QnA - Acid , Bases and Salts
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms

Q8.
Compound X: Sodium Chloride (NaCl) concentrated solution (Brine).
Gas Y (Cathode): Hydrogen (H2H2).
Gas Z (Anode): Chlorine (Cl2Cl2).
Compound B: Bleaching Powder (CaOCl2).

Q9.
) Colour:
Before heating: Blue (CuSO4⋅5H2O).
After heating: White (anhydrous CuSO4).
b) Liquid Droplets: Water of crystallisation lost from the crystals upon heating

Q10.
Reason: Acids like HCl and HNO3HNO3 dissociate in water to produce hydrogen ions (H or H3O+), which are responsible for acidic properties. Alcohol and glucose do not dissociate to give H ions in water

Q11.
Common salt is hydroscopic ie it absorbs moisture from its surroundings. It absorbs water atompsheres from the atmosphere and becomes sticky.
CuSO4.5H2O looses its water of crystalisation upon heating and hence turns from blue to white.
It hygroscopic and absorbs moisture from the air , this leads to increase in volume causing it flow out of the bottle on its own.

Q12.
It only shows change of colour in the wet litmus paper as water is needed for ionisation to take place , no ionisation takes places in dry litmus paper , hence there is no hydronium ions produced to change colour of litmus paper.
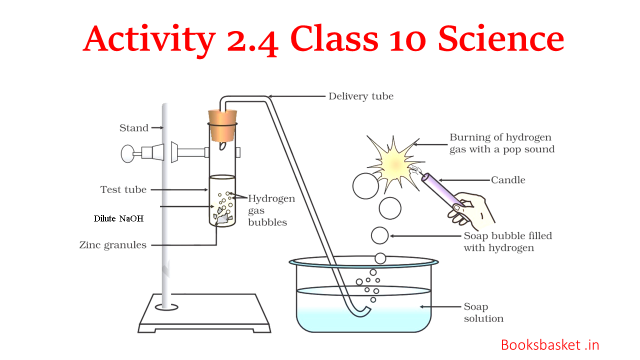

Q13.
3H₂SO₄ + 2Al → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3H₂
2HCl + Na₂CO₃ → 2NaCl + CO₂ + H₂O
Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O
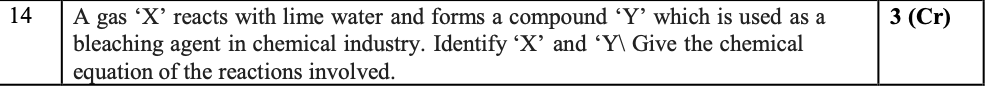
Q14
X - Cl₂
Y - CaOCl₂
Chemical Reaction - Ca(OH)₂ + Cl₂ → CaOCl₂ + H₂O

Q15
Tooth decay starts when the ph of the mouth is lower than 5.5. Tooth enamel made up of calciumhydroxyapatite is the hardest susbtance in the body , it gets corroded when the pH of the mouth goes below 7.5 due to degradation of the food particles that remain in the mouth by bacteria.
The best way to prevent this is to clean mouth using toothpaste which are general basic and can neutralise the excess acid to prevent tooth decay.
Dark blue to violet

Q16
Unlike distilled water , tap water soluble impurities like salts , which undergo dissociation to give free and mobile ions to conduct electricity.
Use your brain
Milkman adds baking soda in summer , to neutralise the excess lactic acid produced during summer months.
Cl - disinfectant
NaOH - soap
H2 - fuels

Q17
CuSO₄.5H₂O ∆→ CuSO₄.5H₂O
Compound with 10 water molecules - Na₂CO₃.10H₂O
2NaHCO₃ ∆→ Na₂CO₃ + H₂O + CO₂
Na₂CO₃ + 10H₂O → Na₂CO₃.10H₂O
Used in glass paper and soap industries
Removing permanent hardness of water

q18.
Methanoic or formic acid is secreted by nettle sting
Dock plant
Baking Soda (NaHCO3)
It is basic in nature
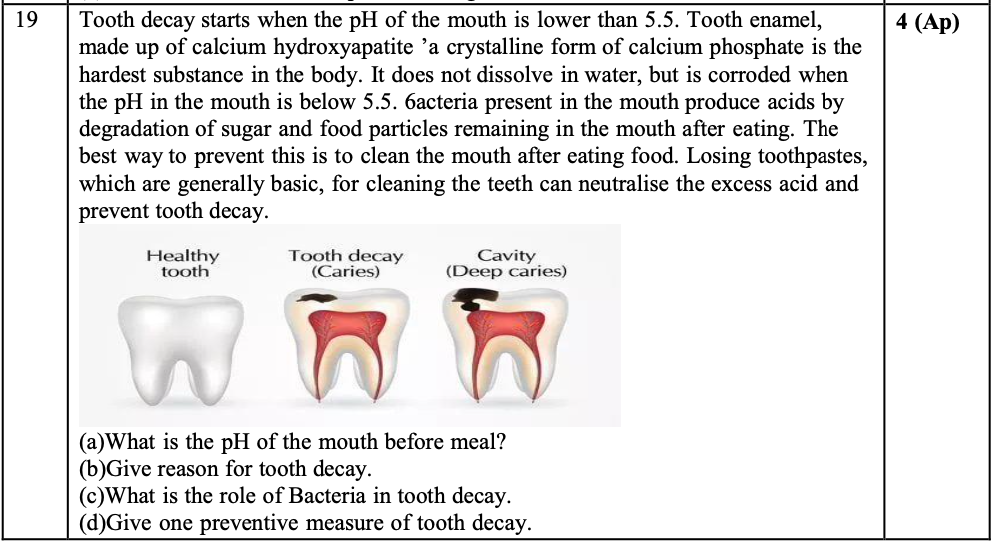
q19.
The pH range is 7-7.8 normally before meal
Check above answer
It secretes acid while breaking down the leftover food in the mouth.
Brush your teeth using toothpaste
Q20.
Less than 40 drops are need if it concenteration , as the conentrated hydrocloric has has more number of hydronium ion in the same volume , hence it neutralises it faster.
From the table we can conclude that 1 ml of NaOh neutralises 10 drops of H2SO4
Since 20 drops measures to 1 ml , 3 ml would be 60 drops.
From above relation we can say that 6ml of NaOH is needed to neutralise 60 drops of H2so4.