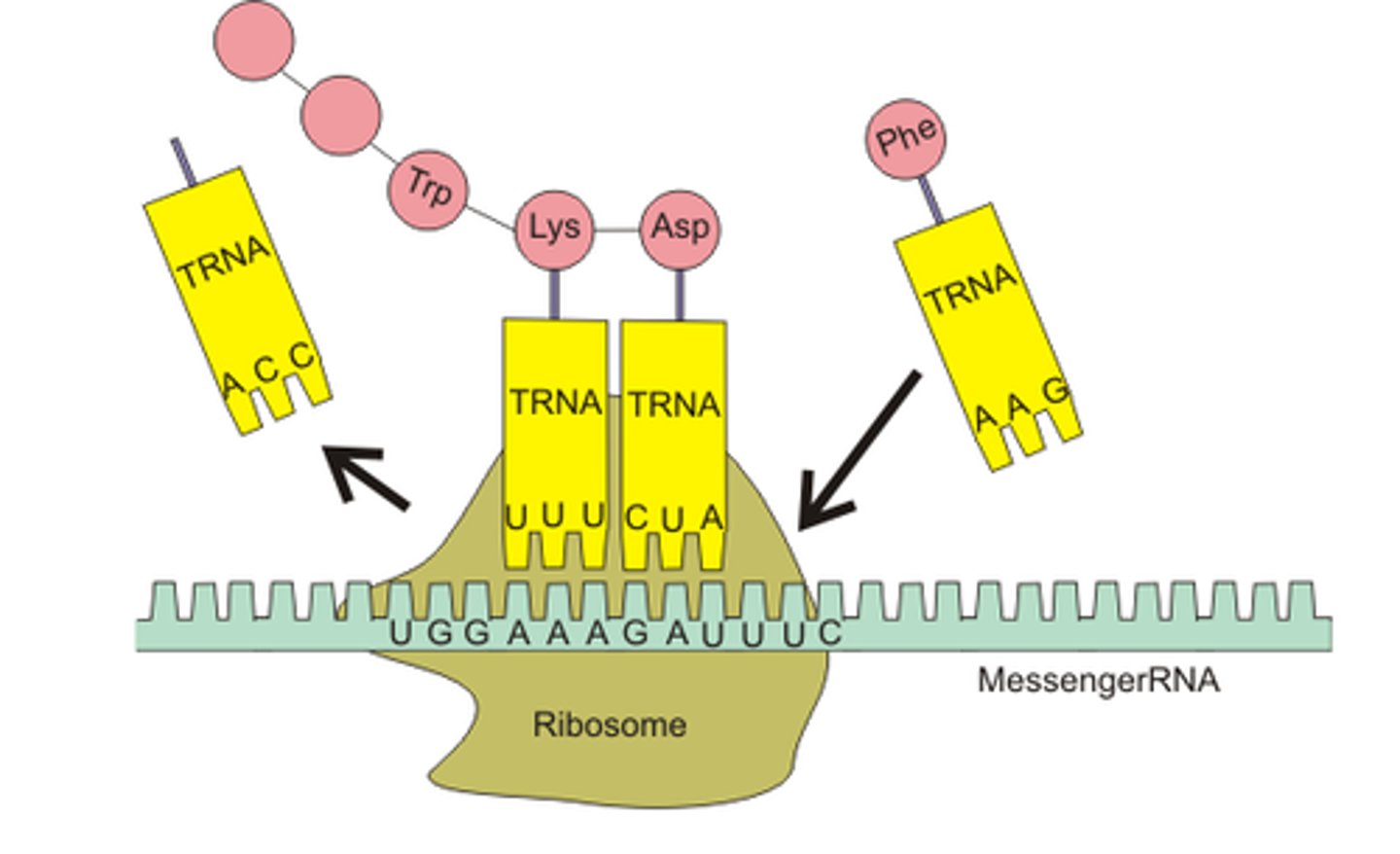
tRNA
An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA
rRNA
-gives physical support for mRNA and tRNA
Ribosomal RNA
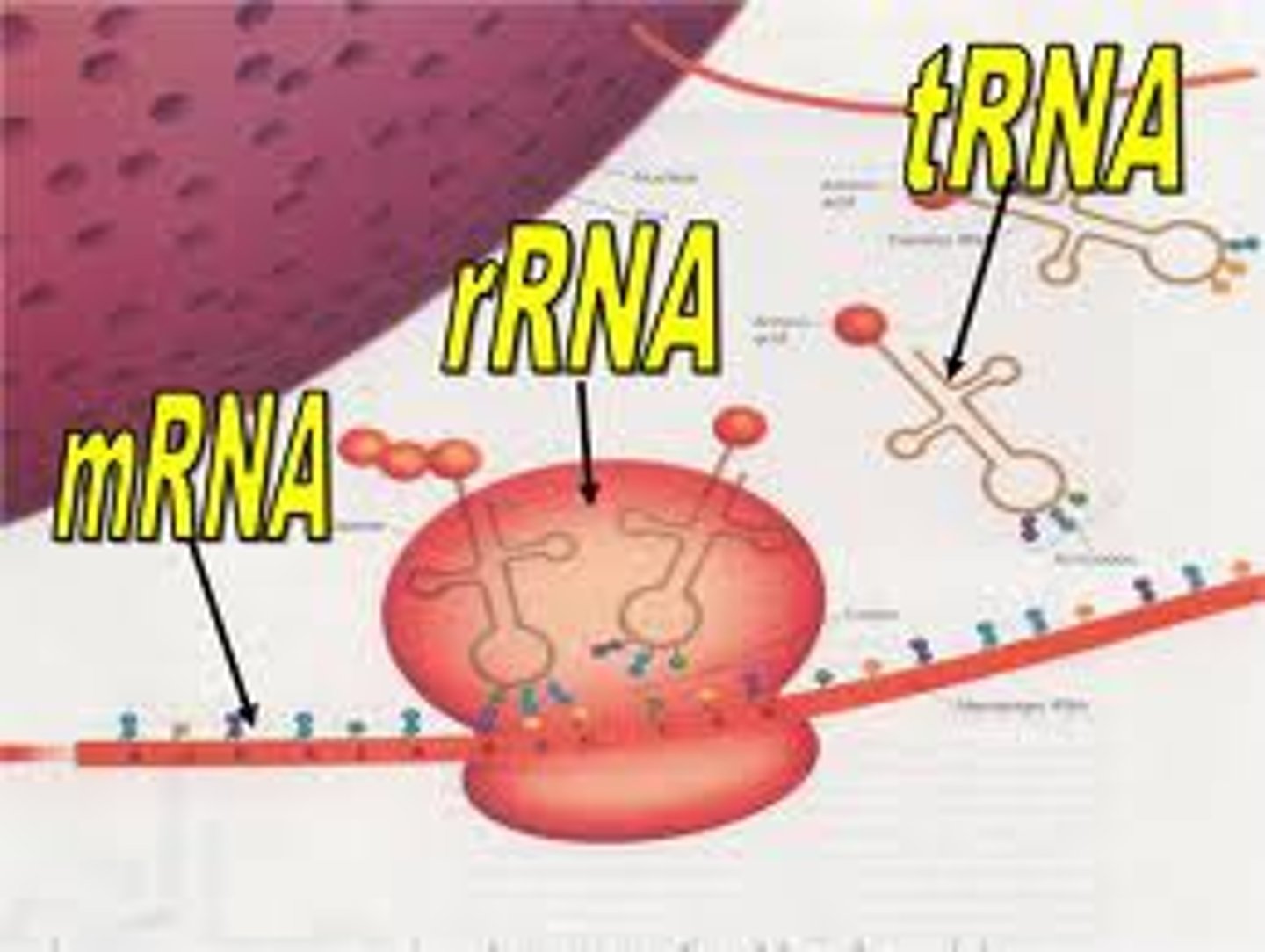
Ribosomes
Cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesized.
A cell organelle constructed in the nucleolus and functioning as the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm; consists of rRNA and protein molecules, which make up two subunits.
Translation
(genetics) the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosomes in the cytoplasm
Decoding of a mRNA message into a polypeptide chain
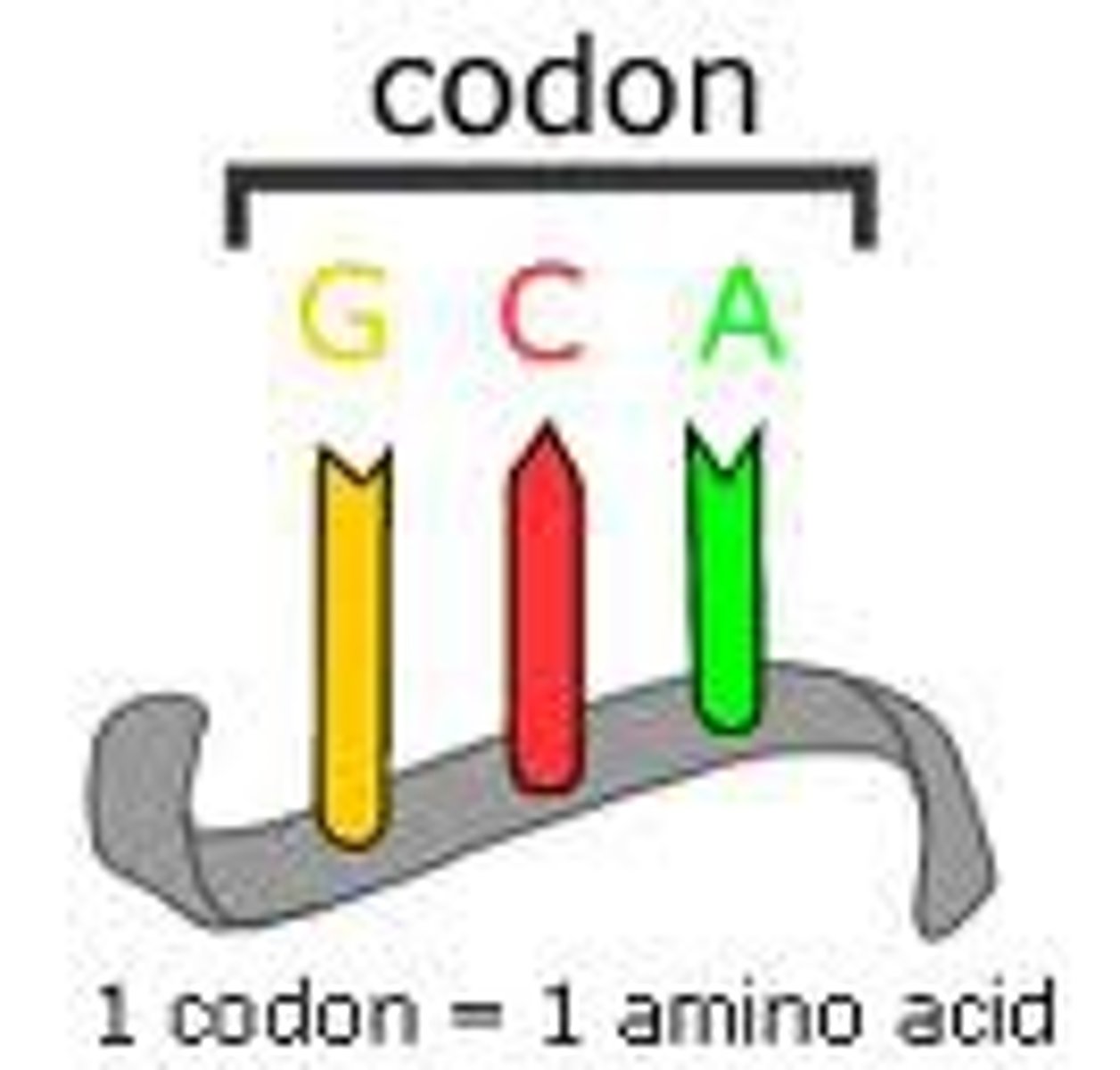
Codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid
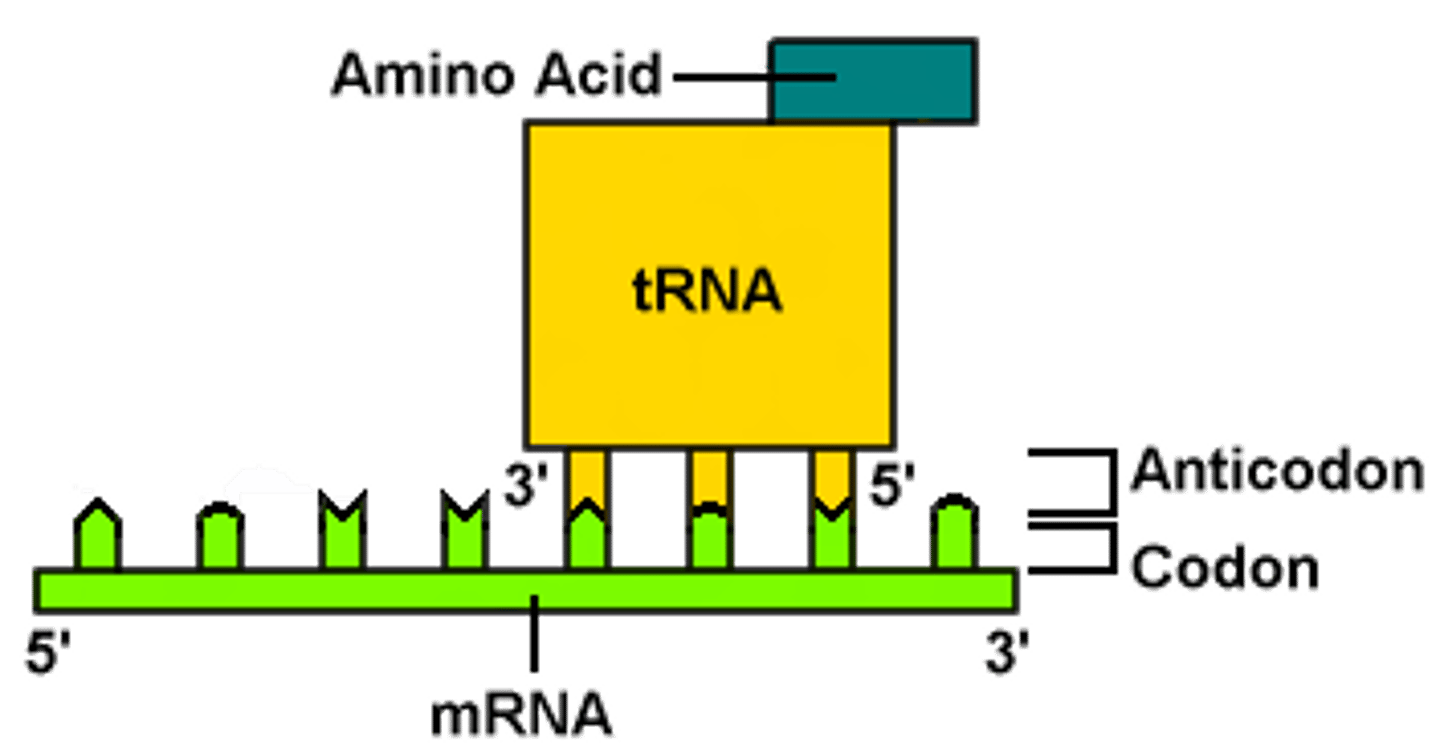
Anticodon
A sequence of three bases of a tRNA molecule that pairs with the complementary three-nucleotide codon of an mRNA molecule during protein synthesis.
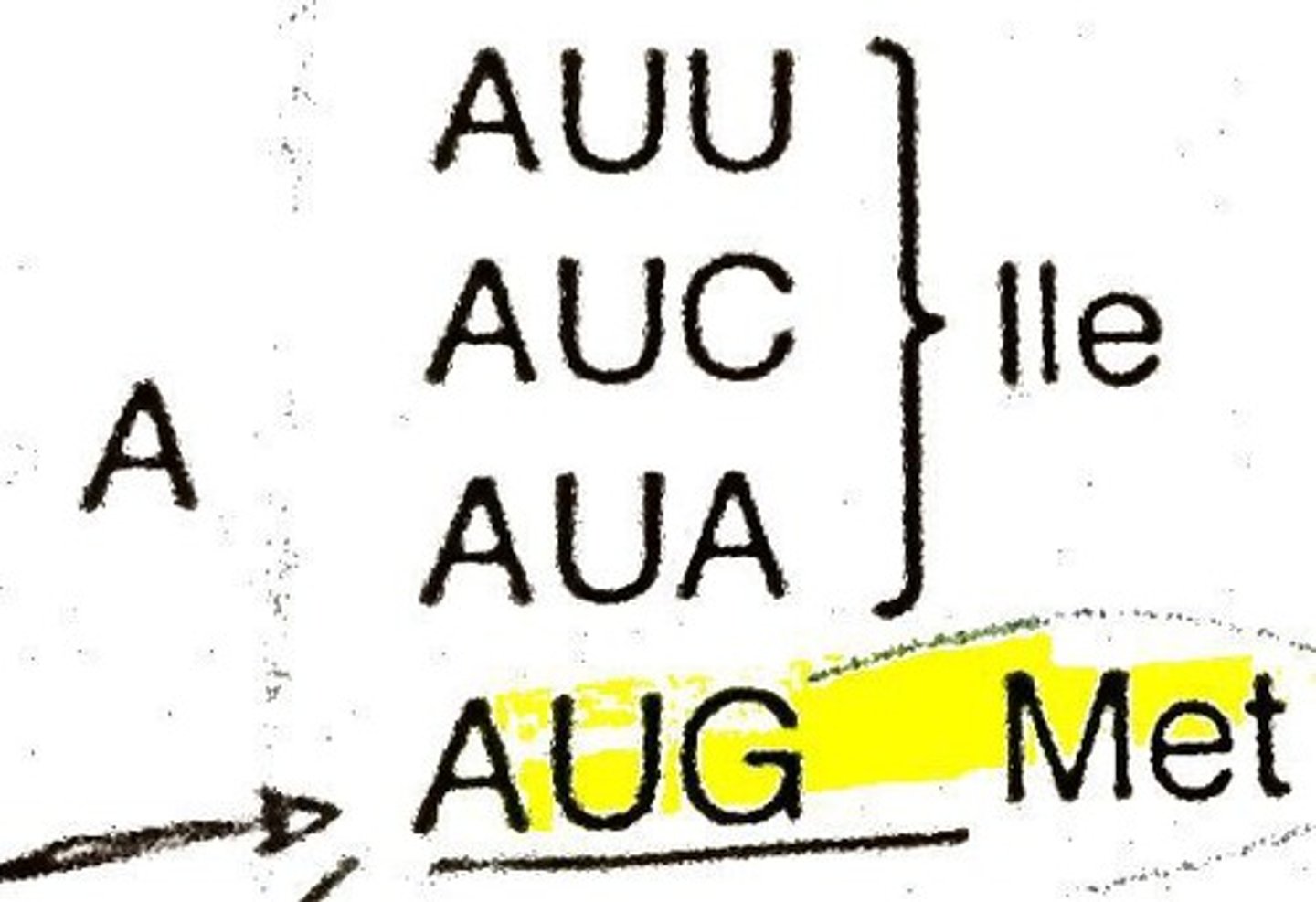
Start codon
AUG; the codon that begins all RNA.
AUG (methionine)
specific codon (AUG) that signals to the ribosome that the translation commences at that point
Stop codon
UAG, UAA, or UGA; the codon that ends all RNA.
Codon that signals to ribosomes to stop translation
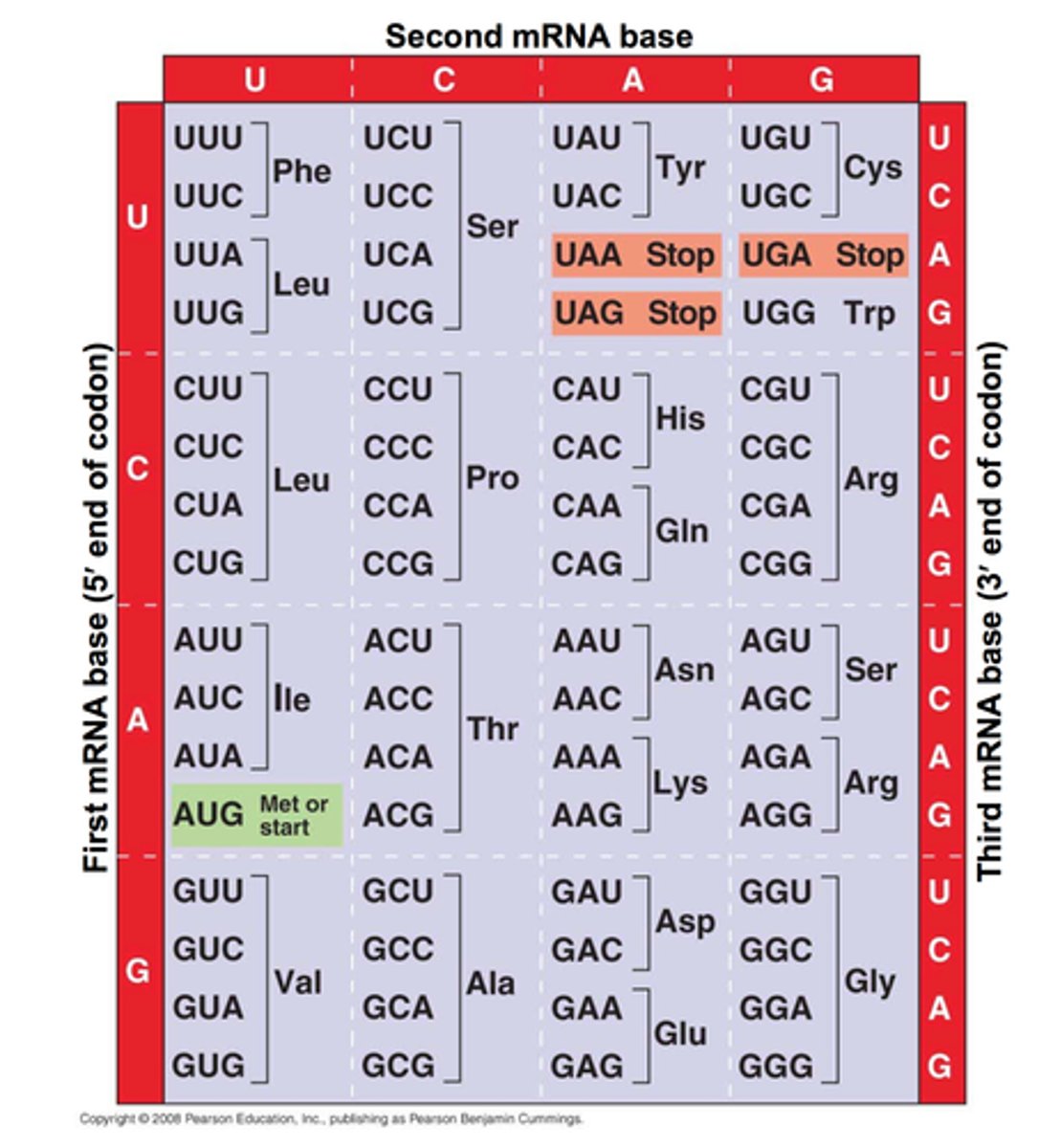
degenerate codon
A codon that specifies the same amino acid as another codon.
more than one codon codes for amino acid
Codon table
shows all 64 codons with the amino acids they code for.
Nucleus
Contains DNA
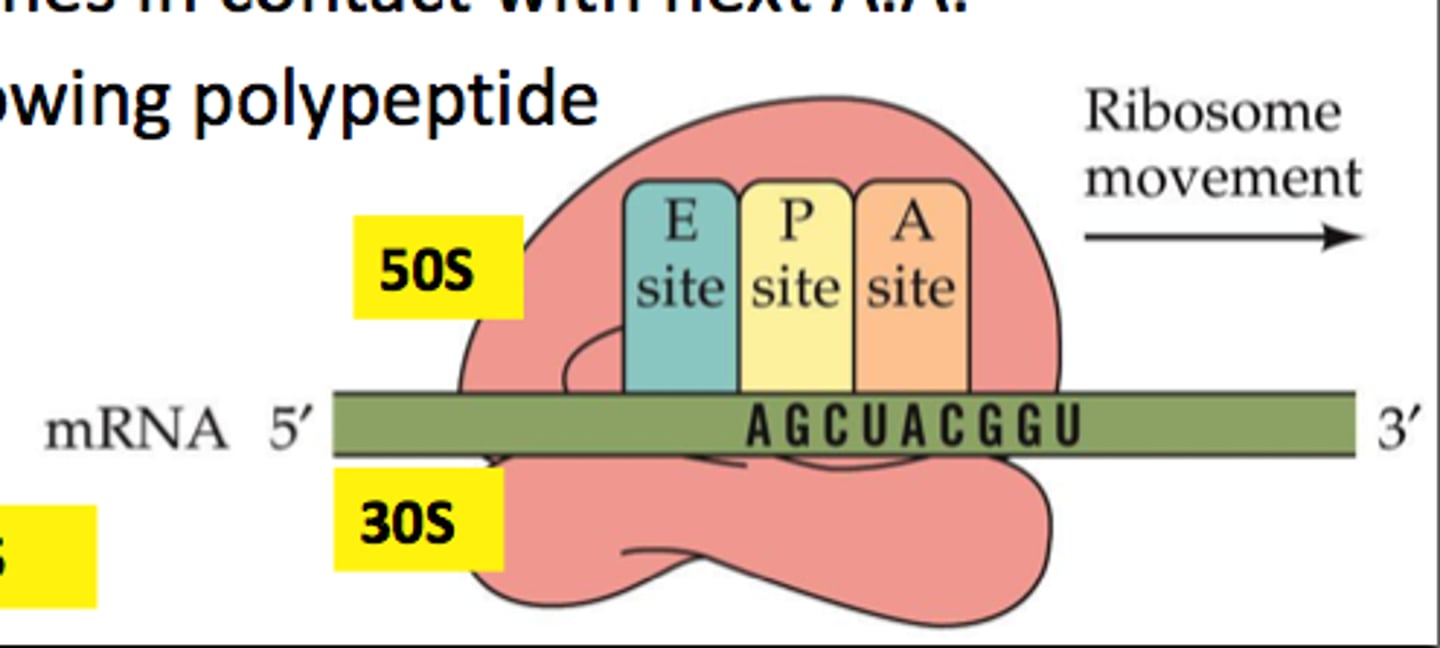
exit site on Ribosomes
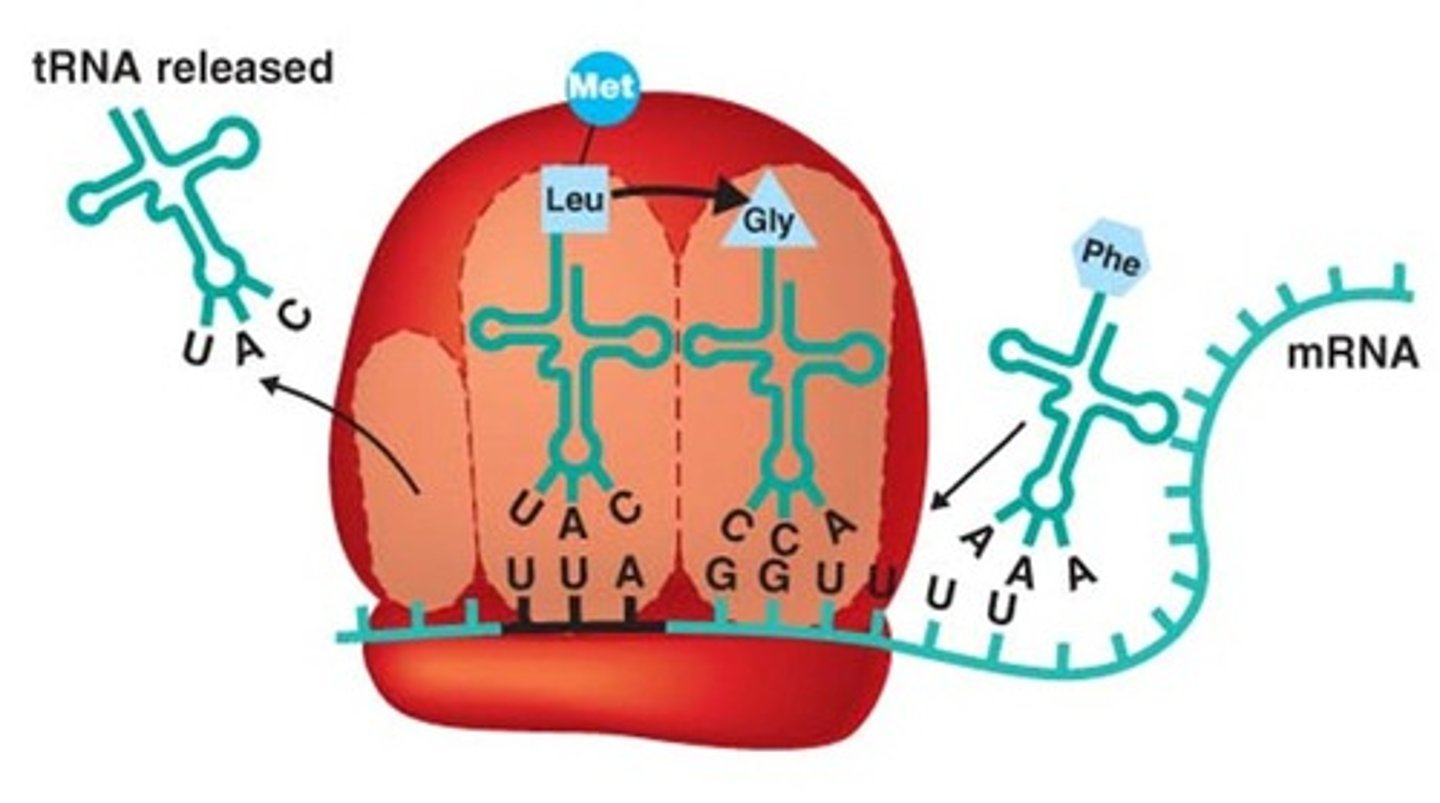
P and A site on Ribosomes
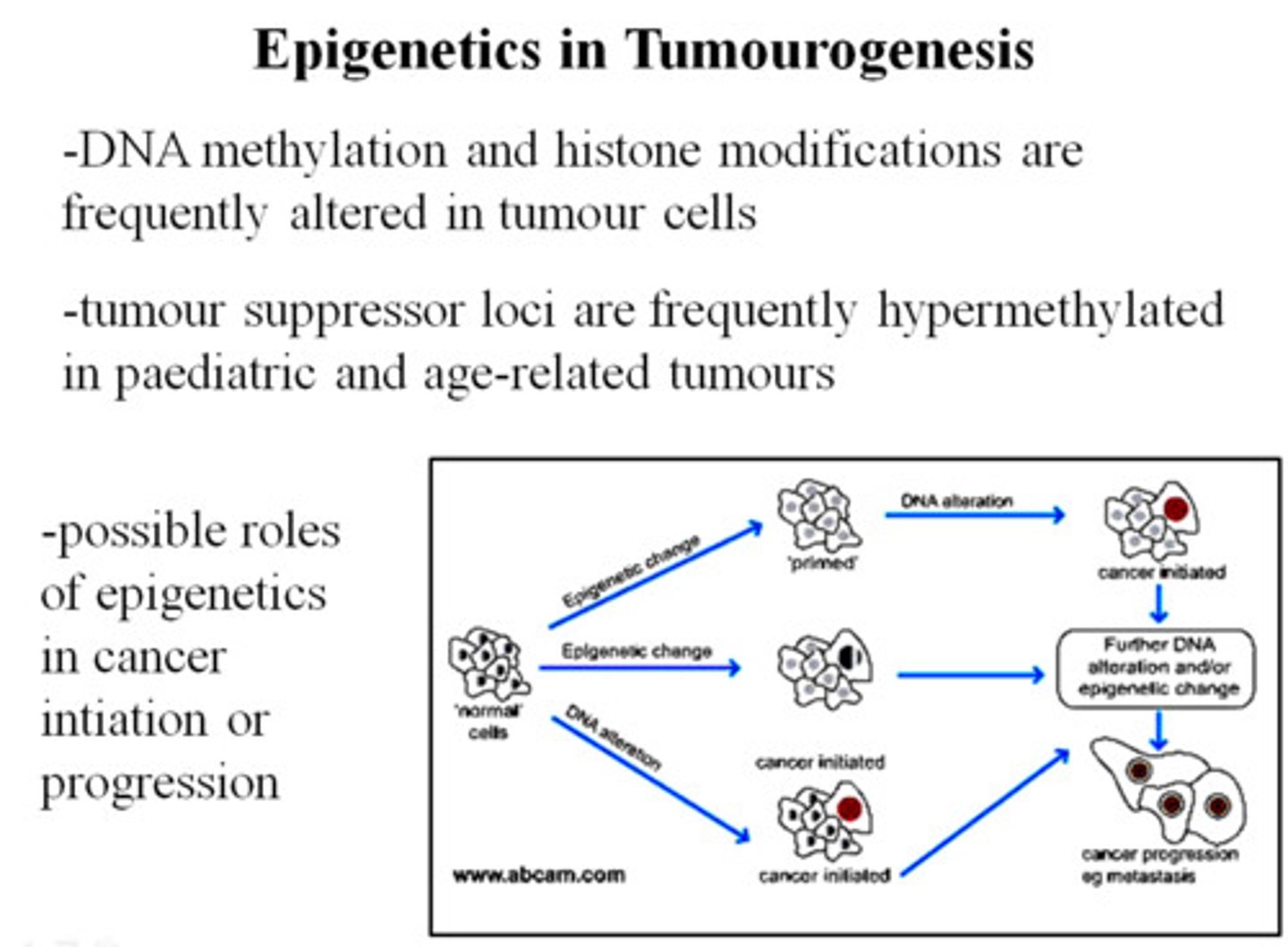
epigenetics
HERITABLE changes in expression of a gene that changes phenotype but not the DNA itself... just changes in chromatin structurer
origin of replication
Site where the replication of a DNA molecule begins, consisting of a specific sequence of nucleotides.
short stretches of DNA having a specific sequence of nucleotides
eukaryote origin of replication
many (maybe in the thousands) origins of replication
prokaryote orgin of replication
one orgin of replication