Honors Chemistry Unit 3 (Modern Atomic Theory)
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
How is the nucleus of a nuclear atom?
positively charged and dense
What structure of an atom contributes the most to the atom’s mass but very little to the atom’s volume.
the nucleus
what is the nucleus of an atom made out of?
protons and neutrons
how many nanometers does red visible light have?
700 nm
how many nanometers does violet visible light have?
400nm
list the visible light spectrum from lowest energy, frequency and longest wavelength to highest energy, frequency and shortest wavelength
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet
list the electromagnetic light spectrum from lowest energy, frequency and longest wavelength to highest energy, frequency and shortest wavelength
radio waves, micro waves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet light, x-rays, gamma rays.
what is wavelength
the length of a wave (m,cm,nm,…)
what is wavelength’s variable
λ (lambda)
what is the unit for wavelength when solving for wavelength?
meters (m)
what is frequency
the number of waves that pass a fixed point in 1 second
what is frequency’s variable
ν (nu)
what is the unit for frequency when solving for frequency?
Hertz (Hz)
What two things of a wave are inversely related
wavelength and frequency
what two things of a wave are directly related
speed and energy
what is speed
all ave energy that travels at the speed of light
what is the variable for speed
c
what does speed (C) equal
speed of light (2.998 × 10^8 m/s)
how can we find speed (C)?
c = λv
what is h?
Planck’s constant (6.626 × 10^-34 J x s)
what does the variable, E, stand for?
the difference in energy levels (Joule, J)
how can we find E? (there’s two equations)
E = hc/λ or E = hv
what is Avogadro’s Number?
6.022 × 10^23
what are periodic trends
recurring patterns down a group or across a period
what is atomic radius
½ the distance between the nuclei of 2 like atoms joined together (pm)
atomic size increases OR decreases down a group?
increases
why does atomic size increases down a group?
because of electron shielding (inner e-s “shield” the valence e-s from the attractive force of the nucleus)
atomic size increases OR decreases across a period?
decreases
why does atomic size increases across a period?
because of nuclear charge (as protons are added to the nucleus, there is more attractive force with the e-s)
what is ionization energy
energy required to remove and e- (kJ/mol)
does (Ei) (Ionization energy) increase OR decrease down a group
decreases
why does (Ei) (Ionization energy) decrease down a group
because of electron shielding (e-s are further from the nucleus so they are more easily removed)
does (Ei) (Ionization energy) increase OR decrease across a period
increases
why does (Ei) (Ionization energy) increase across a period
because of nuclear charge (increased positive charge of the nucleus holds e-s tighter)
In cations, what happens to the size of an ion when it loses a valence e-?
the resulting ion is smaller
why is the resulting ion smaller for cations?
the atoms loses an energy level
the attraction between the remaining e-s and the nucleus is increased
In anions, what happens to the size of an ion when it gains a valence e-?
the resulting ion is larger
why is the resulting ion larger for anions?
the attraction of the nucleus for any one e- decreases
what is an orbital
region of space where there is a 90% chance of finding an electron
what is the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to determine with certainty the location and momentum of a particle
do electrons hang out in orbits or orbitals?
they hang out in orbitals
How many quantum #s are there?
4
What is the 1st quantum # called?
Principal quantum number
what variable (letter) stands for the “principal quantum #”?
n
Principal quantum number
(energy level) describes the main energy level in which the electron is located
What is the 2nd quantum # called?
Angular momentum number
what variable (letter) stands for the “angular momentum #”?
swirly l
angular momentum number
(sublevel) describes the shape of the orbitals
s-sublevel orbital looks like…
sphere
p-sublevel orbital looks like…
dumbell
d-sublevel orbital looks like…
double dumbbell
f-sublevel orbital looks like…
bunch o’ balloons
What is the 3rd quantum # called?
magnetic quantum number
what variable (letter) stands for the “magnetic quantum #”?
m
magnetic quantum number
(orbitals/orientations) describes the number of orbitals per sub level
s-sublevel has how many orbitals?
1
p-sublevel has how many orbitals?
3
d-sublevel has how many orbitals?
5
f-sublevel has how many orbitals?
7
What is the 4th quantum # called?
spin quantum number
what variable (letter) stands for the “spin quantum #”?
m subscript s
spin quantum number
(spin) describes the “spin” of an electron
what are the two possible values for the spin quantum #?
-1/2 and ½ (spin up or down)
Pauli exclusion principle
maximum of 2 electrons per orbita (opposite spins)
Hund’s rule
the most stable arrangement has a maximum # of unpaired electrons (Thanksgiving rule)
Aufbau principle
electrons will occupy the lowest energy orbital available (electrons are lazy)
an orbital is designated by…
its energy level (n) and its sub level (l)
Aufbau Chart
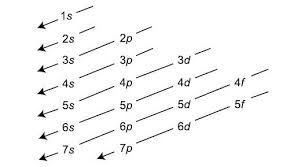
what are valence electrons
electrons in the outermost energy level (involved in bonding)
what do orbital diagrams show?
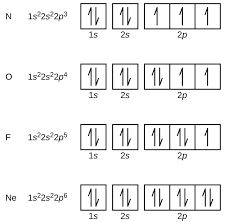
What do electron configurations show
They show how electrons are arranged in an atom
what are the aufbau exceptions (elements) in electron configurations?
Chromium (Cr) and Copper (Cu)
for shorthand electron configuration, where would you need to go first?
to the last noble gas
what is periodicity
a repeating pattern
who arranged the 63 elements by increasing atomic mass
Dmitri Mendeleev
what was a trend in Mendeleev’s periodic table
elements with similar properties fell into the same group
why did Mendeleev leave empty spaces on his periodic table
for elements that have not yet been discovered
Ekasilicon, predicted by Mendeleev, was later discovered as…
Germanium in 1886
who arranged the elements by # of protons
Henry Moseley
what are the groups (families) of the periodic table?
columns of the periodic table (1-18)
elements in the same group have what in common? (2 things)
have similar chemical properties
the same # of valence electrons
what do valence electrons determine?
chemical properties
what are the periods of the periodic table
rows of the periodic table (1-7)
elements in the same period have the same…
valence energy level
alkali metals
group 1 metals (NOT HYDROGEN)
soft metals, very reactive
1 valence electron in s-sublevel (ns1)
form 1+ ions
react with water to form a base and hydrogen gas
alkaline earth metals
group 2 metals
harder, stronger, denser than alkali metals
react with water (not as reactive as alkali metals)
2 valence electrons in s-sublevel (ns2)
Form 2+ ions
halogens
group 17, non-metals
“salt formers” (especially with group 1 & 2 metals)
very reactive
7 valence electrons (ns2 np5)
Form 1- ions
noble gases
group 18, non-metals
8 valence electrons (ns2 np6)
filled with s & p sub levels = STABLE electron configurations
uncreative (also known as inert)
snobs of the periodic table (they don’t like to mix with other elements)
DO NOT FORM IONS
when electrons absorb energy, what happens
electrons wil move up from the ground state to an excited state
when electrons move back down to the ground state, what happens
electrons will release energy as a photon of light
what does the type of light depend on
it depends on the energy difference between the excited state and the ground state
light is…
a wave
when constructive interference happens during a double slit experiment, what’s happening
crests align with other crests and troughs align with other troughs from other waves
when destructive interference happens during a double slit experiment, what’s happening
crests and troughs align
light is not only a wave, it’s also…
a particle!
what is a photon
a particle of light with a. specific amount of energy
what is Bohr’s atom model?
electrons exist in energy levels that are certain distances from the nucleus (orbits)
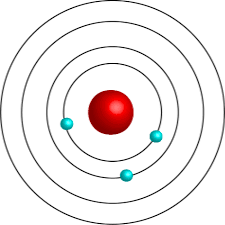
how is the energy of electrons?
they’re quantized
can electrons exist between energy levels?
no
what is a “quantum” of energy
the amount of energy absorbed or released to change energy levels