Chem 103 Exam 1
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What was correct about the Greek’s theories of Atoms
Brownian motion: random motion of atoms and particles, and the idea that the molecular level of a structure of a substance determines the observable properties
What claims did Thomson make about the structure of the atom
The atom was a positively charged structure with various electrons embedded around it.
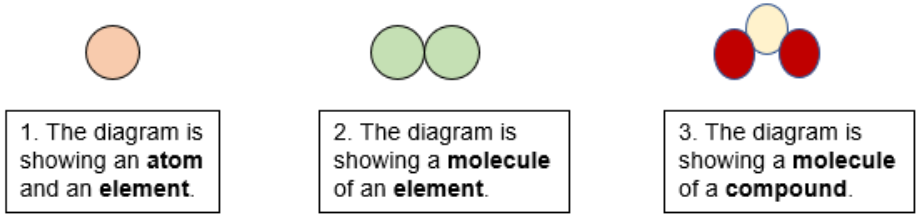
Atom vs Element
Atoms are not visible on the macroscopic level where as elements are a collection of atoms that are visible on the macroscopic level
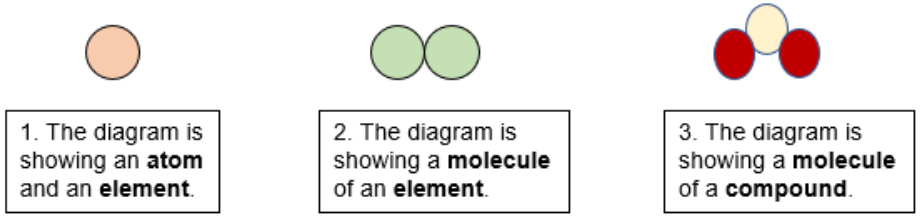
Compound
a pure substance made up of two or more different chemical elements
What parts of daltons atomic theory are true
Atoms of a given element are different from atoms of other elements, compounds are formed by combinations of atoms of two or more elements, and chemical reactions are due to rearrangements of atoms, they’re neither created nor destroyed
What parts of Daltons’ Atomic theory were disproved by Thomson
The idea that elements are composed of indivisible particles(atoms) and that atoms are the smallest unit of matter.
Thomsons plum pudding model of the atom
The idea that atoms contain electrons in a positively charged structure
What was Thomsons evidence that all atoms contain electrons
In the cathode ray experiment the particles of the ray emitted were identical regardless of the type of metal used for the cathode)
What did rutherfords experiment show
The atom is mostly empty space with a small dense positive nucleus in the center of the atom
How did rutherfords experiment show the existence of the nucleus
When the radioactive source was directed through the gold foil most particles went straight through but a few deflected off
What is an interaction?
A force=push or pull
Gravity
responsible for attraction between objects that have mass
Electromagnetic force
Responsible for attraction/repulsion between objects that have an electric charge
Key facts about gravitational forces
objects with mass are sources of gravitational fields and are affected by the gravitational fields of all other objects with mass, they require two or more objects, and are always attractive
How are changes in energy caused
Changes in forces, energy is conserved and cannot be destroyed or created
First law of thermodynamics
energy is never lost, only transferred or transformed
Kinetic energy vs Potential energy
energy associated with motion vs energy associated with the position of a system of objects in a field
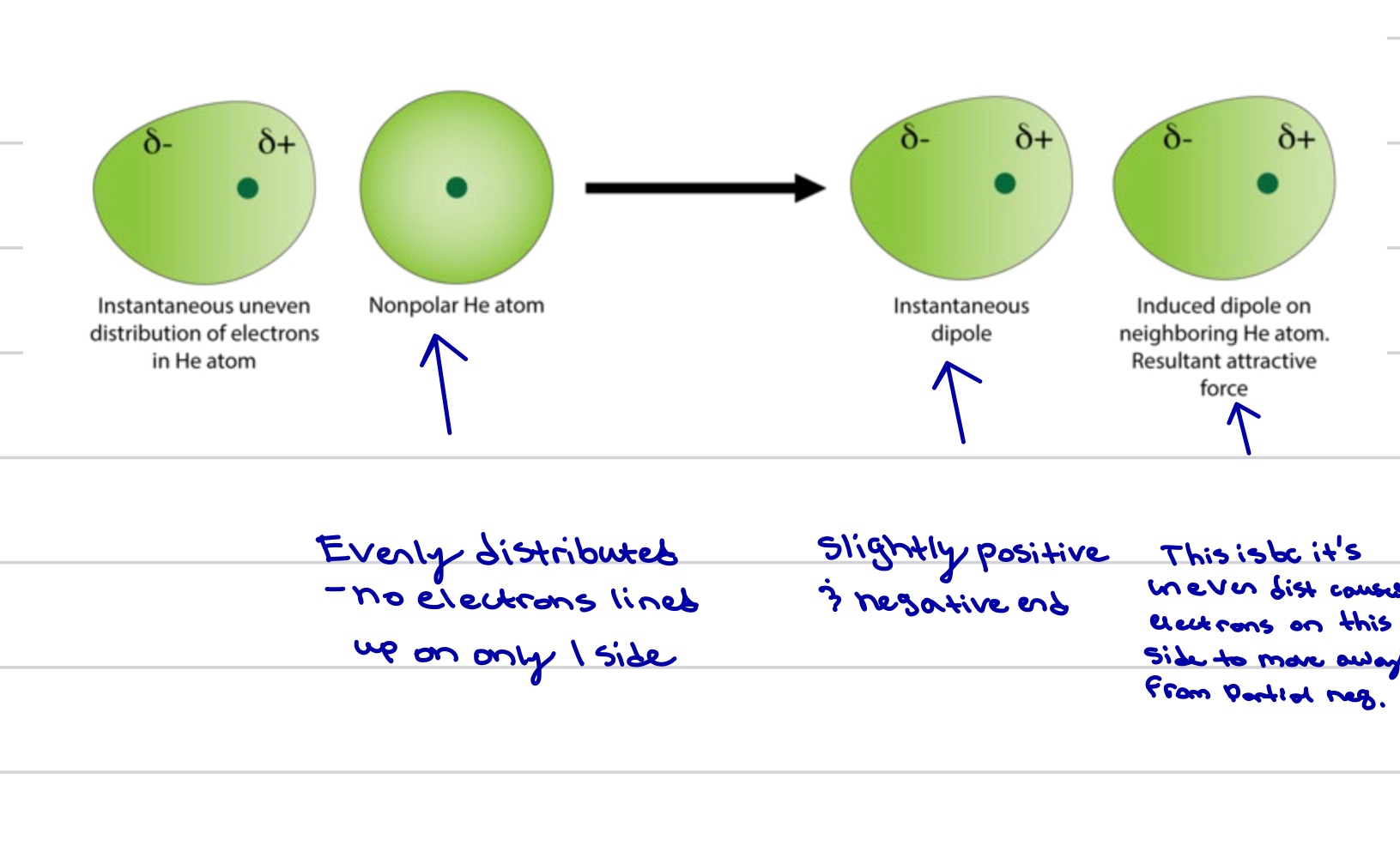
London dispersion forces
Caused by the random movement of electrons in the particle, and instantaneous dipole with uneven distribution of electrons, induces the adjacent atom resulting in an induced dipole on said neighboring atom.
Key ideas of solid states of matter
rigid shape, defined volume which is independent of its shape, not compressible
Key ideas of liquid states of matter
takes on shape of container, molecules move in relation to one another, fixed volume, not compressible
Key ideas of gaseous states of matter
Molecules are apart and moving at high speeds (collisions), no fixed volume or shape, compressible
When two atoms approach each other and get too close what happens?
The electron clouds overlap and the repulsive force becomes dominant
As attractive force brings atoms very close together what happens and what does this do to the potential energy of the system?
Electrons overlap causing the atoms to begin to repel each other in this process the potential energy increases. (attraction is still occuring)
As repulsion slows down the atoms what eventually happens and what does this mean for the potential energy of the system?
the atoms eventually stop and move apart and when this happens the potential energy of the system decreases
As a positive particle moves towards a positive particle what happens to the electrostatic force and the potential energy
The electrostatic force of repulsion increases, and the potential energy increases
As a negative particle moves towards a negative particle what happens to the electrostatic force and the potential energy
The electrostatic force of repulsion increases, and the potential energy increases
As a negative particle moves towards a positive particle what happens to the electrostatic force and the potential energy
The electrostatic force of attraction increases and the potential energy decreases
What happens to energy when a chemical bond is formed?
energy is released
What happens to energy when a chemical bond is broken?
Energy is absorbed
What happens to energy when one chemical bond is broken and one is formed simultaneously
Energy is released or absorbed depending on the strengths of the bonds formed vs broken
At the potential minimum which force is the strongest
ESF attraction= ESF repulsion
Key facts about LDF’S
they increase with the size of the atom/molecule(#of electrons), increase with surface area, and are part of a range of intermolecular forces between particles
Potential energy well
the distance where the attractive forces are maximized and the repulsive forces are minimized
What does potential min represent
The relative stability of the molecule or atom (its resistance to change with how strong the bond is)
What does the distance between the potential min and x-axis represent (potential well)
how much energy would be needed to overcome the interaction (the lower the min the more energy required and vise versa)
How is energy transferred when you change the temperature of a system
Through collision
If we wanted to overcome this interaction and lower the energy in the system, how would this be done
increase the # of atoms to inc the amount of collisions and transfer the kinetic energy which lowers the total energy
Relationship between thermal energy and kinetic energy?
Thermal energy is a measure of the sum of KE (1/2mv²) of all the atoms
Relationship between temperature and KE
Temp is directly related to avg KE (1/2mv²) of the atoms
The more water molecules
the greater the thermal energy
Temp is independent of
the mass of the sample
Diatomic elements
H N Fl O I Cl Br
Why are LDF’S weaker than covalent bonds
LDF’s hold molecules within a substance whereas covalent bonds hold atoms together within a molecule
In H2 in its solid state what holds the nuclei together within the H2 molecule,
Covalent bond
In H2 in its solid state why do molecules of H2 stick to other molecues of H2
LDF’s
At H2’s gaseous state what interactions are present
Covalent bonds are still intact but there is no LDF interaction
When H2 surpasses its boiling point temp>600k what bonds or forces are present
Neither covalent bonds or LDF’S are present
Why does Cl2 have a higher boiling point than Ar
Because Cl2 is a diatomic it has a larger atomic mass, the larger the atomic mass(more electrons) the higher the LDF’s which means the attractive force is stronger requiring a higher boiling point to overcome this interaction.
Grams ←> moles
molar mass
mol a ←> mol b
molar ratio
mol ←>
avogadros # 6.022×10²³
Percent yield formula
Experimental (yield/theoretical yield) *100
Relationship between PE and KE
as one inc the other dec
Solute vs solvent
solute is a minor component, and solvent is a major component
Solution vs mixture
solution: homogenous: same composition all the way through the sample, wont unmix, mixture: heterogenous: different composition depending on sample point, easy to unmix.
Ex of solution vs mixture
salt and water vs chocolate chip cookie
Why would the PE diagram of an atom be further right than the other?
x-axis is distance between the center so if the atom is bigger it will be harder to the centers to be closer so if the atom is bigger it will be further to the right
Why can certain atoms exist as liquid and solid
This is due to the random movement of electrons causing instantaneous dipoles which then induce neighboring atoms these LDFs allow the molecules to be close to one another, as they are in solid or liquid phases.
Determining excess of a reaction
Find the LR convert that to mols of your ER and subtract that from the orginal ER that you found
Determining how many g are produced from a reaction
Find the LR in mols and convert to grams
Calculating concentration
g to mols then M=mols/Liters
Relationship between M and V
M1V1=M2V2