3.4: Carrying capacity
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Population growth models
Mathematical equations that can be used to predict population size at any moment in time.
Some uses: protect endangered species, manage hunting/harvesting, control pests
Exponential Growth (J Curve)
This means there are no limits making it unsustainable. In natural environment, resources become scarce and harmful waste builds up.
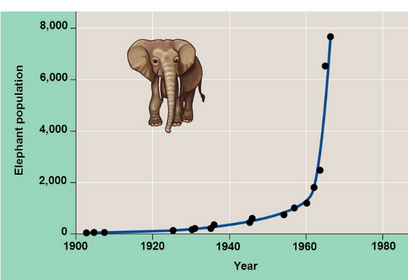
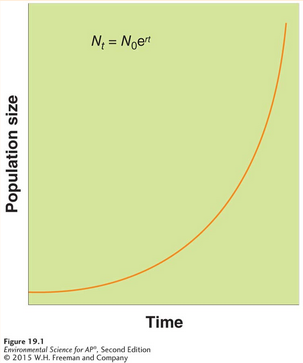
Exponential Growth Formula
A growth model that estimates a population’s future size (Nt )
after a period of time (t),
based on the intrinsic growth rate (r)
and the number of reproducing individuals currently in the population (N0).
(Nt = N0ert)
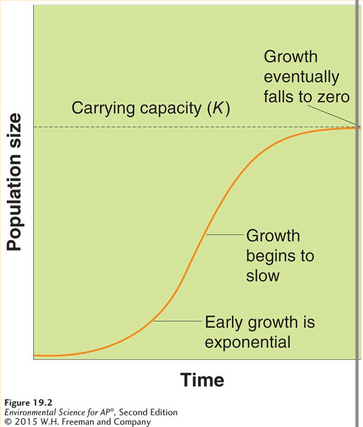
Logistic Growth Model
A growth model that describes a population whose growth is initially exponential, but slows as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the environment.
More realistic because it incorporates environmental limits.
S-shaped curve
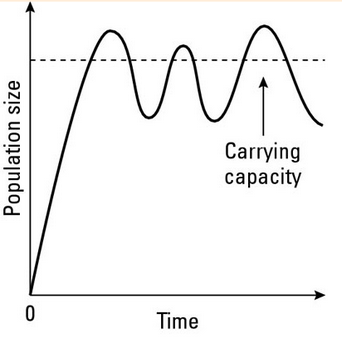
Variations on Logistic Growth Model
If food becomes scarce or other conditions change, a population can experience fluctuations.
Overshoot - When a population becomes larger than the environment’s carrying capacity.
Die-off - A rapid decline in a population due to death.
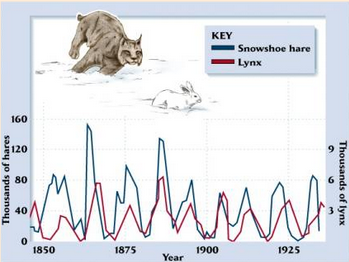
Polynomial Growth
Typical in predator/prey relationships
With food and low predators, prey grow
With more prey, predators then grow
As prey reach carrying capacity, they die off
As prey die, predators also die
With less predation and more food, prey population increases again
Limiting resource
A resource that a population cannot live without and that occurs in quantities lower than the population would require to increase in size.
Carrying capacity (K)
The number of individuals the environment can support over a long period of time. Due to limiting resources AND density dependent limiting factors.
Density Independent Limiting Factors
Any factor limiting the size of a population whose effect is not dependent on the number of individuals in the population.
A factor that could kill all members of the population regardless of whether the population is small or large; things that happen by chance.
does not determine carrying capacity
Density Independent Factors Examples
Climate (unseasonable cold snap)
Natural Disasters – flood, fires, earthquakes, volcanos, tsunamis, hurricanes, etc.
Density Dependent Limiting Factors
Any factor limiting the size of a population whose effect is dependent on the number of individuals in the population.
A factor where an individual’s chance of survival or reproduction depends on the number of individuals in the same area. Has a greater impact on a population as it grows in size.
determines carrying capacity
Density Dependent Factors Examples
Resources – food, shelter, mates
Disease
Predation (more death as population increases)
Build up of toxins
Stress (high density induces stress and makes hormonal changes to animals, reproduce less and die quicker