Male Reproductive System
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
testes
primary male sex organs that produce gametes
sperm
male gametes
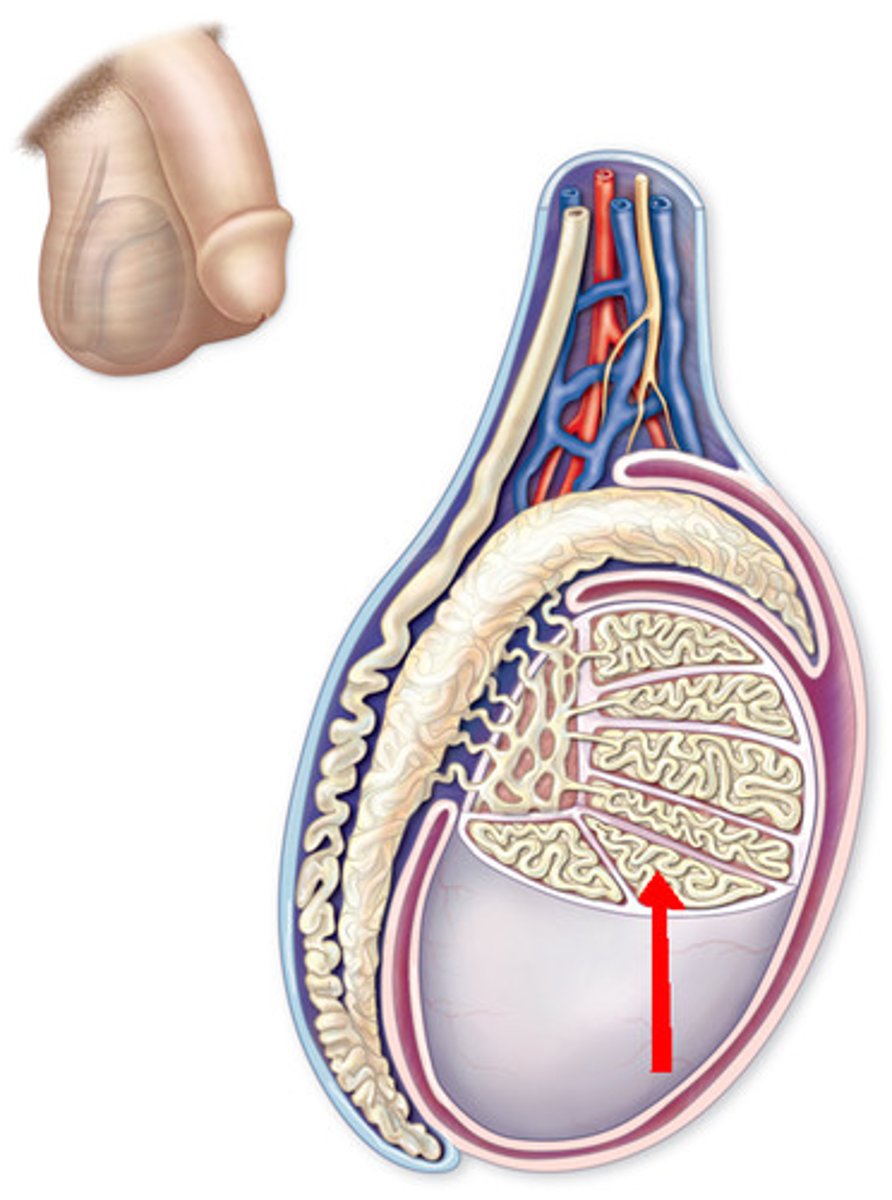
seminiferous tubules
where sperm are produced in the testes
seminiferous tubules (picture)
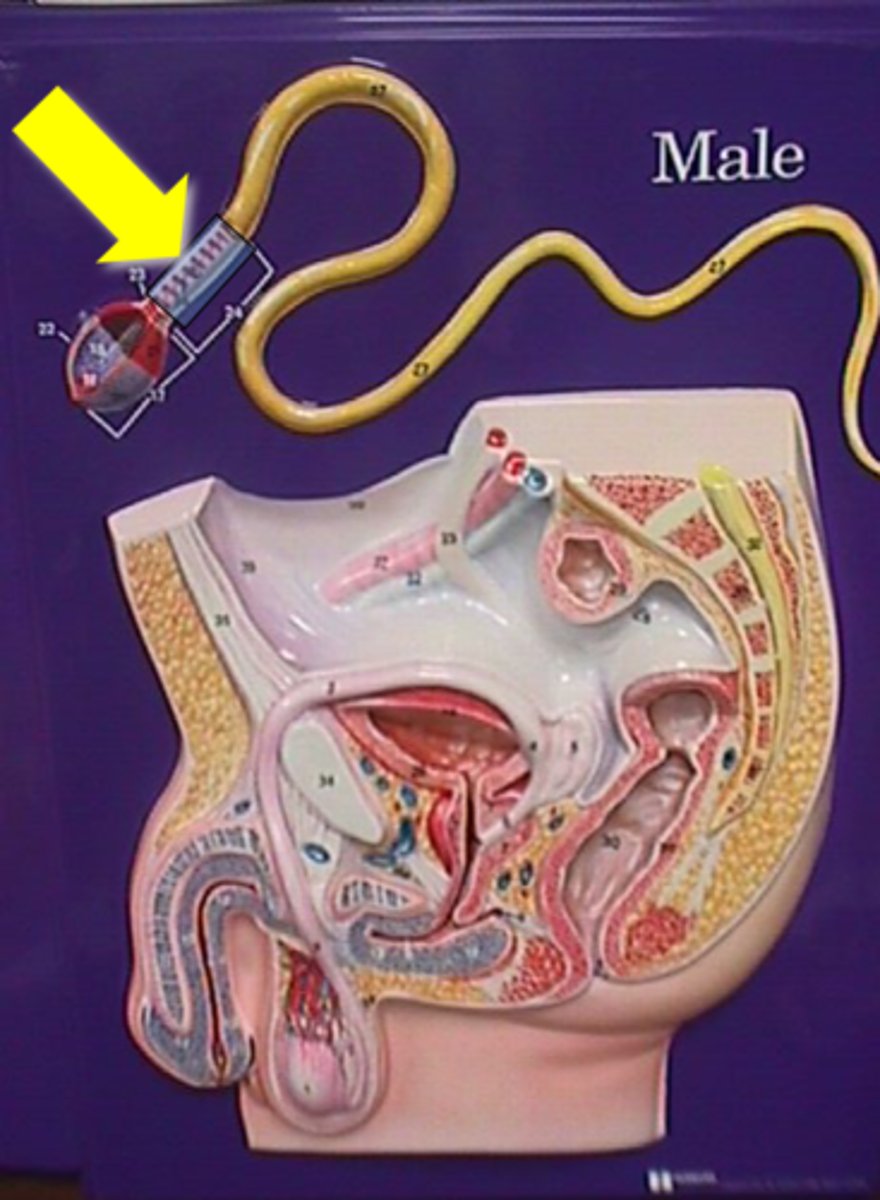
epididymis
the first part of the male duct system; temporary storage site for immature sperm
ductus deferens (picture)
urethra
part of the male duct system that both sperm and urine travel through
urethra (picture)
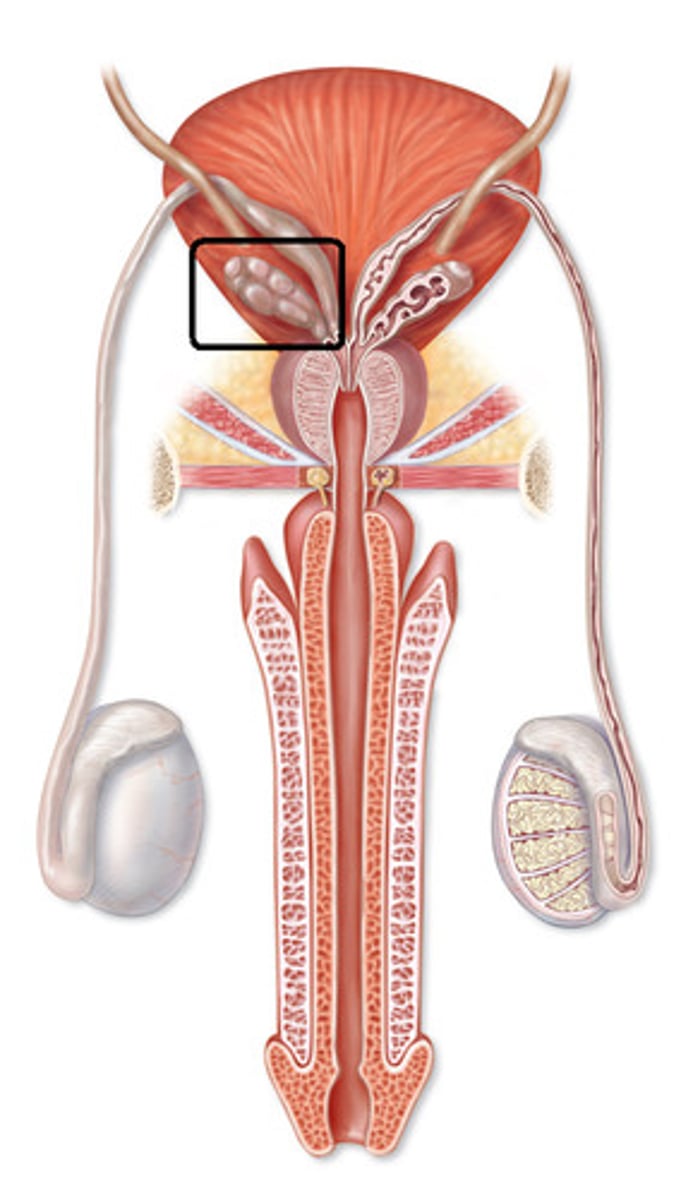
seminal vesicles
produce thick, yellow fluid (60% of semen) that nourishes the sperm and helps activate it
seminal vesicles (picture)
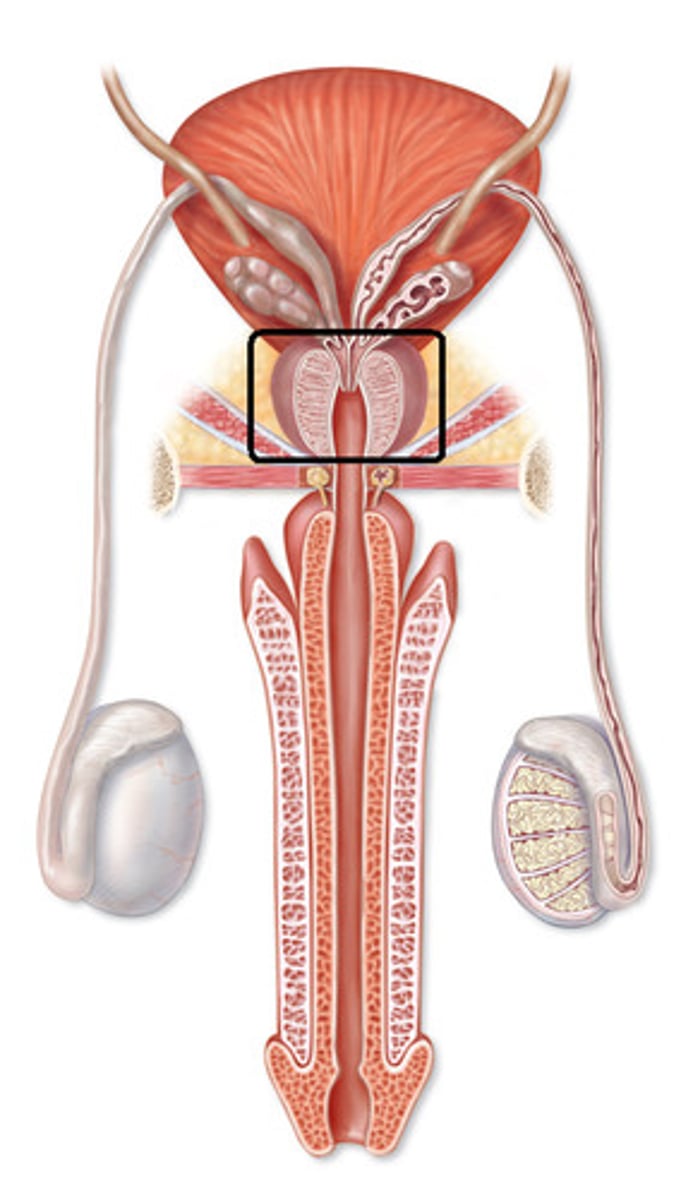
prostate
a doughnut shaped gland that wraps around the urethra and secretes a milky fluid that activates sperm
prostate (picture)
bulbourethral glands
produce a thick, clear mucus that cleanses the urethra of any traces of acidic urine before ejaculation and acts as a lubricant for sexual intercourse
bulbourethral glands (picture)
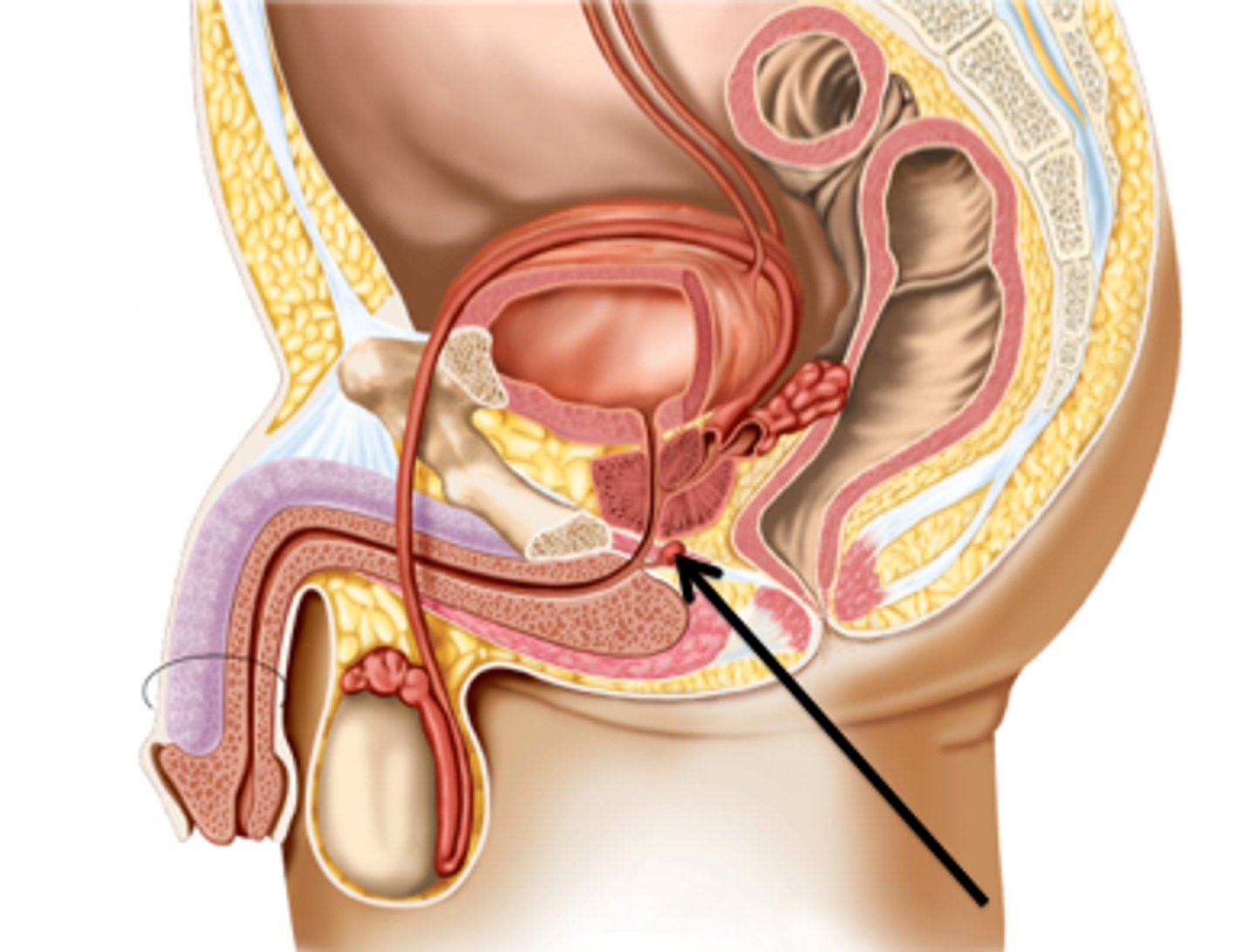
semen
mixture of sperm and accessory gland secretions
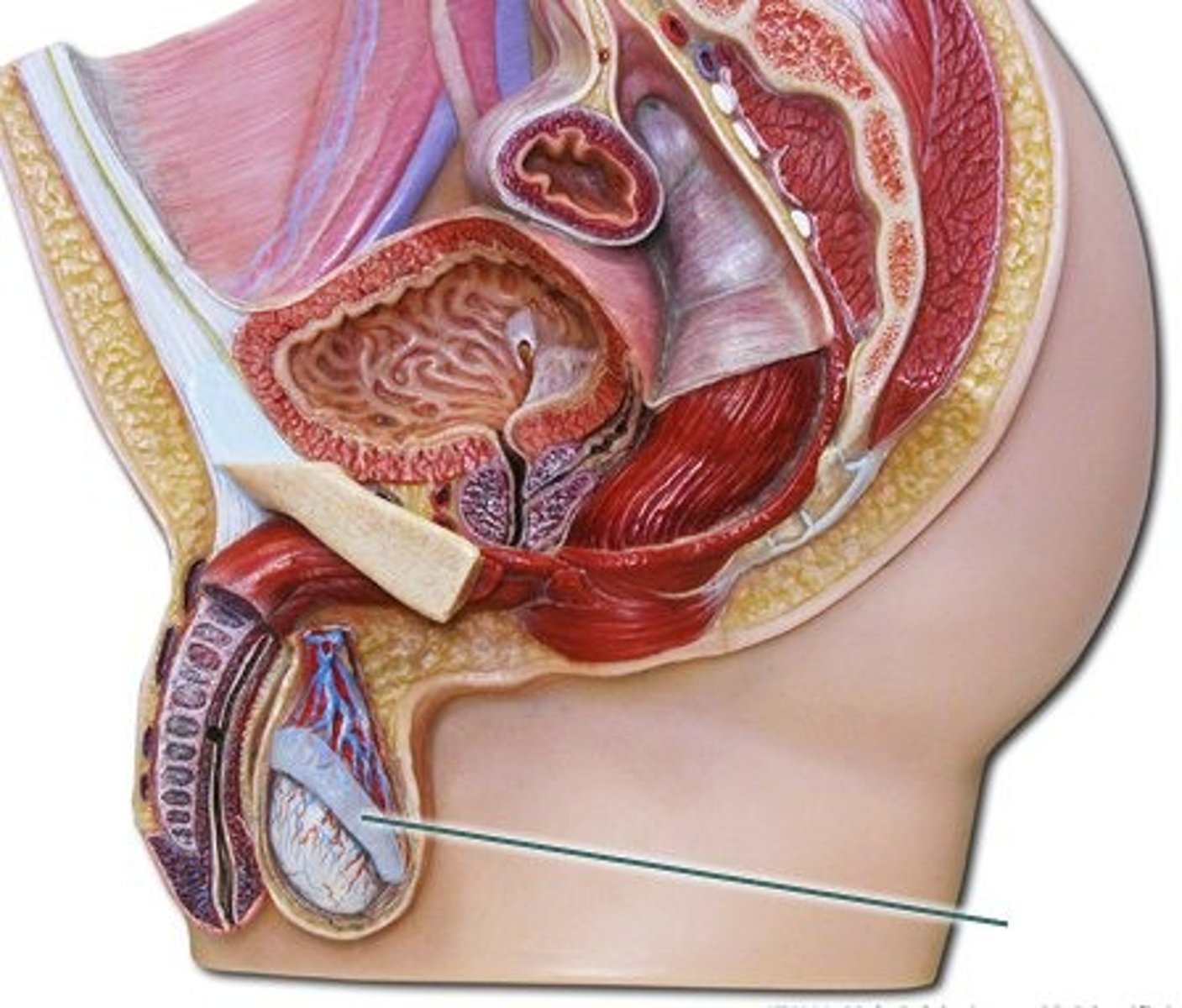
scrotum
a sac of skin that surrounds the testes
penis
organ designed to deliver sperm into the female reproductive tract
erectile tissue
the spongy tissue inside the penis that fills with blood during an erection
spermatogenesis
production of spermatids
spermatogonia
male reproductive stem cell; divides rapidly at birth
FSH in males
hormone released from anterior pituitary gland that activates sperm and testosterone production at puberty
primary spermatocyte
the cell that undergoes meiosis to form the spermatid
spermatid
immature sperm cell
spermiogenesis
the last stage of sperm development when a spermatid matures into a sperm
acrosome
covering over the head of the sperm cell that contains enzymes to help the sperm penetrate through the capsule that surrounds the ovum
acrosome (picture)
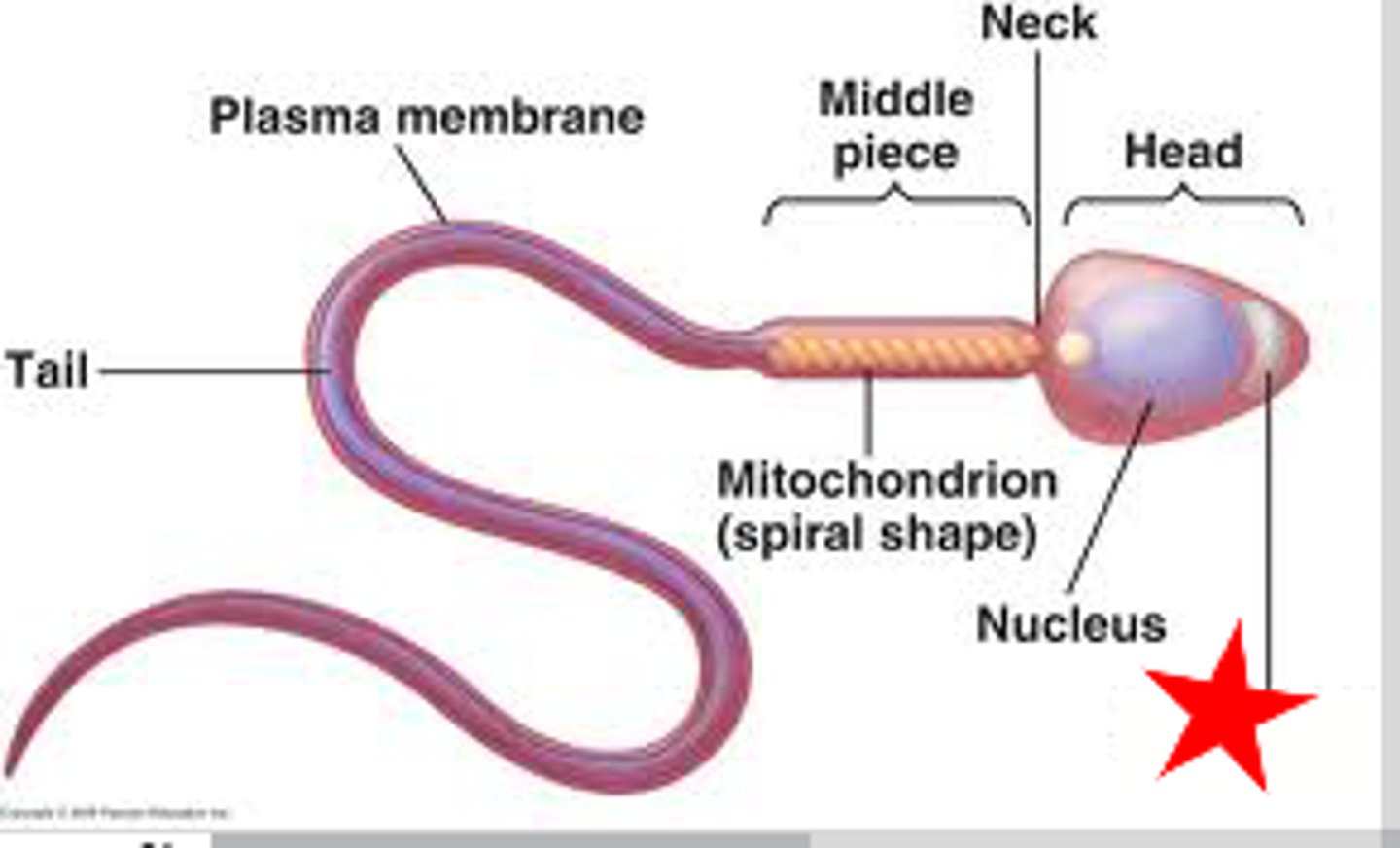
midpiece (picture)
testosterone
Hormone produced in the testes that produces male sex characteristics
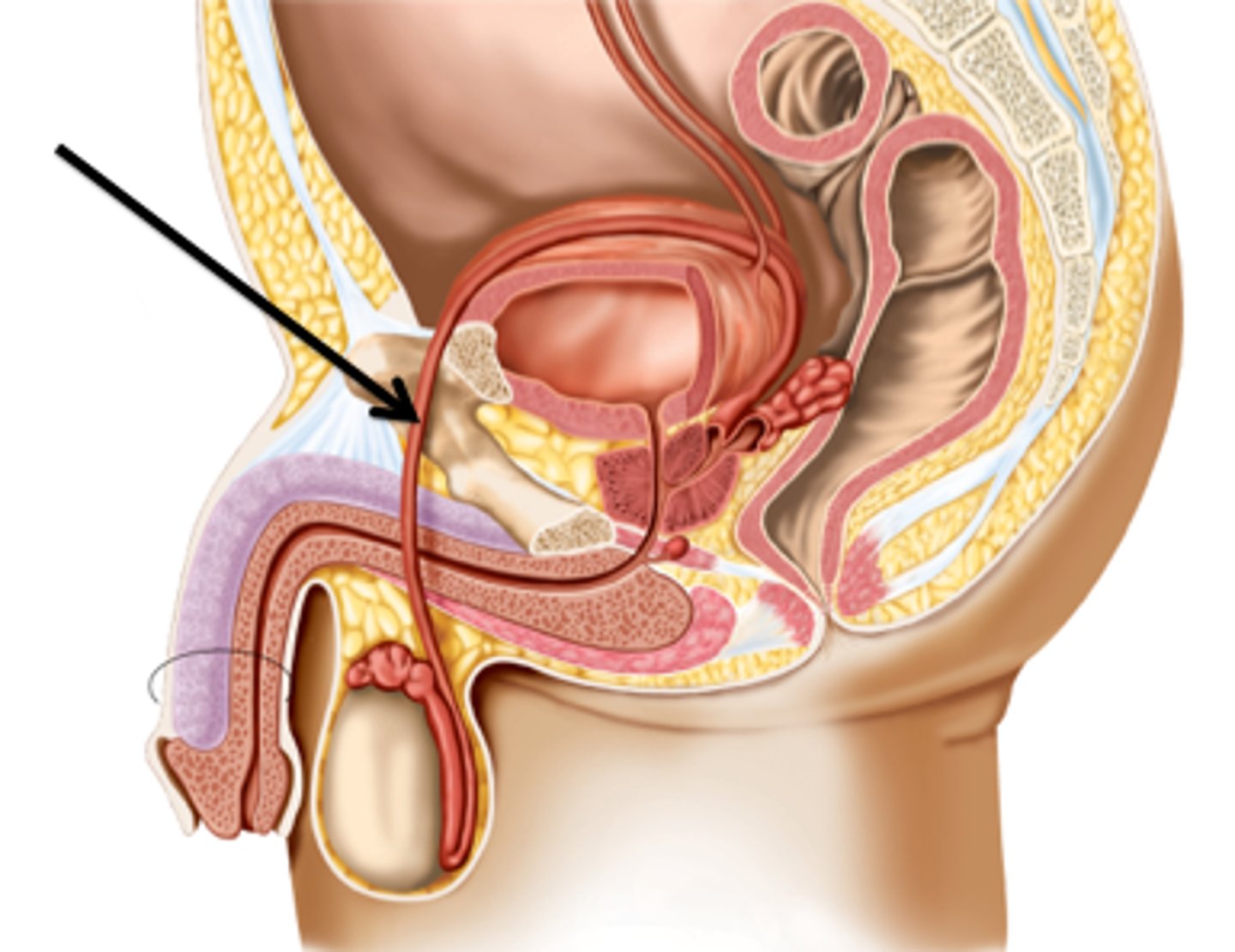
vasectomy
the operation where a man's ductus deference is cut and/or tied off to prevent sperm from entering the rest of the duct system
ejaculation
when peristaltic waves squeeze sperm from the epididymis along to the outside of the male's body
Sertoli cells
cells found within the seminiferous tubules that provide metabolic support for the spermatids
Leydig cells
A cell that produces testosterone and other androgens and is located between the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
Spermatic cord
bundle of fibrous connective tissue containing the ductus deferens, blood and lymphatic vessels, and testicular nerve
glans
Head of penis covered by the prepuce (foreskin)
prepuce
foreskin; loose casing that covers the glans penis; removed by circumcision
LH in males
hormone released from the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates interstitial cells (Leydig) to produce testosterone
Inhibin in males
Hormone released by the Testes and targets the Anterior Pituitary Gland, which then INHIBITS the release of FSH, resulting in a slow down of sperm production
epididymis (picture)
vas (ductus) deferens
long duct that serves as the passageway for sperm for the epididymis to the urethra
spermatic cord
bundle of fibrous connective tissue in males containing the ductus deferens, blood and lymphatic vessels, and testicular nerve
cremaster muscle
Muscle that pulls the scrotum closer to the body in cold temperatures and relaxes to let the testicles be farther away from the body in warmer weather
circumcision (male)
surgical removal of the foreskin
erection
during sexual arousal erectile tissue of the penis fills with blood, causing penis to enlarge and become rigid
The ________ is a long duct in the testicle where sperm develop.
Seminiferous tubule
The essential organs of the male reproductive system are the ________.
Testes
The pouchlike sac where the male gonads are located is called the ________.
Scrotum
The membrane that covers the testicle and also divides the interior into lobes is called the ________.
Tunica albuginea
The ________ are the cells in the testes that secrete testosterone.
Interstitial cells
The primary spermatocyte develops from a cell called the ________.
Spermatogonium
The primary spermatocyte forms sperm cells by undergoing a specialized type of cell division called ________.
Mieosis (Spermatogensis)
The sperm cell contains a(n) ________, which contains an enzyme that can digest the covering of the ovum.
Acrosome
The ________ is a reproductive duct that consists of a tightly coiled tube that lies along the top and behind the testes.
Epididymis
The ________ is a reproductive duct that permits the sperm to move out of the scrotum upward into the abdominal cavity.
Vas deferens (ductus deferens)
The ________ is a gland that secretes a thin, milk-colored fluid that makes up about 20% of the seminal fluid.
Prostate gland
The ________ are a pair of glands that produce a thick, yellowish, fructose-rich fluid that makes up about 60% of the seminal fluid.
Seminal vesicles
The penis is composed of three columns of erectile tissue: one is called the corpus spongiosum, and the other two are called the ________.
Corpora cavernosa
The essential organs of the female reproductive system are the ________.
Ovaries
Another name for a mature ovarian follicle is a(n) ________ follicle.
graafian follicle
The process that produces the female gamete is called ________.
Oogenesis
Meiosis in the female produces one large ovum and three small daughter cells called ________, which degenerate.
Polar bodies
The ________ are the reproductive tubes connecting the ovary and the uterus.
Fallopian tubes (Oviducts, Uterine tubes)
The muscle layer of the uterus is called the _______.
Myometrium
The uterus is composed of two parts: the upper part, called the body, and the narrow lower part, called the ________.
Cervix
The innermost layer of the uterus, which is shed during menstruation, is called the ________.
Endometrium
The ________ is the part of the female reproductive system that opens to the exterior.
Vagina
The ________ glands are glands that secrete a mucuslike lubricating fluid into the vestibule.
Greater vestibular
The milk-secreting glandular cells of the breast are arranged in grapelike structures called ________. These drain into ________ ducts that converge toward the nipple.
Alveoli, Lactiferous
Ovarian hormone that reaches its highest concentration during the secretory phase
progesterone
Pituitary hormone that stimulates the formation of an egg follicle
FSH
Caused by the rapid drop of blood levels of estrogen and progesterone
menstruation
What the egg follicle becomes after ovulation
corpus luteum
estrogen
Ovarian hormone that reaches its highest concentration in the proliferative phase
Phase of the reproductive cycle that begins after ovulation
secretory phase
Term used to describe the egg being released from the ovary
ovulation.
The uterine wall begins to thicken during this phase of the reproductive cycle
proliferative phase
Pituitary hormone that can be called the ovulating hormone
LH