Skeletal System (Definitions)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Support, Movement, Protection, Production of Blood Cells, and Maintenance of Electrolyte and Acid/Base Balance
functions of skeletal system
Bones
major organ of the skeletal system
Ligaments and Cartilages
Accessory Organs of the Skeletal System
80
The axial skeleton has ______ bones of the head, neck, and trunk
126
The appendicular skeleton has ______ bones of the arms and legs and the bones of the pectoral and pelvic girdle
Long Bones
classification of a bone that are longer than they are wide
Femur, Fibula, Tibia, Metatarsal, Phalanges, Humerus, Radius, Ulna, Metacarpal
example of long bones
Short Bones
classification of the bone that is cuboidal-like, length and width are equally proportional
Carpal and Tarsal
example of short bones
Flat Bones
classification of a bone that is almost sheet-like, not rounded and are thin
Skull, Sternum, and Ribs
examples of flat bones
Irregular Bones
classification of bones that are uniquely and irregularly shaped based on the function they serve
vertebrae column and pelvis
example of irregular bones
Sesamoid Bones
classification of bones that are embedded within a muscle formed in response to strain
Patella
example of sesamoid bone
FRONTAL BONE
anterior bone of the skull
PARIETAL BONE
makes up the sides and the roof of the skull
OCCIPITAL BONE
posterior portion of the skull; also the floor, with it at the base of the skull
TEMPORAL BONE
inferior to the parietal bones on the lateral side of the cranium; connected to the Temporomandibular Joint
Temporomandibular Joint
joint connecting the temporal bone and the mandible
Coronal Suture
suture that connects the frontal and parietal bones
Sagittal Suture
suture that connects the 2 parietal bones
Lambdoid Suture
suture that connects the occipital and parietal bones
Squamous Suture
suture that connects the temporal and parietal bones
Sphenoid Bone
forms part of the cranium floor, lateral posterior portions of the eye orbits, and lateral portions of the cranium anterior to the temporal bones
Sella turcica
Sphenoid bone contains ________________
Ethmoid Bone
anterior portion of the cranium, including the medial surface of the eye orbit and roof of the nasal cavity
Nasal Conchae
Ethmoid bone contains the ________________
External Auditory Meatus
ear canal; leads to the eardrum and middle ear; contains hammer, anvil, and stirrup
Malleus
hammer; transmits sound vibrations from the eardrum to the incus
Incus
anvil; passes sound vibrations from the malleus to the stapes
Stapes
stirrup; smallest bone in the body which transfers sound vibrations to the inner ear
Maxillae
forms the upper jaw, anterior portion of the hard palate, parts of the lateral walls of the nasal cavity and the floors of the eye orbits
Mandible
forms the lower jaw, the only movable skull bone
Lacrimal Bones
medial surfaces of the eye orbits
Zygomatic Bones
cheek bones; forms the floor and lateral walls of each eye orbit
Vomer
found at the midline of the nasal cavity; forms the septum with the ethmoid bone
Inferior Nasal Conchae
attached to the walls of the nasal cavity
Palatine Bones
forms the posterior portion of the hard palate and the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
The Spinal Cord
extends from skull to pelvis; flexible and sturdy longitudinal support for the trunk
24 movable vertebrae, Sacrum, Coccyx
what the spinal column contains
invertebral disks
shock absorbers
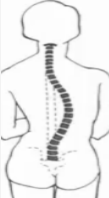
Scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature
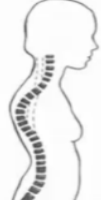
Kyphosis
hunchback; increase in the primary curvature
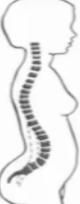
Lordosis
swayback; increase in the secondary curvature
Cervical Vertebra
has 7; supports the neck and possess a unique transverse foramen
Atlas
articulates occipital condyles of occipital bone and supports the head
Axis
possesses the odontoid process (dens) and serves as a pivot point for the atlas
Thoracic Vertebrae
larger vertebra with longer spinous process than the cervical vertebrae where ribs articulate on the facets of the transverse processes and bodies
Lumbar Vertebrae
have heavy and thick bodies to support greater stress and weight; has larger processes for attachment of back muscles
Sacrum
five fused sacral bones and forms the posterior wall of pelvic girdle
Coccyx
tailbone; 3-5 fused rudimentary vertebrae
Sternum
flat bone forming the anterior rib cage
Rib
12 pairs of bones attached to thoracic vertebrae
True Ribs
Ribs #1-#7 attached to sternum directly by coastal cartilages
False Ribs
ribs #8-#12 attach to coastal cartilage and small synovial joints of superior ribs
Floating Ribs
Ribs #11-#12 do not attach anteriorly, no coastal cartilages
Hyoid Bone
found in anterior portion of neck, inferior to mandible; does not articulate with any other bones; used as attachment site for tongue plans
2 clavicles and 2 scapulae
pectoral girdle is composed of:
Clavicle
articulate with sternum and scapula
Scapula
located on each side of vertebral column which is held in place by muscles to allow free shoulder movement
Humerus
arm bone that articulates with scapula (glenoid cavity) at shoulder joint and articulates with radius and ulna at elbow
Radius
lateral bone in the forearm which rotates when the hand is rotated; bony markings include the head and styloid process
Ulna
medial bone in forearm which does not move with hand rotation; bony markings include the olecranon, trochlear notch, and styloid process
Carpals
wrist bones
Metacarpals
bones of the palm of the hand
Phalanges
bones of the fingers
Pelvic Girdle
forms a rigid, bony pelvis, alongside the sacrum and coccyx (tailbone)
2 coxal (hip) bones
Pelvic Girdle is made up of:
Pubic Symphysis
where coxal bones are attached to one another
Ilium, Ischium, and Pubis
coxal (hip) bones that is made up of the fusion of 3 parts from the uppermost to the lowest
Female Pelvis
pelvis that is wider and more shallow, more rounded pelvic brim (oval), larger pelvic inlet/opening, and a curved pubic arch
Male Pelvis
pelvis that has a less rounded pelvic brim that has a smaller pelvic inlet/opening and has a sharp pubic arch
Femur
thigh bone that is the largest and strongest bone in the body — because it is responsible for handling all of the upper body weight
Patella
kneecap that is a sesamoid bone in the tendon that extends to the anterior knee
Tibia
shinbone; larger, medial bone of the lower leg and bears the body weight
Fibula
slender, lateral bone in the lower leg
Phalanges
J.
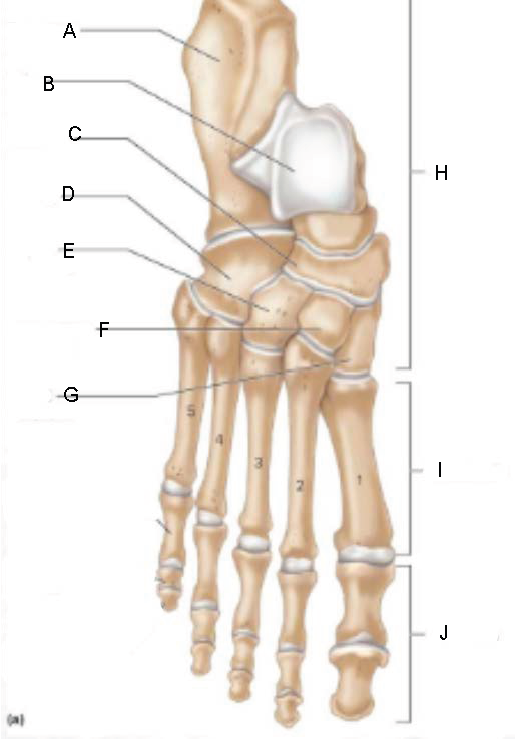
Tarsals
ankle bones
Metatarsals
bones of the instep
Phalanges
Toe bones
8
1
1
1
1
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Cranial Bones in total:
Frontal
Occipital
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Parietal
Temporal
14
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Facial Bones in total:
Vomer
Mandible
Maxilla
Palatine
Zygomatic
Nasal
Lacrimal
Inferior Nasal Conchae
6
2
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Middle Bones in total:
Malleus
Incus
Stapes
1
HOW MANY BONES?
Hyoid
24
7
12
5
HOW MANY BONES?
Vertebrae
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
4
1
1
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Pelvis
Sacrum
Coccyx
Pelvic Girdle
8
2
2
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Lower Limb
Femur
Patella
Tibia
Fibula
6
2
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Upper Limbs
Humerus
Ulna
Radius
4
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Shoulder Girdle
Scapula
Clavicle
25
1
24
HOW MANY BONES?
Thoracic
Sternum
Ribs
28
10
8
10
HOW MANY BONES?
Phalanges (Fingers)
Proximal
Intermediate
Distal
10
HOW MANY BONES?
Metacarpals
16
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Carpals
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetrum
Pisiform
Trapezium
Trapezoid
Capitate
Hamate
28
10
8
10
HOW MANY BONES?
Phalanges (Toes)
Proximal
Intermediate
Distal
10
HOW MANY BONES?
Metatarsals
14
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
HOW MANY BONES?
Tarsal
Talus
Calcaneus
Navicular
Medial Cuneiform
Intermediate Cuneiform
Lateral Cuneiform
Cuboid
206 bones
total bones in an adult body