Lab final
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
The _____ of the muscle refers to where a muscle originates and represents a _____, less movable site of attachment
origin; stronger
the ______ of a muscle refers to where a muscle ends and represents a _____, more moveable site of attachment
insertion; weaker
in muscles, the insertion always moves _____ the origin
towards
muscles that oppose (or work against) each other
antagonist
muscles that work together to perform an action
synergist
the primary muscle producing an action
agonist
moves something away from the midline
abduction
moves the sole of the foot to face medially
inversion
decreases the angle of a joint
flexion
moves the sole of the foot to face laterally
eversion
moves something towards the midline
adduction
increases the angle of a joint
extension
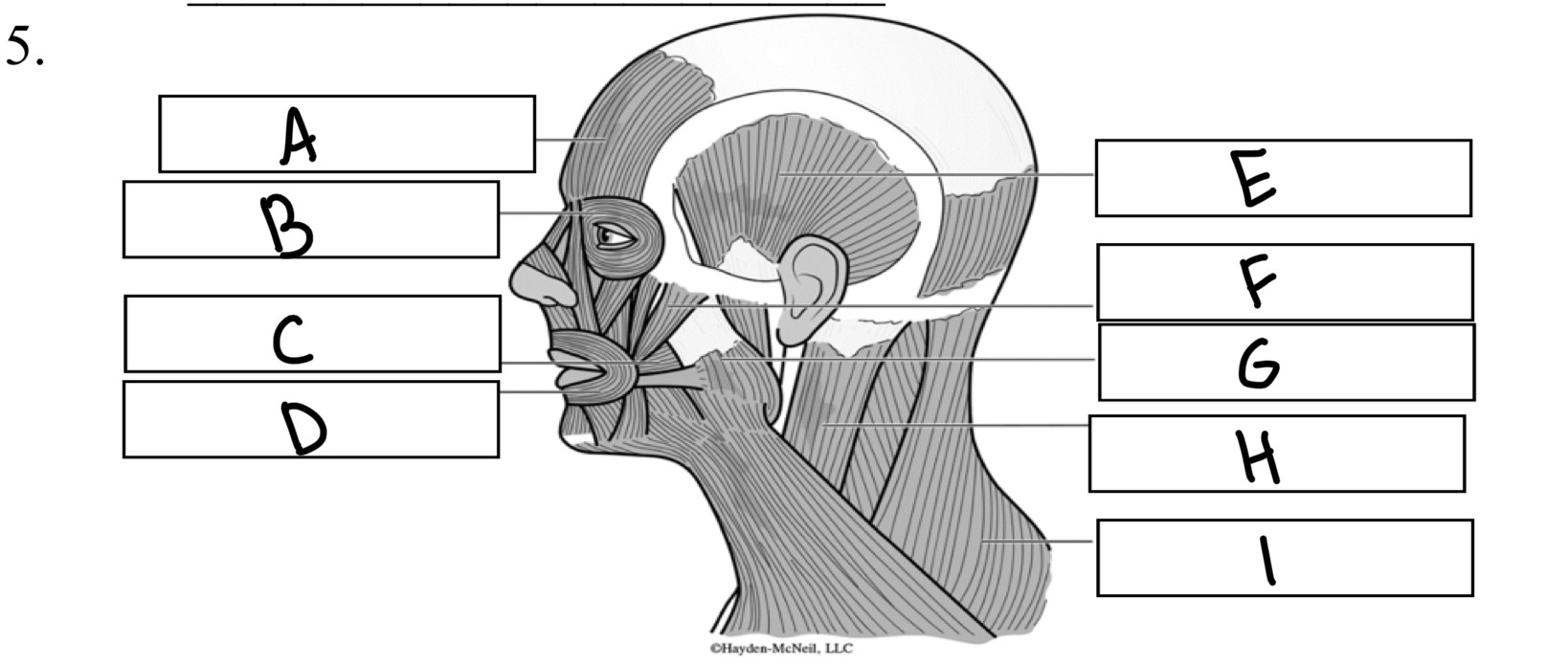
What is A
Frontalis
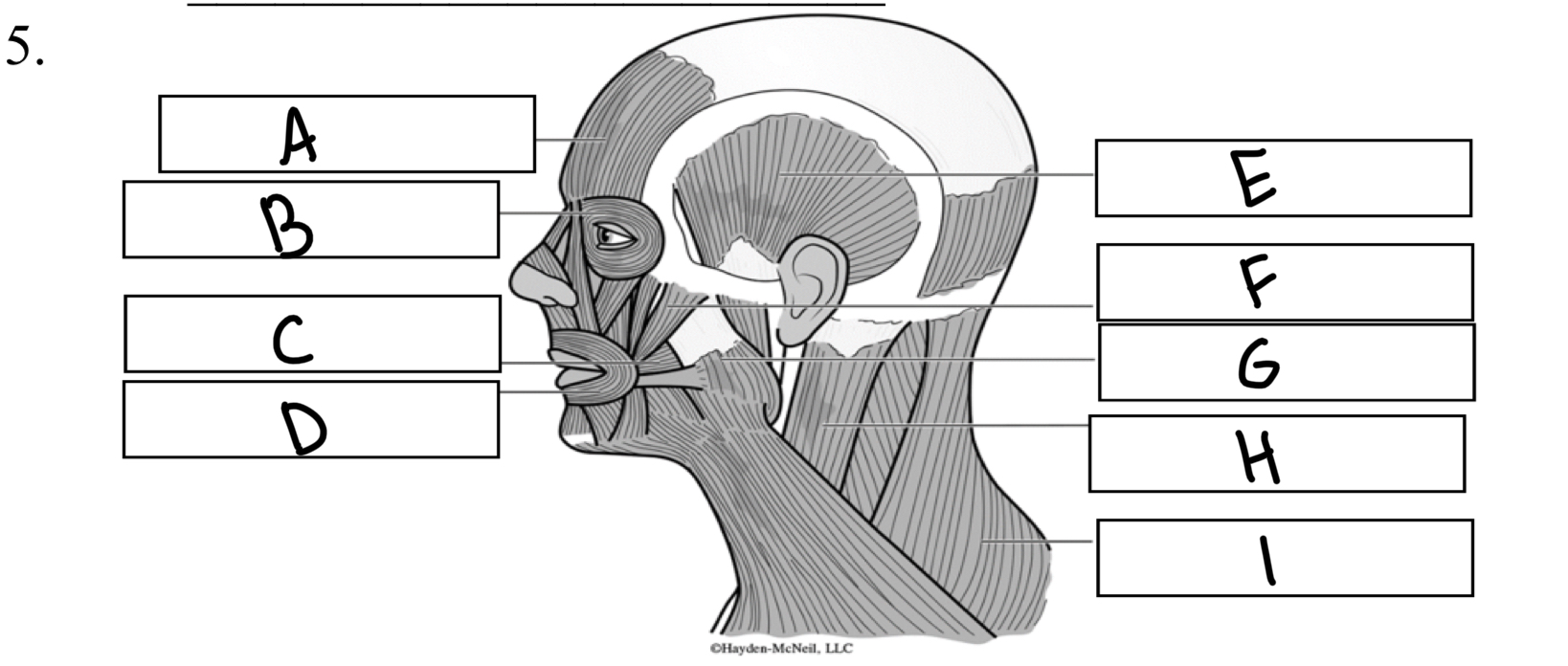
What is B
Orbicularis oculi
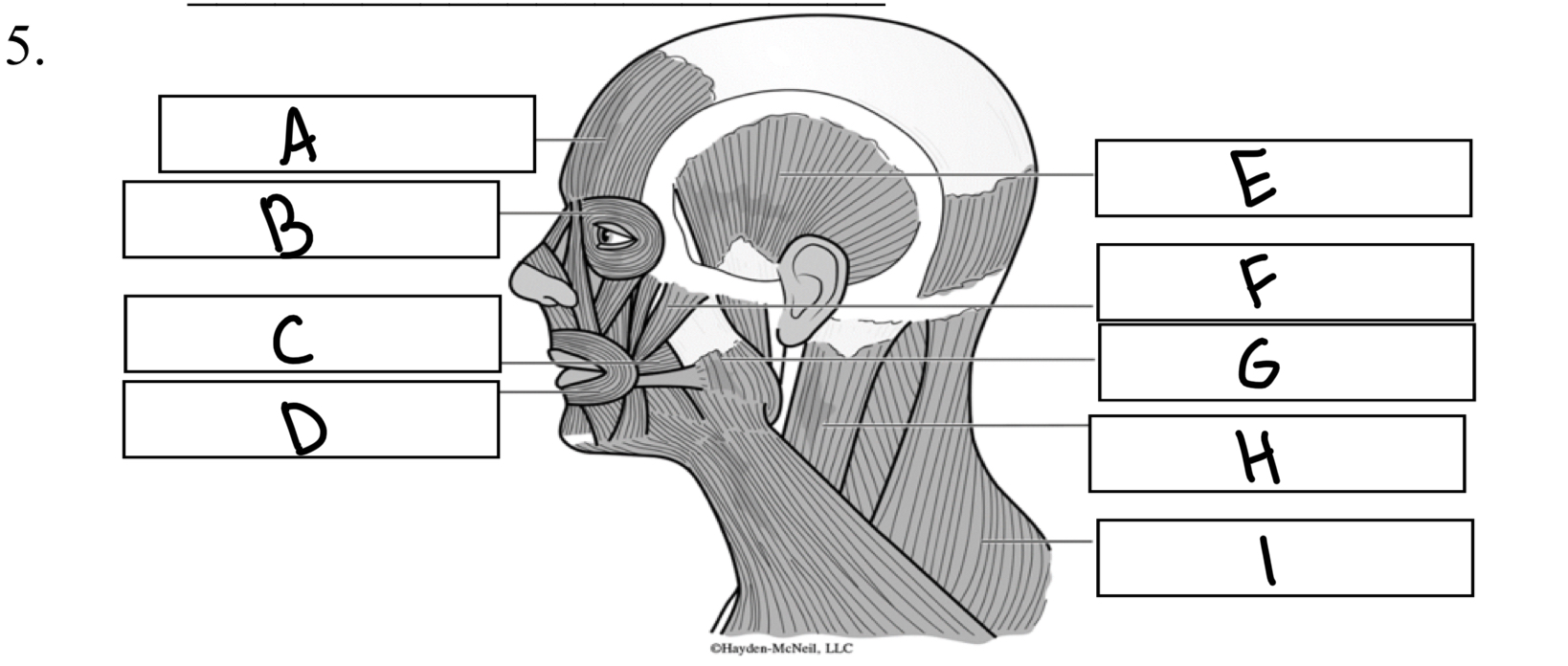
What is C
Buccinator
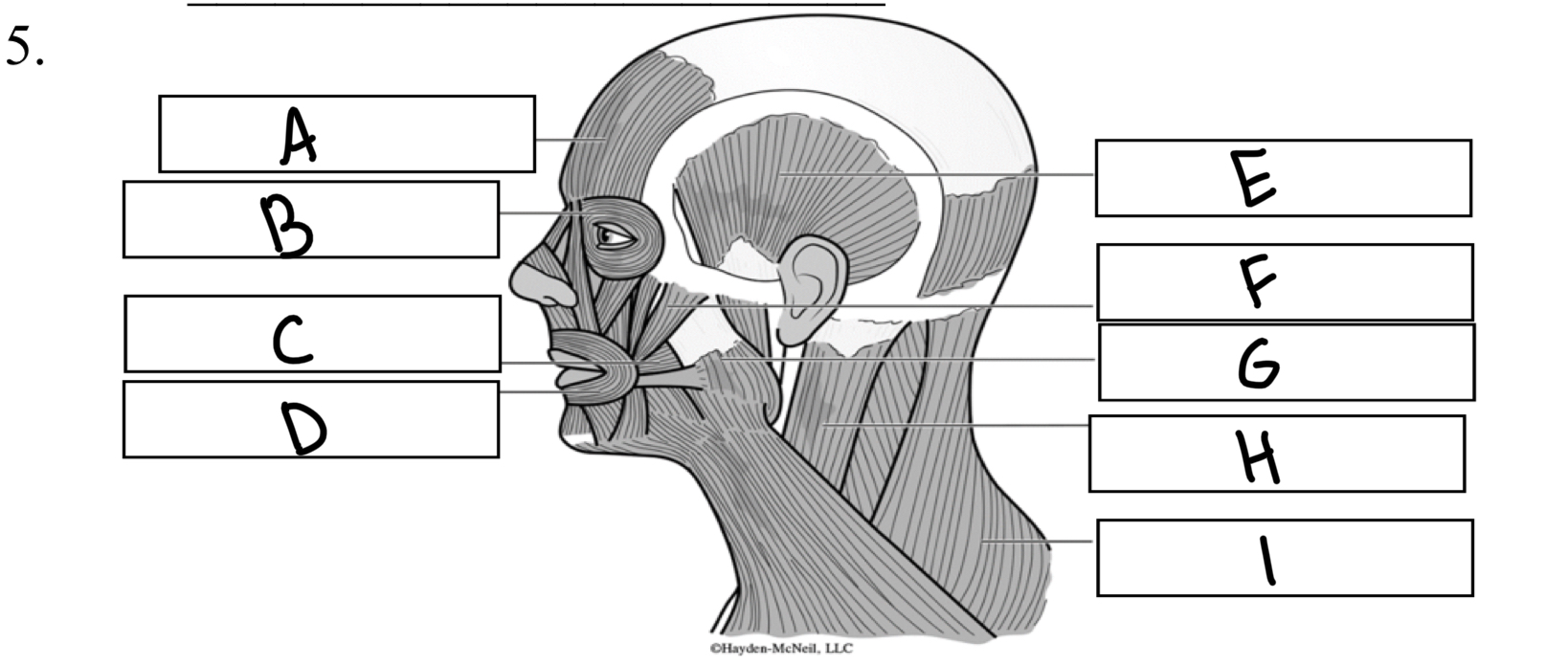
What is D
Orbicularis oris
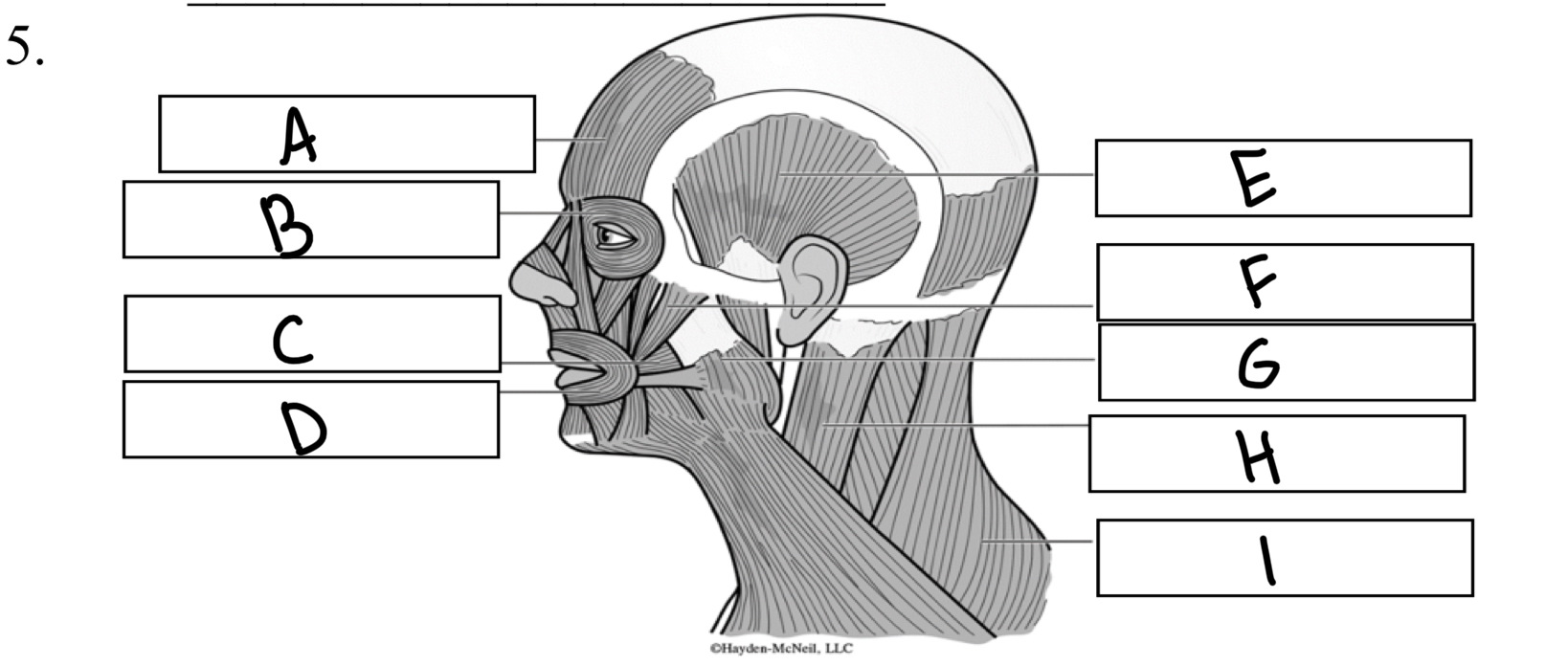
What is E
Temporalis
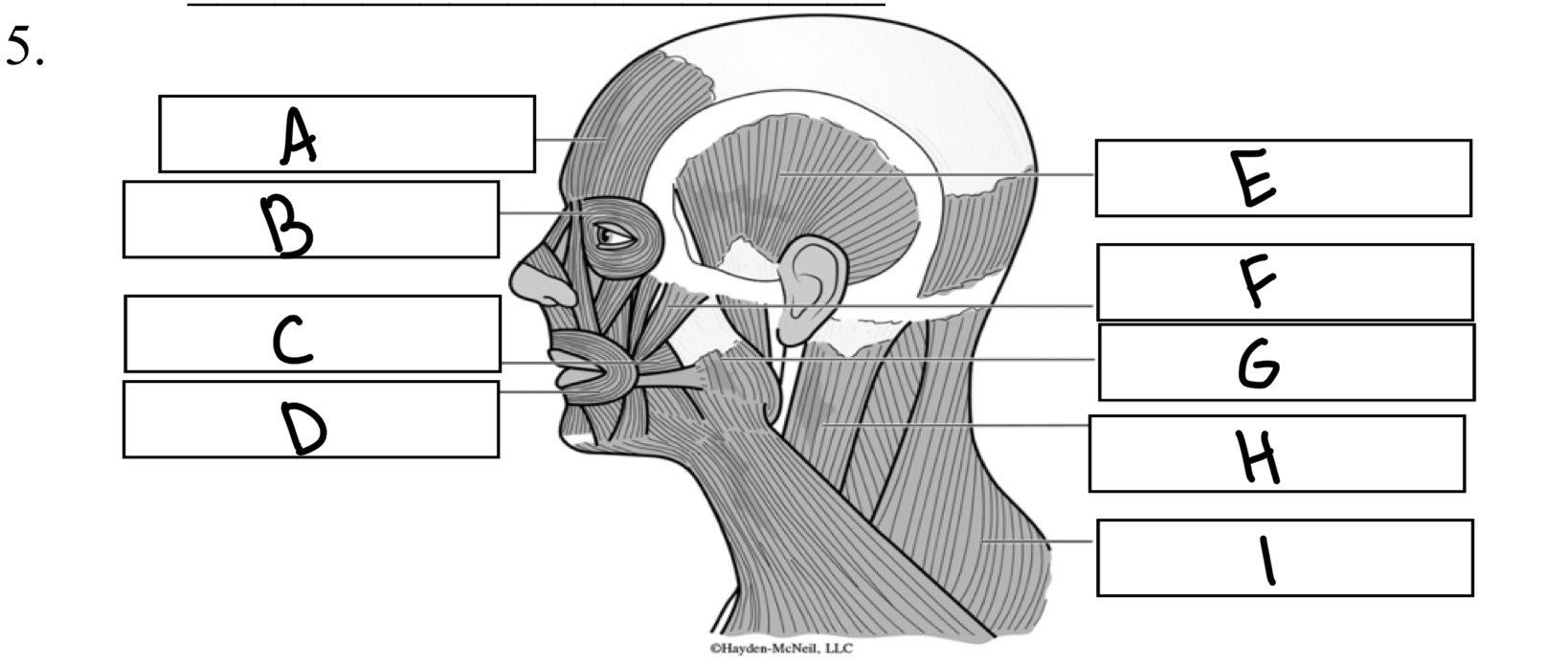
What is F
Zygomaticus
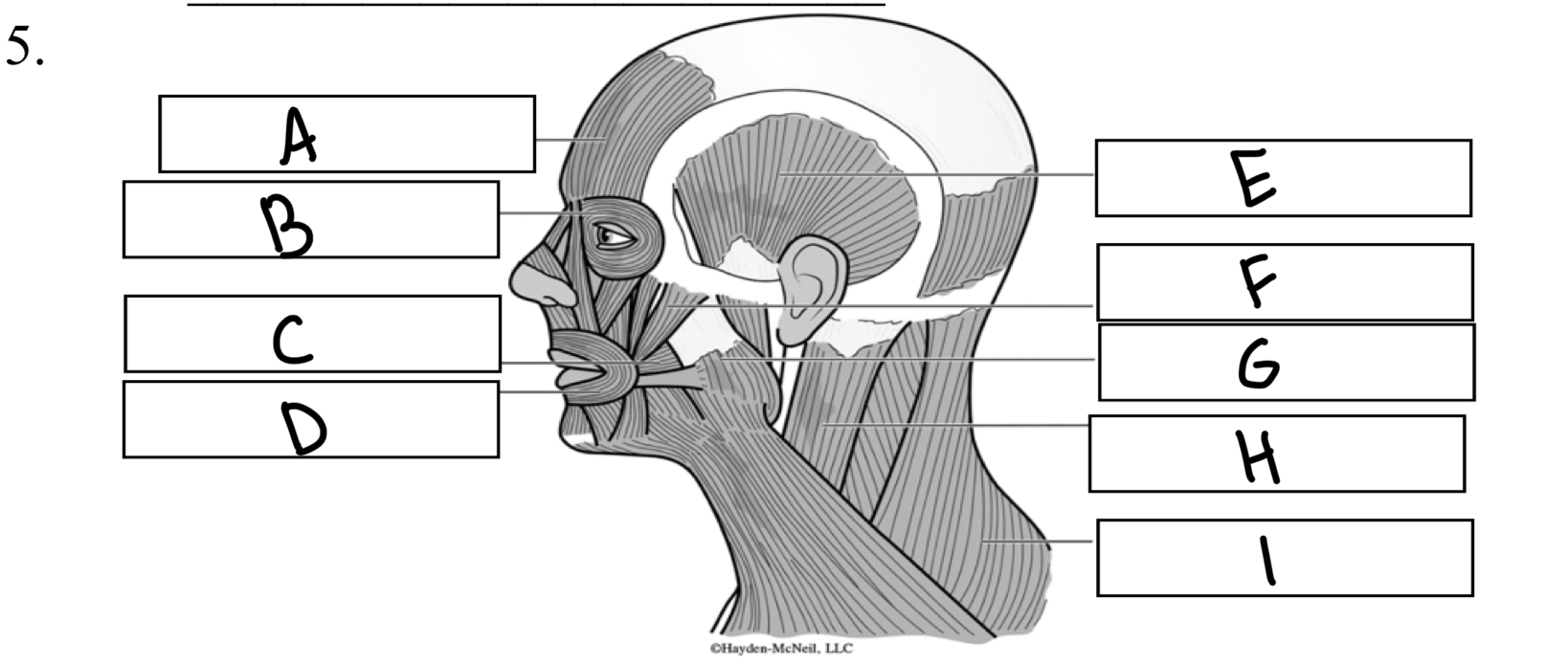
What is G
Masseter
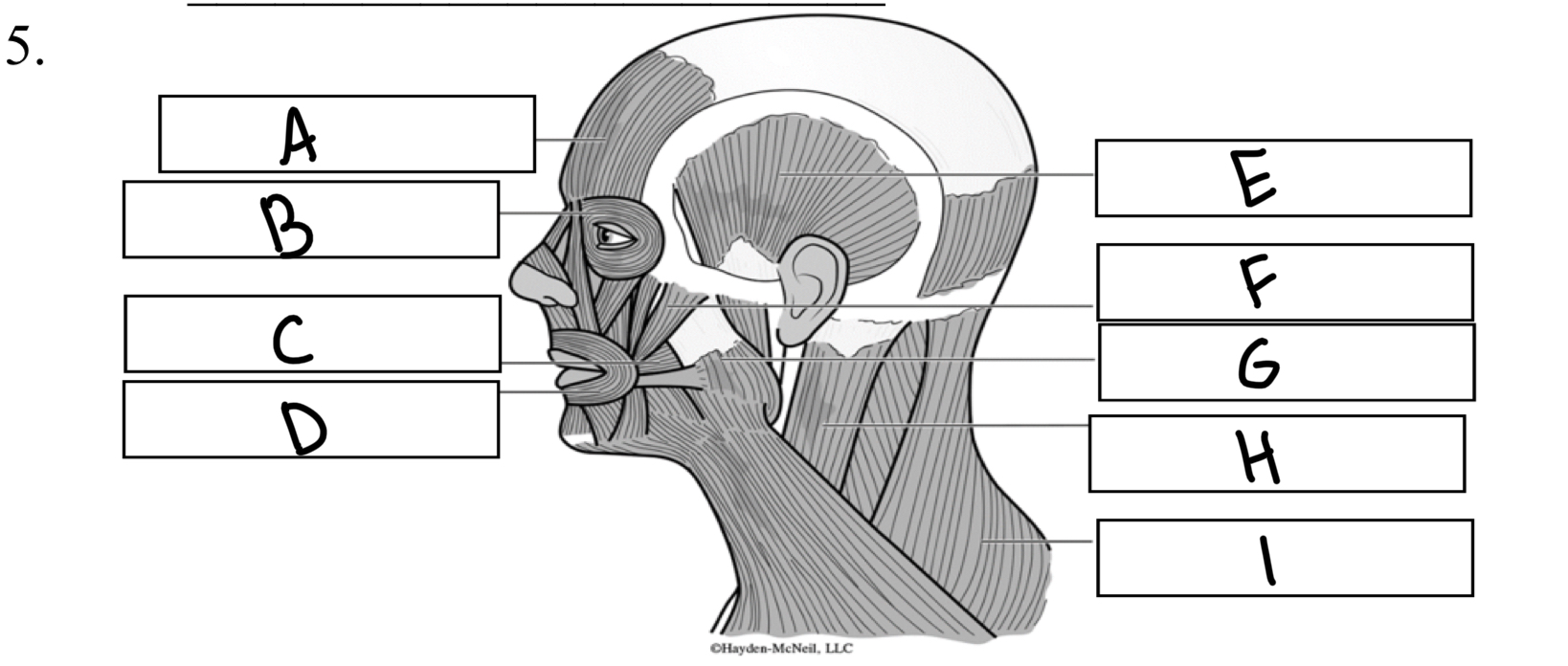
What is H
Sternocleidomastoid
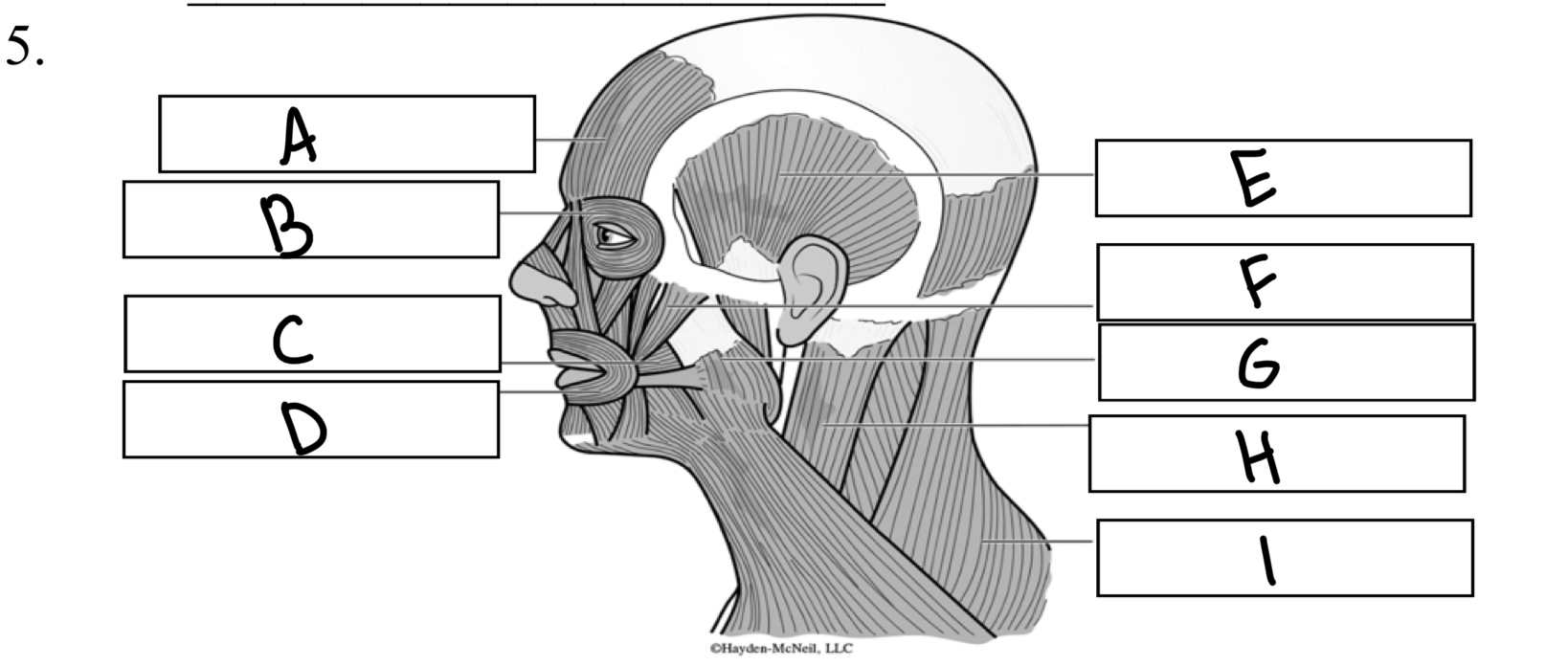
What is I
Trapezius
What is the origin of the zygomaticus muscle?
Zygomatic bone
What is the origin of the temporalis muscle?
Temporal bone
What is the insertion of the zygomaticus muscle?
Skin and muscle at corner of mouth
What is the insertion of the sternocleidomastoid muscle?
Mastoid process of temporal bone
Elevates the corners of the mouth to smile
Zygomaticus
Bilaterally flexes the neck, unilaterally turns the head
Sternocleidomastoid
Closes the jaw, elevates the mandible
Masseter
Primarily functions in closing the eyes
Orbicularis oculi
Raises the eyebrows
Frontalis
Primarily functions in closing the mouth
Orbicularis oris
Draws the corners of the mouth laterally (ex: whistling)
Buccinator
What is the origin of the infraspinatus muscle?
Infraspinous fossa of scapula
What is the origin of the sub scapular is muscle?
Subscapular fossa of the scapula
What is the insertion of the rhomboid (major & minor) muscles?
Medial border of scapula
Elevates the scapulae
Levator scapulae
Abducts the arm
Deltoid
Extends the vertebral column
Erector spinae
Depresses and protracts the shoulder
Pectoralis minor
Flexes, abducts, and medically rotates the arm at the shoulder
Pectoralis major
Protracts the shoulder and rotates the scapula
Serratus anterior
Elevates the rib cage
External intercostals
Compresses the abdomen
Transverse abdominis
What is the origin of the gluteus medius?
Iliac crest
What is the origin of the brachialis?
Distal portion of humerus
What is the insertion of the recuts femoris?
Tibial tuberosity and patella
What is the insertion of the brachioradialis?
Radius
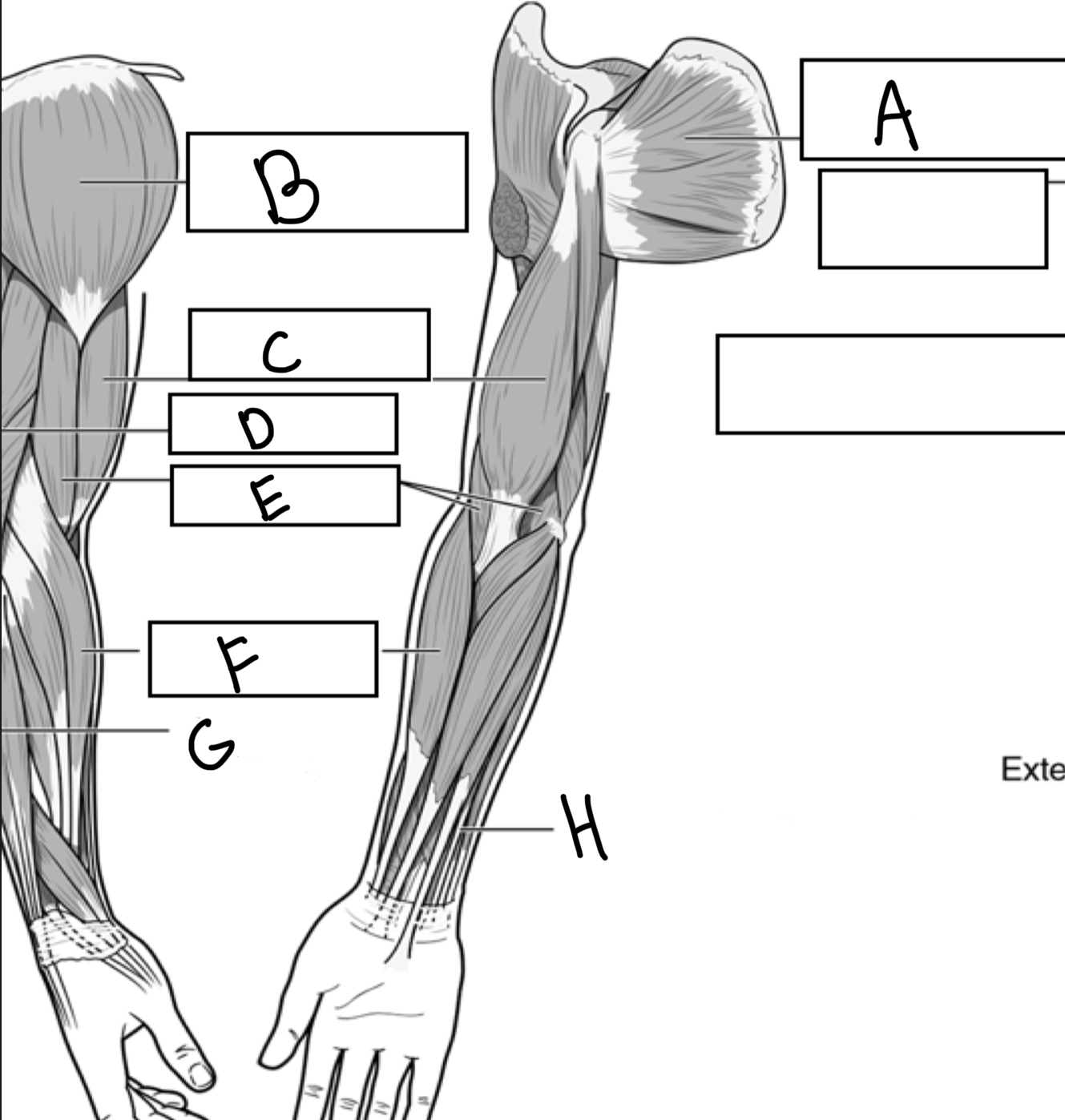
What is A
Subscapularis
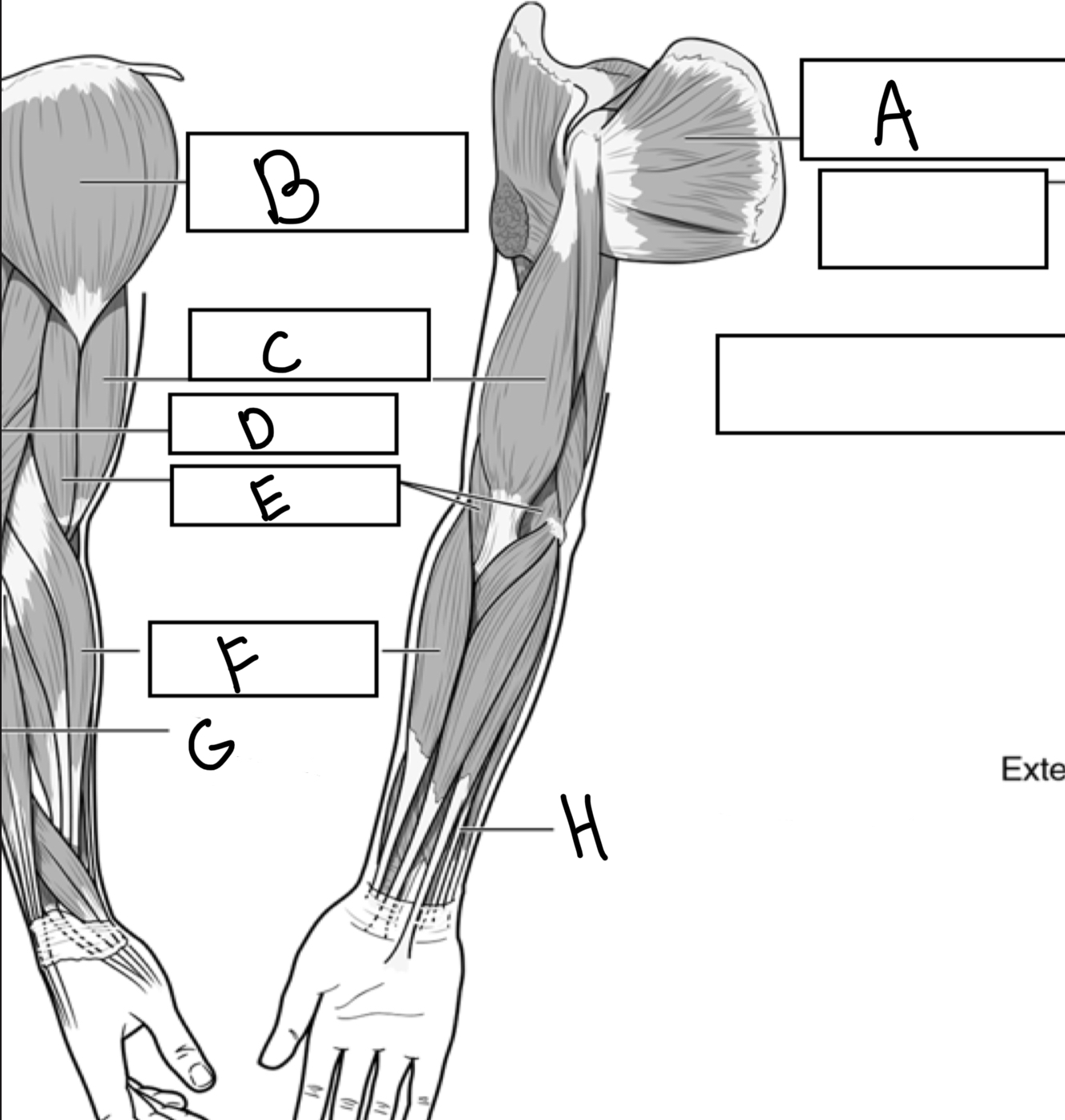
What is B
Deltoid
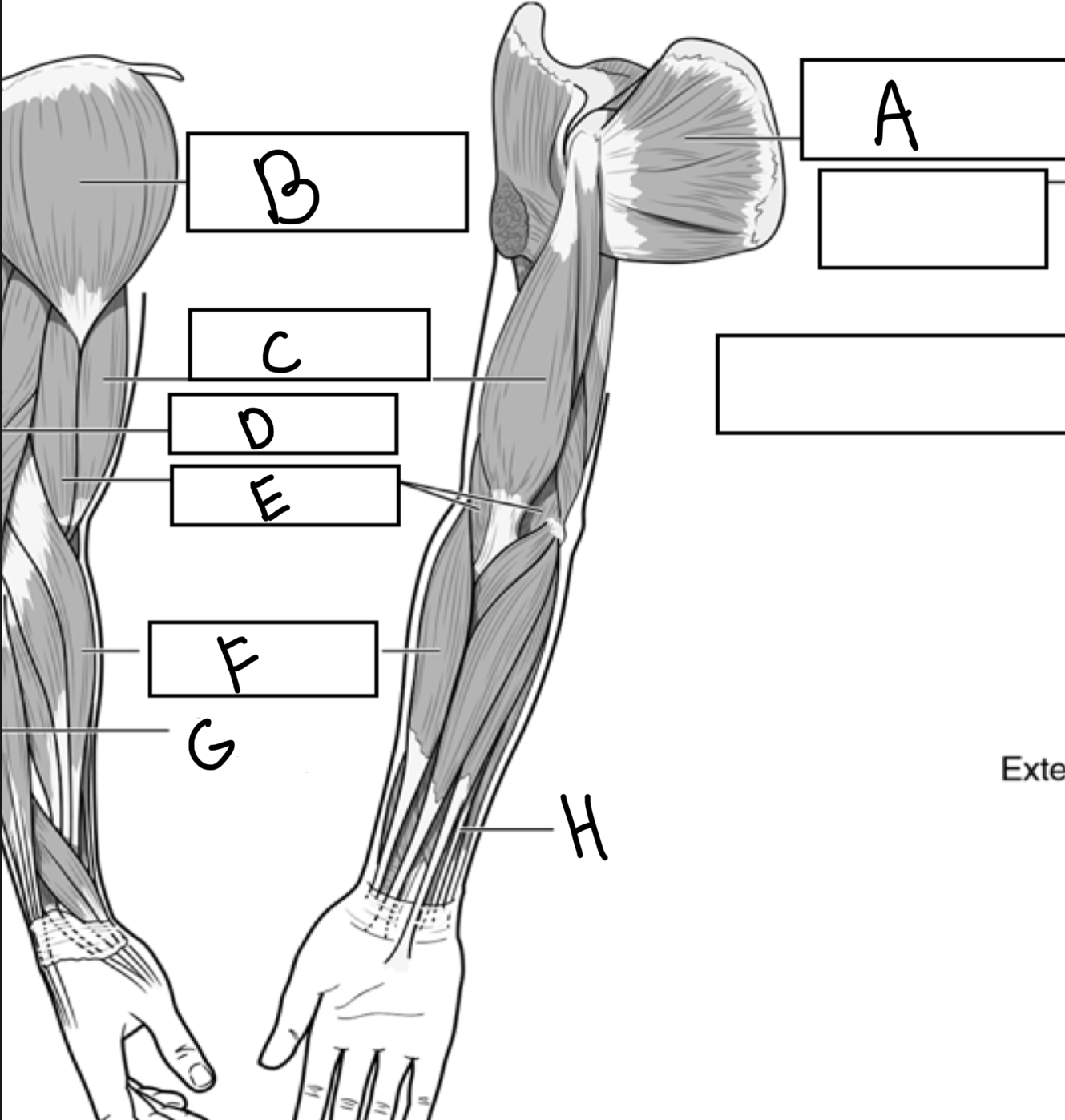
What is C
Biceps brachii
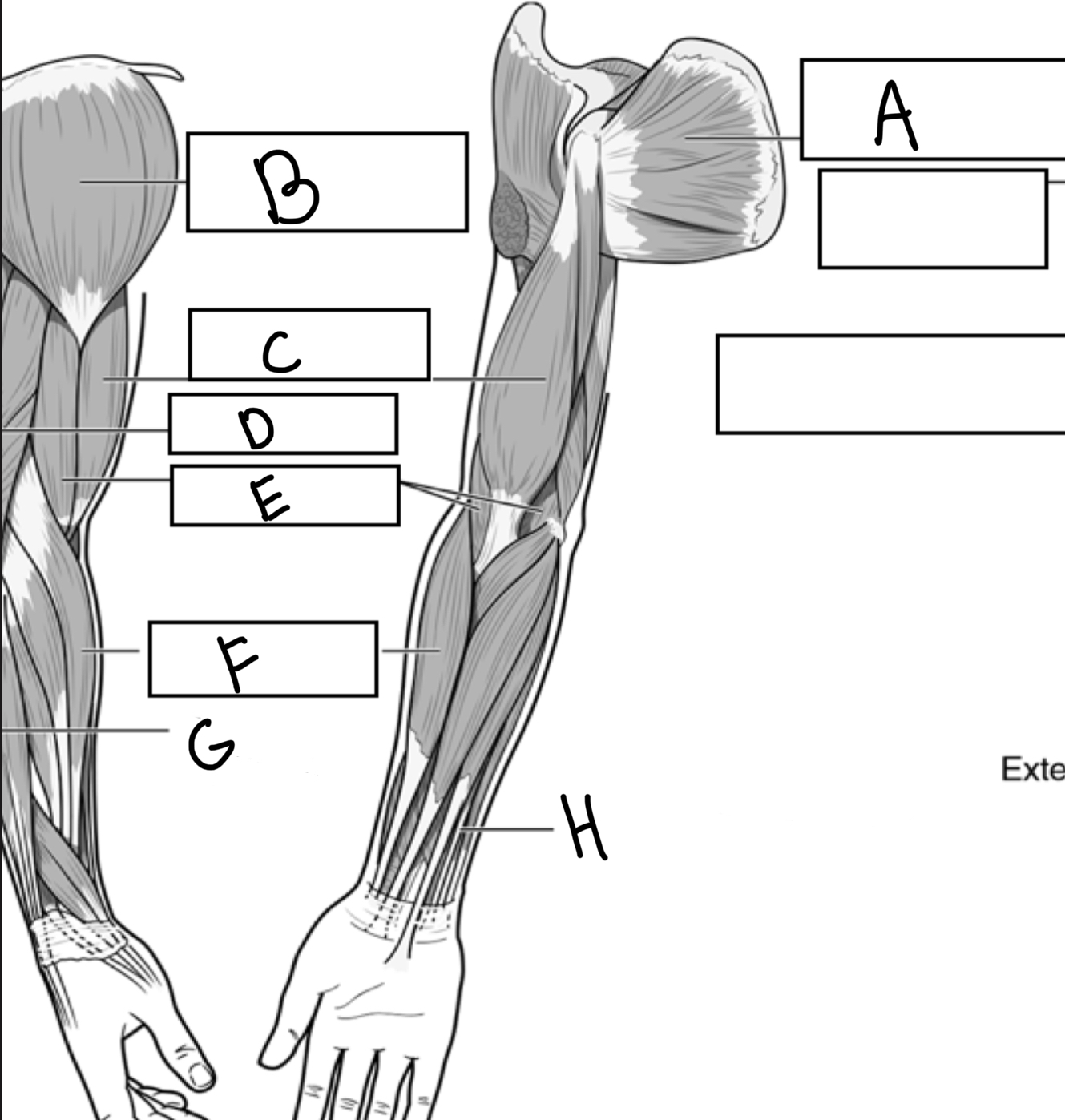
What is D
Triceps brachii
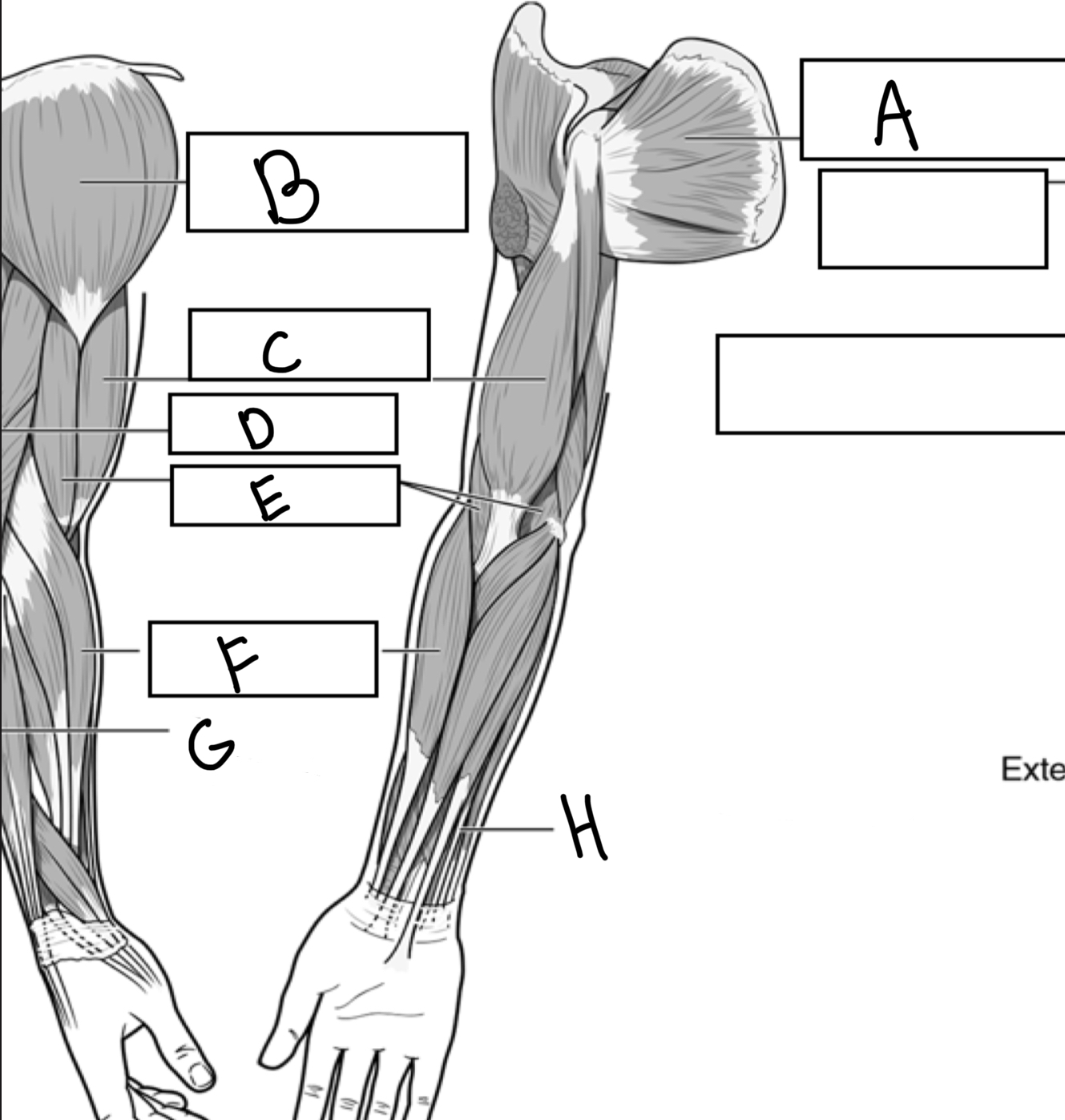
What is E
Brachialis
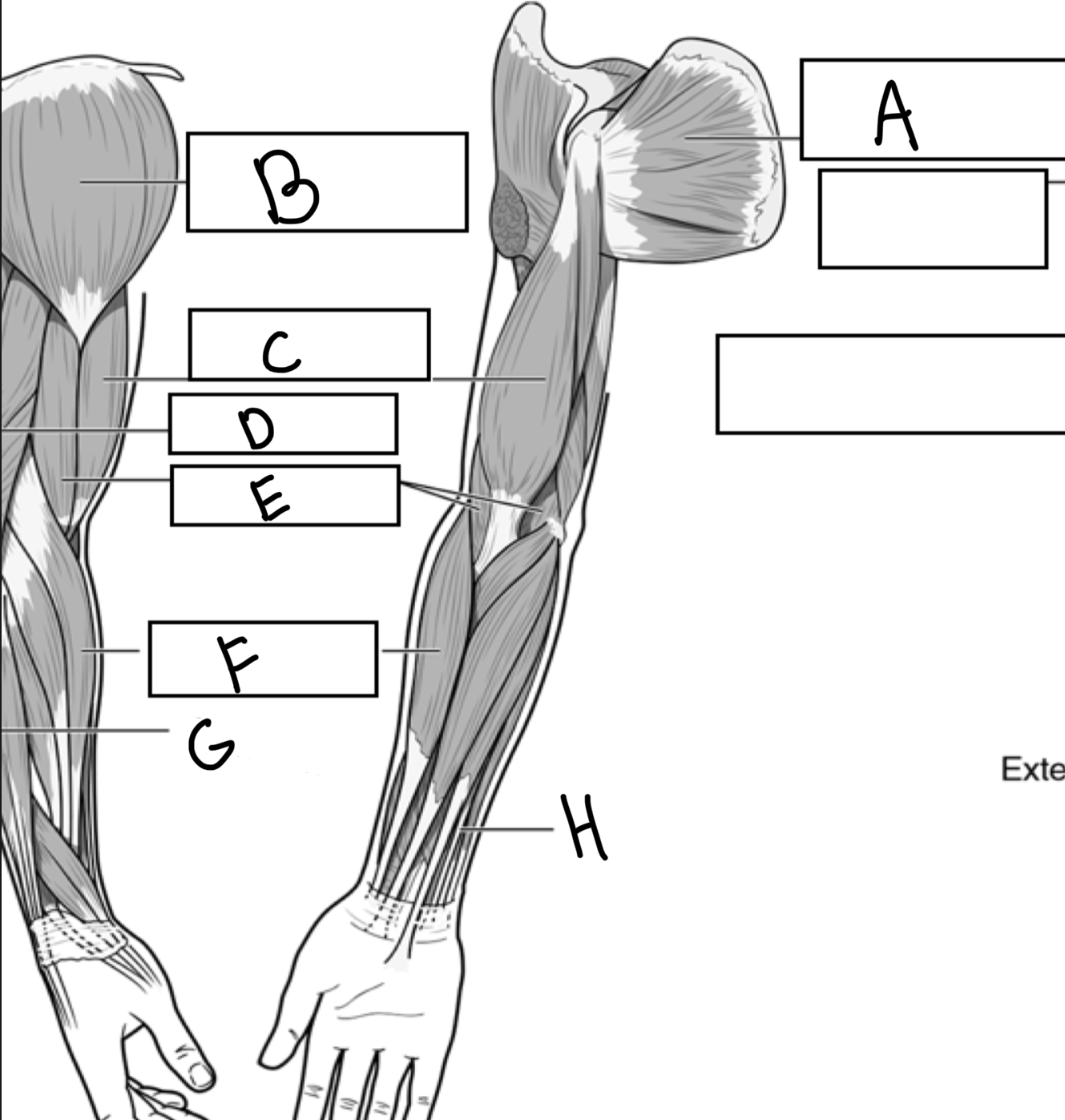
What is F
Brachioradialis
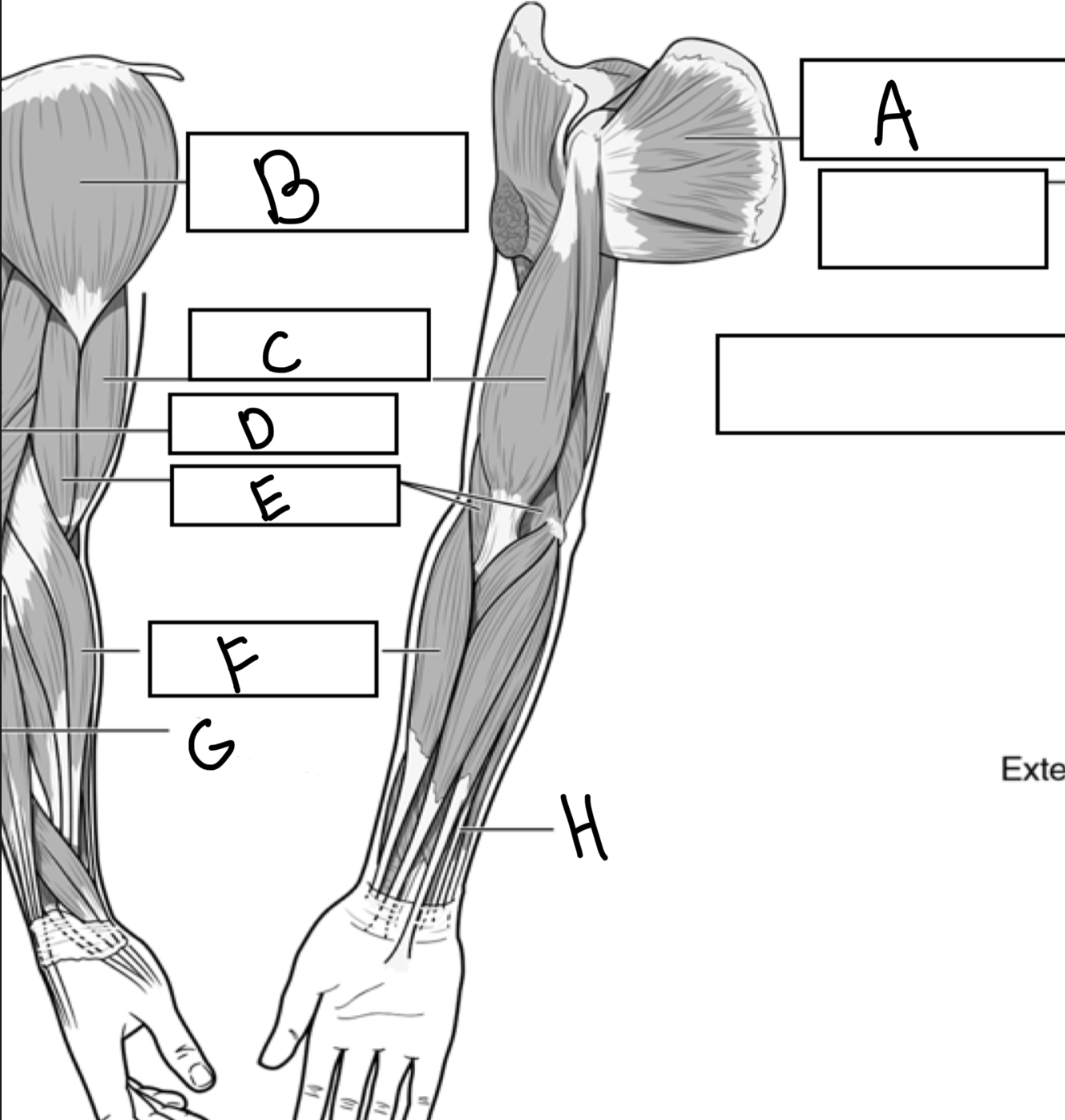
What is G
Extensor digitorum
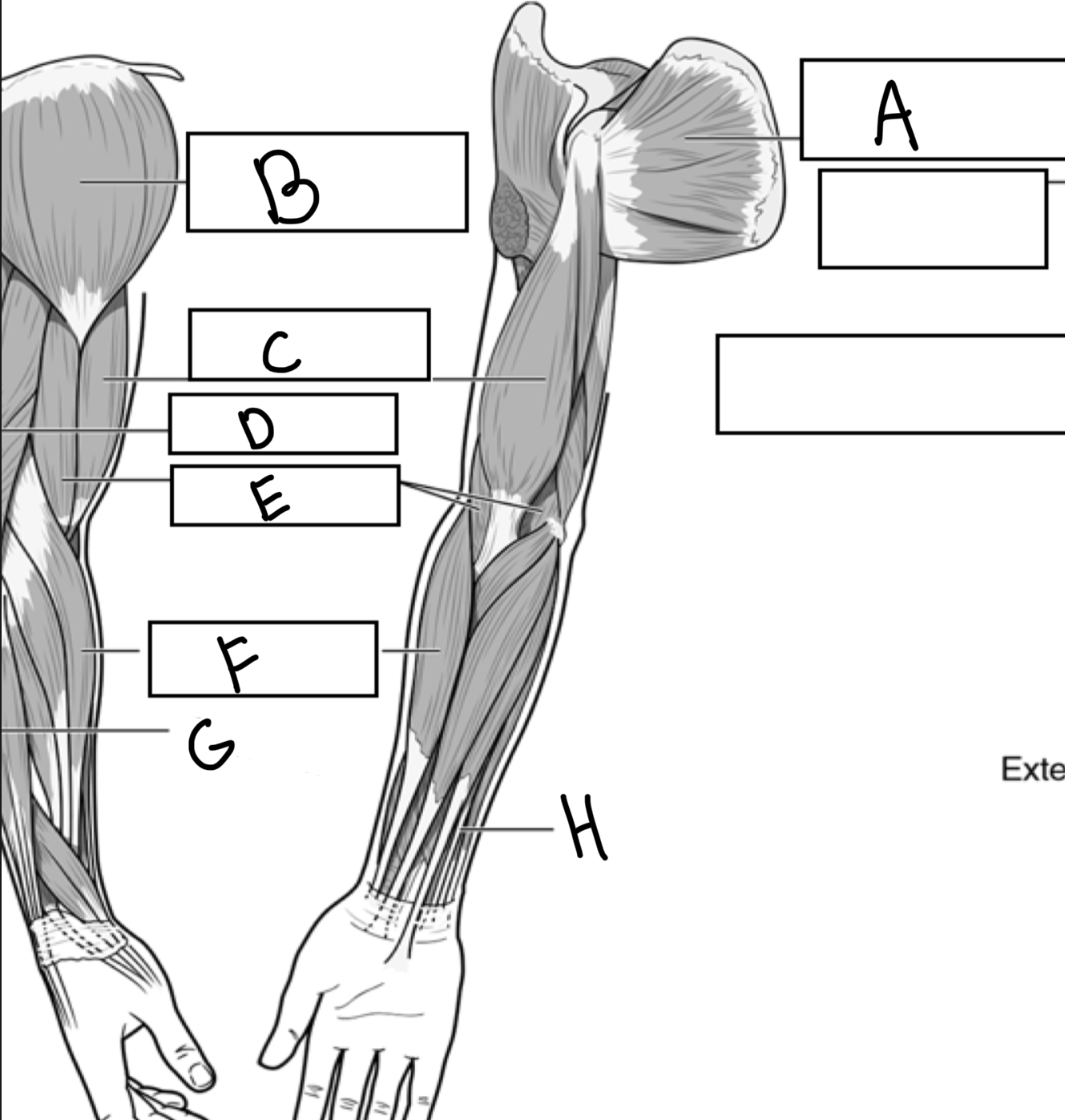
What is H
Flexor digitorum superficialis
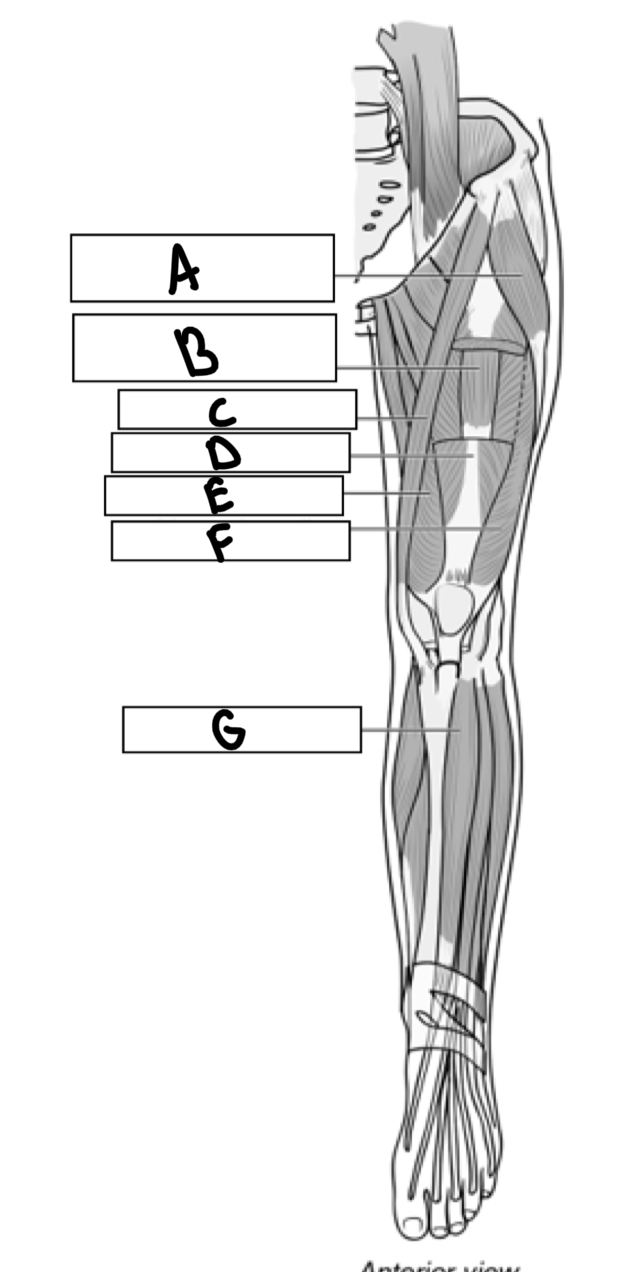
What is A
Tensor fascia
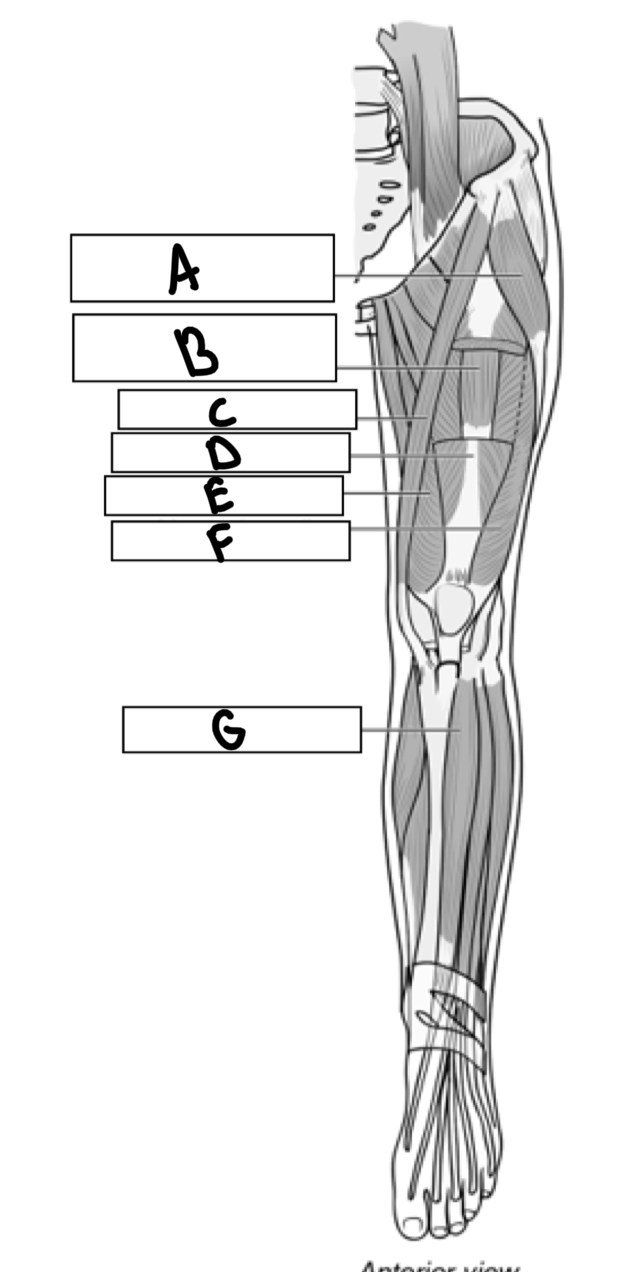
What is B
Vastus intermedius
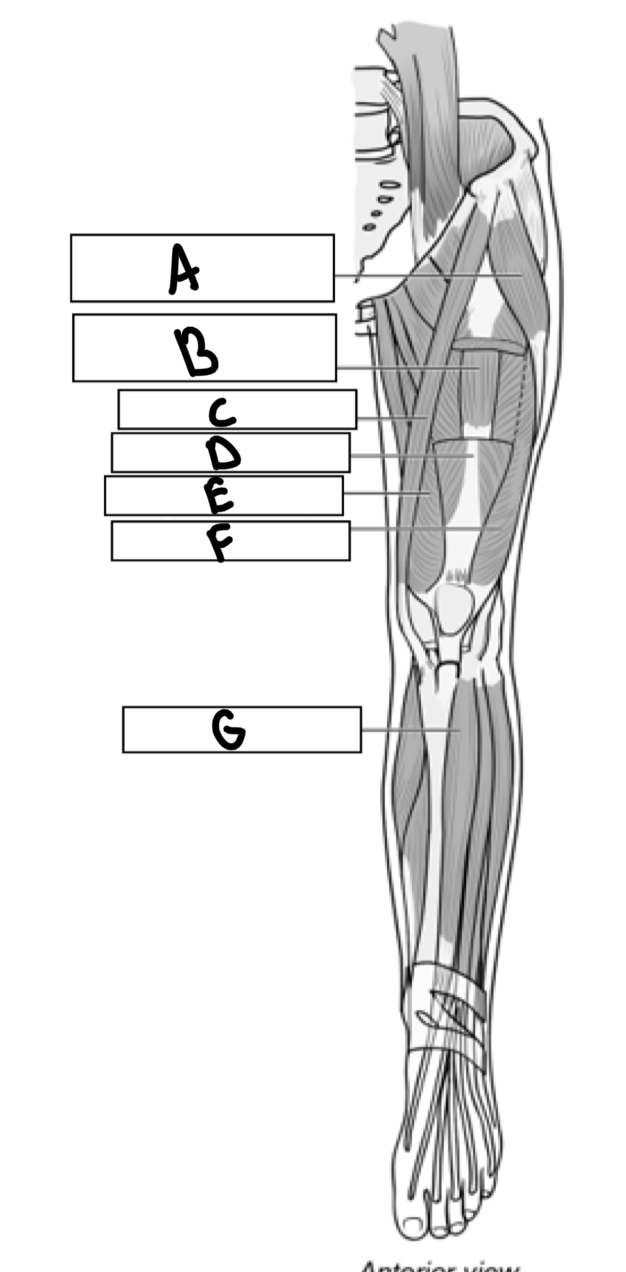
What is C
Sartorius
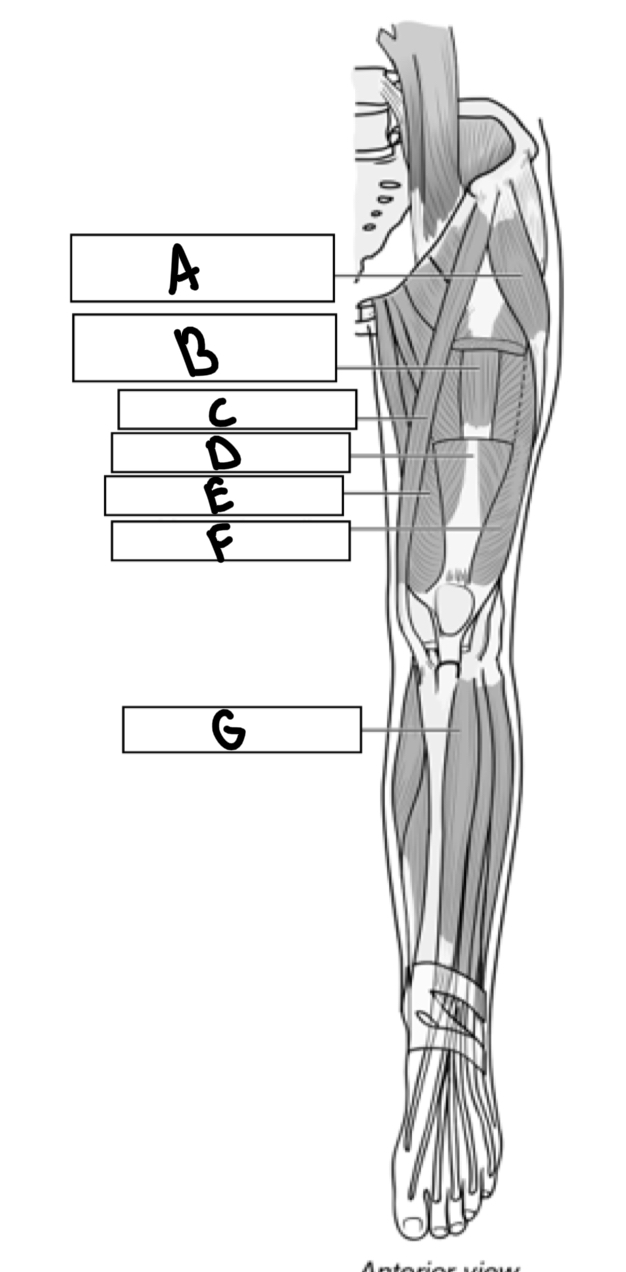
What is D
Rectus femoris
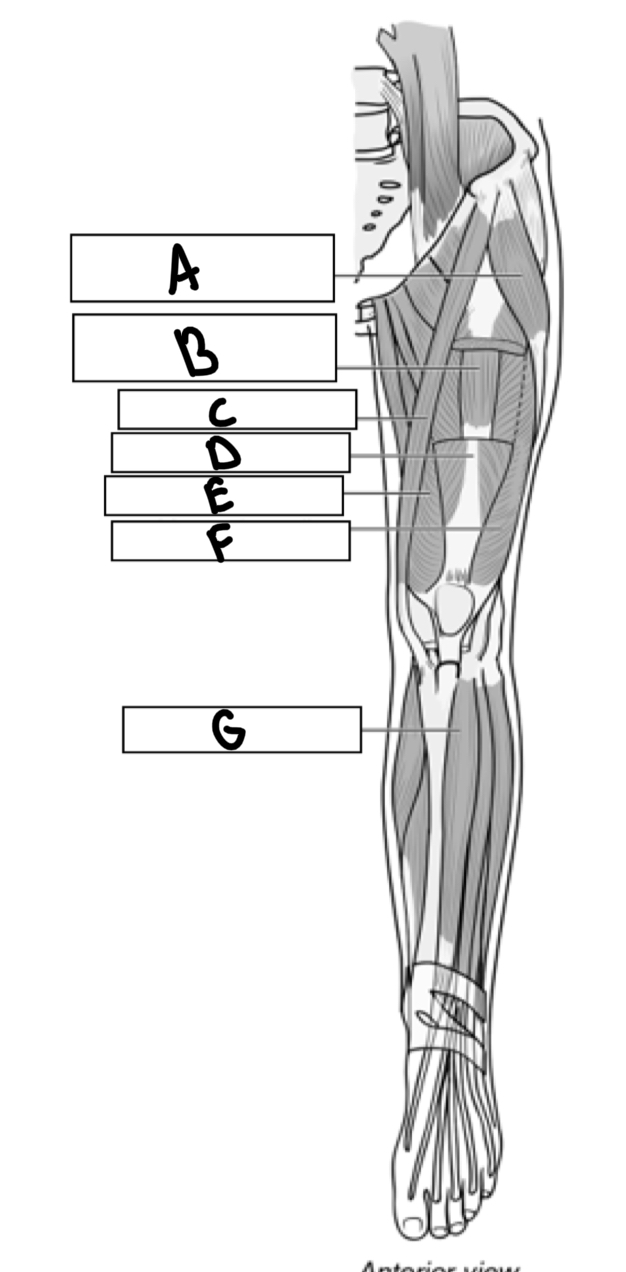
What is E
Vastus medialis
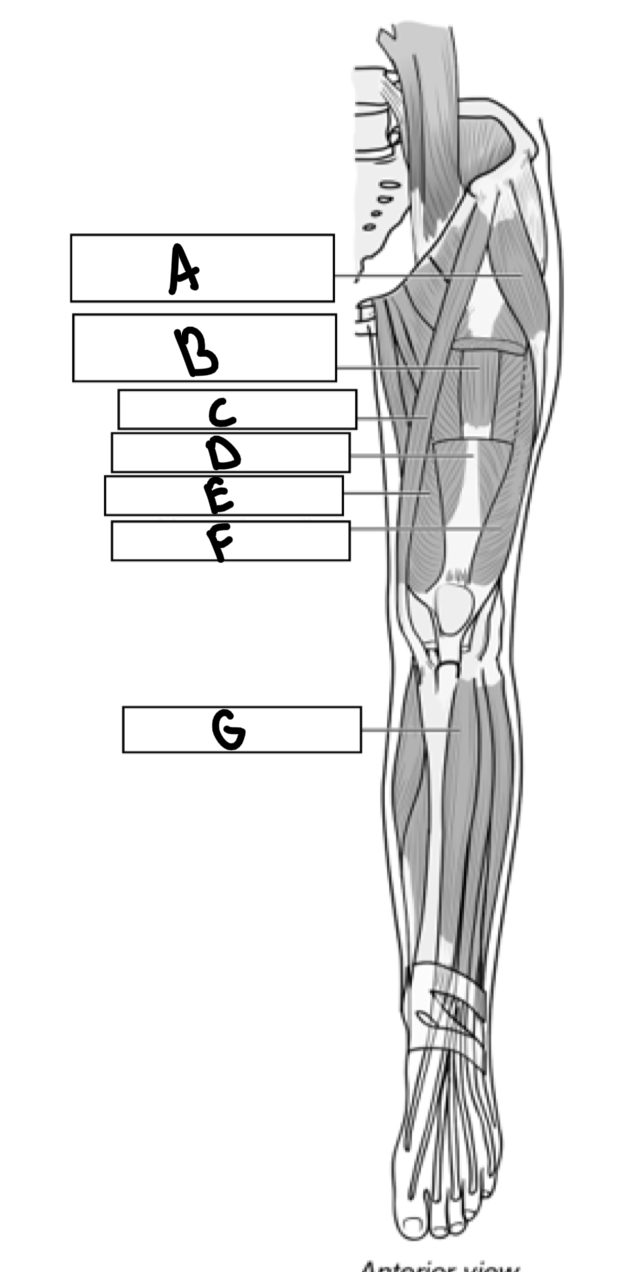
What is F
Vastus lateralis
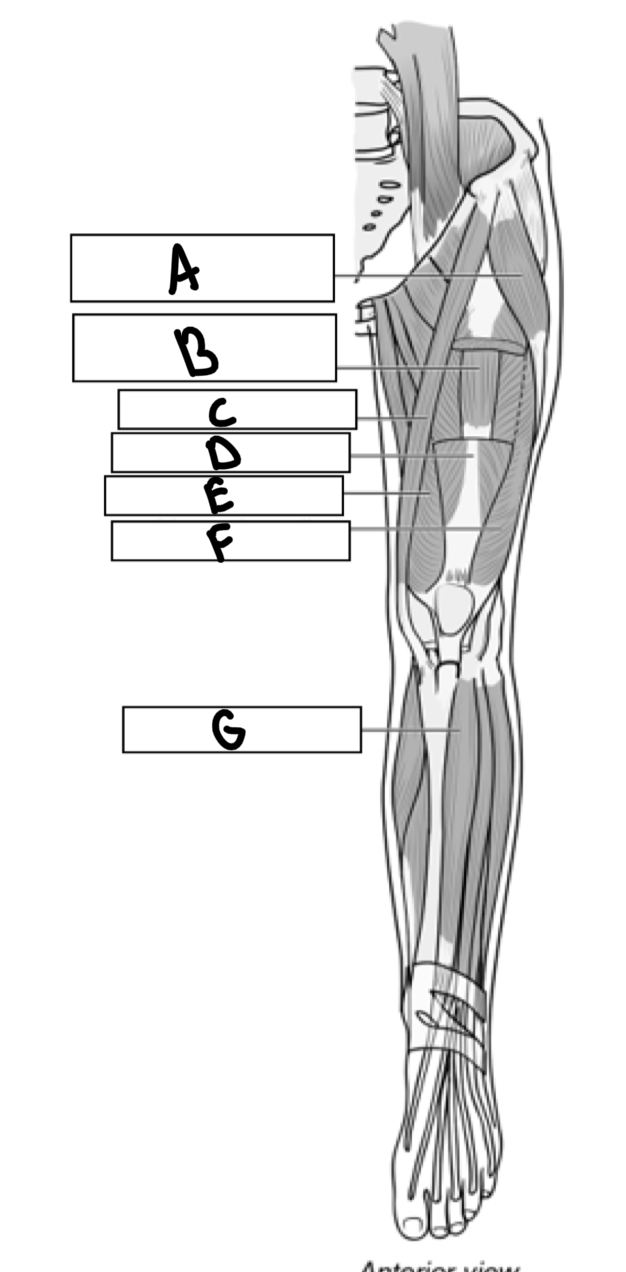
What is G
Tibialis anterior
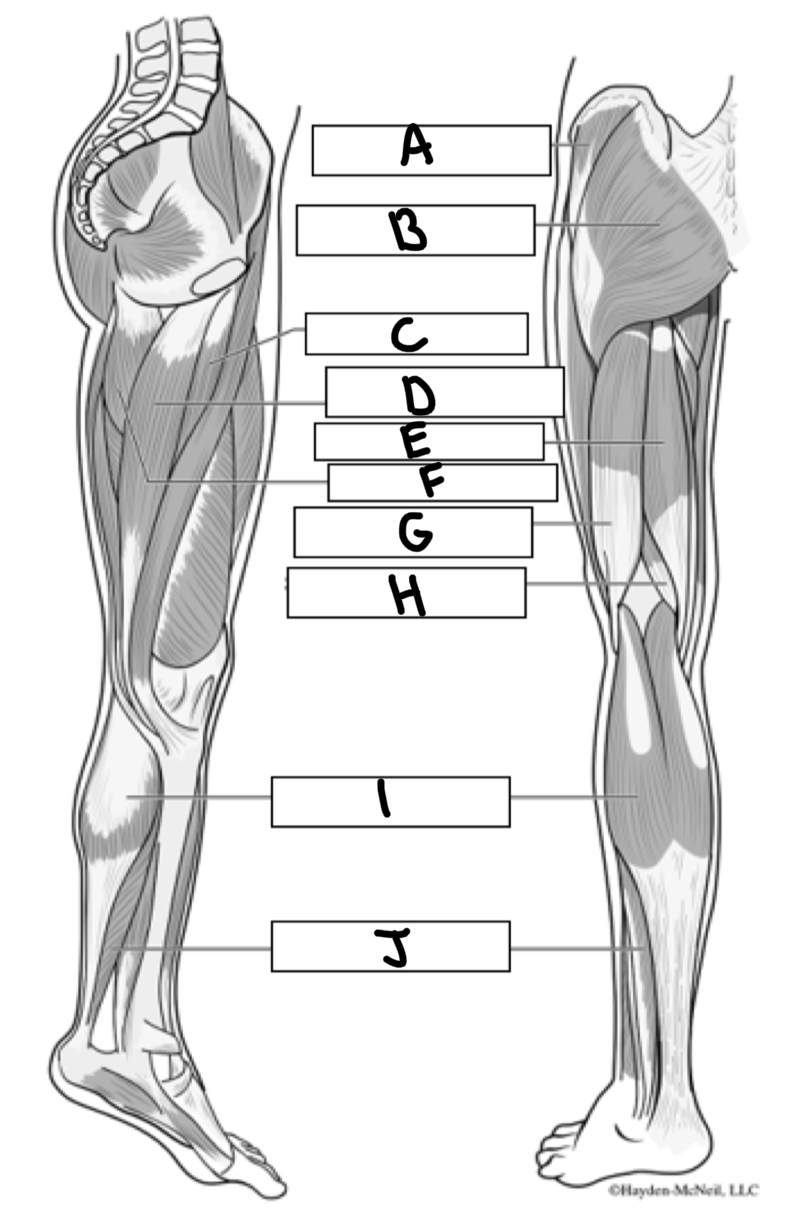
What is A
Gluteus medius
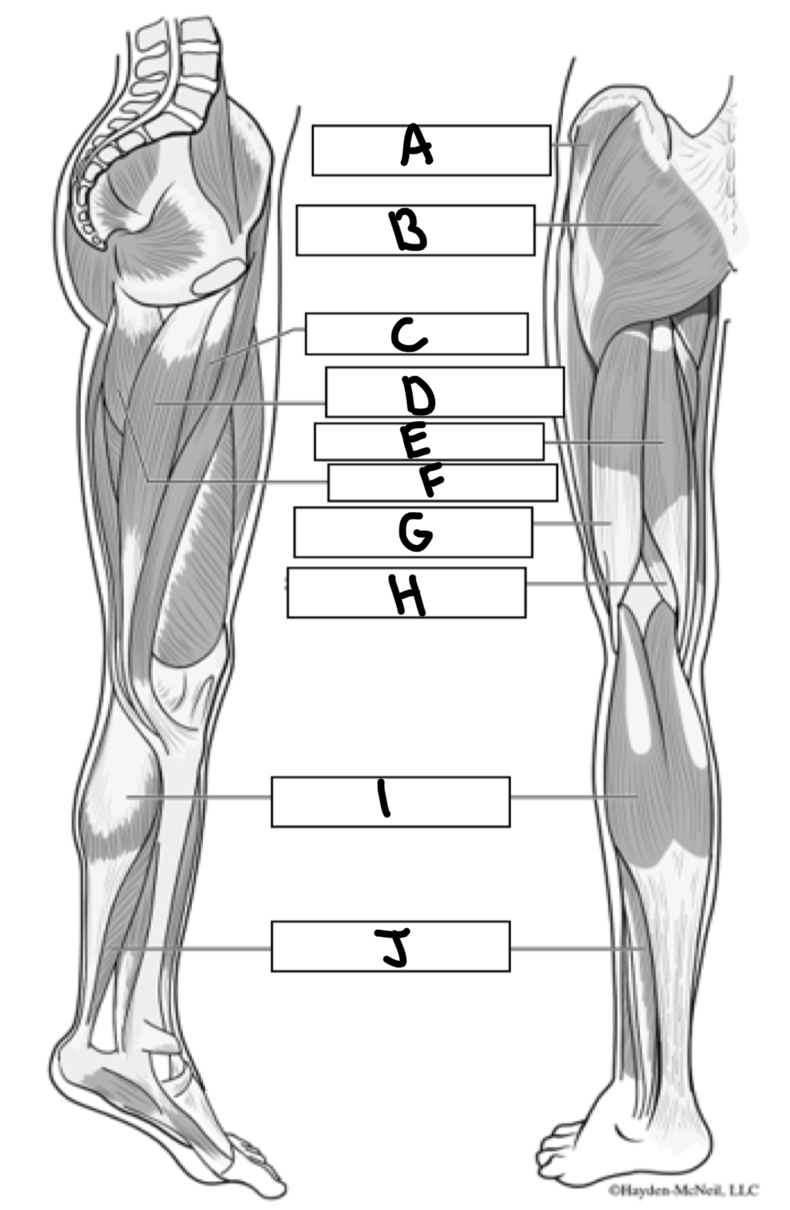
What is B
Gluteus maximus
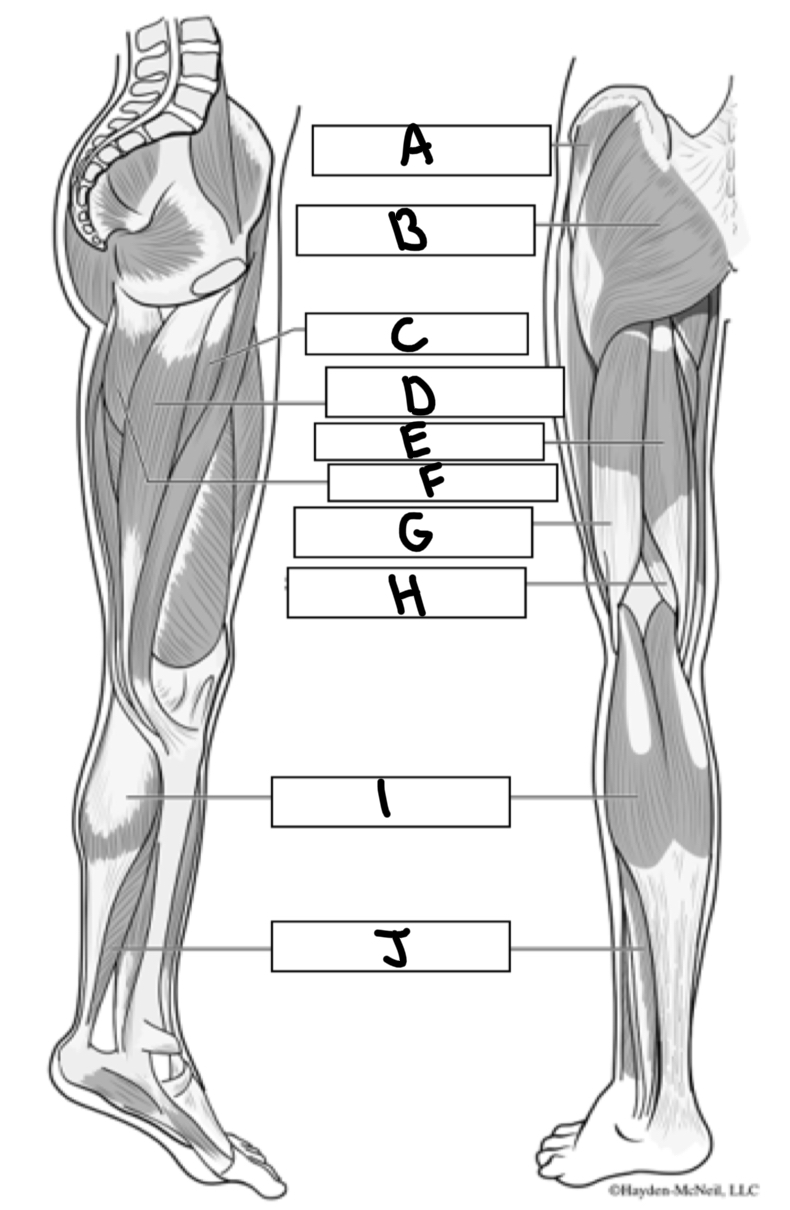
What is C
Adductor longus
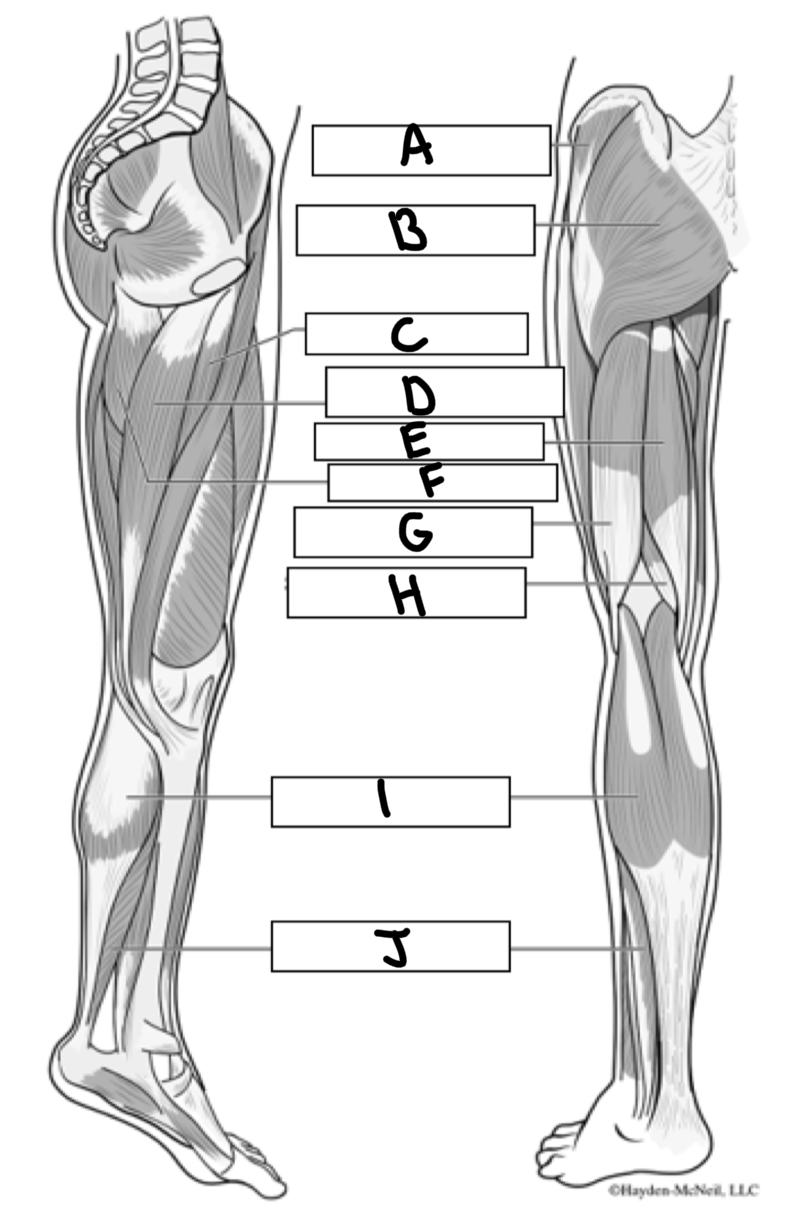
What is D
Gracialis
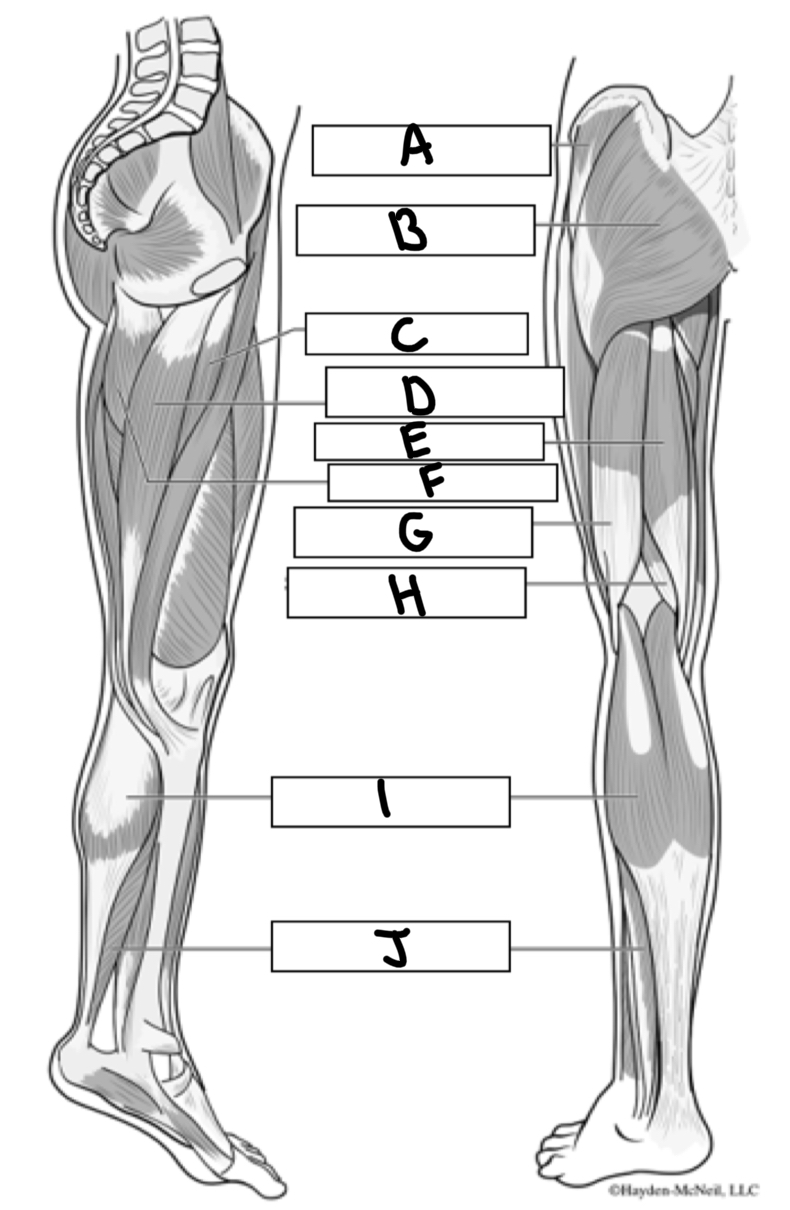
What is E
Semitendinosus
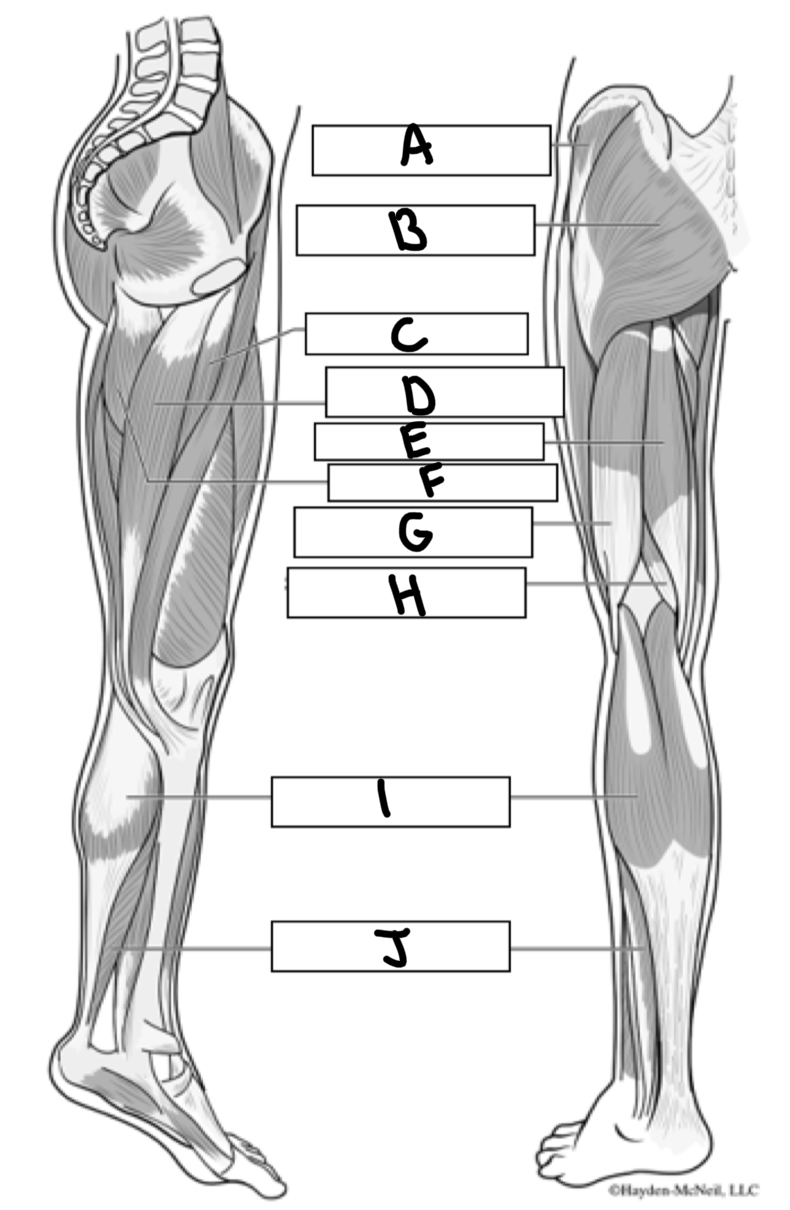
What is F
Adductor magnus
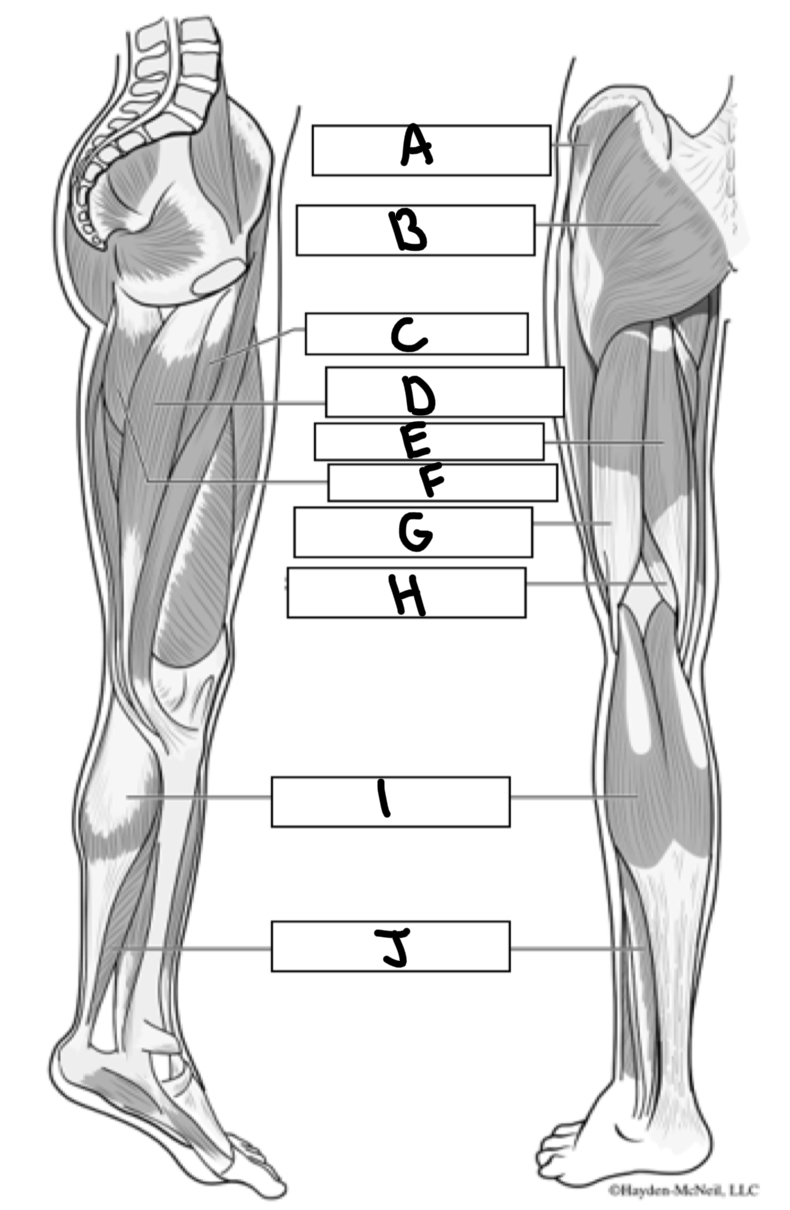
What is G
Bicep femoris
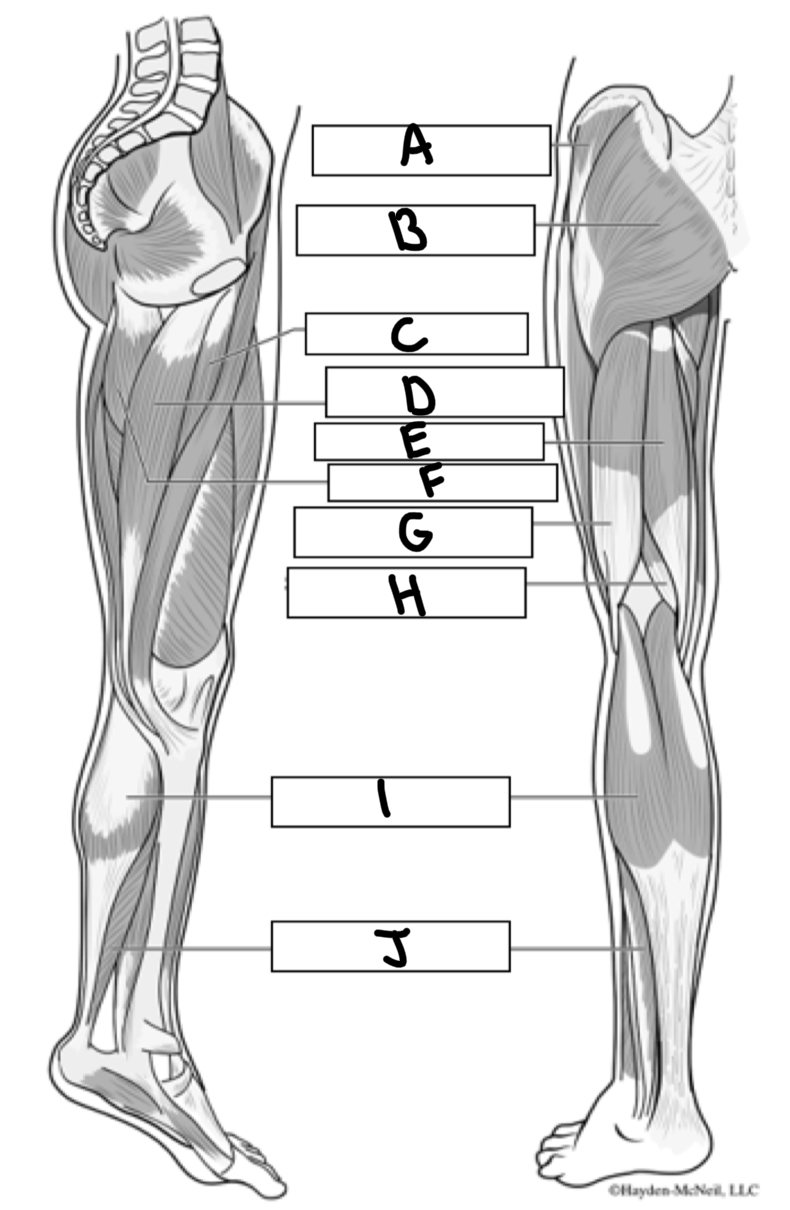
What is H
Semimembranosus
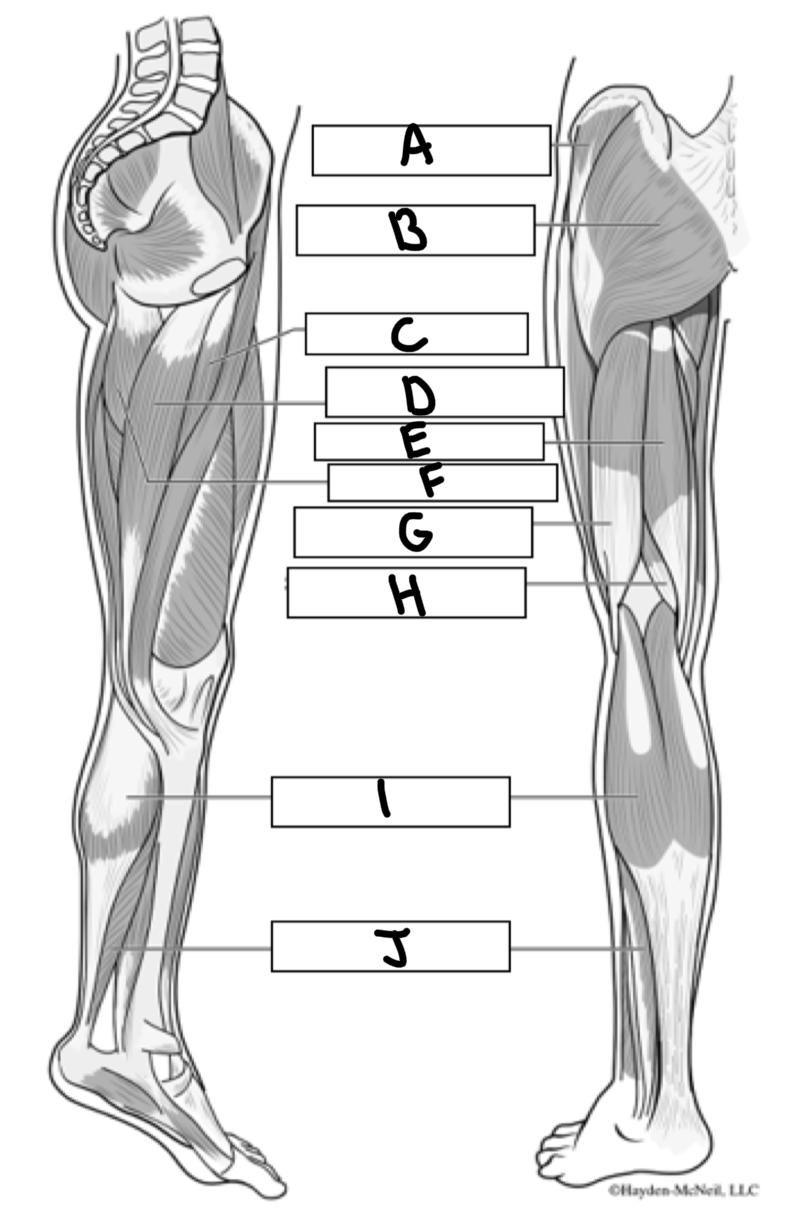
What is I
Gastrocnemius
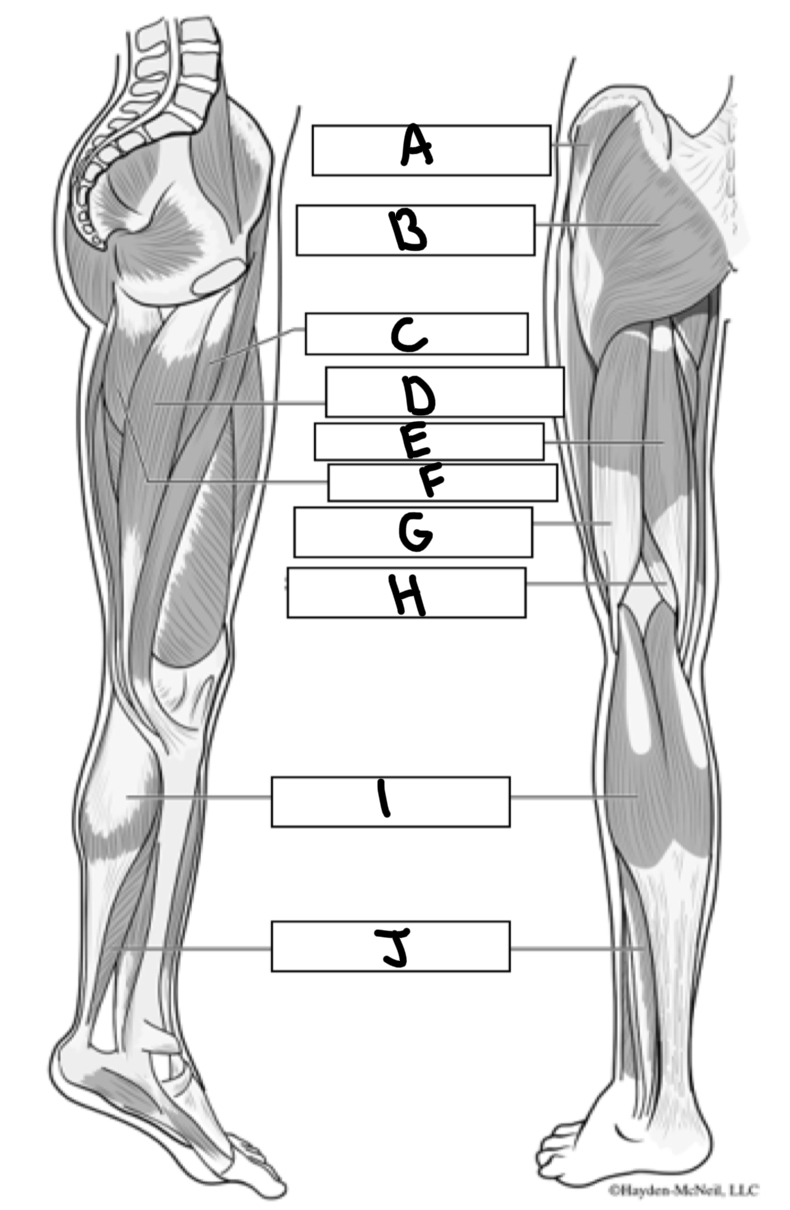
What is J
Soleus
Flexes the forearm as a synergist
Brachialis
Abducts the leg
Gluteus medius
Extends the knee
Vastus lateralis
Extends the thigh at the hip, flexes the knee
Biceps femoris
Dorsiflexion, inverts foot,
Tibialis anterior
Abducts, medically rotates and flexes the thigh at the hip
Adductor magnus
Plantar flexes foot
Soleus
Extends the digits and hand
Extensor digitorum
Extends the thigh
Gluteus Maximus
What are the 4 muscles in the quadriceps?
Rectus femoris
Vastus lateralis/ medialis
Vastus intermedius
What are the 3 muscles in the hamstring?
Biceps femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Which type of muscle is NOT strained?
Smooth muscle
Which type of muscle exhibits branching?
Cardiac muscle
Which type of muscle is under somatic nervous system control?
Skeletal muscle
This type of muscle contraction is characterized by maximal muscle tension and smooth, sustained contraction without relaxation
Complete (fused) tetanus
This is a small involuntary muscle contraction due to a single stimulation
Muscle twitch
_____ are support cells that serve a protective anchoring function in nervous tissue
Glial cells
______ send messages and are considered the functional units of nervous tissue
Neurons
Transmits impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs towards the CNS
Motor (afferent) neuron
Exists between motor and sensory neurons; where integration occurs
Interneurons
Transmits impulses away from the CNS to effector organs
Sensory neuron
What are the 4 types of glial cells in the CNS?
Astrocytes, microglial cells, ependymal, oligodendrocytes
What are the 2 types of cells in the PNS?
Satellite cells and Schwann cells
Surround neuron cell bodies in PNS; control chemical environment around neurons
Satellite cells
Line the cavities of the brain and spinal cord, secreting and circulating cerebrospinal fluid
Ependymal
Produce myelin sheath of the PNS
Schwann cells
Support and anchor neurons to capillaries in CNS; control chemical environment around neurons
Astrocytes
Produces the myelin sheath of the CNS
Oligodendrocytes