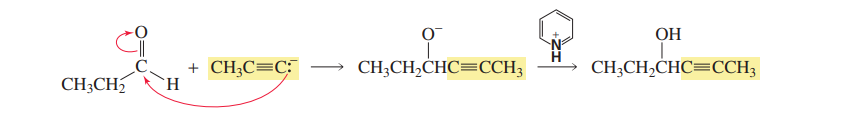Organic chemistry 2- reactions-factoids
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
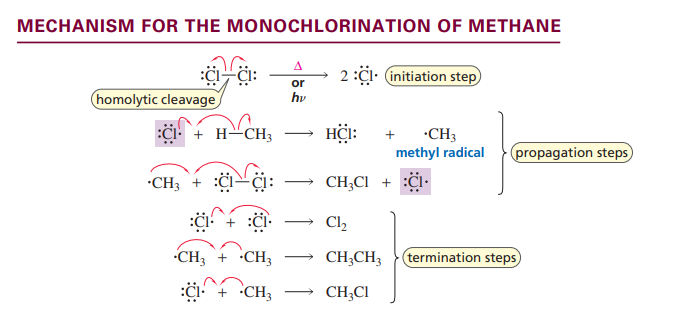
Monochlorination of methane
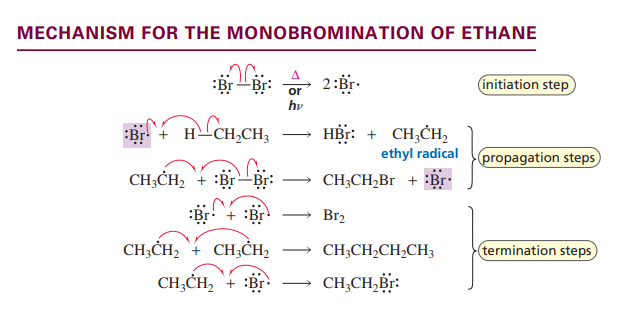
Monobromination of ethane
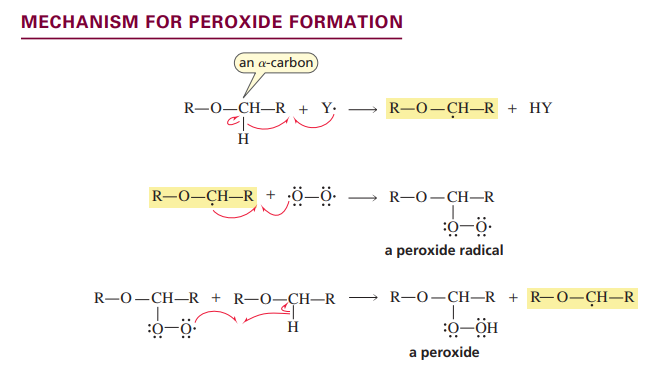
Peroxide formation
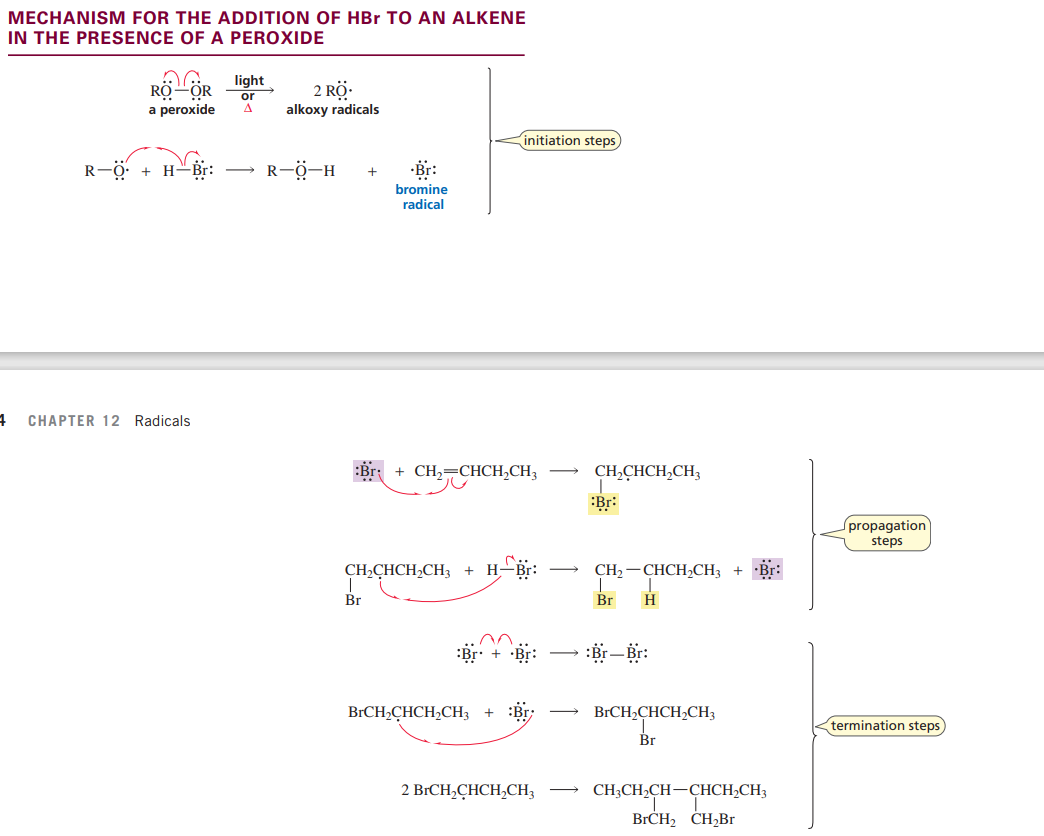
Addition of HBr to an alkene in the presence of a peroxide
Peroxide plays a role in allylic brominations by easily forming radicals, which then react with NBS to generate bromine radicals
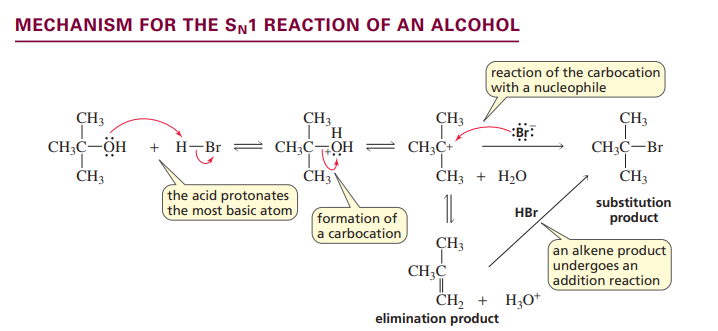
Sn1 reaction of an alcohol
only for tertiary and secondary alcohols
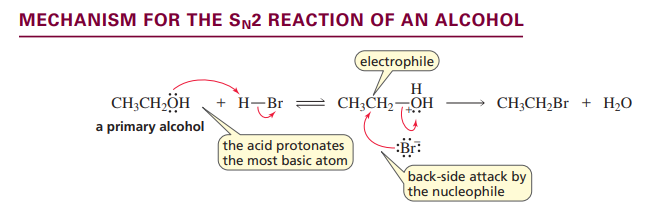
Sn2 reaction of alcohol
Only for primary alcohols
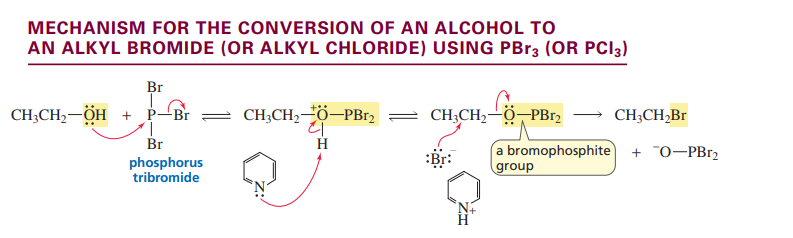
Converting an alcohol to an alkyl bromide using PBr3
Converting an alcohol to an alkyl chloride using SOCl2
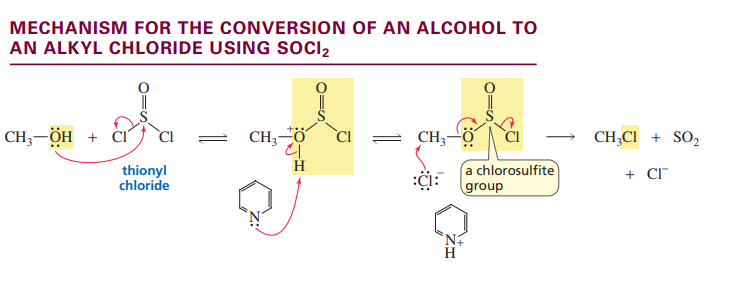
Converting an alcohol to a sulfonate ester
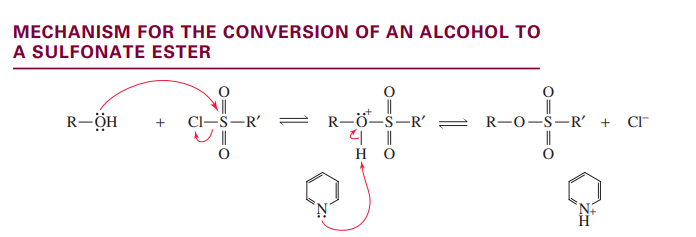
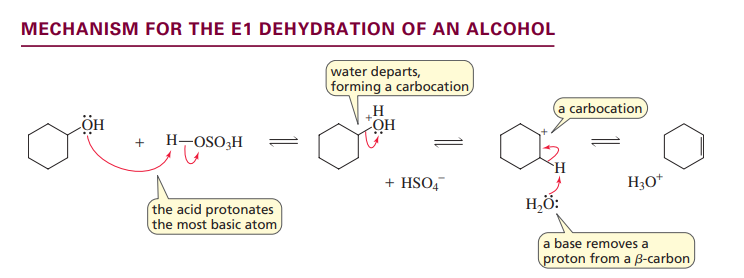
E1 dehydration of an alcohol
secondary and tertiary
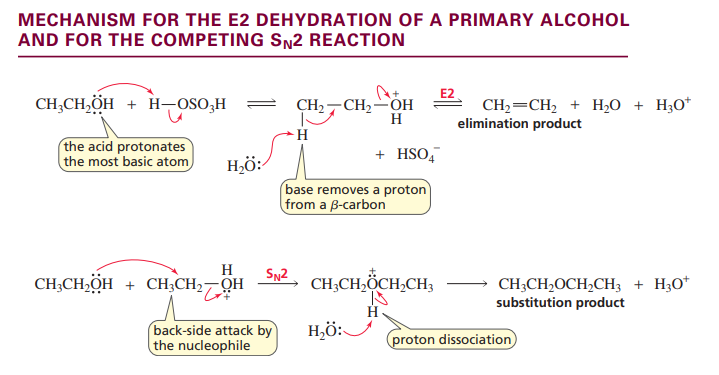
E2 dehydration of alcohol
primary
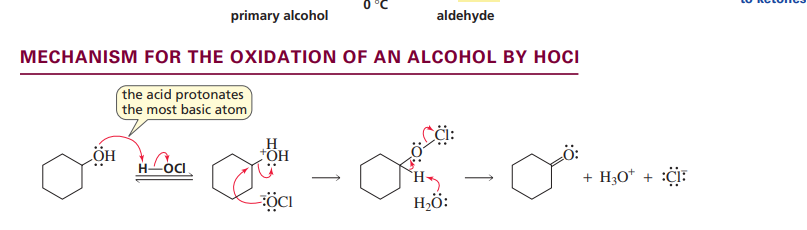
Oxidation of an alcohol
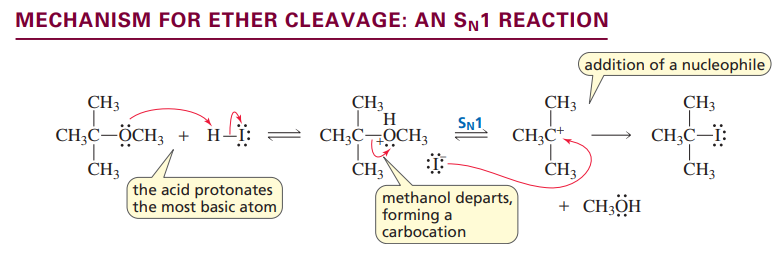
Ether cleavage: Sn1 reaction
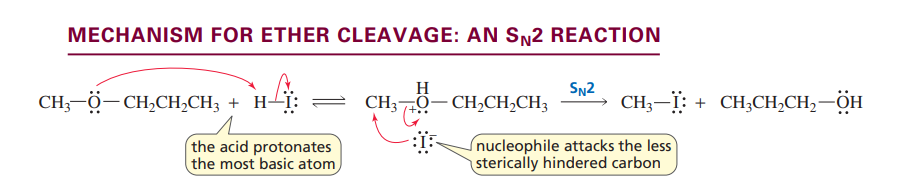
Ether cleavage: Sn2 reaction
Ethers are cleaved with an Sn1 reaction unless the stability of the carbocation requires it to be an Sn2
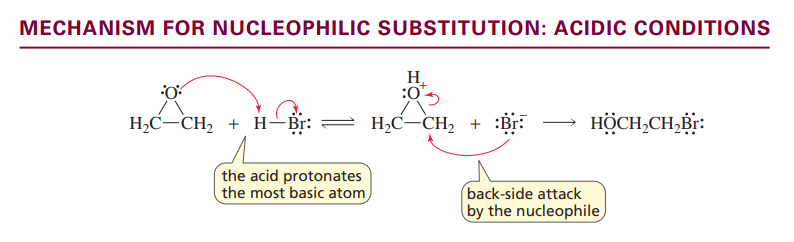
Nucleophilic substitution reaction of Epoxides
ACIDIC CONDITIONS
Under acidic conditions the nucleophile prefers to attack the more substituted ring carbon
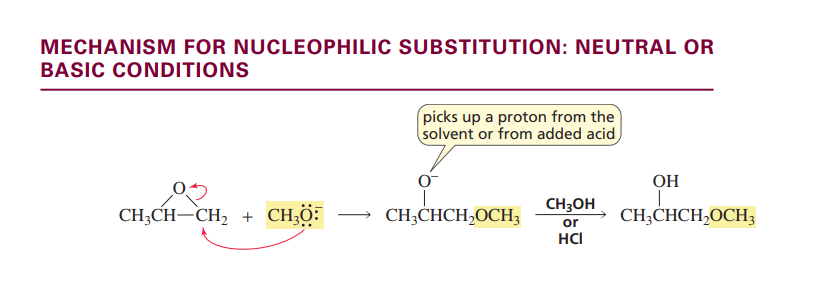
Nucleophilic substitution reaction of Epoxides
BASIC/NEUTRAL CONDITIONS
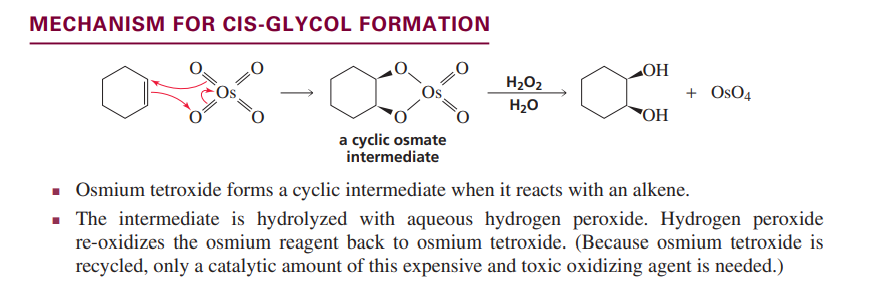
Cis Glycol formation
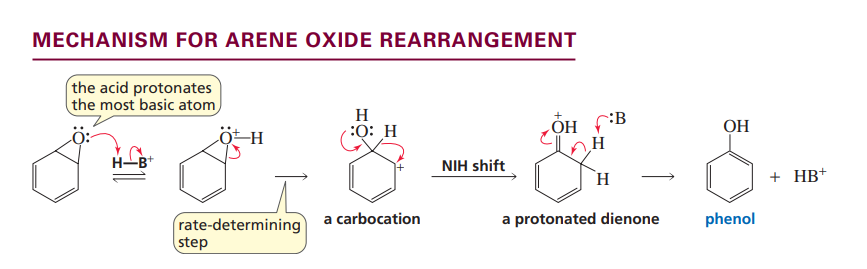
Arene Oxide Rearrangement
NIH shift
Bonus: what decides carcinogenity of arene oxides
The less stable the carbocation upon ring opening, the more carcinogenic it is.
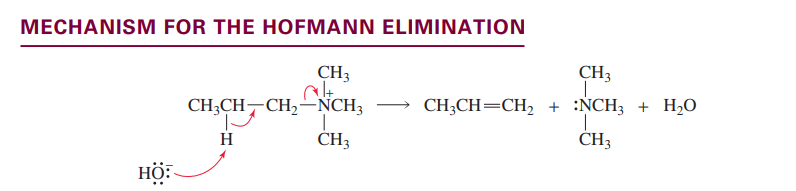
Hofmann-Elimination of a quartenary ammonium
Anti-zaitsev elimination: proton removed from carbon with least protons
This is because that creates the most stable alkene transition state.
Thiols are the analogues of what?
alcohols
Sulfides are the analogues of what?
ethers
Sulfonium ions are the analogues of what
Quart. ammonium ions
The weaker the base the?
better the leaving group
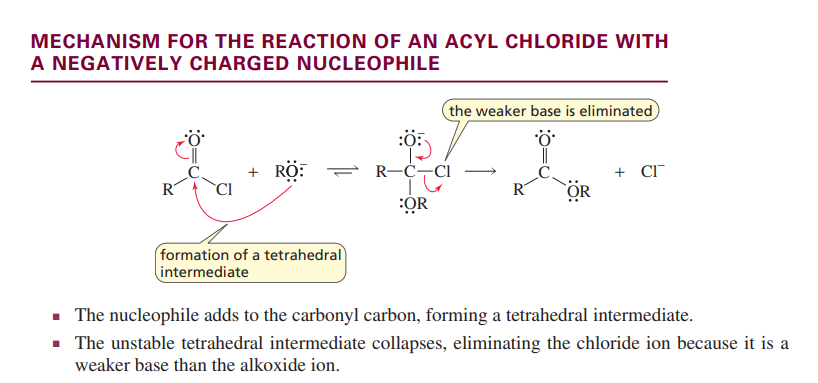
Reaction of an acyl chloride with a negative nucleophile
tetrahedral intermediate is formed
weakest base leaves
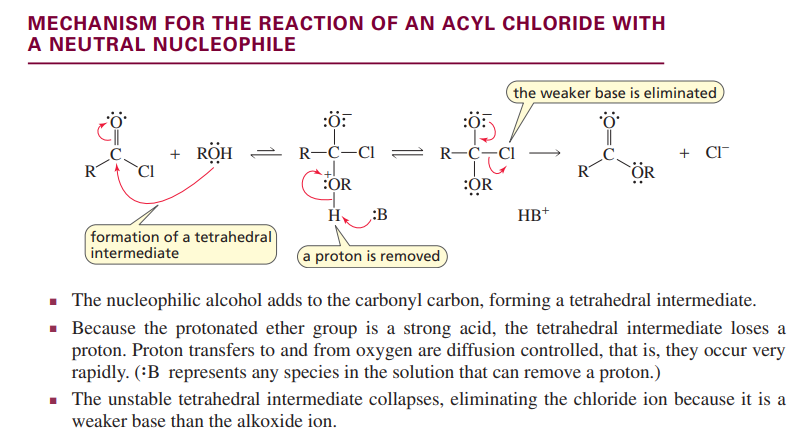
Reaction of an acyl chloride with a neutral nucleophile
Transesterification
The conversion of one ester into another ester
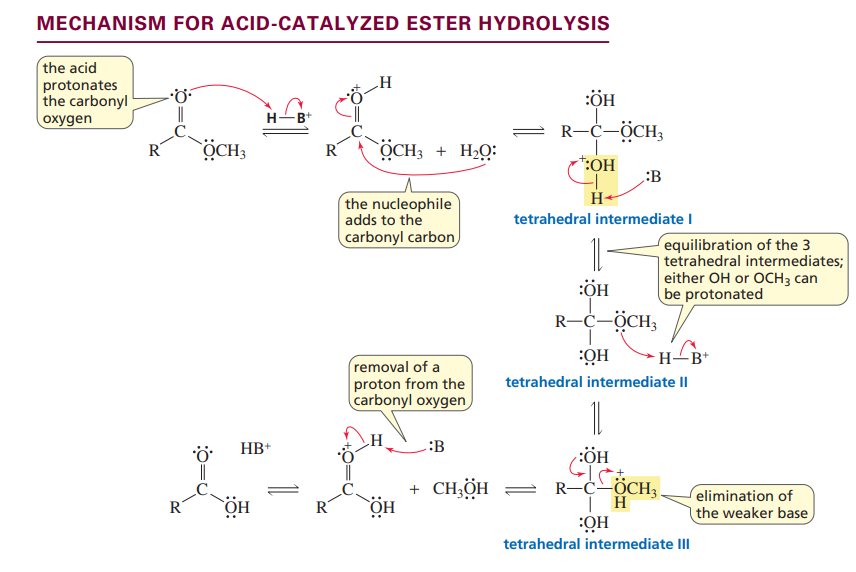
Mechanism for acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis
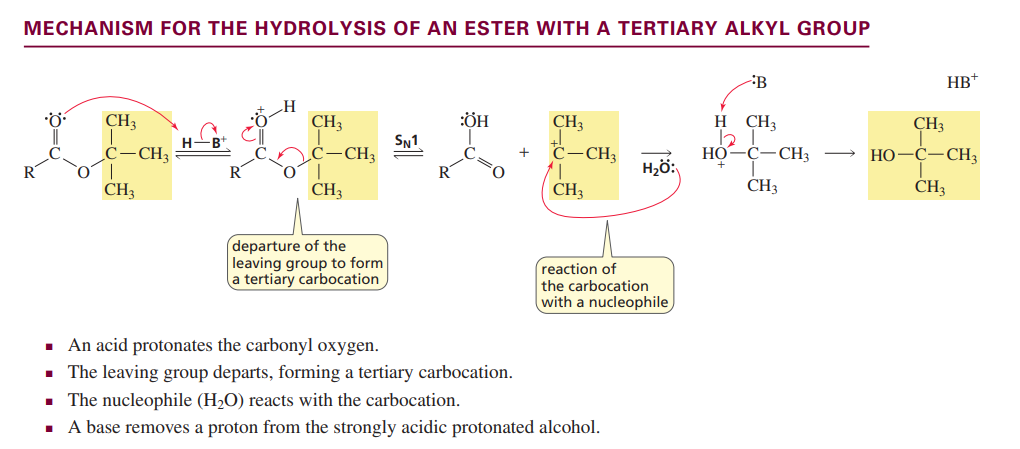
Ester hydrolysis with tertiary alkyl group
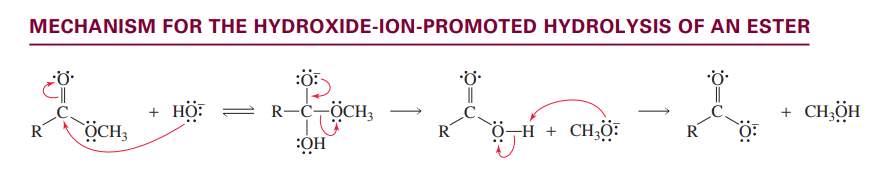
Hydroxide promoted ester hydrolysis
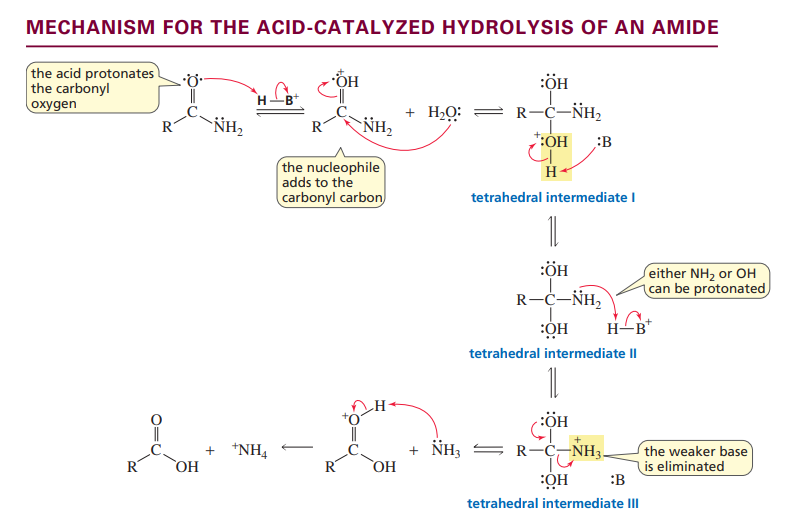
Acid catalyzed amide hydrolysis
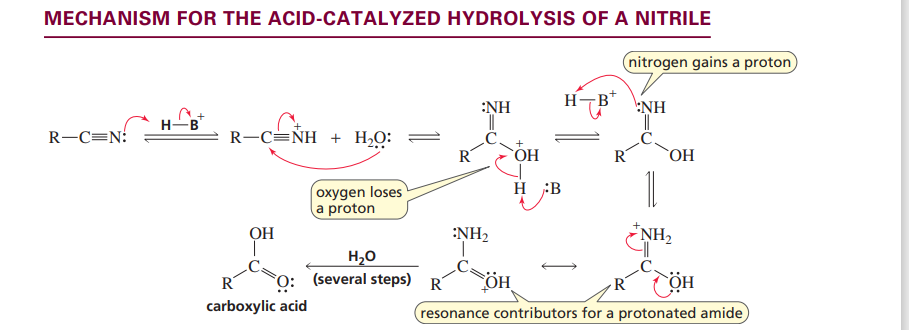
Acid cataylsed hydrolysis of a nitrile
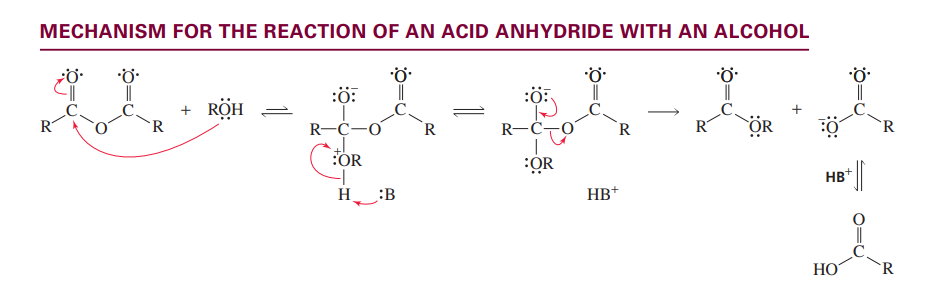
Reaction of an acid anydride with a alcohol
Grignard reagent
Magnesium halide that makes the carbon a nucleophile
Formaldehyde with grignard
Creates a primary alcohol
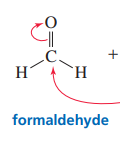
Aldehyde with grignard
Creates a secondary alcohol
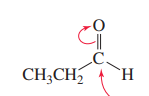
Ketone with grignard
Creates a tertiary alcohol
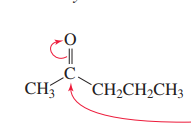
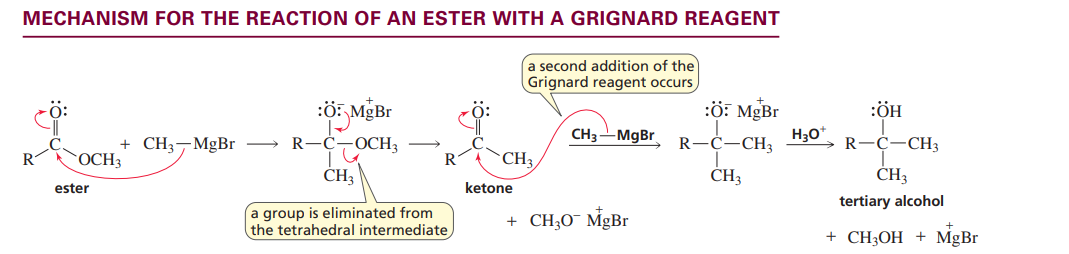
Ester with grignard reagent
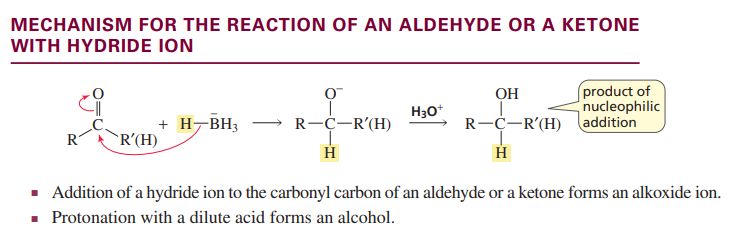
Mechanism for aldehyde/ketone with hydride ion
M
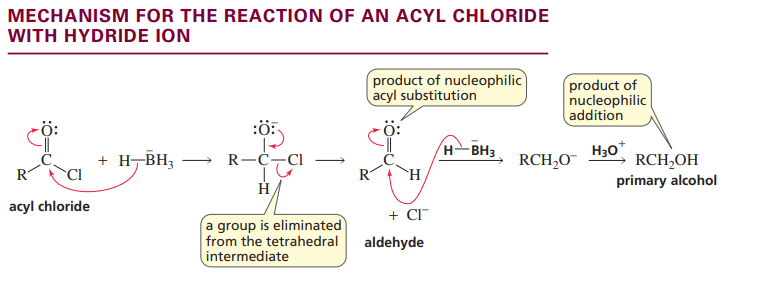
Mechanism for acyl chloride with hydride ion
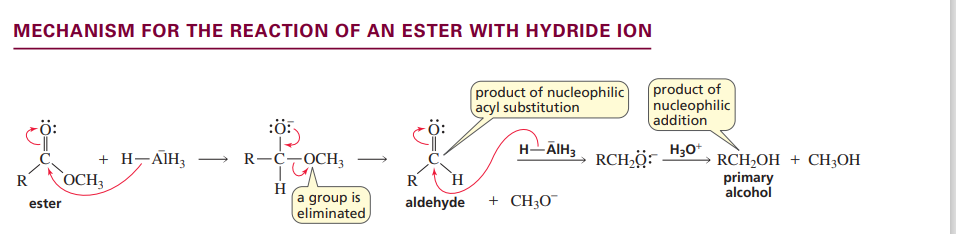
Mechanism for ester with hydride ion
Me
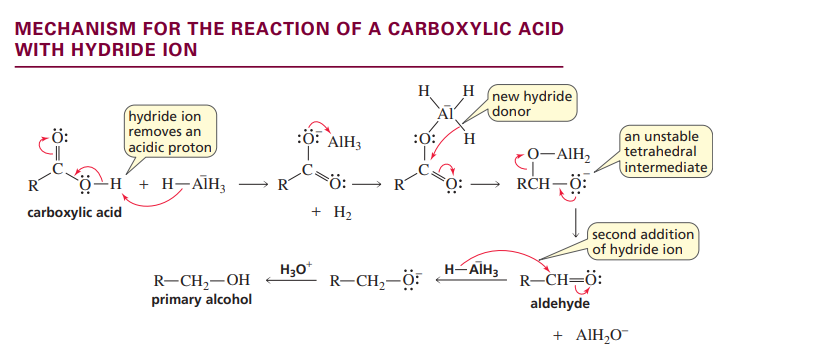
Mechanism for carboxylic acid with hydride ion
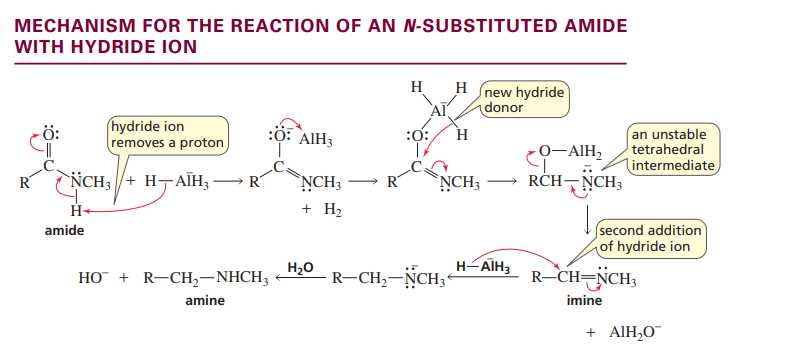
Mechanism forn substitued amide with hydride ion
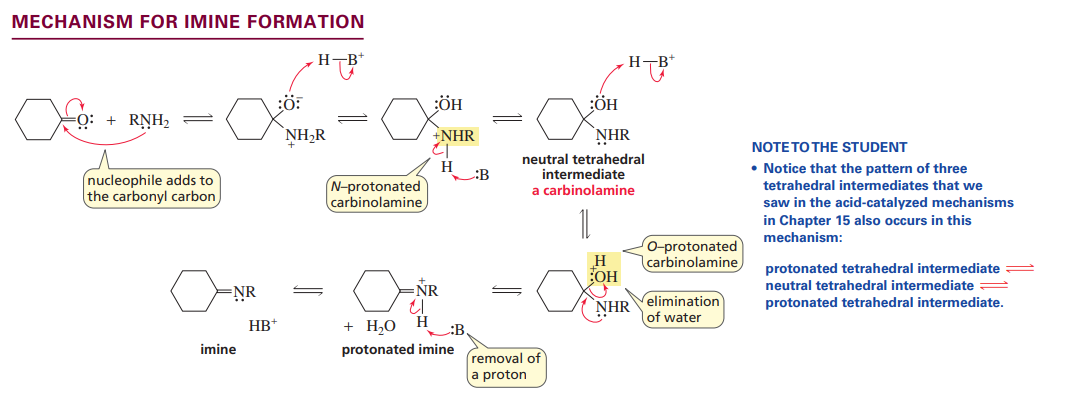
Mechanism for imine formation
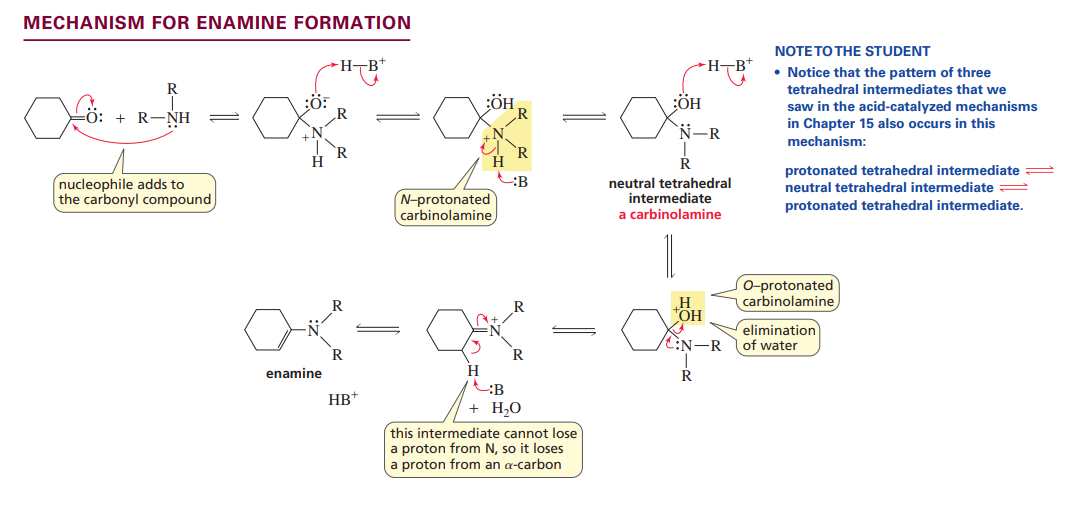
Mechanism for enamine formation
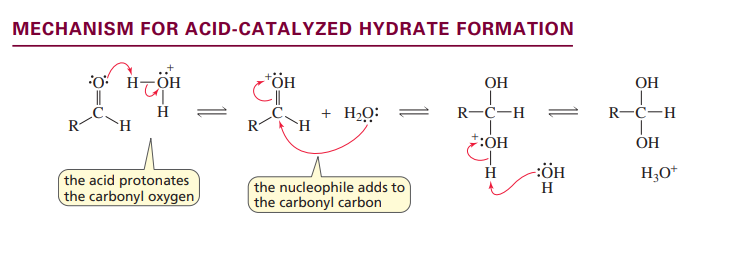
Mechanism acid catalyzed hydrate formation
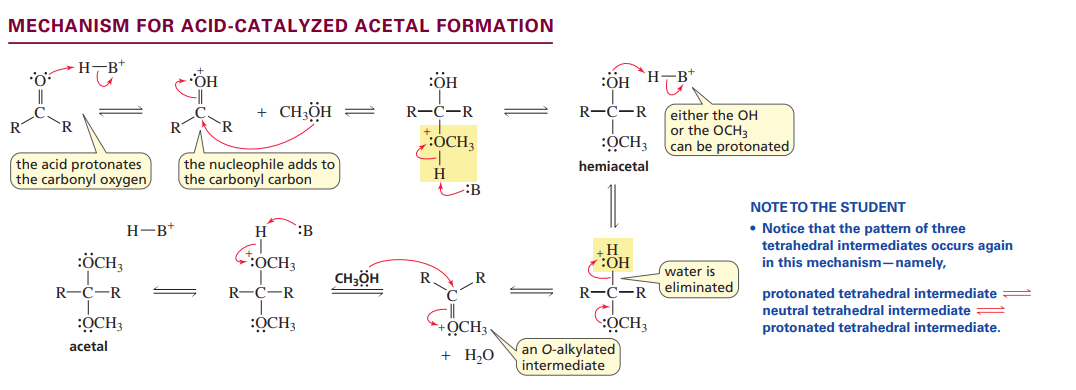
Mechanism acid catalyzed acetal formation
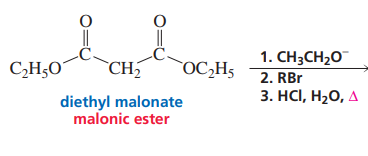
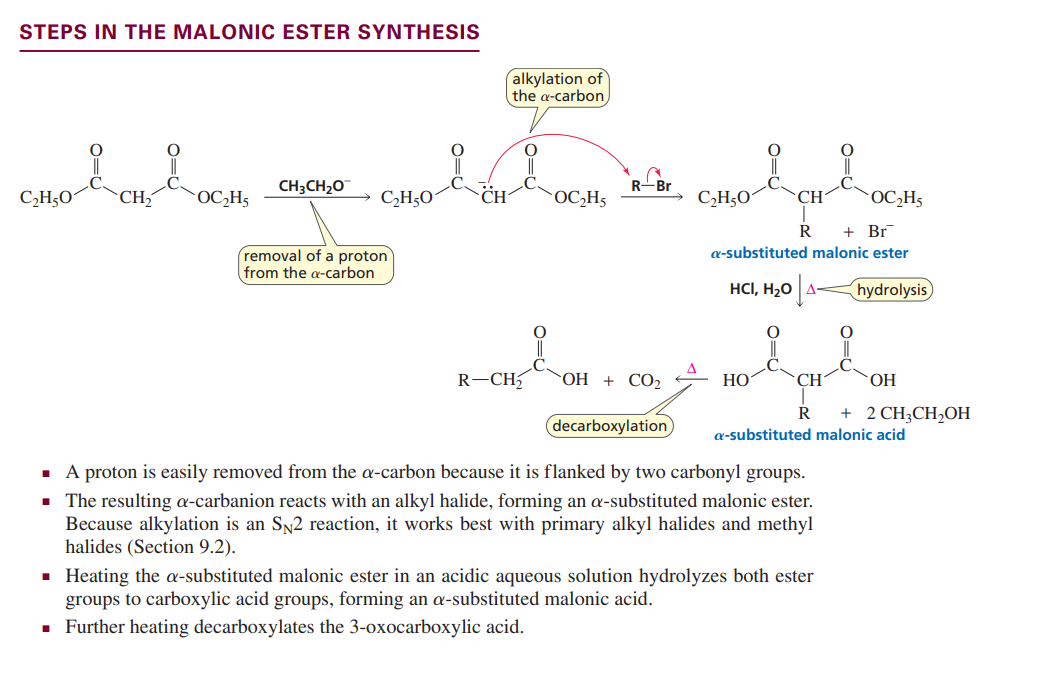
Malonic ester formation
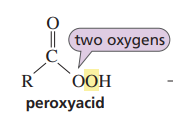
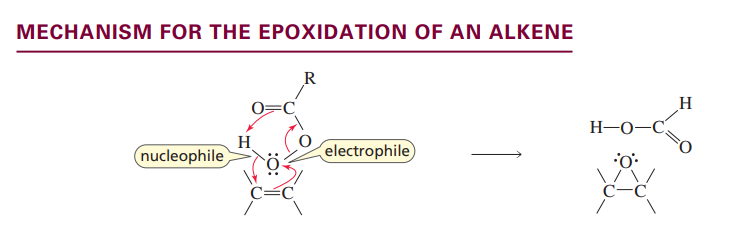
What reactant can form an epoxide?
a peroxy acid
Epoxide formation
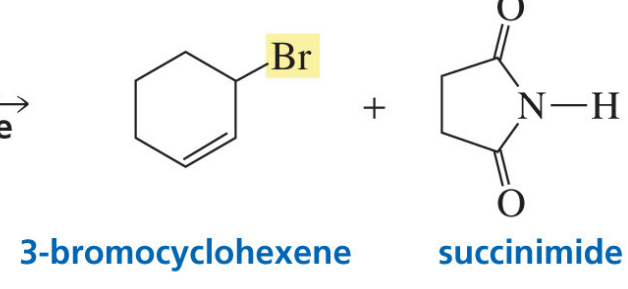
Allylic bromination with NBS
During the acid-catalyzed substitution of alcohols what might occur?
rearrangement, 1.3-hydride shift
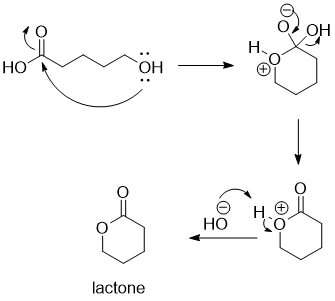
Intramolecular lactone formation
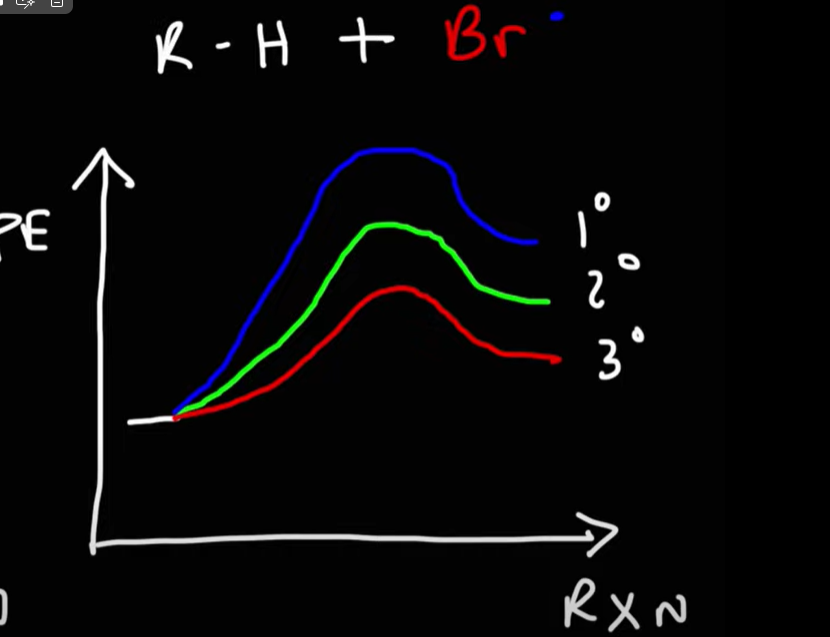
During bromination/chlorination, one is more reactive then the other, Which one and what does this mean ?
Chlorine is more reactive then bromine, as a result bromine will be more selective then chlorine.
Chlorine replaces either the sec or prim hydrogen leading to two products.
Bromine will prefer to replace the secondary hydrogen.
Draw the reaction energy diagram for chlorination
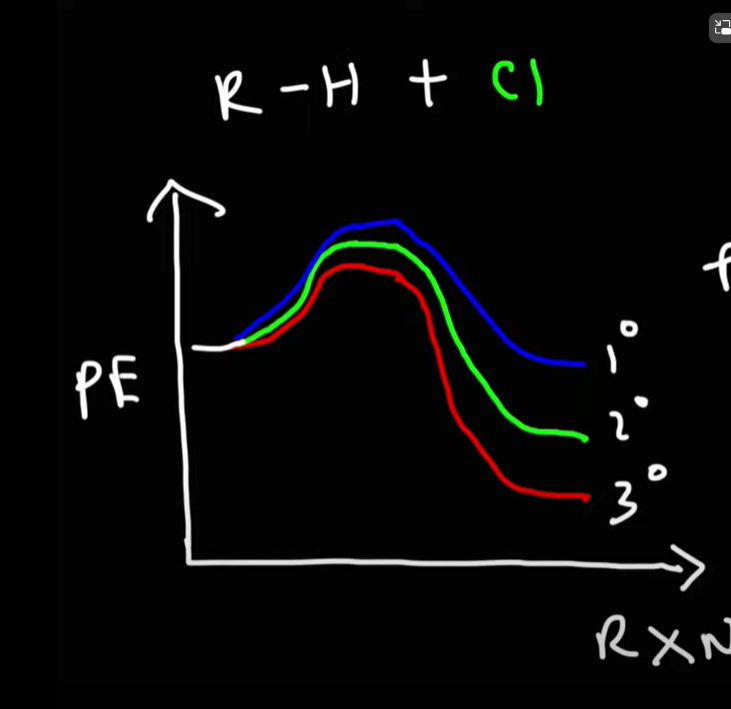
Draw the reaction energy diagram for bromination
Reaction with acetylide ion