Lecture 16: Glasserella, Avibacterium, Gallibacterium, Ornithobacterium, and Strepobacillus moniliformis
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Glasserella parasuis is a commensal bacteria of the porcine ___
Upper Respiratory Tract (URT)

Glasserella parasuis requires what to grow?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD, Factor V)
What are the Virulence factors of Glasserella parasuis?
Capsule
LOS (Lipooligosaccharides)
T/F: Glasserella parasuis is devoid of LPS
True
Glasserella parasuis typically infects what age of pigs?
Post Weaning young animals (4-8 weeks old)
Naive adults and pigs with weak immunity
Peracute infections of Glasserella parasuis can result in septicemia or ______
Death
What factors can pre-dispose a pig to Glasserella parasuis?
Weaning
Transport
Stress
Poor Management
What is Glässers disease?
Infection in pigs caused by Glaesserella parasuis
Causes inflammation of the body's cavities, joints, and brain
Polyserositis, polyarthritis, meningitis
Polyserositis is inflammation with fluid buildup in two or more serous membranes, such as the pleura (around the lungs), pericardium (around the heart), and peritoneum (around the abdomen)
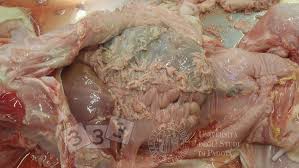
What are the C.S associated with Glasserella parasuis (Glasser’s Disease)?
High fever (41.5°C/106.7°F)
Severe fibrosis of thoracic/peritoneal cavities
Fibrinous polyserositis, polyarthritis, meningitis
Fibrinous exudate on the serosa
Increased amount of fluid

Which 2 bacterium require NAD factor to grow?
Glasserella parasuis
Avibacterium paragallinarum
What are 2 unique factors important to Avibacterium paragallinarum?
NAD (Factor V)
Needs this factor to grow
Haemagglutinin
Attachment factor
Avibacterium paragallinarum is a commensal of the _________
Oro-nasopharynx
Avibacterium paragallinarum causes _______ ____ in chickens, briefly describe this disease
Infectious coryza
It is an acute, contagious, respiratory disease
Avibacterium paragallinarum primarily infects what age of chickens?
Pullets and Laying Hens
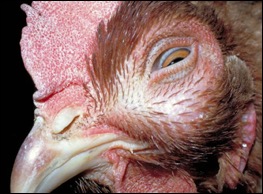
What are the C.S associated with Avibacterium paragallinarum?
Swelling of the infraorbital sinus
Nasal discharge
Sneezing
Which animal does Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale (ORT) infect?
Turkeys
Chickens
What is the main Attachment factor of Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale (ORT)? What does it attach the bacteria to?
Hemagglutinin
It attaches ORT to the ciliated epithelium of airsacs
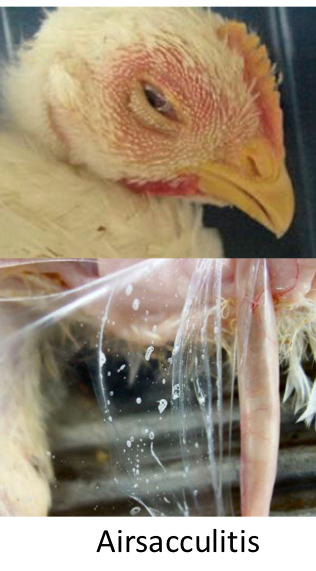
What are the C.S associated with Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale (ORT)?
Mild-Severe respiratory conditions
High mortality rates
Airsacculitis
Worst in Turkeys
Where is Gallibacterium antis found?
Birds
URT and Lower Genital tracts
T/F: Gallinbacterium anatis is NAD-dependent but V-factor independent
True
What are the characteristics of Streptobacillus moniliformis?
Gram _
Shape?
Respiratory pattern?
MOtility?
Gram -
Rod Shaped
Facultative anaerobe
Non-motile
Streptobacillus moniliformis is a resident of the ____________ of which species?
Naso-oropharynx
Rodents and possibly cats
What are the clinical syndromes of Streptobacillus moniliformis in each of these species?
Turkeys
Non-human primates
Humans
Septicemia, arthritis, otitis media, hepatitis, abortion
Caused by rat bites
Polyarthritis, Synovitis
Humans
Rat bite fever
Caused by a rat bite (no shit)
Haverhill fever
Caused by the consumption of contaminated food and water
Streptobacillus moniliformis is a bacteria of rats and is spread via ___ ____
Rat bites (in most cases)
What are the main examples of Gram-negative, non-spore forming anaerobes?
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Dichelobacter nodosus
Bacterioides fragilis
Porphyromonas levii
Prevotella spp.
Gram-negative, non-spore forming anaerobes are _______ pathogens
opportunistic
ie, they cause infections only when a situation presents itself
These are Bacteroides; they work synergistically and are anaerobes (they live inthe Oral+GIT(think there isn’t much oxygen in the GIT so they have to be anaerobic))
A characteristic of Gram-negative, non-spore forming anaerobes is that they produce _____ _____ _____ which results in rancid odor
Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs)
Ex: Butyric acid
T/F: The important Gram-negative, non-spore forming anaerobes are not aerotolerant, and will die if exposed
False, they are aerotolerant (don’t use oxygen but can survive in its presence)
What happens when Gram-negative, non-spore-forming anaerobes infect an animal at the same time?
They work together and are synergistic pathogens
The most common form of infection of Gram-negative, non-spore forming anaerobes is ________
Abscess
Gram-negative, non-spore-forming anaerobes produce a very important product via anaerobic metabolism, what is it and what effects does it have on animals?
Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs)
Lactic Acid
Butyric acid
Inflammatory and cytotoxic effects
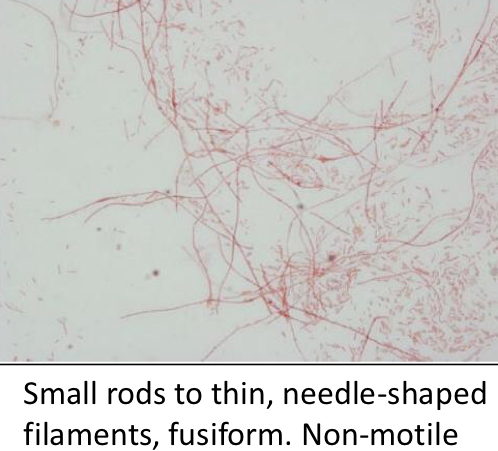
What are the characteristics of Fusobacterium necrophorum
Gram _
Motility?
Shape?
Which VFA does it produce?
Unique features?
Gram -
Nonmotile
Short to filamentous rods with tapering ends
Butyric Acid
Rancid butter odor
What is the main virulence factor of Fusobacterium necrophorum?
Leukotoxin (primarily targets and kills leukocytes (white blood cells), which impairs the immune system's ability to fight infection)
Fusobacterium necrophorum is a major pathogen of ______
Fusobacterium necrophorum causes ______ disease conditions (aka ___________), describe some of these conditions
Necrotic (Necrobacillosis)
Conditions
Liver
Hepatic Abscesses
Feet
Foot rot
Mastitis
Uterus
Fetid discharge (red-brown color)
Only occurs first 2 weeks post-partum
Fusobacterium necrophorum has a synergism with which other bacteria? What diseases does this synergy cause?
Truperella pyogenes
Liver abscesses
Foot rot
Metritis (Inflammation of the uterus)
What specific complex does Fusobacterium necrophorum cause in cattle?How does it occur?
Rumenitis-liver abscess complex (hepatic necrobacillosis)
It affects both the rumen and liver
Caused synergy between T. pyogenes and F. necrophorum
MOA
Feed with high level of carbohydrates
Production of lactic acid (by T. pyogenes) increases the acidity of the rumen, resulting in rumenitis
Rumenitis leads to necrosis of the rumen wall
Bacteria invade the portal circulation and make their way into the liver
What disease does Fusobacterium necrophorum cause in the oral tract of calves?
Necrotic Laryngitis (Calf Diphtheria)
It infects cattle up to 3 years old
How does an calf get Calf Diphtheria (Necrotic Laryngitis)
Endogenous infection through an abrasion in the mucosa of the pharynx and larynx due to ingestion of coarse feed
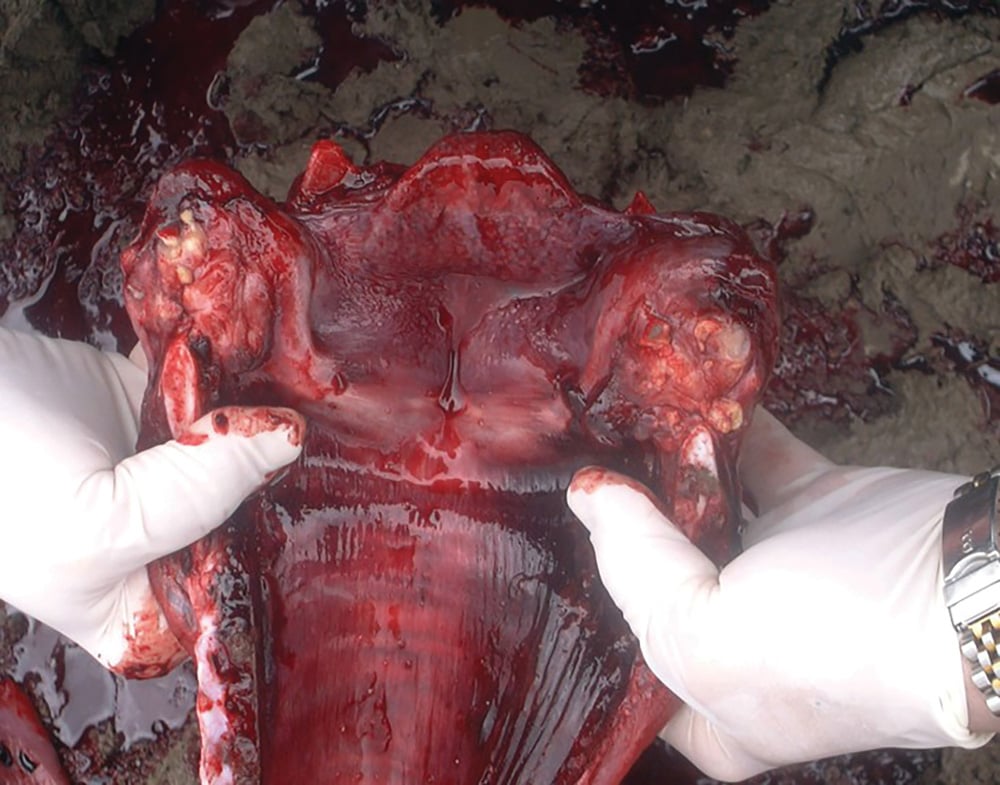
What are some key indicators/signs of Necrotic Laryngitis of calves?
Fetid breath (stank ass breath)
Oral erosions, ulcers, abscesses
Fever, depression, anorexia, salivation
Painful swallowing/cough
What disease does Fusobacterium necrophorum cause in the hooves of cattle?
Foot Rot/Interdigital Necrobacillosis
Major cause of lameness in dairy/beef cattle
Timeframe
Initially a mild cellulitis and swelling between the digits
Develops into fissures/scabs and becomes purulent
Develops into an abscess
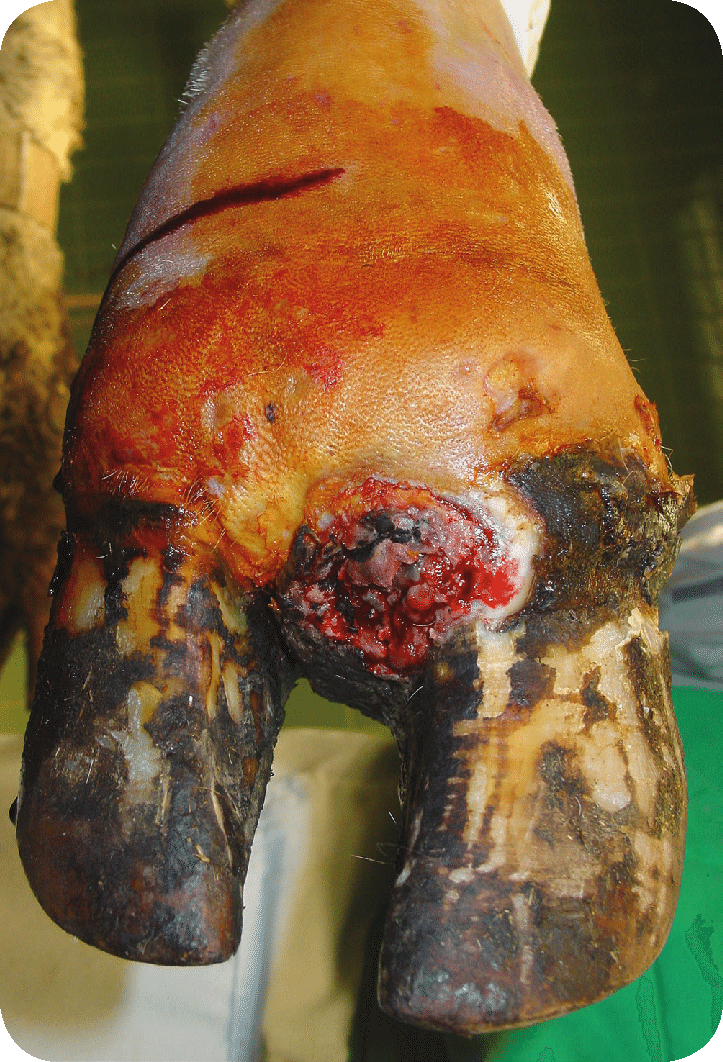
What are the main diseases that Fusobacterium necrophorum causes in animals?
Cattle
Rumenitis-Liver abscess complex (hepatic necrobacillosis)
Necrotic Laryngitis (Calf Diphtheria)
Foot Rot, Interdigital necrobacillosis
Horses
Thrush of the hoof
T/F: Fusobacterium necrophorum can be isolated in an Aerobic culture
False, Fusobacterium necrophorum is Anaerobic
What disease does Fusobacterium necrophorum cause in the hooves of horses?
Thrush of the hoof
Infection of the epidermal tisue of the frog of the horse’s hoof
Characterized by a Foul smell
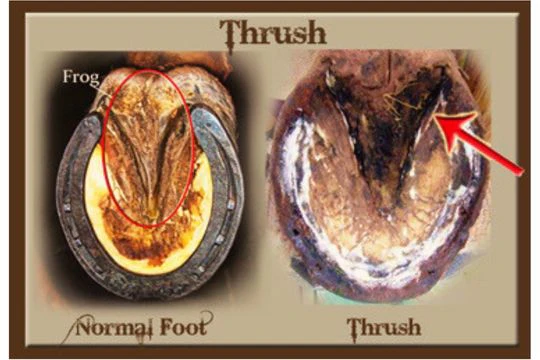
What predisposes horses to Thrush (F. necrophorum)?
Wet Conditions
Poor hygiene
Lack of regular cleaning
Why do abscesses smell so bad?
Volatile Fatty Acids
What are the characteristics of Dichelobacter nodosus?
Gram _
Shape
Gram -
Rods with terminal swellings (Dumbell shaped)
Which animal is the carrier for Dichelobacter nodosus?
Sheep
What are the Virulence Factors for Dichelobacter nodosus?
Type IV fimbriae
Used for attachment
Give the bacteria “Twitching mobility“
Proteases
Degrade tissue matrix
What disease does Dichelobacter nodosus cause?
Foot Rot, Interdigital Necrobacillosis (Similar to F. necrophorum)
How is Dichelobacter nodosus diagnosed?
Distinctive lesion
Odor
Anaerobic culture
What is the relationship between Dichelobacter nodosus and Fusobacterium necrophorum?
They work together to cause foot rot
Dichelobacter nodosus is the primary pathogen
Fusobacterium necrophorum is the secondary opportunistic pathogen that worsens the severity of the disease
Bacterioides cause ___________ ______ and soft tissue infection
intraabdominal abscesses
Some strains of Bacteroides produce an enterotoxin that can cause diarrhea in large/farm animals, what is the name of these strains?
Enterotoxigenic B. fragilis (ETBF)
What does the Enterotoxin (produced by Bacteroides) Fragilysin/B. fragilis toxin do?
Cause fluid secretion, bacterial internalization in enterocytes
_________ and ________ are frequently isolated anaerobes from dog and cat bite wounds
Prophyromonas and Prevotella
What disease does Porphyromonas levii cause?
Summer mastitis in cattle
Prophyromonas and Prevotella causes __________ disease in sheep, which can result in “______ ____“
Periodontal disease
Broken Mouth
T/F: Members of Pasteurellaceae are often commensals of oro-nasopharynx.
True
T/F: Avibacterium paragallinarum is a fastidious organism.
True
Polyserositis in pigs is caused by ------- and the disease is called as --------------
Glasserella parasuis
Glässer’s Disease
The characteristic sign of infectious coryza is ------------
Acute, contagious, respiratory infections in chickens
T/F: Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale causes severe bronchopneumonia in turkeys.
True
T/F: Ornithobacterium rhinotracheale is highly pleomorphic gram-negative rod.
True
T/F:Rat bite fever in humans is caused by Streptobacillus moniliformis
True
T/F: Gram-negative anaerobic rods cause opportunistic infections in their hosts.
True
Synergism between ----- and ----------leads to pyonecrotic lesions in liver of cattle
T. pyogenes and F. necrophorum

T/F: Foul smelling abscess and discharge in large animals suggest site infection with-----
Fusobacterium necrophorum
List three diseases caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum
Rumenitis-liver abscess complex (Hepatic necrobacillosis)
Calf Diphtheria
Thrush of the hoof
Grain overload in cattle predisposes the animal to which pathological condition?
Rumenitis-liver abscess complex (Hepatic necrobacillosis)
Synergism between --- and ---------- causes foot rot in sheep.
Dichelobacter nodules and Fusobacterium necrophorum
Twitching motility due to type IV fimbriae occurs in which gram-negative anaerobic rod?
Dichelobacter nodules (Bc the dicks lift dumbells (shape of bacteria) and their muscles twitch (type IV fimbriae))
T/F: Foot rot is managed by copper sulfate foot baths and vaccination.
True
T/F: Bacteroides fragilis causes abscesses in internal organs and diarrhea
True
T/F: Porphyromonas levii is isolated from mastitis cases in cattle
True
T/F: Porphyromonas & Prevotella spp. are found in mixed infections of foot rot
False, it is known to cause periodontal disease in sheep or mastitis in cattle