Microbiology Material for Exam 1
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Personnel Notes from MicroBio Course
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms

Lucretius
Disease caused by “invisible” living creatures; spontaneous generation (de novo - from scratch)

Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek
Father of MicorBio; drew and described bacteria and protozoa, wee animalcules (microorganisms)

Robert Hooke
first drawing of microorganisms, drew hairy mold, gave description on how to make microscopes
Microbiology development
slow, “not important”, arose in 19th century
Microbiology Applicable to two question
Spontaneous generation? Nature of contagious disease?
Spontaneous Generation
life from non-life (decaying matter) for COMPLEX organisms
Microorganisms
small living things - animal like
Disprooving spontaneous generation led to
germ theory, sterilization, understanding of infection, fermentation, microbial ecology
Van Leeuwenhoek scope


Redi’s experiment debunking spontaneous generation
Three flasks - one open with meat, one sealed with meat, one with fine gauze on top w/meat; maggots formed in the open flask and on top of the gauzed flask.

John Needham Hay Infusion experiment
Boiled hay infusions to kill all living things, and microbes still appeared (later found out his boiling was insufficient), believed in spontaneous generation
Protozoa
single celled eukaryotic (nucleaus) mircoorganisms, animal-like, make own food (heterotophic), after bacteria multiple, protozoa blooms and feed on them, symbionts - help host)
What does every experiment need?
trials, replication, technical vs. biological, and reproduce experiment at least three times

Louis Joblot
described protozoa

Lazzaro Spellazani
described bacterial binary fission
Binary Fission
replicates-singular circular chromosome, grows in size, divides into two genetically identical daughter cells (identical to parents cell, two new genetically identical cells)

Pasteur’s experiment debunking spontaneous generation Swa-neck flask
Broth sterilized with heat, broth allowed to cool; bactria and dust from air settle in bend, broth stays sterile indefinately (for years), flask tilted so that sterile broth comes in contact w/ bacteria + dust frtom air, hours/days later bacteria multiply in broth
results from Pasteur’s experiment
sterilization (killing all organisms), autoclave, high LVL disinfection kills almost everything, disinfection is chemicals on non-living objects

Robert Koch
found spore-like bodies in bacillus anthracis (causative agent of anthrax, a severe disease primarily affecting livestock and humans)

John Tyndall
heat resistant life forms present, dust does carry microbes
Ferdinand Cohn
named heat-resistant forms of bacteria “endospores”
Why do we need sterlization in microbiology?
Clear Culture
Microbes
Microorganisms
Bacteria that form Endospores
Bacillus, clostridia, sporrocina
Galen
theory: imbalance between 4 humours (blood, phlegm, yellow and black bile) called disease

Girolamo Fracastroro
Invisible organisms (germs) called diseases

Agostino Bassi de Lodi
Silkworm disease caused by fungus (Botrytis)
Jacob Henle and Robert Koch
Both studied anthrax
Jacob Henle
established criteria to relate anthrax to Bacillus anthracis (anthrax)
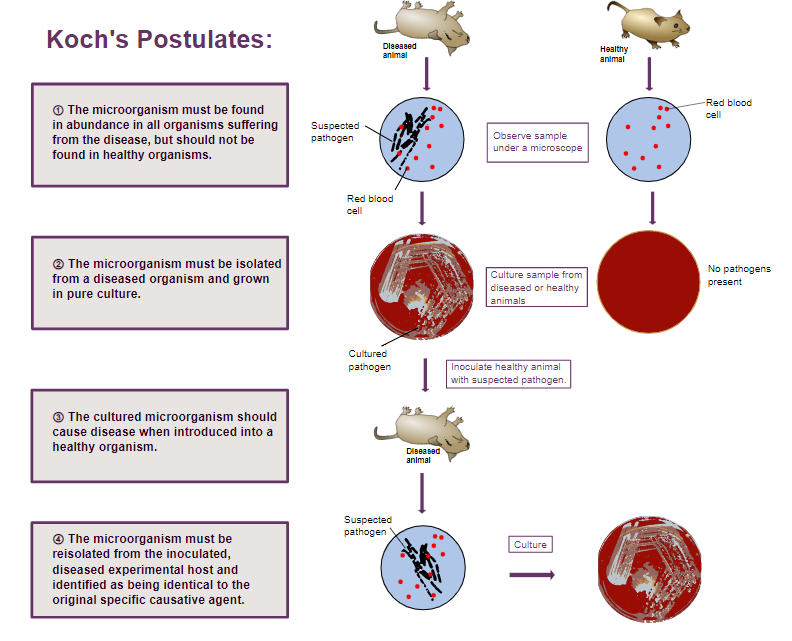
Robert Koch Anthrax
performed empirical studies, used postulates in etiology of tuberculosis
Koch’s Postulates 1
Microorganism present in every case of the disease
Koch Postulates 2
Microorganism must be grown in pure culture
Koch Postulate 3
Same disease when (healthy) second host inoculated with pure culture
Koch Postulate 4
Microorganism must be isolated from the infected host
Virus that doesn’t fit Koch’s postulates
HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus)
Molecular Postulated of Koch revised by Falkow 1
Virulence (level of severity of disease) trait seen with pathogenic strains, not nonpathogenic strains
Molecular Postulated of Koch revised by Falkow 2
Inactivation of gene(s) associated with virulence decreases pathogenicity (genes may be there, but knocked out [mutation/doesn’t work])
Molecular Postulated of Koch revised by Falkow 3
Replacement of the mutated (not working gene) with wild-type (original gene) gene restores pathogenicity
Molecular Postulated of Koch revised by Falkow 4
Gene should be expressed some time during infection and disease process
Molecular Postulated of Koch revised by Falkow 5
Antibodies (produced by B-cell = white blood cells) / immune system cells directed against gene products protect host (RBD)
RBD
Ribosome binding domain
Central Dogma
DNA replicates, transcribed to mRNA then translated to a Protein (chain of amino acids)
Papothogensity
Ability to cause disease
Varalence
level of severity of disease
Disinfect
used for inanimate objects
Antiseptic
safe for human/animal surfaces

Ignaz Semmelweis
hand washing prevents puerperal fever (fatal fever women had after childbirth)

Joseph Lister
Sterilization of instruments with heat (less likely to transfer), phenol as antiseptic
Jenner
first vaccination (smallpox) - subcutaneous (fatty tissue directly under the skin)
Pasteur
rabies vaccination
(current) Most transmissible virus
flu and measles
Can microbial diversity be detected?
only 0.4% of all bacteria in the natural world can be cultured
Great plate count
large discrepancy where the number of microorganisms observed microscopically greatly exceeds the number that can be cultured on plates
Agar
polysaccharide from seaweed; used to culture bacteria
Mother of Microbiology; used Agar
Fannie Eilshemius Hesse

Richard Petri
developed container to hold solidified media (petri dish)

Sergein Winogradsky
described lithotrophy (form of metabolism where an org. obtains energy by oxidizing inorganic compounds), used model ecosystem


Rita Colwell
Vibrios (single-celled and found in brackish and saltwater environments)

Lynn Marguelis
Endosymbiont hypothesis, gave rise to mitochondria nad chloroplasts

Thomas Brock
discovered archaeons (prokaryotic microorganisms)

Norm Pace
sequenced thermophiles (thrive in extreme heat 113 F - 176 F)
Carl Woese and George Fox
described archaeons, used 16S rRNA, developed “domains”

Ruth Patrick
freshwater ecologist and phycologist, biological diversity reflected environmental stress

Terry Hazen
Microbial ecologist, deep water horizon oil spill (lead to understanding of how marine ecosystems respond to and recover from massive hydrocarbon pollution)

Craig Venter
sequencing of bacterial genomes, first to sequence H.influenzae

Claire Fraser
(women) sequencing of bacterial genomes

Karen Nelson
(women) sequencing bacterial genome- thermotoga, showed lateral gene transfer from archaeon to bacteria
Hamilton Smith
Nobel Laureate discovered restriction enzymes, sequencing of bacterial genome with Venter-H.influenzae
Covid-19 Vaccine (Doctors)
Katalin Kariko, Drew Weissman, Kizzmekia Corbett Barney Graham

Neophile
young, inexperienced
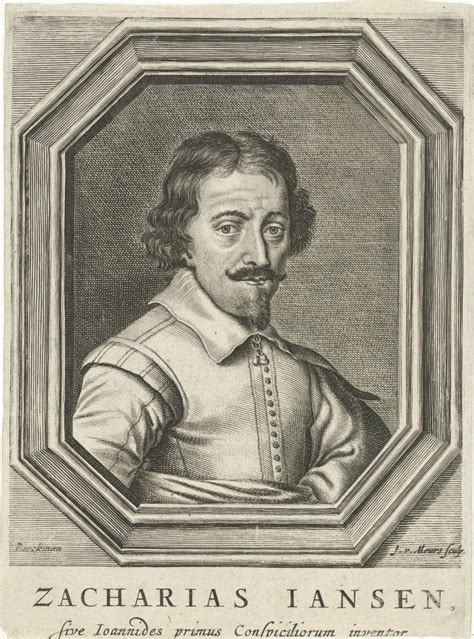

Zacharias Janssen
credited with invention of first microscope in 1590

Christiaan Huygens
First to use two lens eyepiece in compound microscope
Four Ways light might interact with objects
absorption, reflection, refraction, scattering
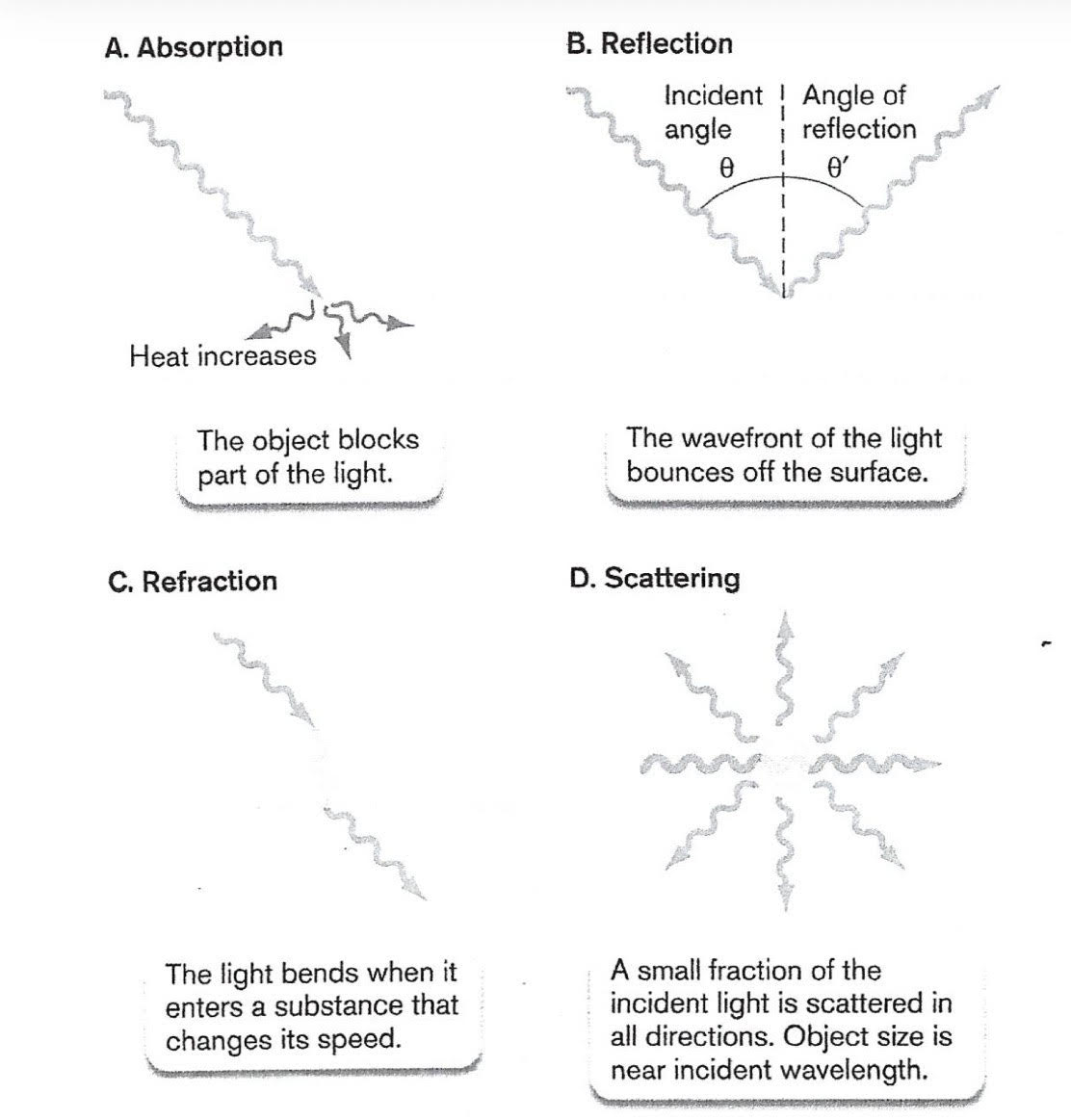
Absorption
Energy gained from particle of light (photon)
Reflection
Wave of light bounces off surface at an angle of reflection theta
Refraction
light bends upon entering substance; key property allowing lens to magnify image
Scattering
wavefront pushed in all directions
refractive index
how much it can bend a light
Resolution
ability to clearly see image; only part of light wavefront enters, causing interference; there is a balance between magnification and resolution
Microscope
accurately enlarge or magnify an object
Contrast (difference between object and background)
Use of dyes for staining; staining process often kills cells
Types of Light Microscopy
Bright field, dark field, phase contrast, differential interference contrast
Types of Electron Microscopy
Scanning EM, Transmission EM
Scanning Probe
Scanning tunneling microscopy, atomic force microscopy
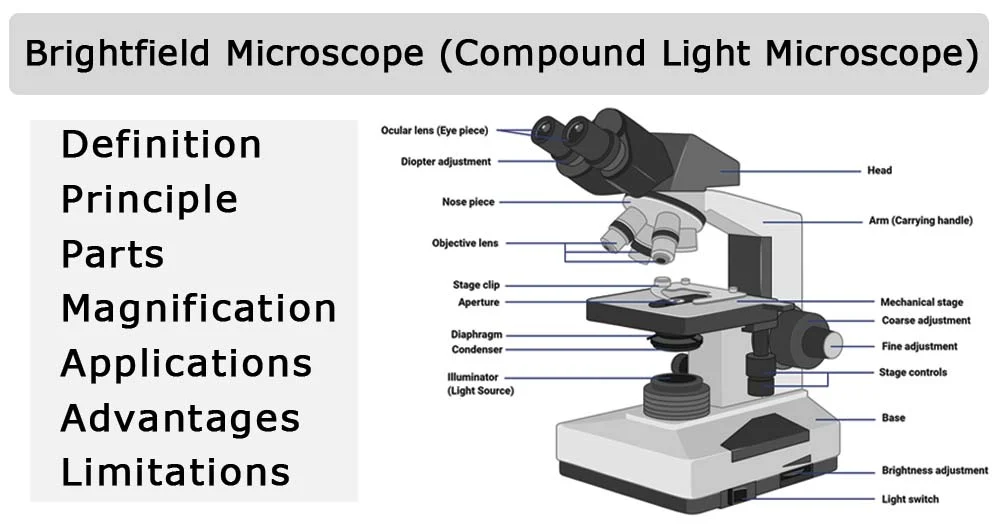
Bright Field Microscopy
typical lab microscope, used for stained and unstained specimens, magnifies image using two lens systems=compound microscope; objective lens is closer to the specimen; ocular lens or eyepiece does final magnification
Part of Light Microscope
ocular lens/eyepiece; objective lens (held by nosepiece); body of microscope (contains mirrors and prisms); stage; substage condenser lens, lens projecting above stage, controls numerical aperture (1.2-1.4); iris diaphragm (controls light entering condenser)
Objective lenses have specific properties
magnification, numerical aperture, focal length (distance required objective lens and top of object being viewed), wavelength of light also important
With increasing lens strength
theta widens and light is lost
0.2 micrometers
200nm
Meet the Microbes: Prokaryote
include domains Bacteria and Archaea; over 12,000+ bacteria as of 2018, new archaeons discovered continuously and bacteria
Meet the Microbes: Eukaryote
Includes fungi, algae, protozoa; reclassified in 2005; Fungi have 99,000+ species
Meet the Microbes: Viruses
acellular-no metabolism; DNA or RNA as genetic material (won’t have both at the same time, possible hybrids); obligate intracellular parasites; 11,273 ‘species’ in 2023; new oned discovered every month
Morphology
cell shape
major morphologies of prokaryotic cells
spherical of ovoid, cylindrical, curved or spiral; some stay grouped/clustered after cell division in characteristic arrangements
(prokaryotic cell) Streptococcus
grape-like clusters of Staphylococcus’, spirochetes (tightly coiled), appendaged bacteria, appendaged bacteria, and filamentous bacteria
Coccus
round
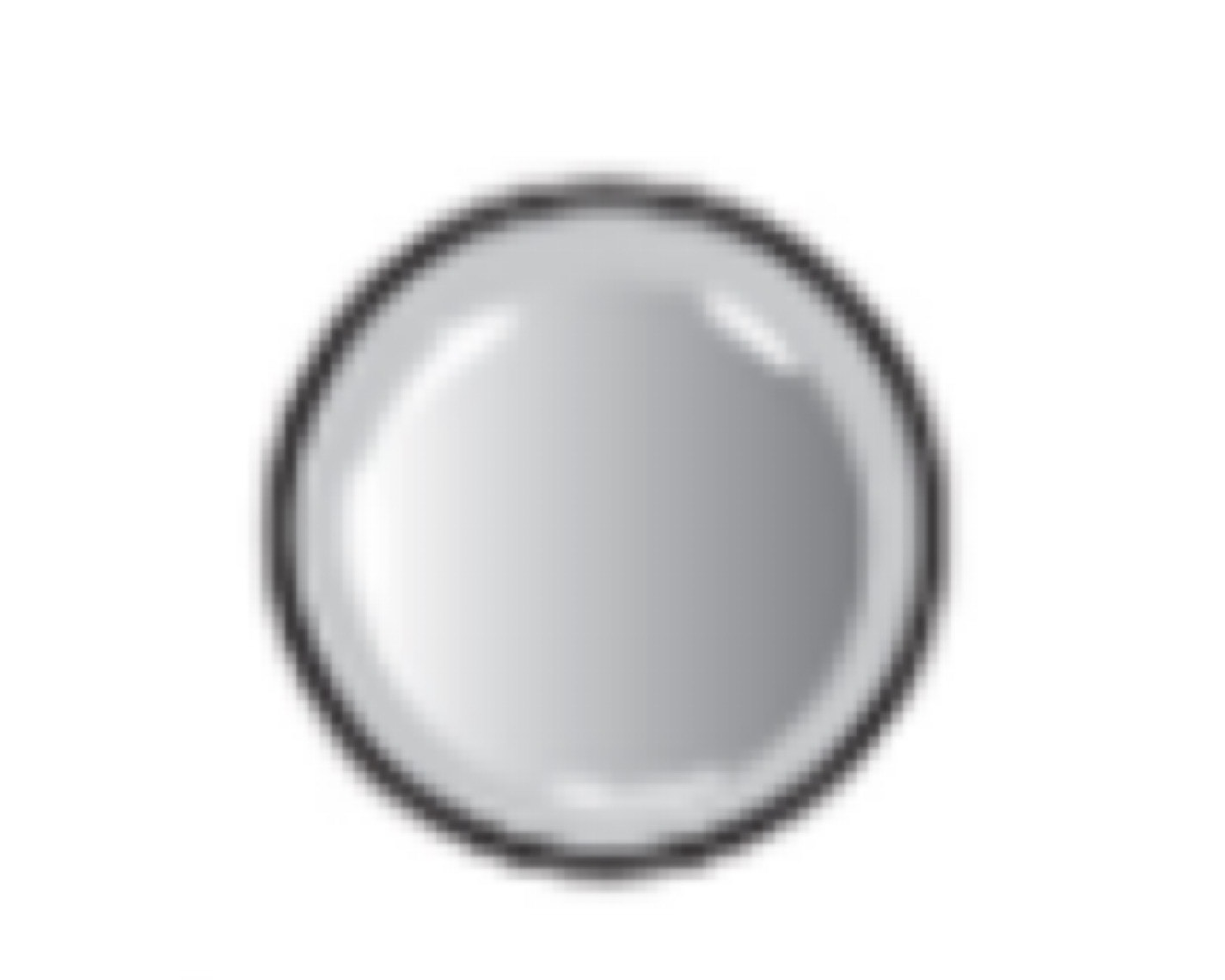

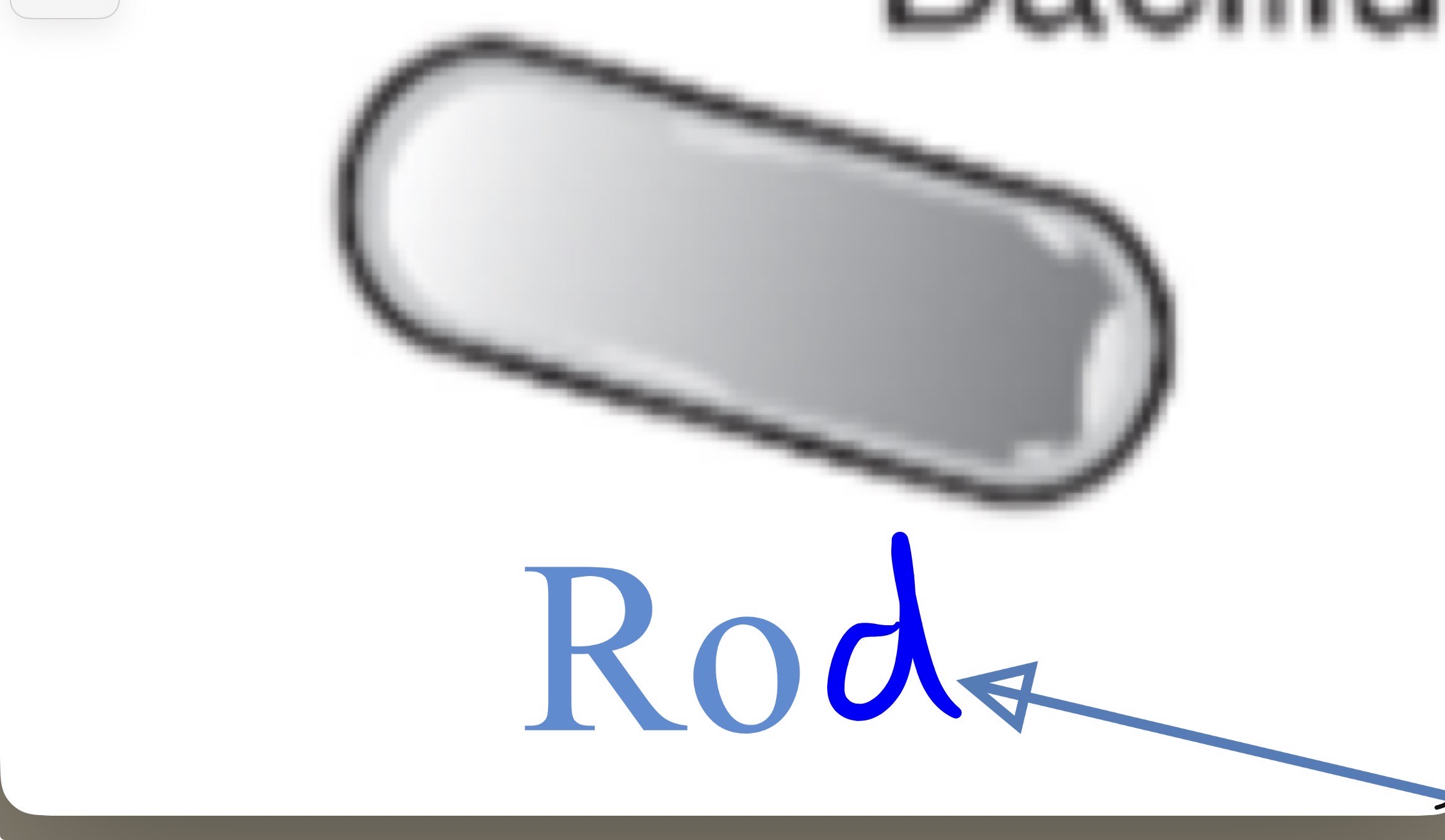
Bacillus
Rod
Coccobacillus
oval (between round and rod shaped)
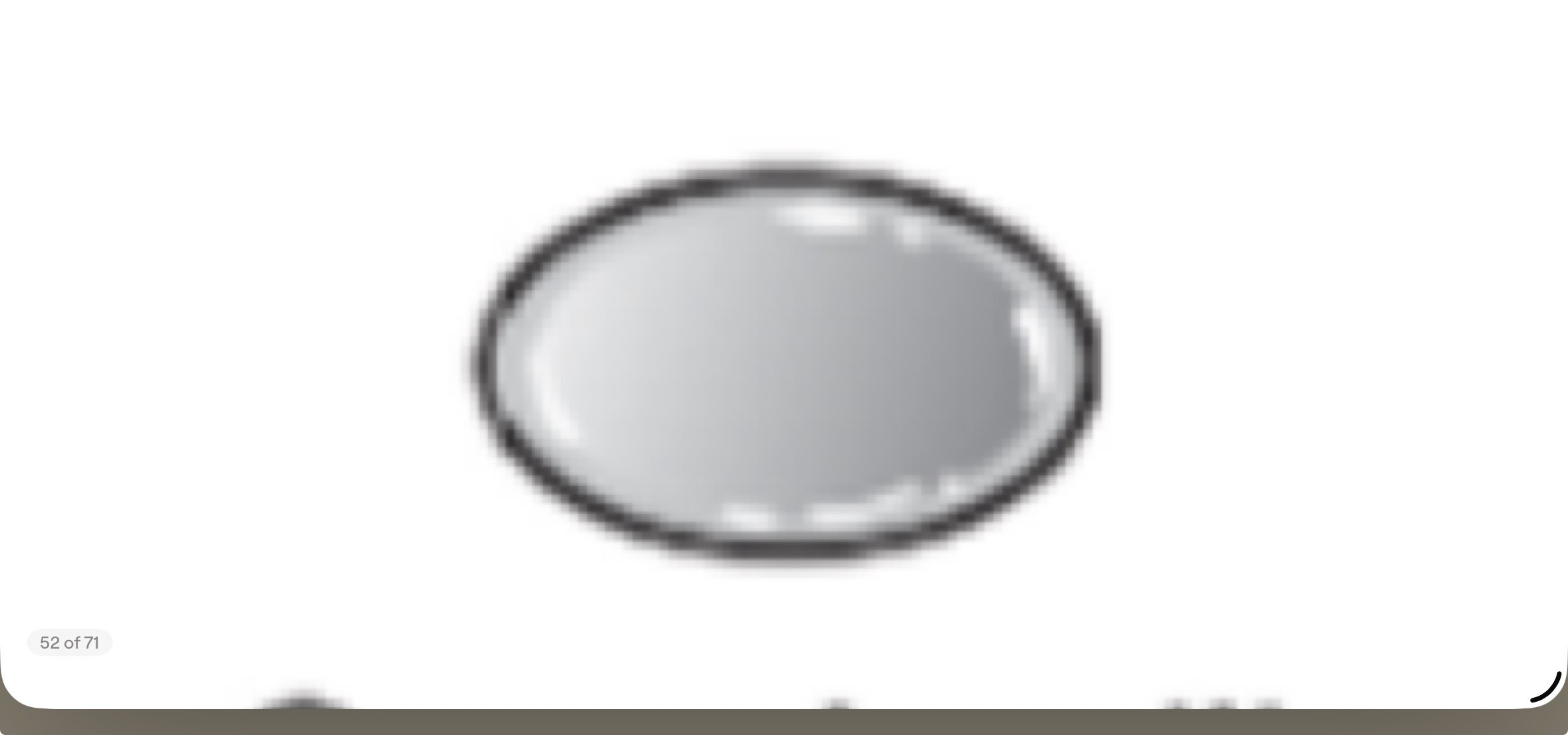

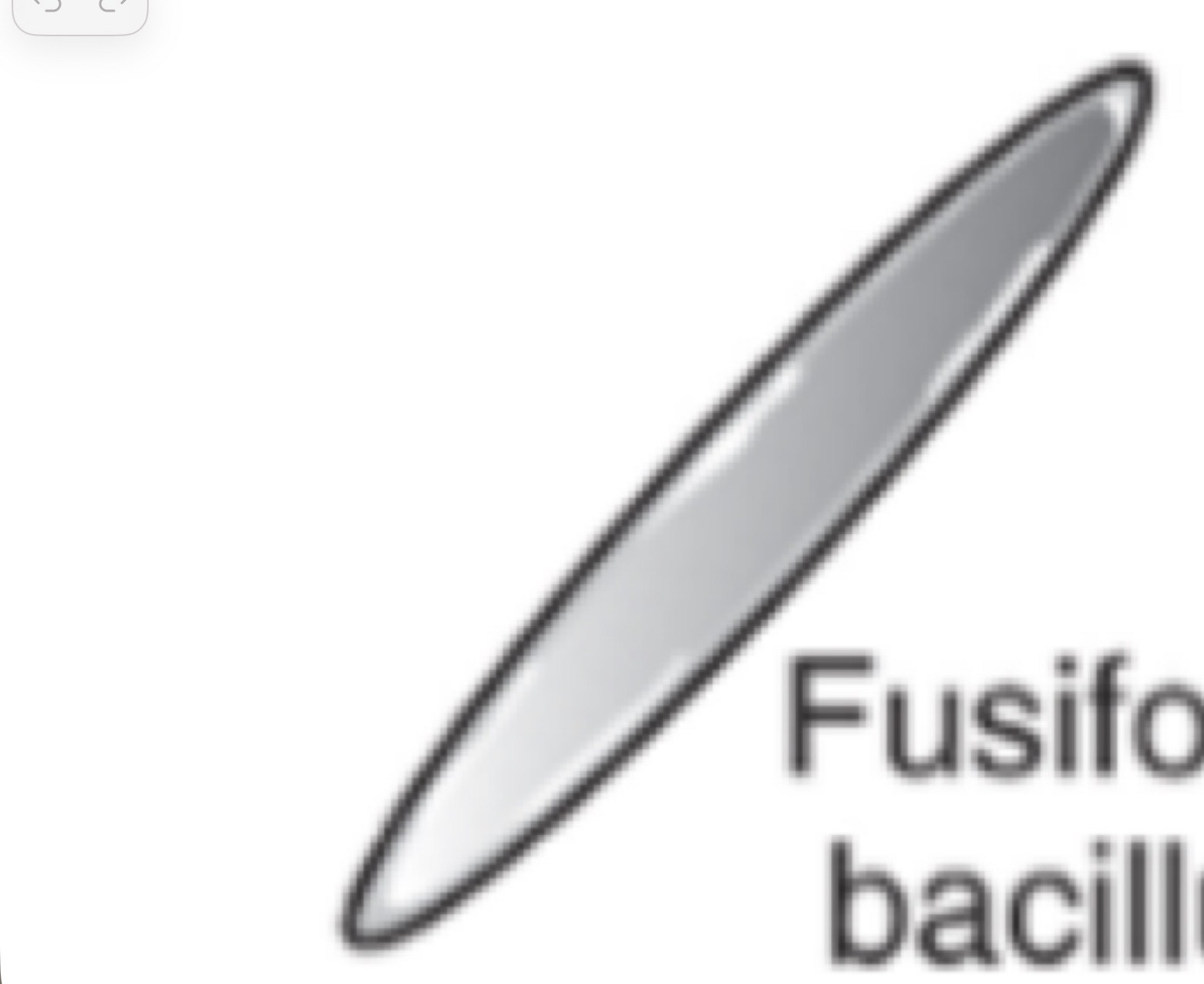
Fusiform Bacillus
Spindle-like (needle shaped)
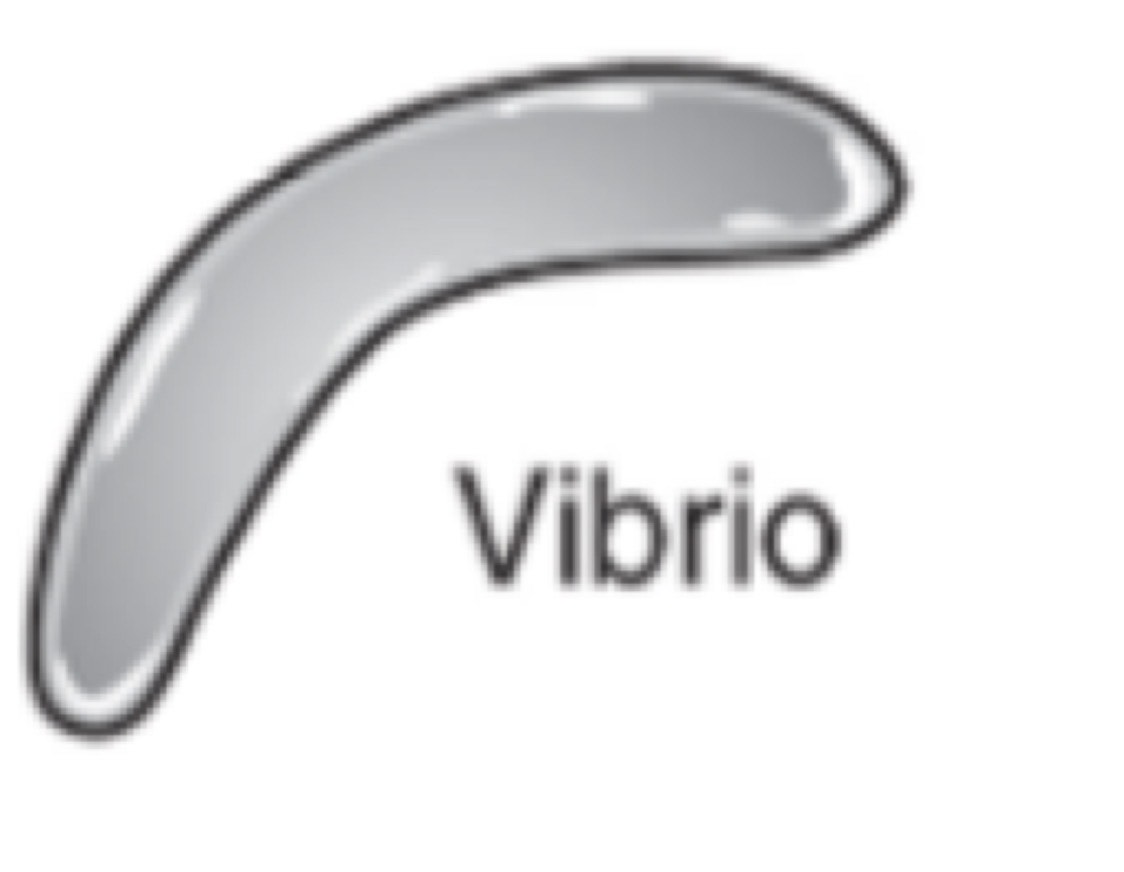
Vibrio
Curved
