MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATION OF THE ELBOW, FOREARM, WRIST AND HAND (P1)
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PART 1: ELBOW (Anatomy review, S&O of elbow )
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Primary role is to position an individual’s hand in the appropriate location to perform its function (fine motor activities, gripping, grasping, etc)
THE ELBOW COMPLEX / ELBOW

How many degrees of freedom?
1 DoF (Flex & Ext)
Does your elbow respond well to trauma?
Nah, it gets cooked (Mostly stabilized by ligaments and dynamic stabilizers; Harder to keep the integrity of the structure)
Magee stuff: Joint also responds poorly to harsh treatment, or incorrect treatment.
Enumerate joints that make up the elbow complex
Ulnohumeral (trochlear joint), Radiohumeral, Superior Radioulnar Joints (rotation)
these joints also make up the cubital articulations
Which joint of the elbow is the most stable?
Ulnohumeral (trochlear joint)
(Also responsible for the carrying angle)
On full extension of the ulnohumeral joint, which part of the olecranon process is not in contact with the trochlea?
On full extension, the medial part of the olecranon process is not in contact with the trochlea
On full flexion of the ulnohumeral joint, which part of the olecranon process is not in contact with the trochlea?
on full flexion, the lateral part of the olecranon process is not in contact with the trochlea.
A small amount of medial and lateral rotation occurs at the ulnohumeral joint, how many degrees of rotation happens in early flexion and which direction does it rotate?
5° of medial rotation occurs
how many degrees of rotation happens in late flexion and which direction does it rotate?
5° of lateral rotation occurs.
The radial side of the elbow has an empty space due to the incongruency of the radiohumeral joint, what direction of dislocation does this cause?
Posterolateral dislocation (Most Common)
Patients with posterolateral rotary instability have pain and discomfort in the elbow along with possible locking, clicking, snapping, or slipping,
most likely noted at ___________ as the arm goes into an extension arc of motion, especially with the forearm _______________.
most likely noted at 40° of flexion as the arm goes into an extension arc of motion, especially with the forearm supinated.
Ligaments found at the medial side of the elbow are/is called the?
Which motion/force does these/this ligament/s prevent?
Ulnar collateral ligament
Valgus force / motion (Force that pushes elbow inward)
Which portion of the UCL houses the Ulnar nerve?
Posterior Ulnar Collateral Ligament
(Common cause for medial elbow pain)
What is the band between the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle called?
The ulnar nerve passes through here as well
Osborne’s band
Sign indicated by loss of the hypothenar muscles and flattening of the palmar metacarpal arch
Masse’s sign
If there is an inability to flex the distal interphalangeal joints of the little and ring fingers what sign is present?
Pollock’s sign
Clawing of the fourth and fifth digits is observable, what sign is present?
Benediction Sign/ Preacher’s Sign/ Duchenne sign
Fan-shaped; stronger than medial ligaments; needs to restrict more dt the absence of the olecranon process and fossa
Lateral collateral Ligaments
the LCL (Lateral Collateral ligament) complex tensioned by the radial head and extensor muscles are important to prevent what type of instability?
Posterolateral rotary instability
Innervation of the elbow:
Musculocutaneous, Radial, Median and Ulnar nerves
Ulnohumeral (Trochlear) Joint:
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Resting position: 70° elbow flexion, 10° supination
Close packed position: Extension with supination
Capsular pattern: Flexion, extension
Radiohumeral Joint:
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Resting position: Full extension and full supination
Close packed position: 90° flexion, 5° supination
Capsular pattern: Flexion, extension, supination, pronation
True or False:
In extension, the medial/ulnar collateral ligament, the anterior capsule, and the ulnohumeral articulation resist valgus translation.
True
True or False:
90° of flexion, the posterior bundle of the medial collateral ligament provides the main restraint against valgus translation
FALSE:
90° of flexion, the ANTERIOR bundle of the medial collateral ligament provides the main restraint against valgus translation
The ulnar collateral ligament has three parts, which along with the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle, forms what structure? and which nerve passes through this structure?
Cubital tunnel (most common area of ulnar nerve impingement)
Ulnar nerve
Injuries that increase the carrying angle put abnormal stress on the cubital tunnel, impingement of the ulnar nerve here can cause what type of palsy?
Tardy ulnar palsy (Chronic)
Cubital tunnel syndrome (Acute)
Superior Radioulnar Joint
Resting position:
Close packed position:
Capsular pattern:
Superior Radioulnar Joint
Resting position: 35° supination, 70° elbow flexion
Close packed position: 5° supination
Capsular pattern: Equal limitation of supination and pronation
What ligament holds the superior radioulnar joint in place?
Annular Ligament
This joint is not a true joint; made up of the radius, ulna and interosseous membrane between the two
Middle radioulnar articulation
True or False:
The interosseous membrane is tense during midprone or neutral position; it also helps prevent proximal displacement of the radius on the ulna during FOOSH.
True
Which ligament found on the LCL whose fibers run at a right angle to the interosseous membrane; assists in preventing displacement of the radius on the ulna during traction/pulling injuries
Oblique Cord
Roots of:
Radial nerve :
Median nerve:
Ulnar nerve:
Roots of:
Radial nerve : C5-C8, T1
Median nerve: C6-C8, T1
Ulnar nerve: C8, T1
pain on resisted extension of the middle finger which suggests compression of the radial nerve at the flexor digitorum superficialis arch manifests in what sign?
Maudsley’s sign
most common site of compression of the posterior interosseous nerve; a fibrous arch in the supinator muscle occurring in 30% of the population.
Canal / Arcade of Frosche
True or false:
Diagnosis of posterior interosseous nerve impingement is often delayed because there is no sensory deficit.
True
(Motor nerve so no sensory deficit)
The radial nerve may also be compressed at:
the entrance to the radial tunnel anterior to the head of the radius,
near where the nerve supplies brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus (leash of Henry),
between the ulnar half of the tendon of extensor carpi radialis brevis and its fascia
distal border of supinator
what syndrome is this called?
Radial tunnel syndrome
elicits pain with little muscle weakness and may mimic tennis elbow
Condition where there is compression of the superficial branch of the radial nerve as it passes under the tendon of the brachioradialis.
Cheiralgia paresthetica or Wartenberg disease/sign
sensory only
and the patient complains primarily of nocturnal pain along the dorsum of the wrist, thumb, and web space.
Pressure between the junction of the ECRL and Brachioradialis reproduces symptoms
Most active and intricate parts of the UE
Does not respond well with serious trauma
Because it highly depends on ligamentous structures (inert) for stability
Trauma = sprain or tearing = instability or deficiencies of the UE kinetic chain
FOREARM, WRIST, AND HAND
True or false:
The UE kinematic chain comprising of the shoulder, elbow, cervical region and hand play an important role in functional activities (IADLs & BADLs)
FALSE:
The UE kinematic chain comprising of the shoulder, elbow, WRIST and hand play an important role in functional activities (IADLs & BADLs)
The FOREARM, WRIST, AND HAND has a protective role both as motor and sensory organ
Sensory = __________ (detection of hazards)
Motor = for _______
Sensory = withdrawal reflex (detection of hazards)
Motor = for ADLs
Objectives of ASSESMENT
_________ of assessment
Which specific structure causes pain, instability, difficulty
Evaluation of _____________
Consequent compensation; how much compensation is happening
Objectives:
Accuracy of assessment
Which specific structure causes pain, instability, difficulty
Evaluation of remaining function
Consequent compensation; how much compensation is happening
Common age for lateral epicondylalgia / tennis elbow
Inflamed tendon d/t overuse & repetitive stresses or strains
In severe cases such as tendinosis, It can happen without any movement
>35 y/o
Type of pain, duration & location of tennis elbow
Aching, Intermittent & Radiating pain until wrist extensors
Note that if caused by tendinosis pain can be CONSTANT
Traction injury affecting the annular ligament & head of the radius; commonly affects younger people
Undeveloped annular ligament = displacement = dislocation of radial head
Nursemaids Elbow
What are the presentations of Nursemaid’s elbow?
Decreased supination and pain on lateral side of the elbow
True or False:
For people with “Blue collar” jobs we have to consider medial and lateral epicondylitis dt repeated flexion and extension.
True
Type of pain, duration and location of Medial epicondylitis
Aching, Intermittent & Radiating pain until wrist flexors
Note that if caused by tendinosis pain can be CONSTANT
What causes systemic presentation on the hands?
Nodes or deformities on the hands = altered mechanics of gripping and functioning of the hand
More common in older patients
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Common MOI for Wrist Fractures & Elbow dislocations
FOOSH
MOI for contusions and displacement of the radius and ulna unto the humerus
Fall on tip of the elbow
True or False
The shoulder complex should also be checked and palpated during a FOOSH / Fall on tip of elbow injury
True:
Force may be transferred to the clavicle causing fracture, Translational forces may affect the labrum.
When considering injuries dt Repetitive stress in sports which type of stress should we consider when it comes to pitching / throwing? (direction of stress)
Valgus stress
What phase of pitching has the most valgus stress?
Late Cocking Phase
What is the type of injury caused by severe valgus extension force to the elbow because of repetitive throwing causing a medial side traction injury (e.g., sprain of the medial collateral ligament) and a lateral side compression/contusion injury
Common in younger population dt undeveloped inert structures
Little leaguer’s elbow
osteochondral damage either on the olecranon process or olecranon fossa can also be present.
If the patient felt a pop followed by pain and swelling on the medial side of the elbow, it may indicate what type of sprain?
Ulnar collateral ligament sprain
If the pop was more centrally located in the elbow, followed by a weakness in elbow flexion, what structure is affected?
The distal biceps may be ruptured
Other Pertinent Pt Hx (Summary)
Referral of pain from cervical spine
paraesthesia, pins and needles, can be nerve root affectations with distal manifestations
Multiple joint diseases
RA, Scleroderma, systemic conditions
Specific activities that increase or decrease the pain
Sports, weightbearing activities, occupational demands
Snapping on the medial side of the elbow
Ligamental or nerve
Previous hx of overuse or trauma
Occupation / Sports
Demographics in the Subjective examination include:
Initials, Age, Medical Hx (Htn/DM/Asthma), Handedness, Gender
Which conditions should be considered when the patient is a female?
Women = ↑ ligamentous laxity leading to an increased carrying angle (Note in PA)
Women are more predisposed to RA
Chief Complaint:
What are the most common areas of pain for the elbow wrist and hand?
medial, lateral, and above the elbow
anterior wrist which radiates to the hand, with medial distribution (carpal tunnel)
Pain on specific finger (mallet)
If patient complains of instability of the elbow what structures should you assess?
Inert Stabilizers / Ligament Stability
Significant Weakness + Pain during MMT indicates what type of tendon injury?
Low grade strain
Significant Weakness + No Pain during MMT indicates what type of tendon injury?
Tendon Rupture
If the patient complains of Heaviness (tires easily) with numbness, paresthesia/tingling sensation (usually radiating) what structure may be affected?
Nerve may be compressed
Find out where the nerve is compressed
Term for the combination of proximal and distal Sx (compression at the nerve root paired with compression of the distal nerve structure)
Double crush syndrome
Pain Assessment
Refresh ur brain this shit the same

HPI (read to refresh)
When and how did it start?
How long has the problem been present
Mode of onset
insidious, sudden, congenital
Mechanism of injury
FOOSH, direct blow, repetitive trauma
Activities altered or increased
Significant changes in training or use
Pertinent events related to injury
Course of symptoms
Acute = 48-72 hrs
Subacute = >2 wks
Chronic = 2-6 months
MD consultation (Also HPI)
Ancillary Procedures
Radiographic findings, MRI, EMG-NCV
Prescribed Medications
NSAIDS, Pain killers
Management provided
Orthosis, surgical repairs, casts
Referral to Rehab
Adjust treatment based to function the patient currently has
PMHx
Previous injuries of the same area or other areas (UE kinematic chain)
Treatment or meds given, recovery
Steroids - leads to osteoporosis, joint laxity
Corticosteroid - stops inflammation = ↓bone density = osteoporosis
Analgesics - day of tx, no symptoms (pain) leads to a false negative
Family History (RA)
Previous PT session
Physical and Social Environment
Family support (especially geriatric and pediatric)
Pertinent house furniture or appliances (UE related)
Lifestyle and Work
Occupation (type of work, usual position, ergonomics)
Hobbies, recreational activities, sports
Knowledge on stretching, warm-up and cooldown, protective equipment
Smoker, drinker, diet, sleep considerations
Pt’s Goal (alam mo na to)

for SUBJECTIVE what should we focus on?
Focus on MOI and HPI with correlation to C/C = good diff dx
OBJECTIVE EXAMINATION (skip VS)
OI (read)
Manner of arrival (protective guarding of arm)
Mental Status/Orientation
Body Type (ectomorph, mesomorph, endomorph)
Attachments
Adaptive devices (sling, splint, forearm band, orthoses, cast)
External fixators
Head to foot observations (OI): (Read)
Change in color
Cyanotic (Lack of bloodflow)
Redness/Erythema (Persistent inflammation or vascular compromise)
Scars or wounds
Bruising or hematoma
Ecchymosis (Muscle tears)
Hematoma (Blood clotting)
Bruising (d/t trauma)
Change in texture (OI) (Read)
Dry & scaly skin (dec sympathetic activity)
Smooth, shinny, glossy (inc sympathetic) = predisposed to wounds and scarring dt increased calcium deposit
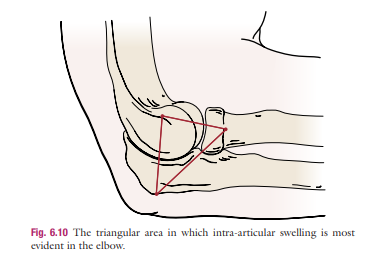
Swelling (OI) (Read)
Localized (bursa or extraarticular) / Generalized (intraarticular)
Landmark: Medial and lateral epicondyle
(+/-) Postural Deviations
most common type of localized (extraarticular) swelling: ___________
most common type of localized swelling: olecranon bursitis
landmark for anthropometrics to measure generalized (intraarticular) swelling : __________
Lateral elbow / epicondylar area
Deformities of the elbow (OI AND PA)
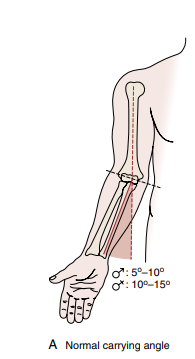
Carrying angle
Cubitus varus/cubitus valgus
Normal carrying angle for
MALE:_______
FEMALE:________
Normal carrying angle for
MALE: 5–10 degrees (11° to 14° dalawa value ni magee ang gulo)
FEMALE: 10 -15 degrees (13° to 16°)
Note that cubitus valgus is normal, but excessive cubitus valgus is a deformity
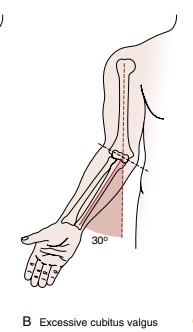
This is characterized by an excessive carrying angle with sprain on medial elbow and compression of lateral elbow
Cubitus Valgus
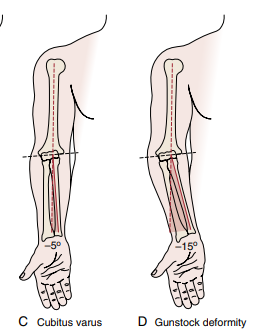
This is characterized by a decreased/negative carrying angle with sprain on lateral elbow and compression of medial elbow
Cubitus Varus / Gunstock deformity (more severe varus dt trauma)
General Reminders for PALPATION
Usually done last because of pain but documented p OI
Take note of
Muscle tone, spasm, guarding, Endfeel
Skin temperature
subluxation/dislocation
Edema (pitting or non-pitting)
Lymphatic issue
Tenderness
Crepitations
Tightness
Contracture
Taut Bands, Nodules, Trigger Points
Joint play
PALPATION OF THE ELBOW
Patient’s arm should be relaxed
Patient position: Supine or Sitting
Anterior aspect elbow → Medial lateral→ Lateral → Posterior
Anterior elbow palpation
Inspect the the biceps tendon, brachialis, brachial artery Coronoid Process, head of Radius, and radial tuberosity in the cubital fossa
The median and musculocutaneous nerves are also found in the fossa, but they are not palpable. Pressure on the median nerve may cause symptoms in its cutaneous distribution.
If the patient is complaining of pain and/or tenderness along the anteromedial humerus, radius, or ulna, especially after repeated stress, with possibility of periostitis results in what?
Humeral shin splints or Forearm splints
precursors to stress fractures.
Medial elbow palpation
Inspect wrist flexor–forearm pronator groups of muscles, MCL and ulnar nerve (the nerve is not directly palpable, but pressure on the nerve often causes abnormal sensations in its cutaneous distribution.)
Lateral elbow palpation
Inspect wrist extensor muscles, brachioradialis and supinator, LCL and annular ligament
If the examiner palpates the lateral epicondyle, the posterior radial head, and the olecranon tip, the anconeus “soft spot” will be found within this triangle. Pressure applied over the patient’s lateral forearm about 3 to 5 cm (1.2 to 2 inches) distal to the elbow crease (over the supinator muscle) with the wrist in full supination will cause pain if there is pathology in the radial nerve
Posterior elbow palpation
Inspect the Triceps, Olecranon Process and Olecranon Bursa
ANTHROPO- METRIC MEASUREMENTS:
Measurement to compare muscle bulk
Limb Girth Measurements
Measurement for swelling (Golden standard)
Volumetric Measurements
N = 10mL difference
Swelling =30-50 mL difference
Deep Tendon Reflex
Biceps =________
Triceps = ________
Brachioradialis = ________
Biceps = C5-C6
Triceps = C7-C8
Brachioradialis = C5-C6
A normal functional position of elbow:
90° of flexion & Forearm between pronation and supination
The forearm may also be considered to be in a functional position when slightly pronated, as in writing. From this position, forward flexion of the shoulder along with slightly more elbow flexion (up to 120°)
most ADLs are performed at ranges between _______ of flexion and between ______ of pronation and _____ of supination
most ADLs are performed at between 30° and 130° of flexion and between 50° of pronation and 50° of supination
A triangle is formed by the olecranon process and the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus when the arm is flexed to 90° this triangle is sometimes called the what?
Triangle sign
Ligament that runs from an abnormal spur on the shaft of the humerus to the medial epicondyle of the humerus which is present in 1% of the population
ligament of Struthers
Median nerve passes here and can be compressed
If the median nerve is compressed at the Ligament of Struthers what syndrome is this called?
Humerus supracondylar process syndrome
Inital = Sensory loss (aka nauuna sensory loss)
Secondary = motor loss
Wrist and finger flexion + thumb movements are most affected
If the median nerve is compressed where it passes through the two heads of pronator teres what syndrome is this called?
Pronator syndrome / Proximal median nerve entrapment
Muscles below pronator teres affected; pronator teres normal
Impingement of the anterior interosseous nerve leads to what syndrome?
Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome / Kiloh-Nevin syndrome or sign
Impaired flexor pollicis longus, lateral half of the flexor digitorum profundus, and pronator quadratus muscles
Characterized by the “OK-sign”