Chem 2 lab final UF
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Alpha
stopped by paper
Beta
stopped by metal
gamma
stopped by lead
k
rate constant
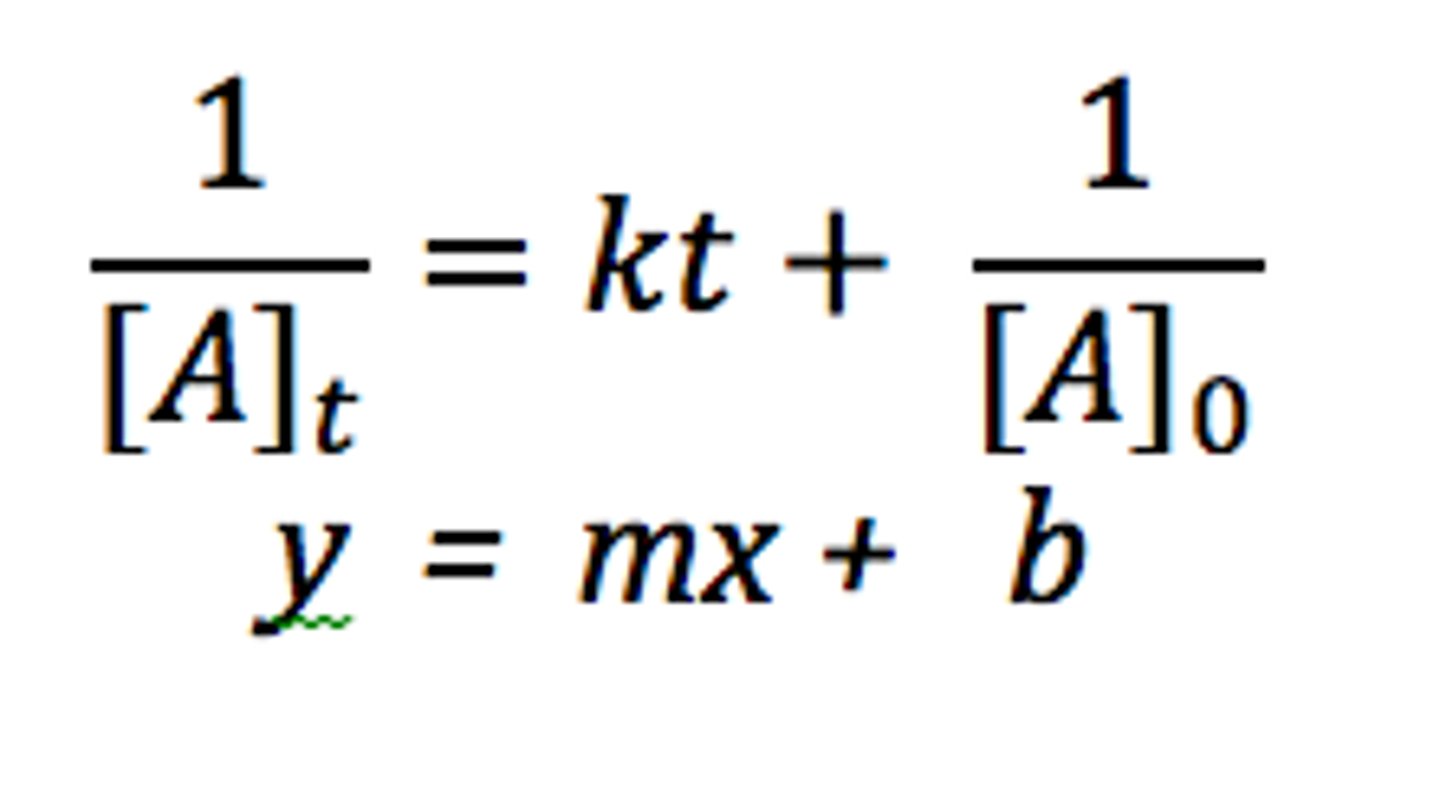
zero order
[A] vs time
first order
ln[A] vs time
second order
1/[A] vs time
range
maximum - minimum value
percent error
experimental-actual/actual
Beers law
explains the relationship between absorbance, at a given wavelength and concentration, A = εbc
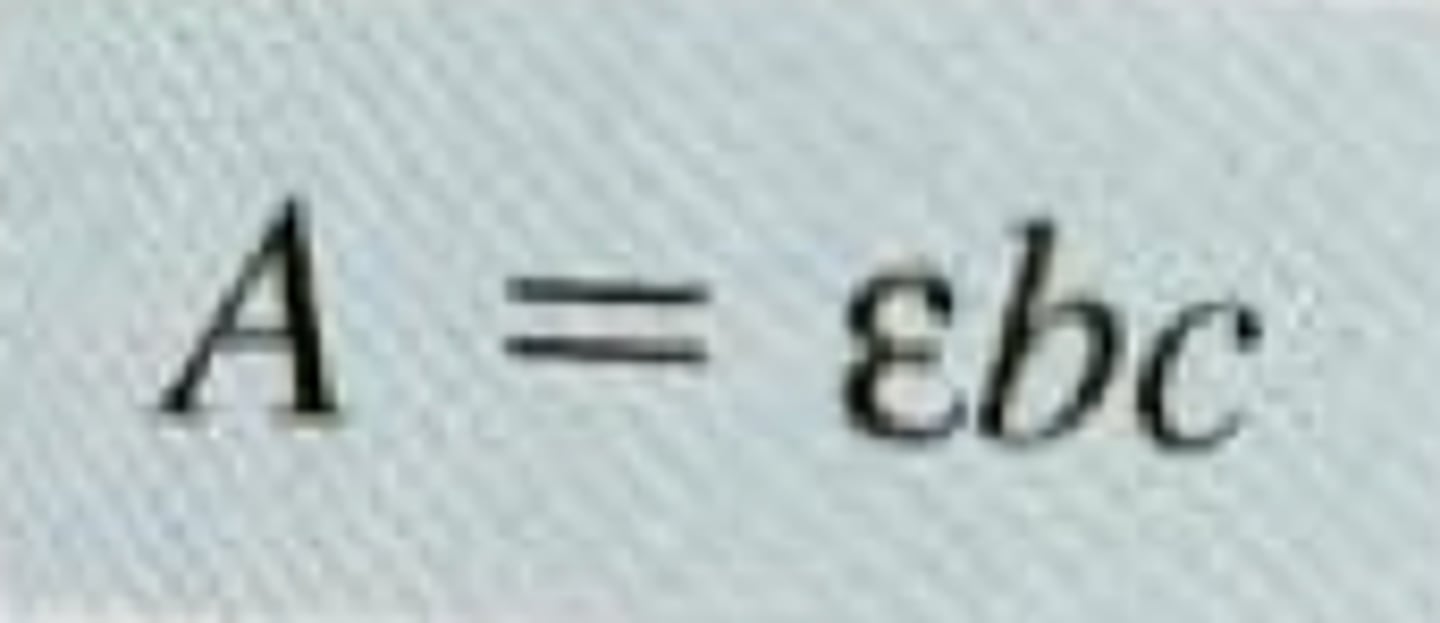
Dilution
the process of reducing the concentration of a solution by adding more solvent to it.
M1V1=M2V2
Serial Dilution
stepwise dilution process
Spectrophotometer
An instrument used to measure the intensity of light at different wavelengths in a sample.
Transmittance
measure of the amount of light that passes through a substance or medium
Red
650-750nm
orange
580-650nm
yellow
560-580nm
green
490-560nm
blue
430-490nm
violet
400-430nm
Equilibrium
The rates of forward and reverse reaction are equal
Kc
equilibrium constant for reactions based on concentrations
Kp
equilibrium constant for reactions based on partial pressures
Le Chatelier's Principle
When a chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed, it returns to equilibrium by counteracting the disturbance
Acid-base indicator
a weak organic acid whose color differs from that of its conjugate base
Ksp
solubility product constant
Titration
technique used to determine the concentration of a substance in a solution by reacting it with a known volume and concentration of another substance (titrant)
Analyte
the substance in a solution whose concentration is being determined through titration
Equivalence point
the point at which the two solutions used in a titration are present in chemically equivalent amounts
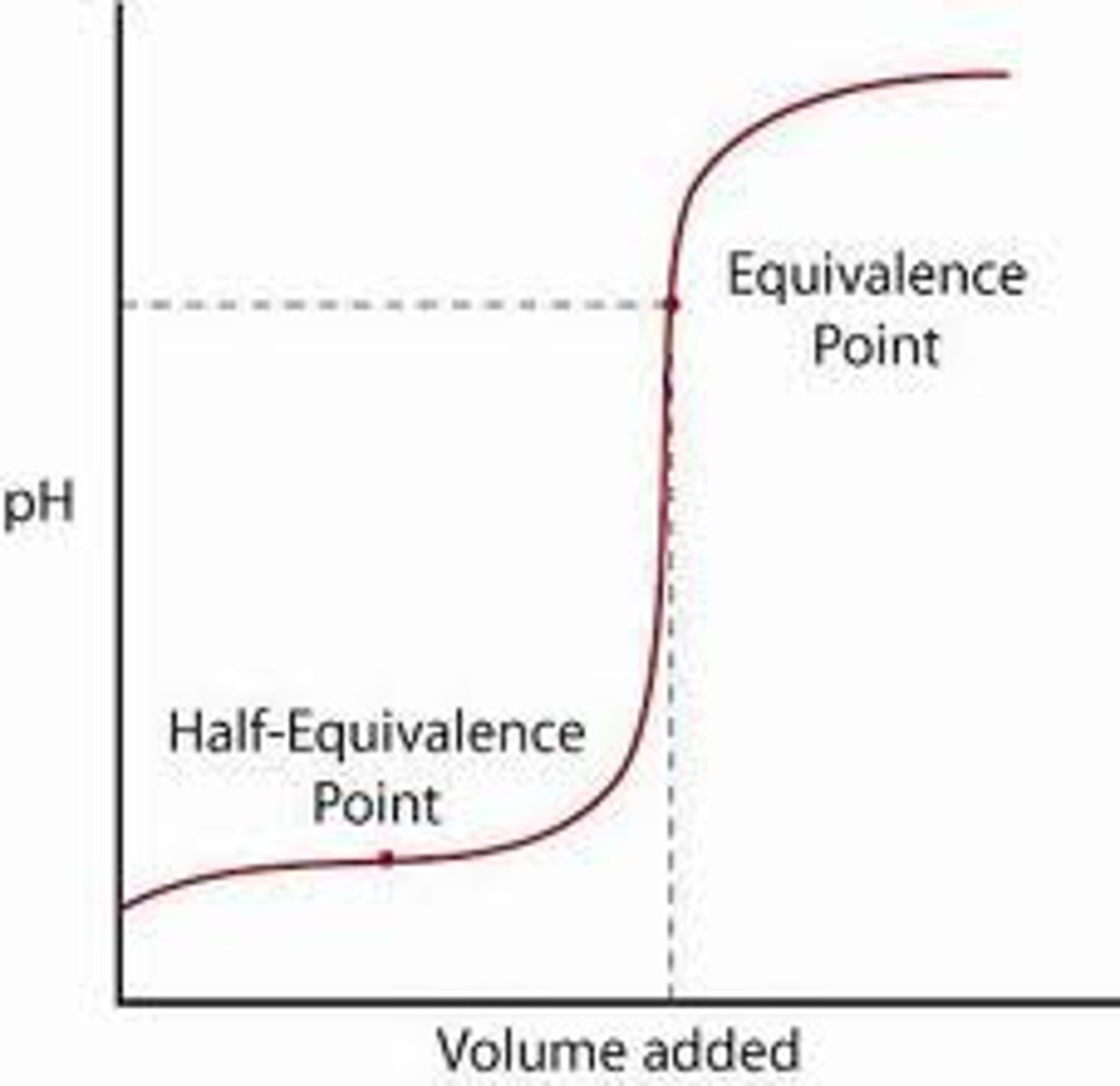
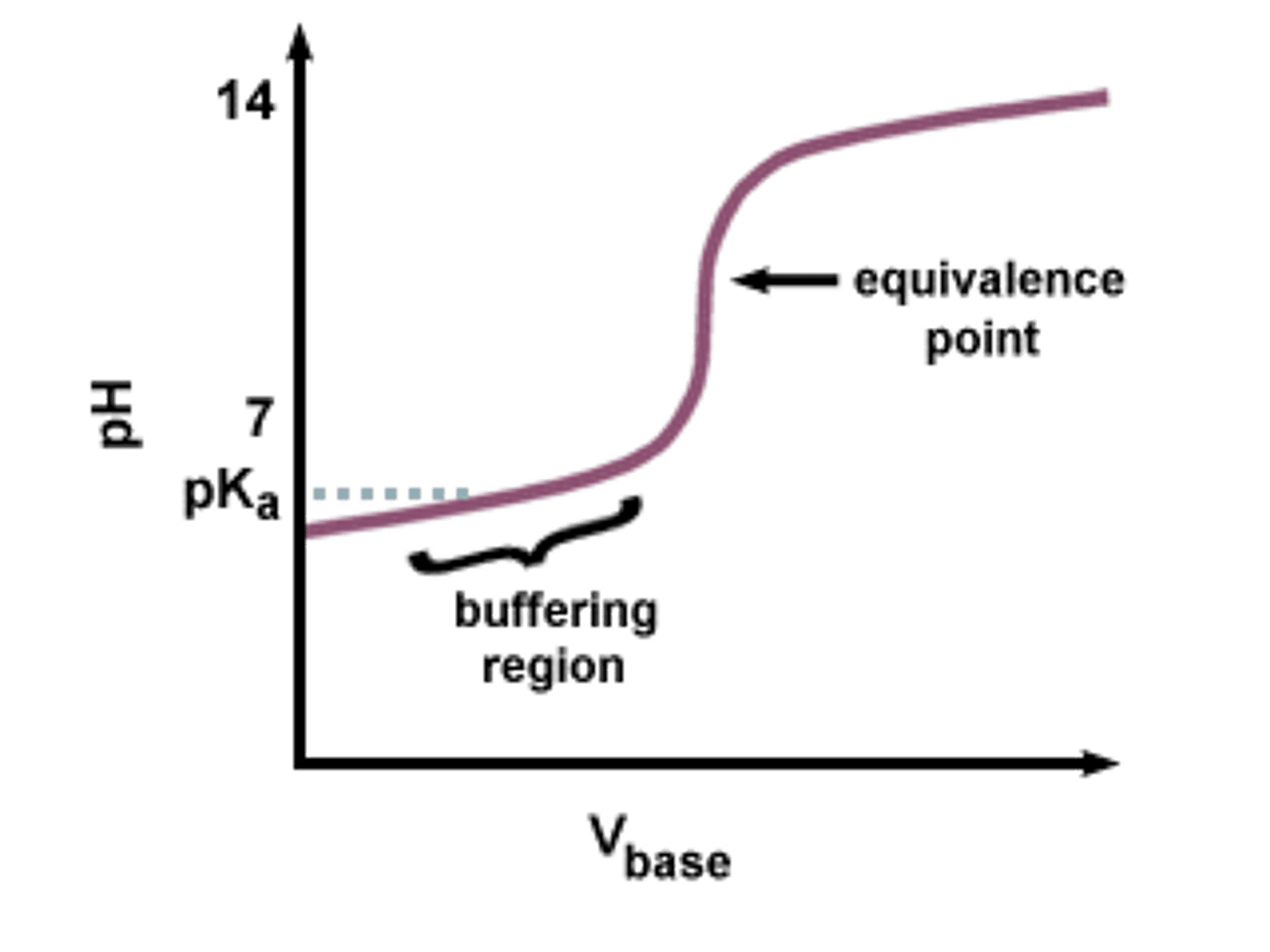
Buffer region
A section of the titration curve where the pH changes gradually as acid or base is added
Calibration
Regular adjustments to tools to keep them accurate.
Buffers
solutions that have a weak acid and its conjugate base, or vice versa.
gel electrophoresis
technique for sorting molecules or fragments of molecules by length
Cathode
Black, negative, samples are put here first
Anode
Red, positive, samples travel here
Entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness, S
Gibbs free energy change
determines whether a reaction is spontaneous or requires energy. negative G=spontaneous
Second law of thermodynamics
all spontaneous processes involved in increase in the entropy of the universe
Galvanic cell
An electrochemical cell powered by a SPONTANEOUS redox reaction that produces an electric current flow; also called a voltaic cell.
Electrolytic cell
Uses an electrical current to drive a non spontaneous reaction
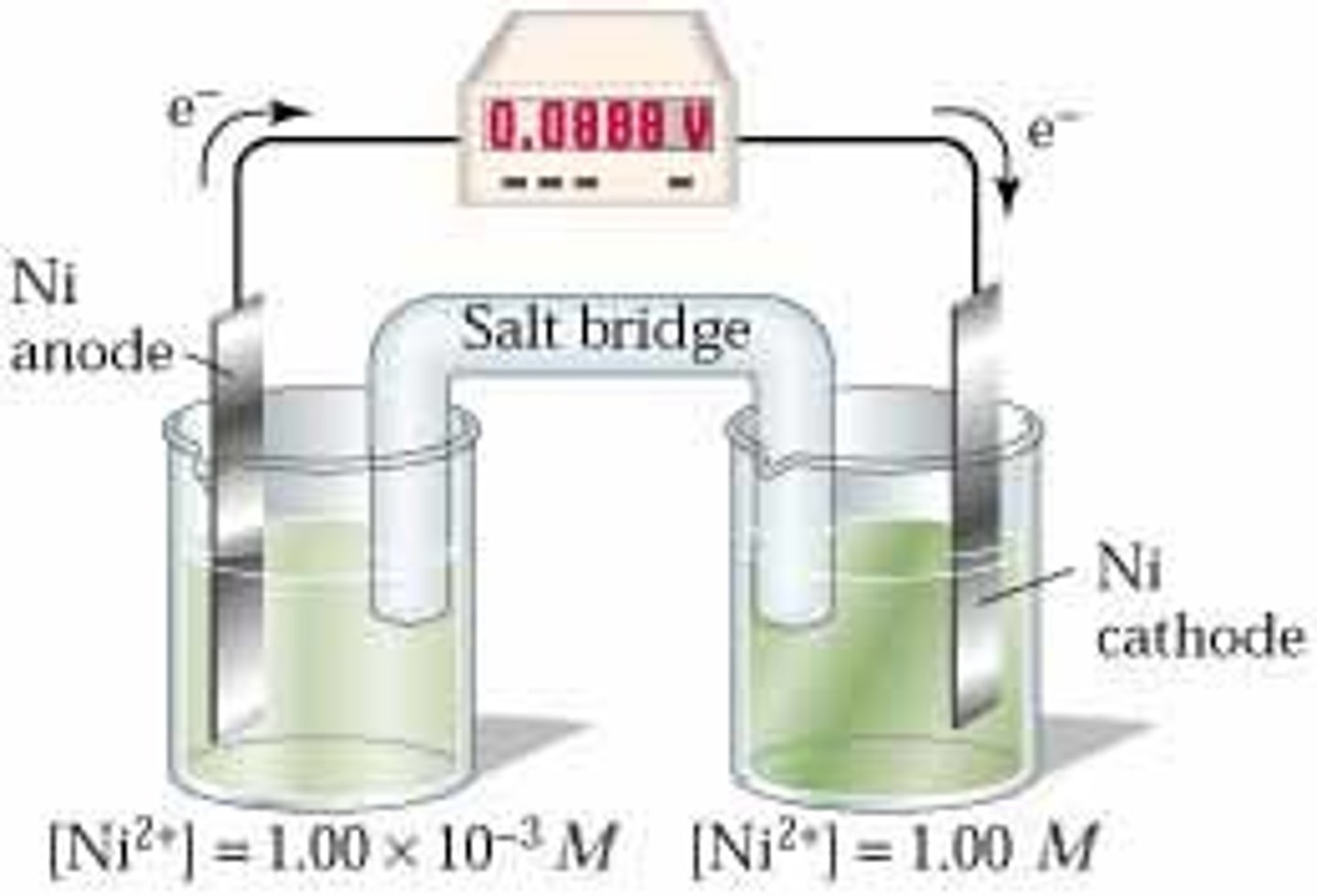
concentration cell
a galvanic cell in which both compartments contain the same components, but at different concentrations
Complex ion
Central metal cation bonded to ligands
Isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties