Digestive system
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Digestion
The process of breaking down food into molecules that body can use
Calorie
Amount of energy needed to raise temperature 1 gram of water 1 degree C
Undernutrition
Undernutrition results when a diet does not provide enough chemical energy
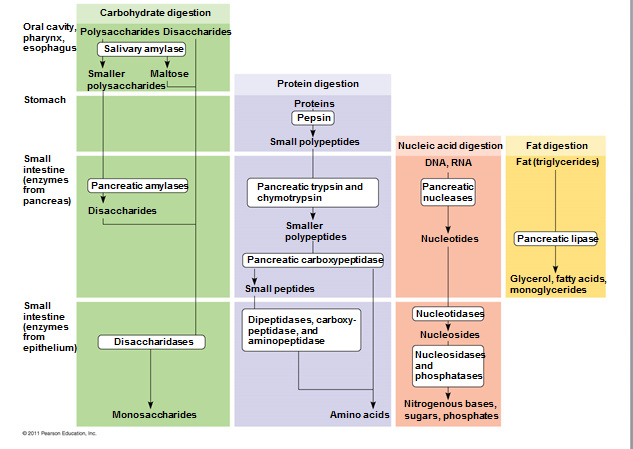
Processes in digestive system
ingestion -> digestion -> propulsion -> absorption -> defecation
Digestive system
consists of the alimentary canal extending from the mouth to the anus, plus accessory organs that empty into the alimentary canal
Alimentary canal, or gastrointestinal (GI) tract: beginning at the mouth, through pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and ending at the anus
Accessory digestive organs: teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
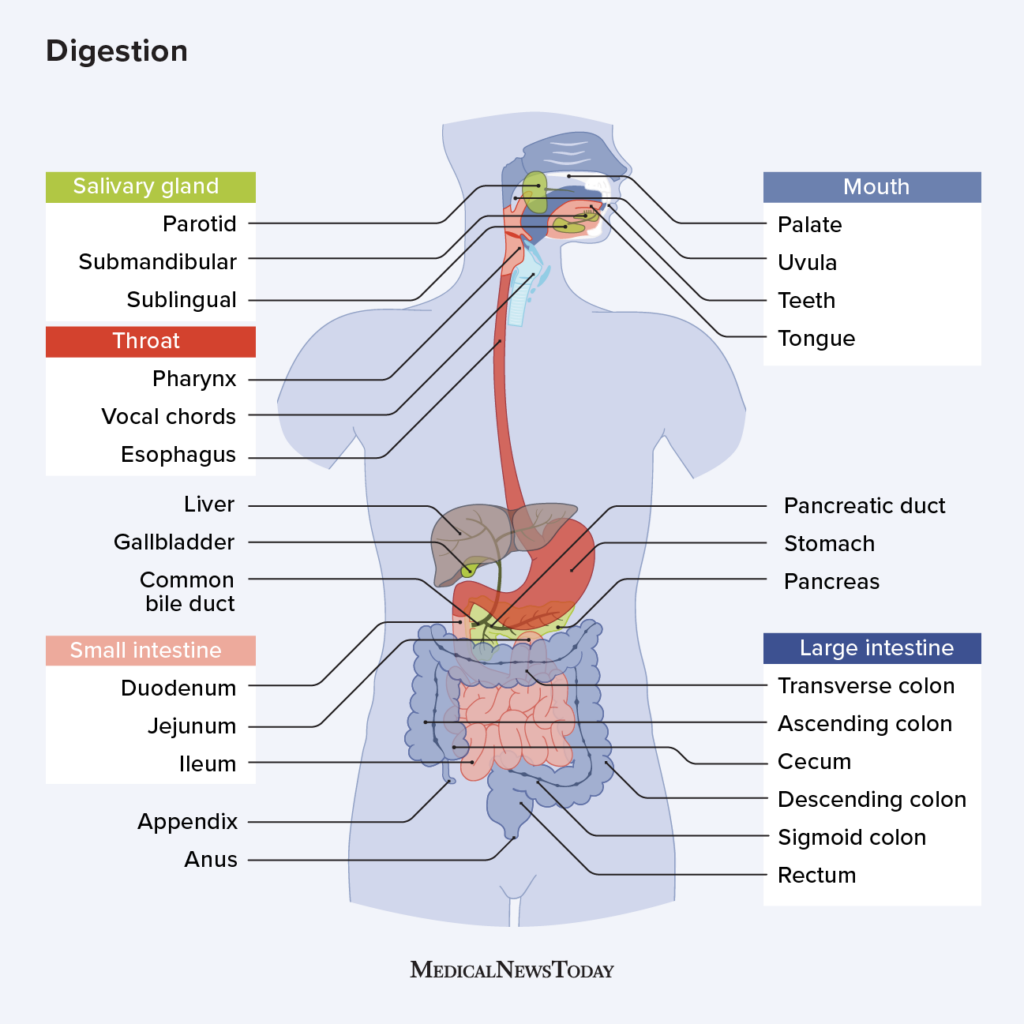
Mouth
ingests food
Mechanically breaks up solid particles using saliva
Prepares food for chemical digestion
Chemically digest a part of carbohydrate.
Starting digestion
Mechanical digestion: teeth
Saliva moistens and lubricates the food as it is chewed.
Saliva contains:
+) amylases, enzymes that breaks down starch into monosaccharides and dextrin.
+) mucus, a viscous mixture of water, salts, cells, and glycoproteins
After being chewed and moistened, food is forced into pharynx by swallowing action and passed into the esophagus.
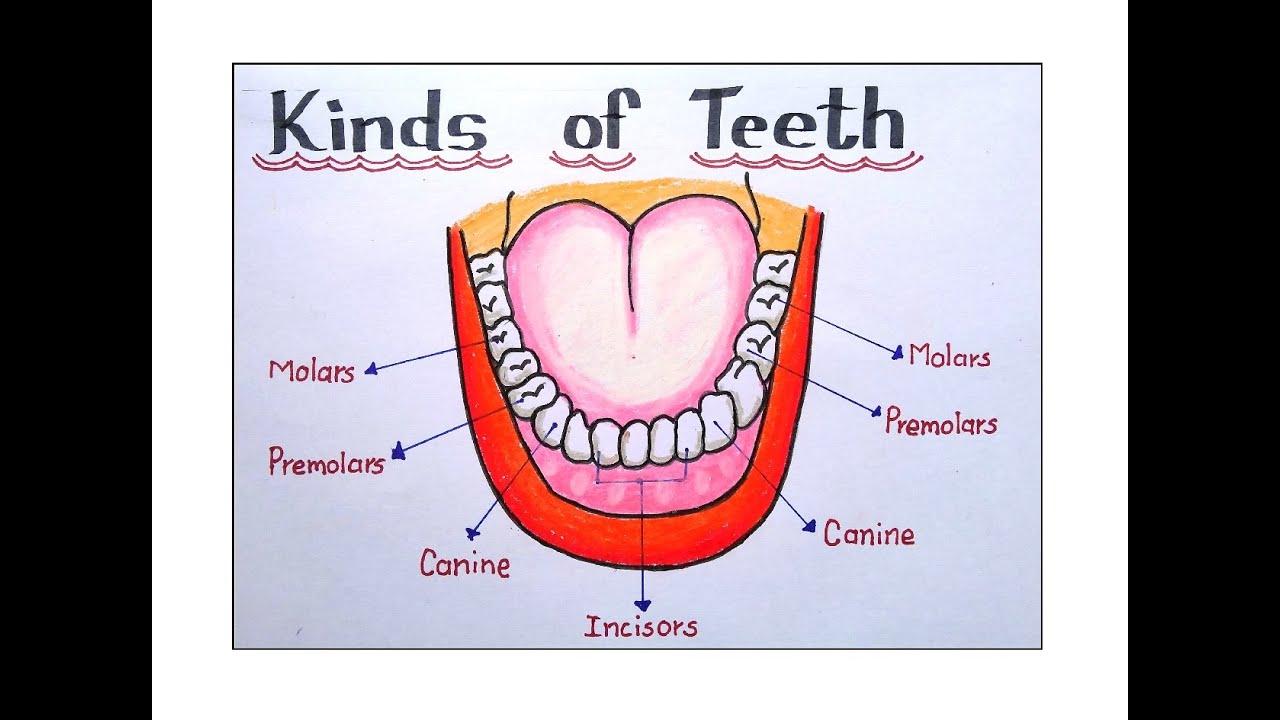
teeth
Milk teeth: 20
Permanent teeth: 32
Incisors: cutting and gnawing
Canines: tearing
Molars and premolars: grinding and shearing
Pharynx
An open area that begins at the back of the mouth, serves as a passageway for both air and food.
The pharynx muscular walls function in swallowing.
A flap of tissue called the epiglottis prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing.
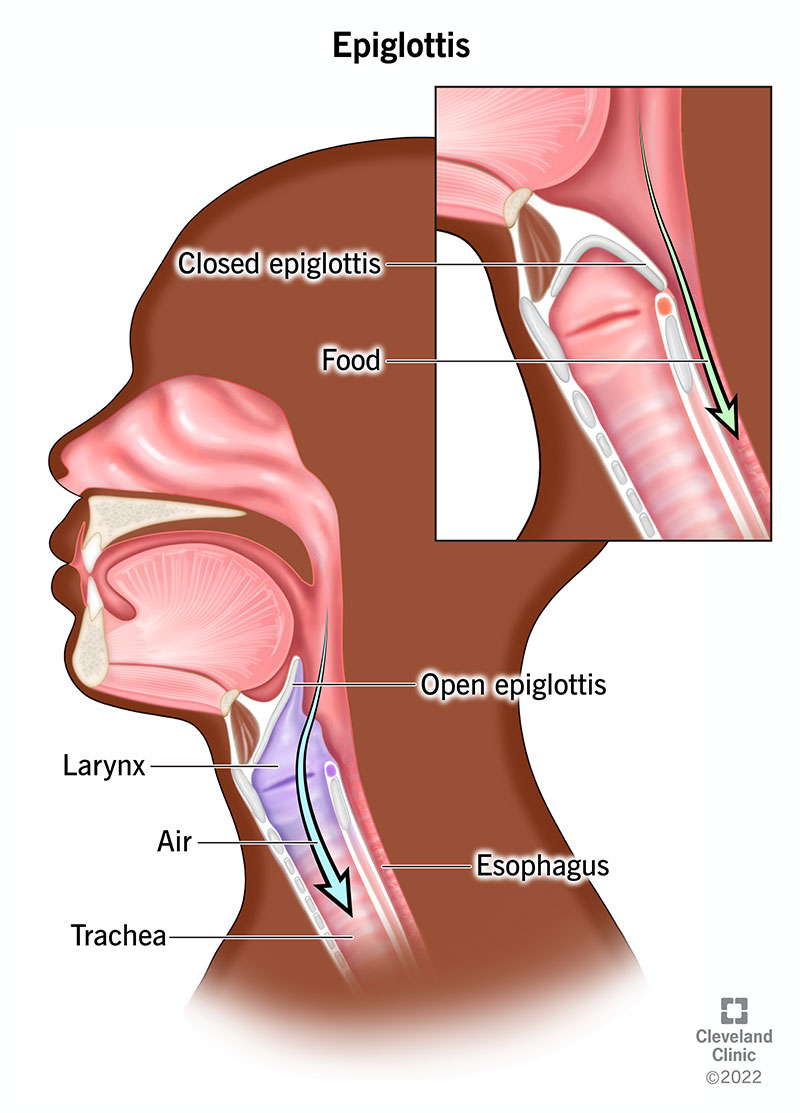
Swallowing mechanism
- Divided into 3 stages:
+) Voluntary stage where saliva is mixed with chewed food
+) Swallowing begins and the swallowing reflex is triggered.
+) Peristalsis transports food in the esophagus to the stomach.
The esophagus
A long tube that connects the mouth to the stomach
2 muscle layers: inner circular layer and outer longitudinal layer.
Peristalsis is a process of coordinated contractions and relaxations of the circular and longitudinal layers, pushes the bolus onward
The stomach
A J-shaped, pouch-like organ
The cells that line the inside of the stomach release gastric juice (hydrochloric acid)
The mixture of digested food and gastric juice is called chyme
Sphincters prevent chyme from entering the esophagus and regulate its entry into the small intestine.
The stomach anatomy
Three layers of muscle:
a longitudinal layer
a circular layer
a diagonal layer
Cardiac sphincter: a circular muscle between the esophagus and the stomach closes to prevent the food from reentering the esophagus.
Pyloric sphincter: a circular muscle between the stomach and the small intestine, regulates the flow of digested food to the small intestine
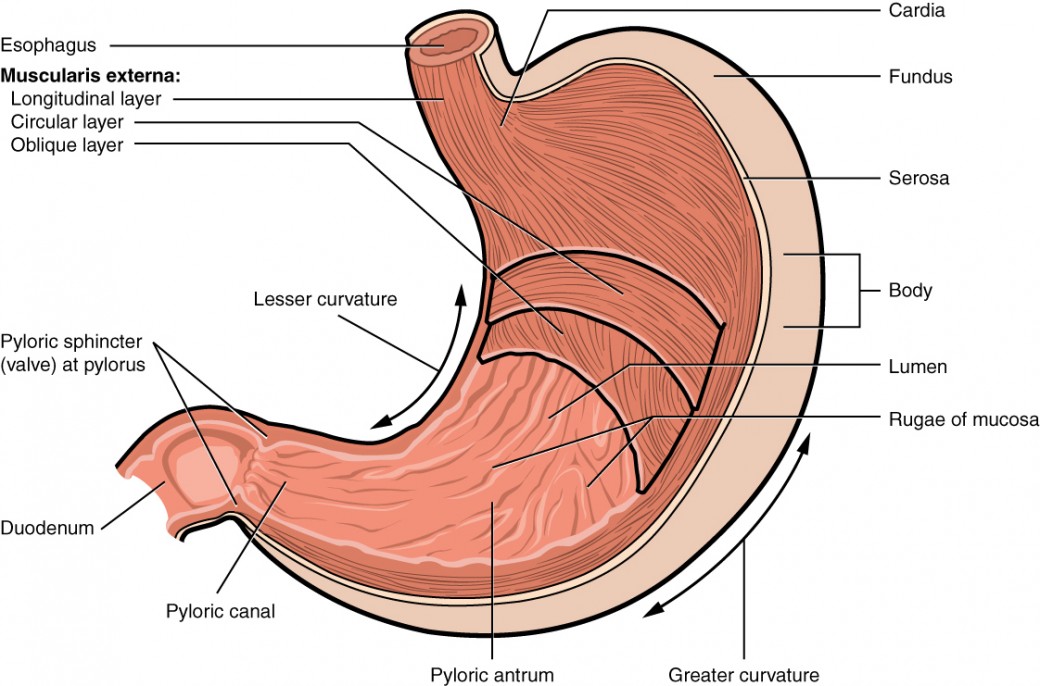
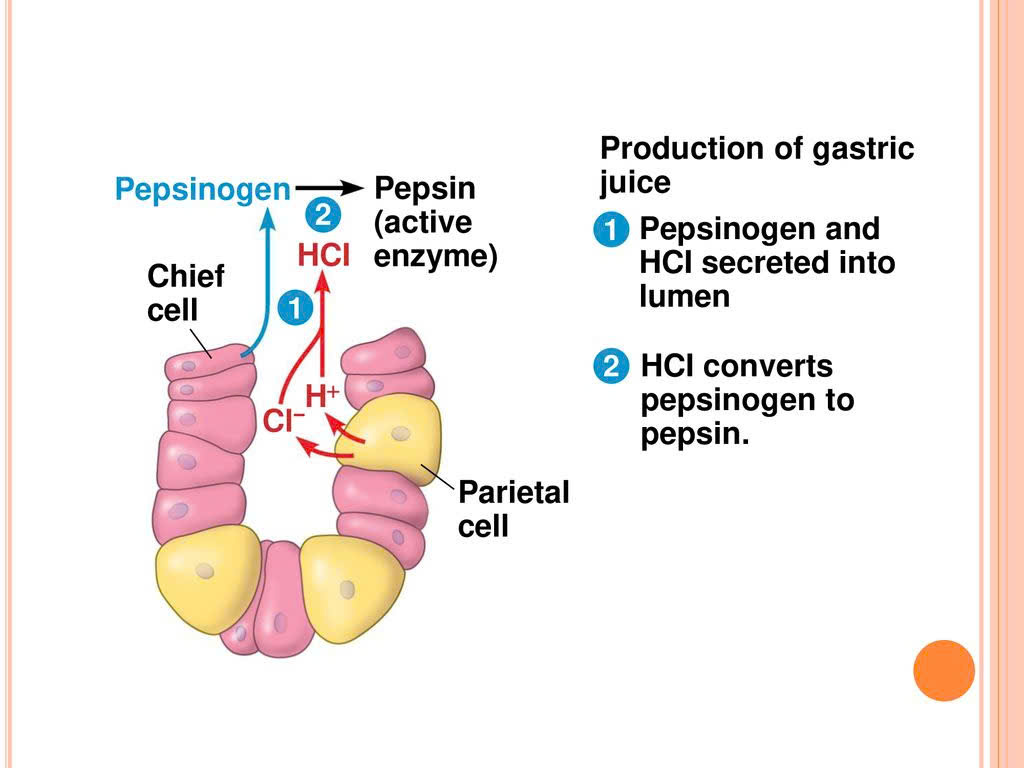
the stomach and its secretions
Gastric glands secrete mucus, digestive enzymes, and hydrochloric acid (gastric juice).
Parietal cells secrete hydrogen and chloride ions separately into the lumen of the stomach => Hydrochloric acid ensures a low pH (1.5-2.5) to dissolves minerals and kills bacteria that enter the stomach along with food.
Chief cells secrete inactive pepsinogen, which is activated to pepsin when mixed with hydrochloric acid in the stomach => Pepsin breaks down proteins into peptides.
Mucus protects the stomach from gastric juice.
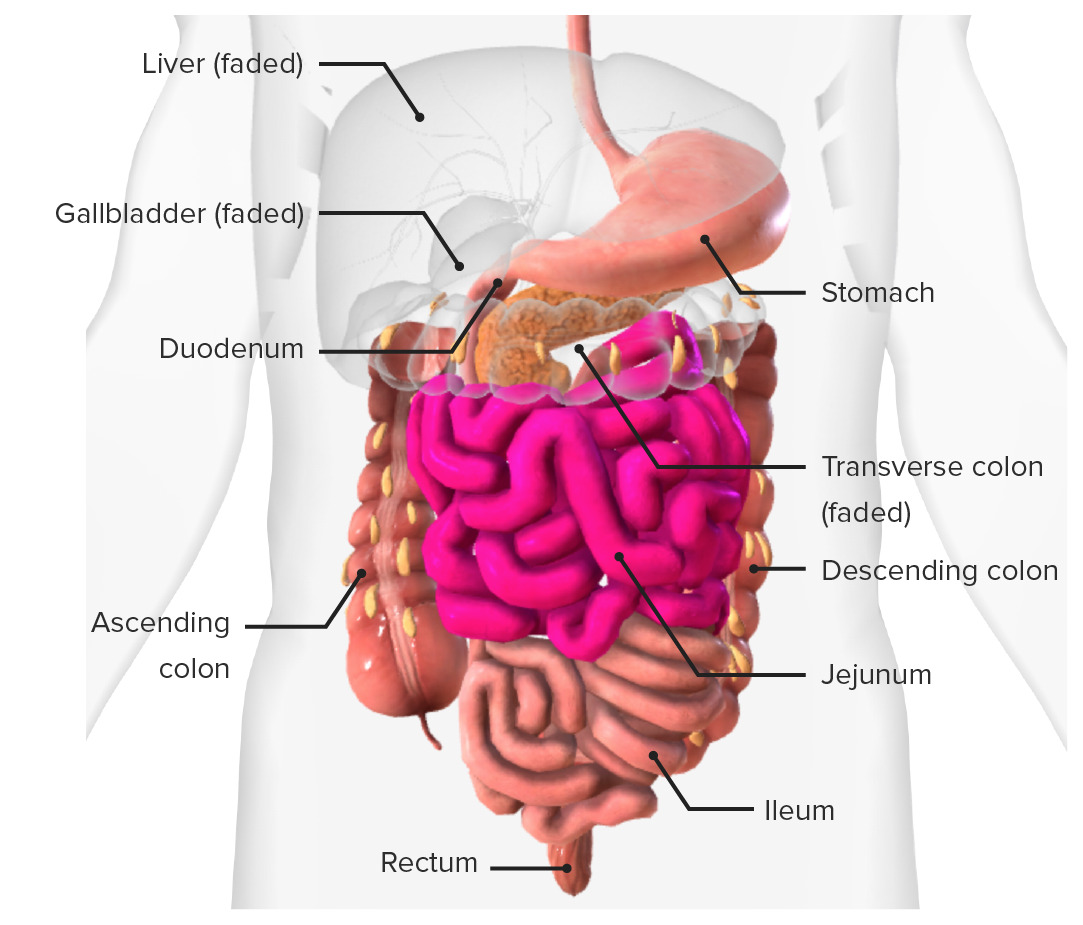
regions of small intestine
Food passes from the stomach into the small intestine. => Main function in the digestion and absorption of nutrients
Duodenum contain glands that secrete mucus and receive the pancreatic secretions and the bile from the liver through a common duct.
Jejunum and Ileum contain folds and villi (Ileum fewer than Jejunum)
movements of the small intestine
The wall of the small intestine has 2 types of movements: segmentation and peristalsis
+ Segmentation refers to contractions and constrictions that serve to bring chyme into digestive juices and to encourage absorption.
+ Peristalsis moves nondigested remains toward the large intestine.
Composition of small intestine
Pancreatic enzymes (amylase, lipase) are released into the first part of the small intestine
The lining of the small intestine is covered with fingerlike projections called villi, which increase the surface area available for absorption of nutrients
Digestion is completed in part of the small intestine
Most digestion takes place in the duodenum
The pancreas, liver, and gallbladder aid in digestion
+) pancreas: digest fat and protein, carbohydrate, nucleic acid
+) bile from the liver/gallbladder: digest fats
Liver
Large organ located to the right of the stomach.
Secretes bile, which aids the breakdown of fats
=> Bile promotes the absorption of fatty acids and the fat-soluble vitamins A,D,E and K
Liver functions
Detoxifies blood (removing and metabolizing poisonous substances)
Stores iron (Fe2+) and the fat-soluble vitamins.
Makes plasma proteins, such as albumins and fibrinogen, from amino acids.
Produces urea after breaking down amino acids.
Destroys old red blood cells; excretes biliburin, a breakdown product of hemoglobin in bile
Helps regulate the blood cholesterol level, converting some to bile salts
Pancreas
Lies behind the stomach.
Acts as an endocrine gland, producing hormones that regulate blood sugar levels: insulin and glucagon.
Produces sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes stomach acid
Produces enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids.
Absorption
The small intestine has a huge surface area, due to villi and microvilli that are exposed to the intestinal lumen
The hepatic portal vein carries nutrient-rich blood from the capillaries of the villi to the liver, then to the heart.
Chylomicrons
Epithelial cells absorb fatty acids and monoglycerides and recombine them into triglycerides.
These fats are enclosed by phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins to form water-soluble chylomicrons.
Chylomicrons are transported into a lacteal, a lymphatic vessel in each villus
Lymphatic vessels deliver chylomicron-containing lymph to large veins that return blood to the heart
The large intestine
Contains 4 parts: Cecum, Colon (ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid), rectum, anus
Similar to the movements of the small intestine but slower and less frequent than that of small intestine
Movements include:
Mixing movements
Peristalsis
No digestion takes place in the colon
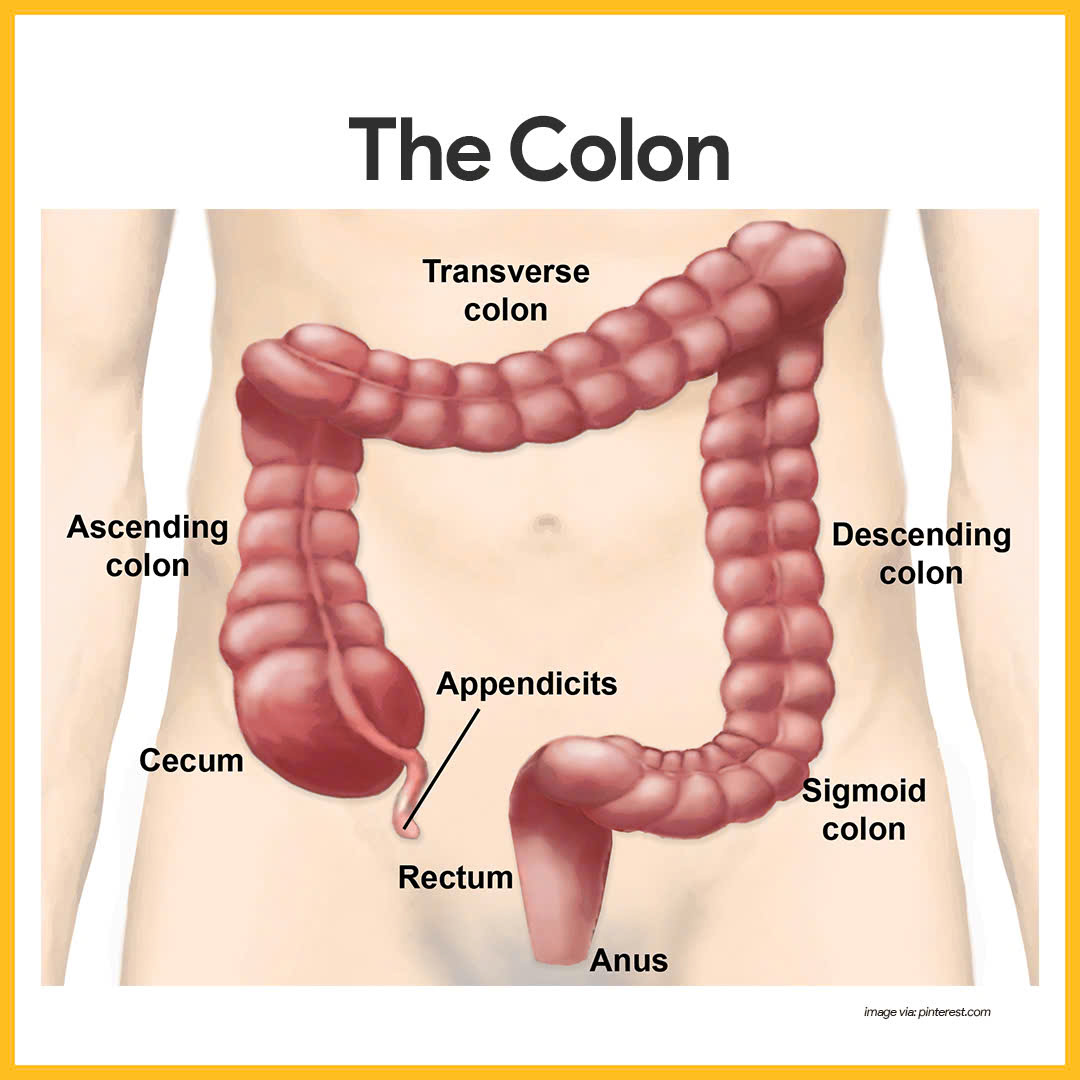
The large intestine contains many bacteria
Some synthesize important vitamins
Some, like E.coli, can cause illness
Functions of some parts in the large intestine
The colon helps to maintain the body's fluid balance, recover water that has entered the alimentary canal.
The cecum aids in the fermentation of plant material and connects where the small and large intestines meet.
Human cecum has an extension called the appendix (plays a very minor role in immunity)
Undigested material forms the solid feces
Stored in rectum
Eliminated through anus
2 sphincters between the rectum and anus control bowel movements.
Chemical digestion in human digestive system