Plant Cell Organelles & Visualization Techniques for Biology Students
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the primary focus of the BI 368 course on plant cells?
To identify various cell organelles and discuss the approaches used to visualize them.
What plant species is used to study staminal hairs in this course?
Tradescantia pallida
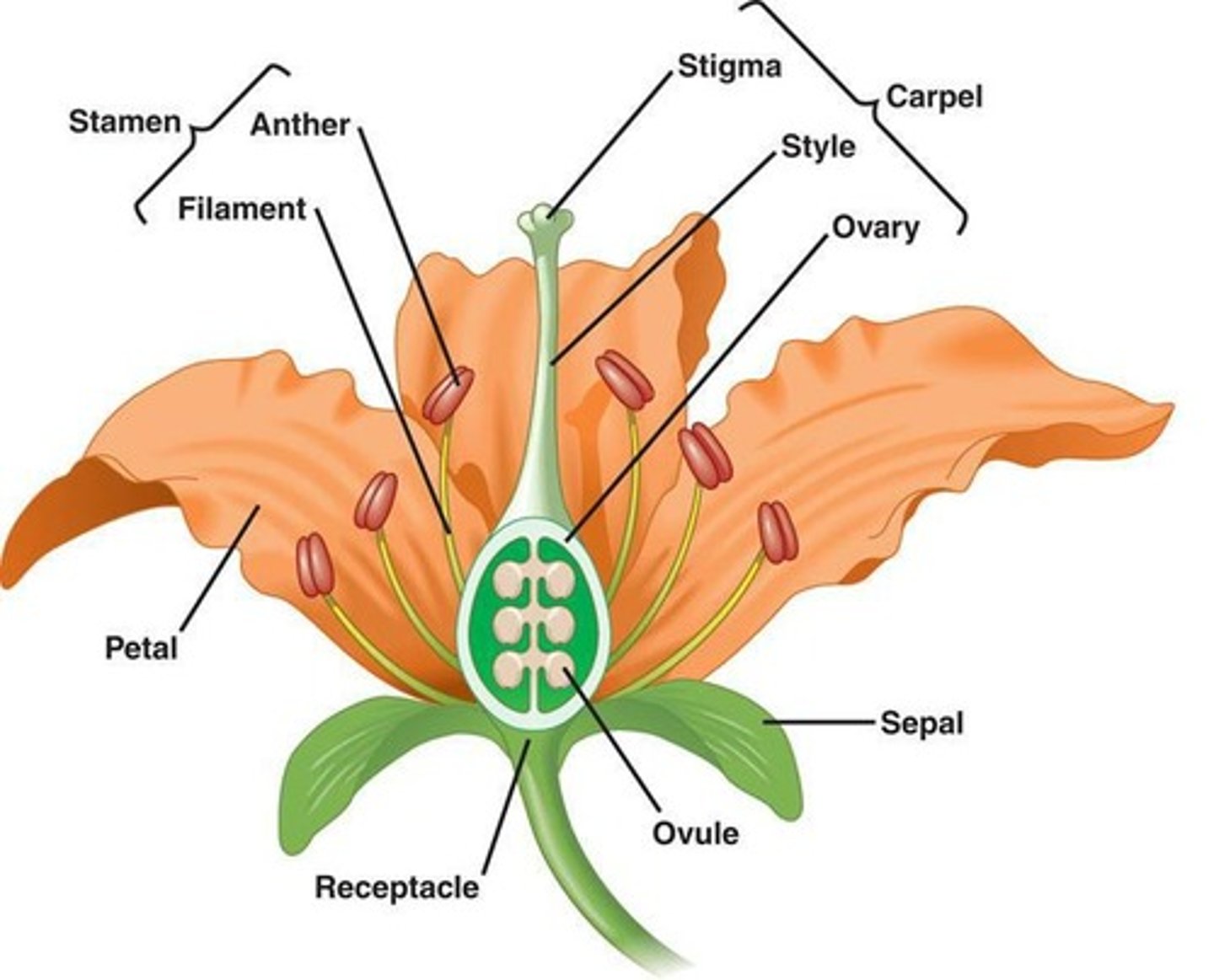
What are stamens in plant biology?
Male reproductive structures that include anthers and filaments.
What are trichomes?
Hairs present on filaments comprised of a series of individual cells.
Why do the cells of Tradescantia pallida staminal hairs appear purple?
Due to the presence of anthocyanins in vacuoles.
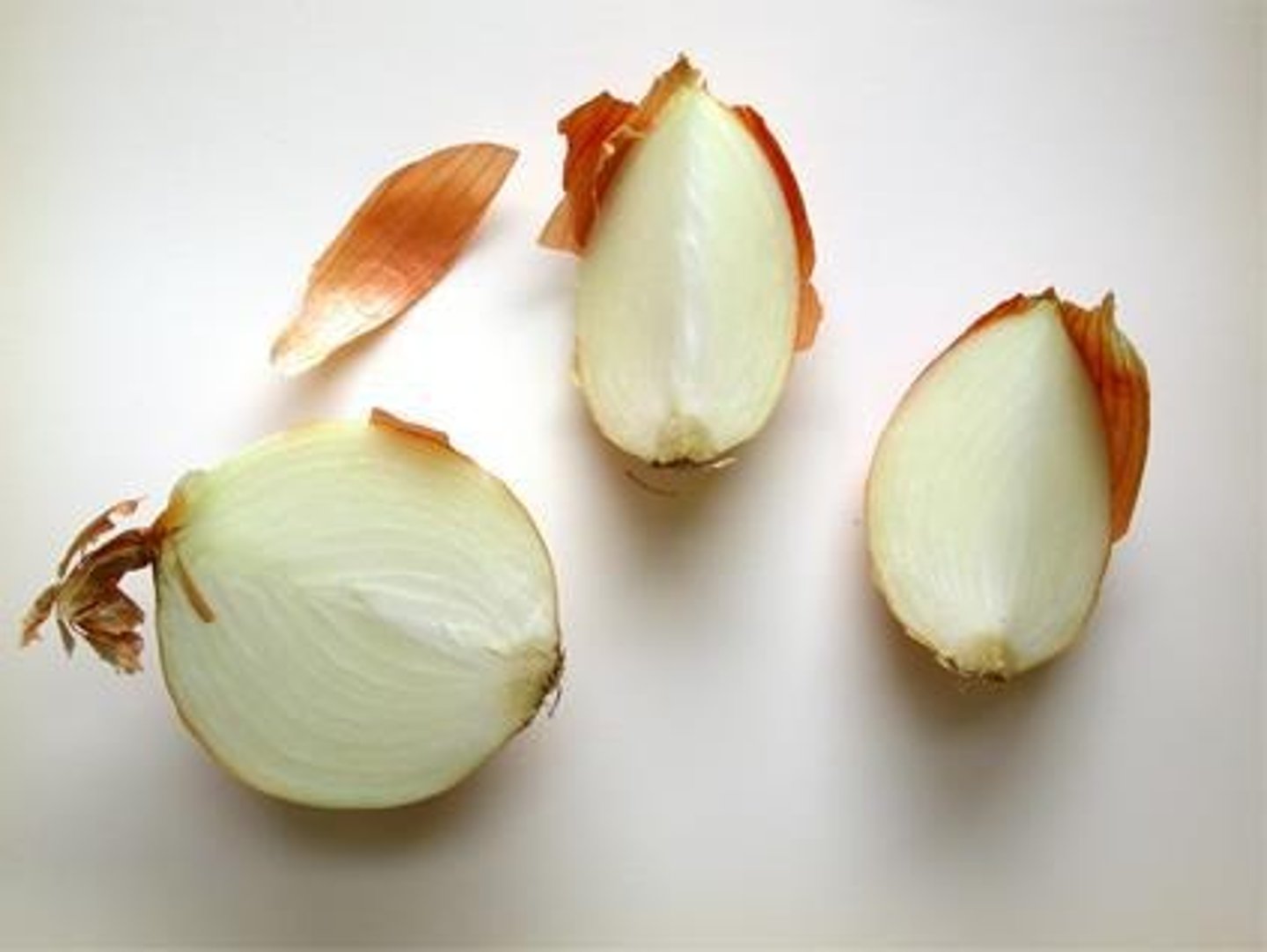
What is the first step in preparing an onion epidermal peel for observation?
Slicing the fleshy scale leaves of onion (Allium cepa) into sections.

What is 'optical sectioning' in microscopy?
A technique that allows for 3D visualization by moving the focal plane through the tissue.
What structures are visible in an onion epidermal peel?
Cell wall, nucleus, and cytoplasmic strands.
What is cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis)?
The movement of organelles and molecules within the cell along the cytoskeleton.
What type of light do typical lab microscopes use?
White (visible) light, which can be transmitted or reflected.
What is the purpose of epifluorescence microscopy?
To visualize structures that fluoresce under specific wavelengths of light.
What is the endosymbiont theory related to plastids?
It suggests that plastids are self-perpetuating organelles with a double unit membrane involved in energy processing.
What is visible in Asparagus fern cladophylls when viewed with UV epifluorescence?
Red chloroplasts.
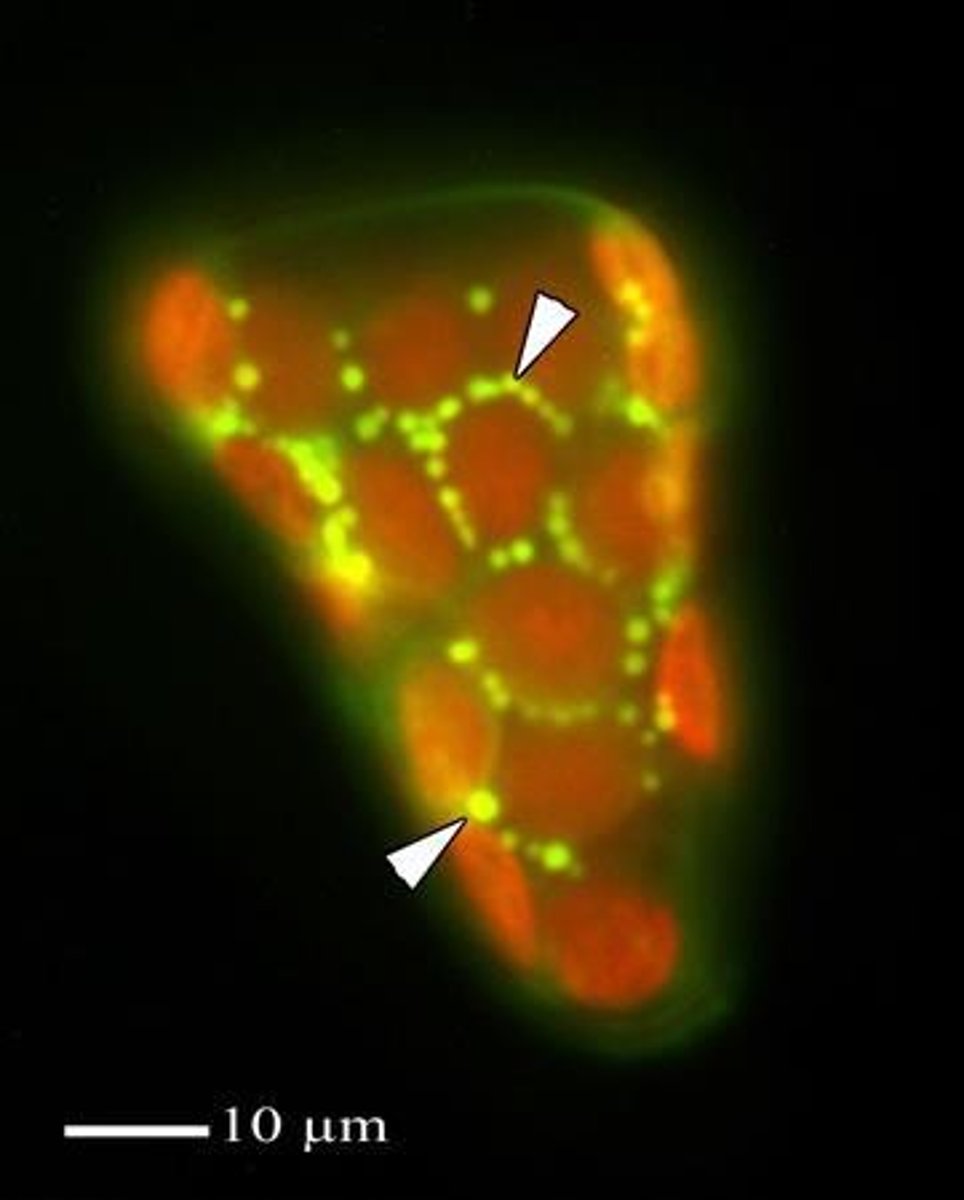
How are mitochondria visualized in Asparagus fern cells?
By staining with Rhodamine 123 and viewing under blue light epifluorescence.
What is the significance of using various wavelengths of light in epifluorescence?
Different wavelengths cause structures to glow or fluoresce based on their composition.
What are the steps involved in preparing an onion epidermal peel?
1) Slice into sections, 2) Separate scale leaves, 3) Remove epidermis, 4) Transfer to slide, 5) Add coverslip.

What is the role of vacuoles in plant cells?
To store substances such as anthocyanins that contribute to color.
What structures can be observed in Elodea canadensis during cytoplasmic streaming?
Cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuole.
What is the relationship between cytoplasmic streaming and human muscle contractions?
Cytoplasmic streaming uses mechanisms similar to those found in muscle contractions.
What is the purpose of adding a coverslip when preparing a slide?
To protect the specimen and improve the clarity of the image.
What are the main components of a flower that students should be able to label?
Stamens, petals, and other reproductive structures.
What is the origin of mitochondria?
Mitochondria originated from a prokaryote that was engulfed and could undergo aerobic respiration.
What is the origin of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts originated from a smaller prokaryote capable of photosynthesis that was engulfed.
What are the three types of plastids?
1. Coloured plastids (chloroplasts, chromoplasts) 2. Colourless plastids (leucoplasts) 3. Proplastids.
What are chloroplasts responsible for?
Chloroplasts contain chlorophylls and are involved in photosynthesis.
What pigments do chromoplasts contain?
Chromoplasts contain carotenoids, which can appear yellow, orange, or red.
What are amyloplasts and their function?
Amyloplasts are colourless plastids that store starch.
What do proteinoplasts store?
Proteinoplasts store proteins.
What do elaioplasts store?
Elaioplasts store lipids.
How can chloroplasts change during fruit ripening?
Chloroplasts may become chromoplasts as fruit ripens.
What is polarizing microscopy?
A technique using polarizing filters to allow light in one plane to pass, enhancing visibility of crystals.
What happens to light in polarizing microscopy?
Light moves in waves in all orientations, but polarizing filters restrict it to one plane.
What is the effect of crystals in polarizing microscopy?
Crystals change the plane of polarized light, causing them to shine against a dark background.
What are anthocyanins?
Anthocyanins are red, orange, or blue water-soluble pigments found within vacuoles.
Where can anthocyanins be found?
In vacuoles of plants such as African violets and geraniums.
What are ergastic substances?
Compounds synthesized by plants with little turnover, including crystals, pigments, and phenolics.
What types of crystals are considered ergastic substances?
Types include prismatic, druse, and raphide crystals.
What is the role of calcium oxalate in plants?
Calcium oxalate can act as an antifeedant.
What is the significance of the Maltese cross pattern in starch grains?
It results from the crystalline nature of starch grains observed under polarized light.
What is the function of leucoplasts?
Leucoplasts are involved in storage and do not contain pigments.
What is the difference between proplastids and plastids?
Proplastids are undifferentiated plastids that can develop into various types of plastids.
What are the characteristics of druse crystals?
Druse crystals are typically found in clusters and can be seen in various plant tissues.
What is the function of raphide crystals?
Raphide crystals are needle-shaped and can serve as a defense mechanism against herbivores.