chapter 14- chem 30
4.7(3)
Card Sorting
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:05 PM on 5/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
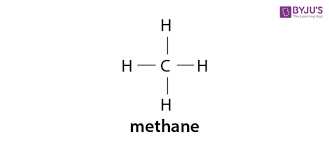
picture
akane
2
New cards
alkane- what type of bonds?
single
3
New cards
are alkanes saturated?
yes- each carbon is bonded to as many other atoms as possible
4
New cards
are alkanes aliphatic compounds?
yes
5
New cards
aliphatic compounds
contain no benzene ring
6
New cards
general formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
7
New cards
homologous series
any set of molecules that differ by one specific unit- ik CH2. Alkanes form homologous series
8
New cards
do some practice about modelling and naming alkanes
find questions in notes/textbook (pg 549, 550)
9
New cards
physical properties of alkanes
gas at standard temps, LDF acts on them, boiling points of small alkanes are below 25 degrees celsius, as length of the carbon chain increases- intermolecular force become stronger and medium length are liquid at standard temp, very long ones are waxy solids, not soluble in water
10
New cards
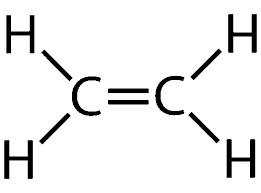
identify this
alkene
11
New cards
are alkenes aliphatic?
yes
12
New cards
practice drawing and naming in textbook (pg 554,555)
in textbook
13
New cards
physical properties of alkenes
non-polar and do not dissolve in water. First 3 alkenes are gasses at standard temp, intermediate sized ones are liquids, boiling points are slightly lower than alkanes.
14
New cards
general formula for alkene
CnH2n
15
New cards
what type of bond- alkenes
double
16
New cards
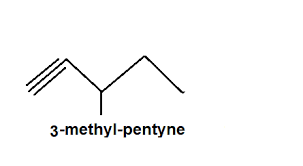
identify this
alkyne
17
New cards
are alkynes aliphatic?
yes- they lack a benzene ring
18
New cards
what type of bond is in an alkyne
triple
19
New cards
general formula for alkynes
CnH2n-2
20
New cards
are alkynes and alkenes saturated or unsaturated?
they are both unsaturated
21
New cards
practice naming and drawing alkynes (pg 556,557)
in textbook
22
New cards
physical properties of alkynes
non-polar, insoluble in water, the first few are gases, alkynes have higher boiling points than their corresponding alkanes and alkenes. the linear structure of them, and the triple bond cause them to attack one another more strongly than alkenes and alkanes,l so it takes more energy to overcome the forces.
23
New cards
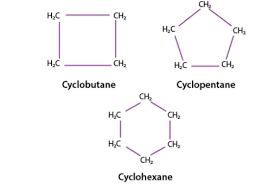
identify
cyclic hydrocarbon
24
New cards
are cyclic hydrocarbons aliphatic
yes- lacking a benzene ring
25
New cards
properties of cyclic hydrocarbons
can be alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes, they are non-polar, they form rings
26
New cards
practice naming and drawing (559,560)
in text
27
New cards
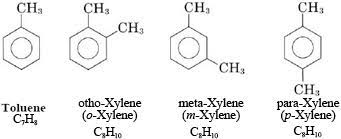
identify this
aromatic hydrocarbon
28
New cards
aromatic hydrocarbons
derived from a benzene ring, have intense aromas, benzene is liquid at standard temp, similar boiling points to the aliphatic hydrocarbons of the same length.
29
New cards
practice naming and drawing (pg 562)
textbook
30
New cards
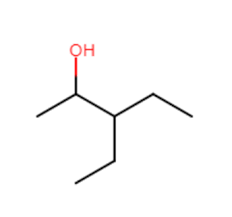
identify
alcohol
31
New cards
alcohols
hydrocarbon derivative that contains an -OH. small alcohols are polar. as the hydrocarbon chain becomes longer, the non-polar characteristics make them insoluble in water. boiling points of pure alcohols are much higher than the alkanes. all straight chain alcohols with fewer than 12 carbons are liquid at standard temp.
32
New cards
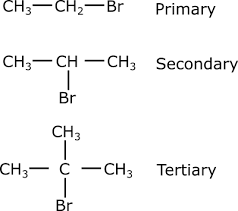
identify this
alkyl halide
33
New cards
alkyl halides
Hydrocarbons that contain at least one halogen atom.
34
New cards
practice alkyl halides (569,
in textbook
35
New cards
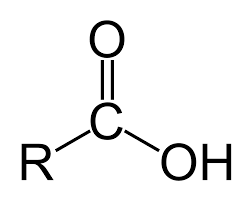
identify this
carboxylic acid
36
New cards
carboxylic acids
contains a carboxyl group- COOH. very polar, boiling points much higher than other hydrocarbon derivatives. Short chain- liquids, longer are waxy solids. Soluble in water (1-4 carbons), less soluble (5-9), insoluble (10+) Weak acids.
37
New cards
practice naming and drawing carboxylic acids (570)
text
38
New cards
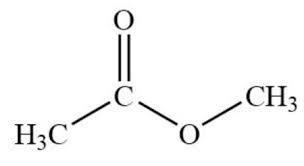
identify this
ester
39
New cards
practice naming and drawing esters (572)
text
40
New cards
ester physical properties
the C=O group makes them somewhat polar, but without the OH they cannot form H bonds. Boiling point lower than corresponding alcohols, and carboxylic acids. Smaller esters are liquids at standard temp, and longer chains are waxy solids. Esters with 4 or less carbons are soluble, any more is not. volatility allows them to generate aromas.