Research Methods Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/234
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:49 PM on 10/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
235 Terms
1
New cards
WHO definition of health
a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
2
New cards
research
the process of systematically and carefully investigating a subject in order to discover new insights about the world
3
New cards
health research
investigation of health and disease or any of the factors that contribute to the presence or absence of physical, mental, and social health among individuals, families, communities, nations or the world population
4
New cards
Epidemiology
The study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states in specific populations, and the application of this study to control of health problems
5
New cards
Biostatistics
application of statistics to biological and medical problems. This is one of the basic sciences of public health, applied in the analysis of vital and health statistics and in the use of statistical tests for associations, correlation, significance levels, etc.
6
New cards
Determinants of health
investigation of health and disease or any of the factors that contribute to the presence or absence of physical, mental, and social health among individuals, families, communities, nations or the world population
7
New cards
clinical reserach
evaluates the best ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat adverse health issues that adversely affect individuals and families
8
New cards
population health research
focuses on the health outcomes and the determinants of health in groups of humans
9
New cards
biological research
looks at changes at human cellular level that can be related to the health outcomes
10
New cards
5 step research process
1. Identify a study question
2. Select a general study approach
3. Design the study and collect data - measure variables
4. Analyze data - measures of occurrence/associations, causation, bias confounding
5. Write and share a report about the findings - publish, present
2. Select a general study approach
3. Design the study and collect data - measure variables
4. Analyze data - measures of occurrence/associations, causation, bias confounding
5. Write and share a report about the findings - publish, present
11
New cards
brainstorming
process of generating long lists of spontaneous ideas about possible research questions
12
New cards
aspects of making research question
interest, aptitude's, applications, mentors
13
New cards
interest
what are my interests? what diseases have effected me or family?
14
New cards
Aptitudes
what knowledge/skills do i already have? What methods am i prepared to apply?
15
New cards
applications
what studies would help improve health related practices or policies?
16
New cards
Mentors
what are areas of expertise of my profs, teachers, other mentors? What data would be available to me through my mentors?
17
New cards
concept mapping
visual listing of ideas and grouping them to reveal relationships
18
New cards
question on Exposure, Disease, Population (EDP) structure
"Is [exposure] related to [disease/outcome] in [population]?"
19
New cards
exposure
personal characteristic (socioeconomic status), behaviour (smoking), environmental encounter (pollution), or intervention (treatment) that might change the likelihood of developing a health condition
20
New cards
disease/outcome
observed event such as the presence of disease in a participant in an observational study or the measured endpoint in an experimental study
21
New cards
Population
a group of individuals, communities, or organizations with identifiable similar characteristics
22
New cards
Population
A group of individuals, communities, or organizations with identifiable similar characteristics
23
New cards
Standard of Health Research
PICOT
24
New cards
what does PICOT stand for
P - patient, population group, and problem being studied
I - Intervention that will be tested?
C - control group, what will intervention be compared to
O - outcome of interest
T - Timeframe for follow-up?
I - Intervention that will be tested?
C - control group, what will intervention be compared to
O - outcome of interest
T - Timeframe for follow-up?
25
New cards
What makes a good research question?
real question, testable, generalizable, purposeful
26
New cards
4 key questions to refining study questions
1. What is the one well-defined research question that the study will answer?
2. What specific aims, objectives, or hypotheses will enable the key question to be answered?
3. Would a conceptual framework be helpful for guiding the design, analysis, and interpretation of the study and its results?
4. Is the proposed study feasible? Is there a high likelihood that the research team will be able to answer the study's main research question?
2. What specific aims, objectives, or hypotheses will enable the key question to be answered?
3. Would a conceptual framework be helpful for guiding the design, analysis, and interpretation of the study and its results?
4. Is the proposed study feasible? Is there a high likelihood that the research team will be able to answer the study's main research question?
27
New cards
study goal
single overarching objective of a research project or the main question that a research project seeks to answer
28
New cards
specific objectives
Carefully described action that will help the researcher make progress toward achieving the big-picture goal
- Most studies in the health sciences have two to four specific aims, with three the most typical number
- Most studies in the health sciences have two to four specific aims, with three the most typical number
29
New cards
sequential objectives
chronological list of actions that will achieve the main goal
30
New cards
independent objectives
related but independent objectives. When one objective is not achieved, it will not prevent successfully completion of the other objectives
31
New cards
SMART acronym
Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Timely
32
New cards
theoretical frameworks
a set of established models in the published literature that can inform the components and flows of the conceptual framework for a new research study
33
New cards
why use models in health research?
To organize our thoughts
To explore determinant/health relationships in a systematic manner
As a guide for analysis
To identify 'modifiable' factors for intervention
To explore determinant/health relationships in a systematic manner
As a guide for analysis
To identify 'modifiable' factors for intervention
34
New cards
Lalondes Model - A New Perspective on the Health of Canadians
considered to be first modern government doc in Western context to propose the health field look beyond the biomedical health care system.
Proposed health field = human biology + environment + lifestyle + health care organization
Proposed health field = human biology + environment + lifestyle + health care organization
35
New cards
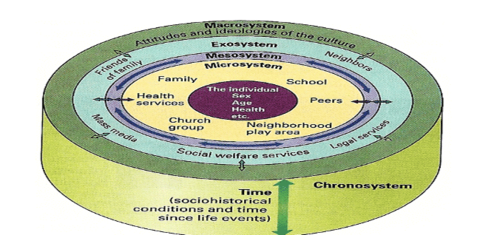
Eco-Social Model
consists of the microsystems, mesosystems, macrosystems, exosystems, chronosystems
36
New cards
conceptual model
a researcher sketches using boxes and arrows to illustrate the various relationships that will be evaluated during a study
37
New cards
translational research
bridges basic research and clinical research by applying scientific discoveries to the improvements of clinical outcomes
--> the aim of this research is to move research from the lab to clinical care settings - apply to real life
--> the aim of this research is to move research from the lab to clinical care settings - apply to real life
38
New cards
Public Health
actions taken to promote health and prevent illnesses, injuries, and early deaths at the population level
39
New cards
MeSH (Medical Subject Headings)
vocab thesaurus that can be used for searches of mediline and other health science databases
40
New cards
risk factor
an exposure that increases individual's likelihood of experiencing a particular disease
41
New cards
protective factors
exposure that reduces an individual's likelihood of subsequently experiencing a disease or outcome
42
New cards
nonmodifiable risk factors
risk factor for a disease that cannot be changed through health interventions
43
New cards
3 levels of preventive action
primary prevention, secondary prevention, tertiary prevention
44
New cards
primary prevention
encompasses health behaviours and other protective actions that help keep an adverse health event from occurring in people who do not already have the condition
Ex; nutritious diet, exercise, sleep, vaccinations
Ex; nutritious diet, exercise, sleep, vaccinations
45
New cards
secondary prevention
detection of health problems in asymptomatic individuals at an early stage when conditions have not yet caused significant damage to the body - can be treated more easily
Ex; cancer screening, blood pressure checks, audiovisual checks
Ex; cancer screening, blood pressure checks, audiovisual checks
46
New cards
Teriatary structure
interventions that reduce impairment, minimize pain and suffering, and prevent death in people with symptomatic health problems
Ex; medications, surgery, palliative care
Ex; medications, surgery, palliative care
47
New cards
Comorbidity
2 or more adverse health conditions at the same time
48
New cards
EDPs
exposures, diseases, and populations
49
New cards
Evidence based medicine (EBM)
uses results of rigorous research studies to optimize clinical decision making
50
New cards
Testability
ability of a research question to be answered using experiments or other types of measurements
--> good research question must be testable
--> good research question must be testable
51
New cards
purposiveness
states that research projects should be designed to answer one well-defined research question
52
New cards
Hypothesis
informed assumption about the likely outcome of a well-designed investigation that can be tested using scientific methods
53
New cards
conceptual framework
researcher sketches using boxed and arrows to illustrate the various relationships that will be evaluated
54
New cards
Health belief model
considers health behavior change to be a function of perceived susceptibility to an adverse health outcome
55
New cards
Feasibility study
an evaluation of the likelihood that a task can be completed with the time, money, tech, and other resources that are available
56
New cards
how is data in health research usually collected?
via sampling
57
New cards
target population
broad population to which the results of a study should be applicable
58
New cards
source population
subset of individuals from the target population from which the potential study participants will be sampled
59
New cards
sample population
individuals from a source population who are invited to participate in the research project
60
New cards
study population
compromises the eligible members of the sample population who consent to participate in the study an complete required study activities
61
New cards
probability sampling
Involves using selection techniques wherein the probability of selecting each sampling unit is known
62
New cards
simple random sampling
participants randomly selected, each person has an equal chance of being selected
63
New cards
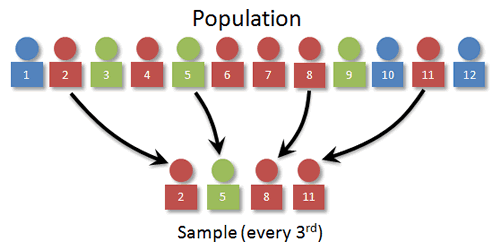
systematic sampling
after a random start point, every nth person is selected
64
New cards
stratified sampling
Random samples from distinct groups
- Geography (urban, rural, suburban)
- Sex (male, female, other)
- Geography (urban, rural, suburban)
- Sex (male, female, other)
65
New cards
cluster sampling
- Natural clusters (schools, neighbourhoods) rather than individual units are selected
- Observation are made on all units within a cluster
- Cluster sampling of schools
- All eligible children within each school included
- Observation are made on all units within a cluster
- Cluster sampling of schools
- All eligible children within each school included
66
New cards
multistage sampling
- Primary sampling units are selected (e.g. municipalities)
- Secondary units selected within primary units (e.g. individuals)
- May have more levels
- Secondary units: city blocks
- Tertiary units: individuals
- Secondary units selected within primary units (e.g. individuals)
- May have more levels
- Secondary units: city blocks
- Tertiary units: individuals
67
New cards
convience sample
Selection from a nonprobability-based source population due to ease of access to those individuals, schools, workplaces, organizations, or communities
68
New cards
purposive sampling
Recruitment of the participants for a qualitative study based on the special insights they can provide
69
New cards
selection bias
members of the study population are not representative of the source population from which they are drawn --> when healthier or educated people are more likely to volunteer for research
70
New cards
types of selection bias
exclusion, healthy worker, berksons
71
New cards
Berkson's bias
can occur when cases and controls for a study are recruited from hospitals and therefore are more likely than the general population to have comorbid conditions
72
New cards
Healthy Worker Bias
can occur when participants are recruited from term-72occupational populations and therefore are systematically healthier than the general population
73
New cards
Exculsion Bias
occurs when different eligibility criteria are applied to cases and controls, such as when controls with health conditions related to an exposure are excluded but cases with those comorbidities are not excluded
74
New cards
vulnerable populations
might have limited ability to make an autonomous decision about volunteering to participate in a research study
ex; young children, Some individuals with serious health issues, People in prison and some other socially marginalized populations
ex; young children, Some individuals with serious health issues, People in prison and some other socially marginalized populations
75
New cards
Type 1 error (false positive)
occurs when a study population yields a statistically-significant test result even though a significant difference or association does not actually exist in the source population
76
New cards
Type 2 error (false negative)
occurs when a statistical test of data from research finds no significant result even though a significant difference or association actually exists in the source population
77
New cards
interview
process of verbally asking a participant questions and recording that person's responses
78
New cards
self-administered survey
questionnaire form that participants complete by themselves, using either a paper-and-pencil version or online
79
New cards
Semi-structured interview
interviewer starts with a list of open-ended questions that will be asked of each participant, but these questions or lists of topics are merely starting points for eliciting responses from participants
80
New cards
probing
interviewing technique that prompts an interviewee to provide a more complete or specific response
81
New cards
Interview Pros and Cons
pros - can train interviewers to ensure the accuracy and completeness of each questionnaire
cons - may require major time commitments, expensive
cons - may require major time commitments, expensive
82
New cards
questionnaire pros and cons
Pros - cost- and time-efficient
Possibly of approaching a large number of participants
The best way to get honest answers to sensitive questions
Cons - Problematic for low literacy populations, and those who have limited Internet access or be unfamiliar with computers
Possibly of approaching a large number of participants
The best way to get honest answers to sensitive questions
Cons - Problematic for low literacy populations, and those who have limited Internet access or be unfamiliar with computers
83
New cards
interviewer bias
interviewers systematically question cases and controls or exposed and unexposed members of a study population differently, such as probing only individuals they believe to have the disease or exposure of interest for more information
84
New cards
uniformity
easiest to accomplish when all interviewers are provided with the tools they need to follow a standardized set of procedures
85
New cards
close-ended questions
allow a limited number of possible responses
- Date and time questions
- Numeric questions
- Categorical
- Date and time questions
- Numeric questions
- Categorical
86
New cards
open-ended questions
allow an unlimited number of possible responses
87
New cards
Practical Considerations
order of questions, getting the right answer, data recording methods, layout and formatting, back translation, pilot testing
88
New cards
Order of Questions
better to start with easy or at least general questions before moving to more difficult or sensitive questions
89
New cards
Getting the correct answer
mix up questions to prevent habituation and get accurate answers
90
New cards
Habituation
error that occurs when participants become so accustomed to giving a particular response (like "agree... agree... agree...") that they continue to reply with the same response even when that does not match their true perspectives
91
New cards
data recording method options
1. Record the responses on paper and to enter or scan them into a computer later
2. Have interviewers or participants enter responses directly into a database -->Eliminates the need for later data entry, Some populations are uncomfortable with computer technology
2. Have interviewers or participants enter responses directly into a database -->Eliminates the need for later data entry, Some populations are uncomfortable with computer technology
92
New cards
pilot testing
A small-scale preliminary study conducted to evaluate the feasibility of a full-scale research project
93
New cards
Key informants
individuals selected to participate in a qualitative study because they have the expertise relevant to the study question
94
New cards
Confidence interval
statistical estimate of the range of likely values of a parameter in a source population based on the value of that statistic in a study population
--> how 'good' an estimate is
--> Narrow CI indicates more certainty about the value of the statistic than a wide CI
--> how 'good' an estimate is
--> Narrow CI indicates more certainty about the value of the statistic than a wide CI
95
New cards
Power
ability of a test to detect significant difference in a population when differences do exist
- the power of statistical tests increases when a large number of participants are included
- the power of statistical tests increases when a large number of participants are included
96
New cards
Exposure measurement
available dose - Cumulative vs. current
administered dose - The amount that comes in contact
absorbed dose (uptake) - The amount that enters the body
Active dose (biologically effective) - That actually affects the specific target organ
administered dose - The amount that comes in contact
absorbed dose (uptake) - The amount that enters the body
Active dose (biologically effective) - That actually affects the specific target organ
97
New cards
ratio
Relationship between 2 numbers
Numerator NOT necessarily INCLUDED in the denominator
ex; (binary) sex ratio
Numerator NOT necessarily INCLUDED in the denominator
ex; (binary) sex ratio
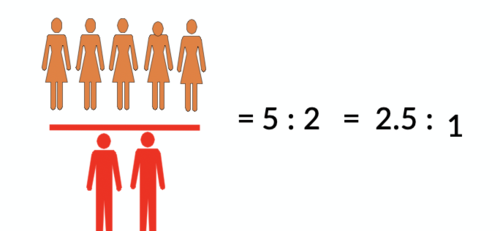
98
New cards
proportion
Relationship between 2 numbers
Numerator NECESSARILY INCLUDED in the denominator
Proportion always ranges between 0 and 1
Numerator NECESSARILY INCLUDED in the denominator
Proportion always ranges between 0 and 1
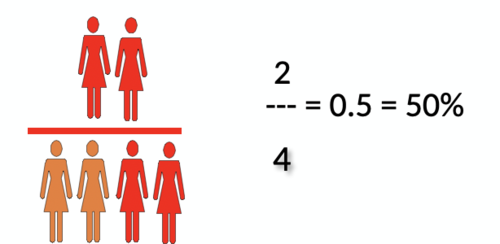
99
New cards
odd
the probability of an event occurring relative to it not occurring
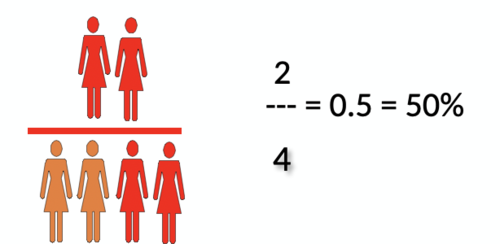
100
New cards
rate
speed of occurence overtime
numerator = # of events observed for a given time
denominator = population where events occur (population at risk)
numerator = # of events observed for a given time
denominator = population where events occur (population at risk)