Business Management - Topic 4
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
What is a market?
A place where buyers and sellers come together or interact, a location, or a type of product
What is marketing?
The processes involved in identifying and satisfying customer needs
What is a product oriented business?
Business that prioritizes R&D of high quality and specialized products over market research, inward facing
What are advantages of being product orientated?
Can focus on creating a different product to competitors that is higher quality and has a USP
Can get patents for new products
Lack of competition
What are the disadvantages of being product orientated?
High risk, unsure if customers will be interested
High costs of investment
What is a market orientated business?
Business that puts the wants and needs of the customers above everything else, only develops products after understanding the market
What are the advantages of being market orientated?
Lower risk
Increased number of repeat customers due to better product-market fit
What are the disadvantages of being market orientated?
No USP
Market research must be right
Slow to adopt to changing market conditions
What is market share?
The value of a single company’s sales or revenues compared with the sales of all businesses in a market in a specified time
What is the equation for market share?
Market share = product sales ÷ total market sales x 100%
Market share = number of units sold by the company ÷ total number of units sold in the market x 100%
What is market growth?
The increase in sales revenue or sales volume in an individual market over time
What is the equation for market growth?
Market growth = (total market sales at the end of time period - total market sales at the start of time period) ÷ total market sales at the start of time period x 100%
What is a market leader?
The product or brand with the highest market share
What are advantages of being a market leader?
Easier to access different distribution channels
Brand recognition
EoS
Leaders have control over the “right” price for a product
How does a market leader benefit the customers?
Products become more valuable the more people use it
Market leaders can set lower prices if they have EoS
Businesses can use revenue to further develop products
What are disadvantages of being the market leader?
Lack of innovation may attract new competition
May face DoS
How does a market leader negatively affect customers?
Large businesses can abuse their power
No guarantee for lower prices
No competition will lower the motivation to innovate
How does a market leader negatively affect the economy, society, and the environment?
Market leaders have power to sway politics
Can easily gain support for mergers and acquisition to remove competition
Can resist trade unions
Can find tax loopholes
What is the BCG Matrix?
A tool to help businesses that have multiple products to decide on their marketing strategies by comparing market share of the product and the potential market growth
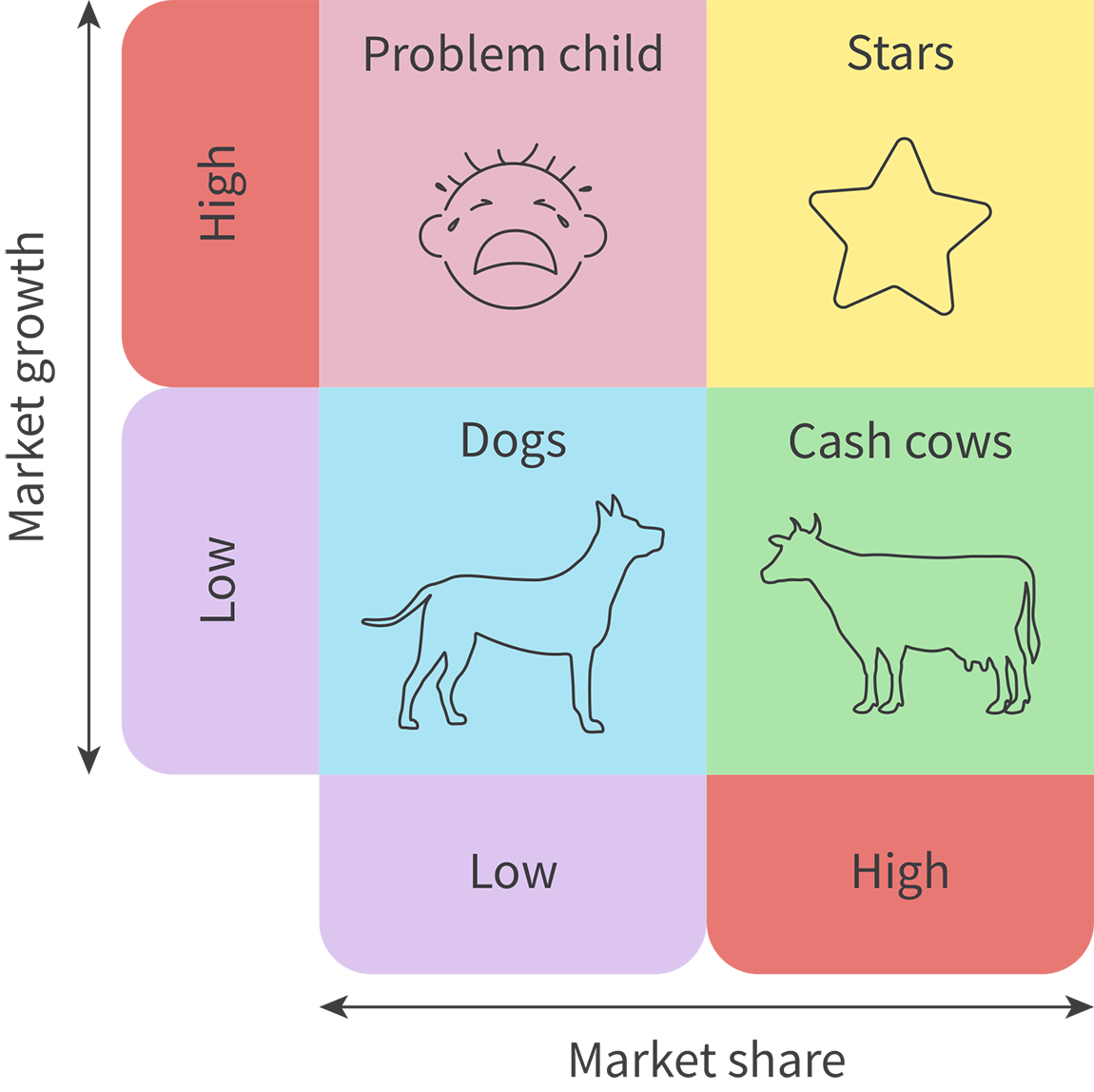
What are cash cows (BCG Matrix)?
High market share, low market growth
Likely to be in the mature stage of a product life cycle with an established customer base
Will need less money for marketing
Will have high sales revenue
Focus promotion on maintaining loyalty
What are dogs (BCG Matrix)?
Low market share, low market growth
Likely at the end of its product life cycle or is a niche product competing in mature low-growth markets
What are stars (BCG Matrix)?
High market share, high market growth
Revenue is likely to grow strongly
Requires significant investment to sustain growth
Focus marketing around attracting new customers and establishing a brand image
What is a problem child (BCG Matrix)?
Low market share, high market growth
Often launched in response to competitor’s growth
To gain market share investment is required
What is a marketing plan?
A document that outlines the entire marketing process of a business
What are elements of a marketing plan?
Marketing objectives
Marketing budget
Segmentation and target market
Market research
Marketing strategies (marketing mix)
Control tools (tools used to assess success)
What is segmentation?
Splitting a population into groups with similar needs or characteristics
What is the target market?
The consumer segment at which a business aims its marketing messages
What is geographic segmentation?
Dividing by geographic location (country-based, regional by continents, regional by state and country, urban vs. rural)
What is demographic segmentation?
Dividing by age, gender, occupation, socio-economic group, etc.
What is psychographic segmentation?
Dividing by lifestyle and personal interests (sports, music, food, movies, books, etc.)
What are advantages of segmentation?
Identify gaps and opportunities in the market
Design more suitable products
Reduce waste of resources
Diversify and spread risks by targeting different segments
What is targeting?
Selecting the most appropriate segment for a marketing campagin
What is a product positioning map?
A visual representation of how various competitors might attempt to position their brands in the eyes of consumers by displaying 2 attributes on a cartesian plane (usually price and quality or price and age)
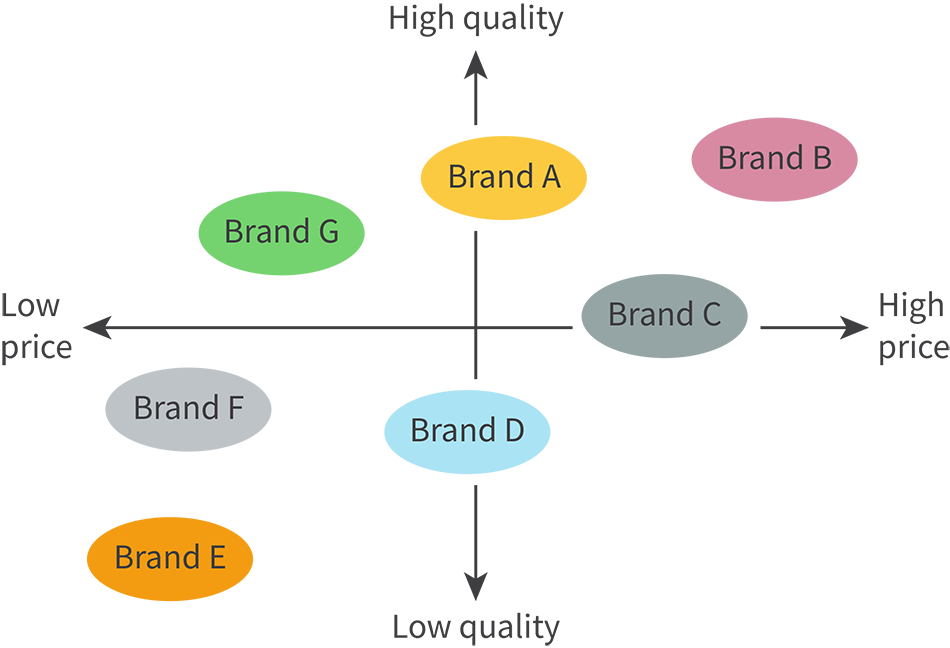
What are the uses of product positioning maps?
Identify market segments whose wants and needs aren’t fulfilled
Establish gaps and opportunities in a market
Help identify closest competitors and threats of a business
Use info to target appropriately
What are niche markets?
Small part of a larger market that have very specialized wants or needs or those that are different from the larger market (eg. clothes for very tall people, gluten-free bread)
What type of promotion is normally used in a niche market?
Below the line
What is the advantage of being in a niche market?
Less competition can increase customer loyalty and allow for higher prices
What are the disadvantages of being in a niche market?
Tends to have low quantity of sales
Less reach
Little growth potential
What is a mass market?
A market for goods that are produced in very large quantities
What type of promotion is normally used in a mass market?
Above the line
What are the advantages of being in a mass market?
EoS
High quantity of sales
What is the disadvantages of being in a mass market?
More competition = lower prices = lower profit margin
What is USP?
A feature that distinguishes a product or brand from its competitors
What is differentiation?
Differences between a business’s product or service from its rivals
What are product USPs?
Unique product design, first of its kind, patents
What are price USPs?
Offer the lowest (only for those who have significant EoS) and highest prices (can indicate exclusivity)
What is promotion USP?
Promoting effectively to lead to customer loyalty and a positive brand image
What is place USP?
Being in a convenient location, a global business, or in the right distribution channel
What is a process USP?
Positive interactions with employees, good customer service
What is a physical evidence USP?
Experience is different to other businesses (layout, interior design, temperature, presentation)
What is a process USP?
High efficiency to increase speed and improve customer service
What is Porter’s Generic Strategies?
4 strategies to help businesses consider how to respond to the external environment by considering 2 brad strategies against the target market
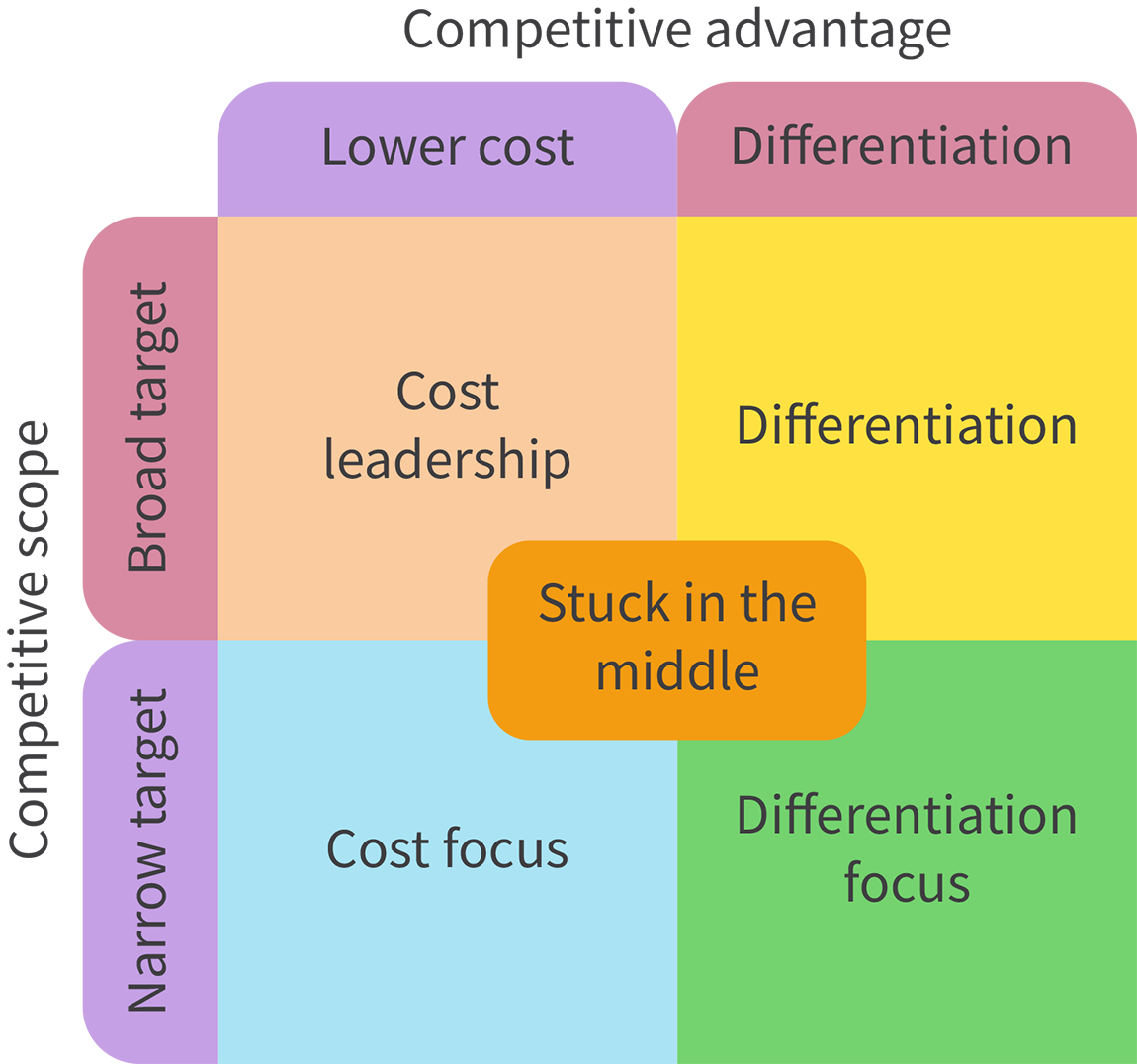
What is cost leadership (PGS)?
Lower cost, broad market
Business becomes the low-cost producer by reducing unit costs with EoS or increased efficiency
Suitable for markets with standardized products and hard to differentiate
What is differentiation (PGS)?
Differentiation, broad market
Business makes a product better or different with a USP
Can charge premium is successful
Profits will increase if costs stay in control
What is cost focus (PGS)?
Lower cost, narrow market
Business becomes the low-cost producer in a niche market
Usually for basic products
What differentiation focus (PGS)?
Differentiation, narrow market
Business produces specialized or differentiated products for a niche market
Product must be very high quality, very exclusive, or provides a special charactristic that the niche market wants
Can charge a premium to compensate for a small market
What is stuck in the middle (PGS)?
Business isn’t differentiated enough and costs are too high relative to competitors so the business has low profits or losses. Must change strategies by cutting costs or differentiating and focus on a broad or narrow market
What is the purpose of market research?
Gain info on customers and competitors
Identify wants and needs
Understand consumer purchasing behavior
Identify potential market change
Establish customer likes and dislikes
Test products
Evaluate existing markets
Investigate new possibilities in existing or new markets
Identify human needs (social ent.)
What are methods of primary research?
Surveys (large # of respondents in a short time, can gather quantitative data)
Interviews (longer, qualitative, allows for follow up questions)
Focus group (interview conducted with a small group of individuals, usually with similar characteristics, participants may get financial rewards)
Observations (natural reactions of customers are studied, individual consumers can be followed, record route in a store, which promotions they notice, or clicks they make on a website)
What are methods of secondary research?
Market analysis (pay agencies to do new research or buying pre-existing market analysis reports)
Academic journals (publications from educational or research institutions, Harvard Business Review, Jstor, Google Scholar)
Government publications (population stats, social trends, economic conditions, usually free and reliable)
Media articles for current local or national info
Online content (social media and social media analytics, e-commerce sales data, press release, company reports)
What are the benefits of primary research?
Direct info about taste and preferences
Provide info about resources for purchase
Provides unique info that gives a competitive advantage
What are limitations of primary research?
Expensive and time-consuming
May need to train employees to carry out research
Can be difficult to construct
What are benefits of secondary research?
Low cost
Provides broader contextual info
Pre-published info is available
What are limitations of secondary research?
Must rely on others’ research
Info wanted may not exist
Existing info may not fit the business
What is quantitative research?
Numerical data
What is qualitative research?
Non-numerical data (opinions)
What is a sample?
A subset of individuals from a given population that is used to make some estimation or prediction of the whole population
What are the 2 categories of sampling methods?
Probability sampling (each subject has the same chance of being selected)
Non-probability sampling (not all subjects have an equal chance of being selected)
What is random sampling?
Everyone in the population has the same chance of being selected to take part in the research, most representative of the population, probability sampling
What is quota sampling?
Divides the population into strata (subgroups based on a characteristic) and a small sample is taken from each stratum based on convenience, non-probability, faster and easier, less expensive than random, takes into account population proportions
What is convenience sampling?
Sample is made up of whoever is willing to take part, least representative, non-probability, simple, limited uses
What are descriptive statistics?
Tools used to present and interpret data collected (mean, mode, medium, standard deviation, charts, infographics, quartiles)
What is product (marketing mix)?
The result of a production process where resources are used to create a good or service to satisfy a want or need
What is the product life cycle?
A model to help businesses make decisions about a product’s marketing mix
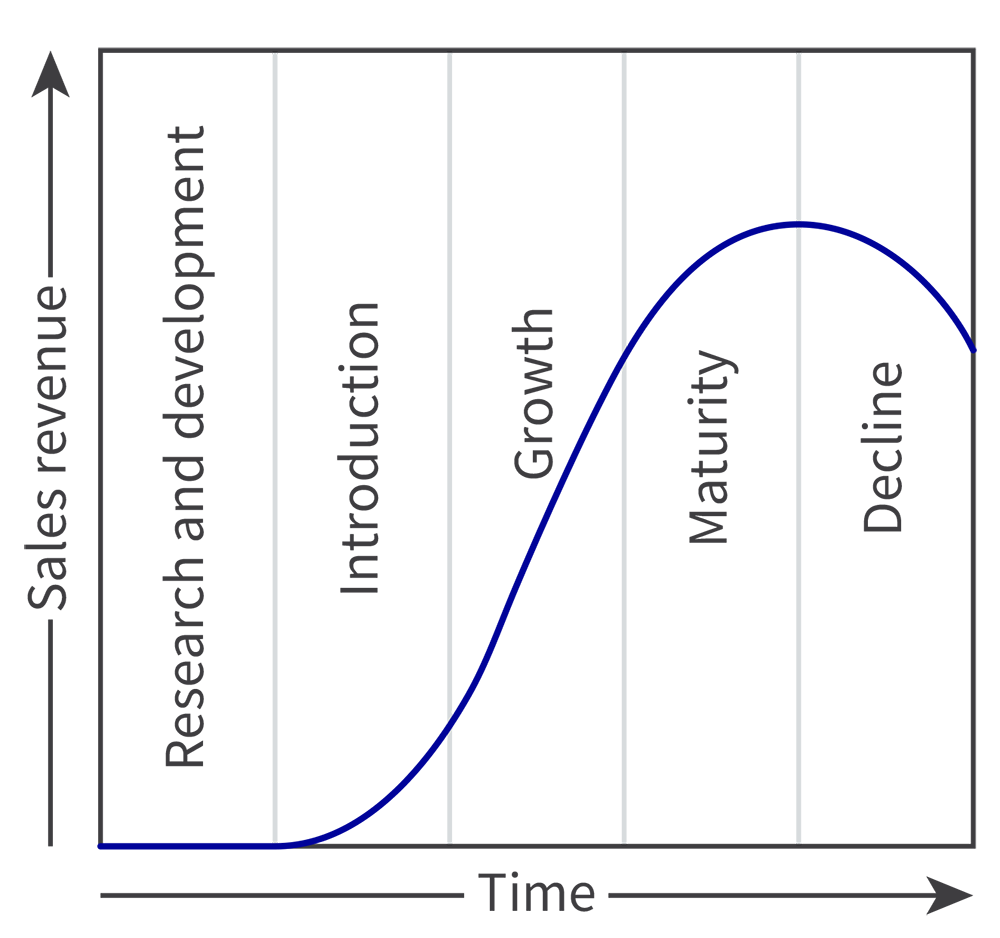
What is R&D?
Everything before the product is released
No sales
Market research
Product development and testing
Preparing production (finding suppliers, facilities, initial stock produced, promotion can be done to create a “buzz”)
What is introduction (product life cycle)?
Product is released
Likely for sales to be low
Focus on promotion USP
Pricing and distribution is important to consider
What is growth (product life cycle)?
Sales accelerate
Pricing strategies might change and distribution may need to expand
Promotion focuses on raising awareness in new target markets
What is maturity (product life cycle)?
High and steady sales revenue
Slower growth rate
Saturated market
Focus on building customer loyalty
Can decrease marketing budget
What is decline (product life cycle)?
Falling sales or loss of market share
Loss of USP due to high competition
Product may no longer satisfy needs
Can still be profitable
Price may reduce
Distribution channels may shift to discount retailers
What are extension strategies (product life cycle)?
Methods to extend the maturity stage
Easier and cheaper than starting new
Find new target market (market research can be costly)
Redesign packaging (customers may feel tricked or disappointed)
Add new or different features to the product (can be developed quickly and at a low cost but loyal customers may not like the change)
Reduce prices (can damage image or be perceived as lower quality)
New promotional strategies to change mental model of how the product is used
What is a brand?
A name, symbol, or design used to identify a product or company
What is brand awareness?
The degree to which consumers recognize a product by its name or special characteristics (Nike ‘swoosh’)
What is brand development?
The process of creating and making a new strong brand which allows the company to launch secondary products with ease (Cadbury’s 20+ variations)
What is brand loyalty?
Customers continue to buy from a brand, even with alternative options, essential during hard times
What is brand value?
How much a brand is worth as an intangible asset, how much someone would pay for the brand
Why is packaging important?
Helps the product stand out from competitors
Represents the brand
Protects the product
Communicates info to customers
Promotes the product
Can be a USP
Ease of use
What is cost-plus pricing?
All costs + a fixed or percent mark up
Easy to use, all costs are covered, doesn’t take into account market pricing
What is penetration pricing?
Setting prices low to attract new customers to a new product or service
Short-term strategy to improve brand loyalty, good for repeat purchase products, helps secure large market share early on, low profit margin
What is loss leader pricing?
Larger businesses with a large product portfolio prices lower than their production costs to attract customers to buy another, more expensive product
Very risky
What is predatory pricing?
Prices are so low that competitors are forced ut of the market
May be illegal in some countries and is impossible to maintain
What is premium pricing?
High prices to create a positive perception, makes value seem higher
People may not be willing to pay, will have a small target market
What is dynamic pricing?
Selling the same product to different customers at different prices (change according to customer, change based on time, change based on competitors, change based on demand)
What is competitive pricing?
Pricing the same as competition, no USP
What is contribution pricing?
Variable costs + mark up
Each product will contribute a portion to the payment of fixed costs
May be difficult to identify direct and indirect costs
What is price elasticity of demand (PED)?
Analyzes how the demand is affected by changes in price
PED = % change in demand ÷ % change in price
What does it mean if PED>1?
Price elastic demand
A change in price will have a proportionally greater change in demand
What does it mean if 0<PED<1?
Price inelastic demand
A change in price will have a proportionally smaller change in demand
What does it mean if PED = 1?
Unitary elastic demand
A change in price will have an equal change in demand
What are factors that can determine PED?
Number and closeness of similar goods, the more similar goods the more elastic because if prices increase by a lot demand will drop by even more as they will buy from another product
Time period, customers may not have time to react to changes in price so it is inelastic
What is promotion?
The use of advertising, sponsorships, sales promotion, and personal selling to inform and persuade customers