CHEMISTRY HALOGENOALKANES
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Halogenoalkanes are much more reactive than...
Alkanes
Halogenoalkanes uses
To make PVC, Teflon and some anaesthetics
As solvents
In pharmaceuticals
Halogenoalkane bond polarity
In halogenoalkanes, the C-X bond is polar as the halogen atoms are more electronegative than the carbon atoms
Primary halogenoalkanes
Halogen bonded to a carbon atom which has 1 carbon atom bonded to it
Secondary halogenoalkanes
Halogen bonded to a carbon which has two carbons bonded to it
Tertiary halogenoalkanes
Halogen bonded to a carbon which has three carbons bonded to it
As you go down group 7, the polarity of the bond will decrease as...
The halogens become less electronegative as you go down the group
Halogenoalkanes solubility in water
The halogenoalkanes are not very soluble in water. In order for a halogenoalkane to dissolve in water you have to break attractions between the halogenoalkane molecules and the hydrogen bonds between water molecules. The energetics of the change are sufficiently unprofitable that very little dissolves.
As the chain length of halogenoalkanes increases, so does the...
Boiling point as the van der Waals are stronger due to there being more electrons
As you go down group 7, the boiling points of halogenoalkanes...
Decreases as the dipole-dipole interactions are weaker due to the atoms being less electronegative
As you go down group 7, the C-X bond enthalpy...
Decreases as the shared electrons are less attracted to the nucleus
As you go down group 7, the reactivity of the halogenoalkanes...
Increases as its easier to break the C-X bond
Ozone (O3)
2O3 ⇌ 3O2
Ozone is a gas present in the upper atmosphere. It absorbs UV light but is reformed in a reversible reaction:
Depletion of the ozone layer causes...
Increased risk of sunburn, skin cancer and cataracts
An increased rate of global warming
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Organic molecules containing chlorine, fluorine and carbon
CFCs uses
Short chain - Aerosol propellants, refrigerants, blowing agents for expanded polystyrene
Long chain - Dry cleaning and de-greasing agents
CFCs properties
Inert
Low boiling point
Insoluble in water
Non-toxic
Non-flammable
In the atmosphere, CFCs decompose to give...
Chlorine free radicals which decompose ozone, causing a hole in the ozone layer. They were banned and replaced by safer compounds such as HCFCs (hydrochlorofluorocarbons) and chlorine-free compounds. As they are inert, a large number of CFCs still remain in the atmosphere and it will take many years for the ozone layer to recover.
CFCs decomposing ozone steps
UV light causes the CFC to break apart homolytically to form a chlorine free radical, which acts as a catalyst
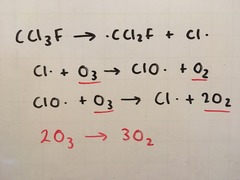
Nucleophiles
Electron pair donors. Contain a lone pair and either a negatively charged ion or a atom with a δ- charge. Donates a lone pair of electrons to an electron deficient atom to form a covalent bond. Shown with a negative charge and a lone pair
Common nucleophiles
OH-
NH3
CN-
Nucleophilic substitution
When a nucleophile attacks a halogenoalkane and replaces a leaving group (a halogen atom)
Hydrolysis
Splitting a molecule apart by reacting it with water
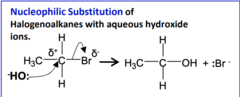
Nucleophilic substitution to form alcohols
A hydrolysis reaction which uses the nucleophile :OH-. The halogenoalkane reacts with warm dilute aqueous NaOH or KOH (< 170°C). Ethanol is used as a solvent to ensure the halogenoalkane and NaOH or KOH mix. It is done with heat under reflex
Halogenoalkane → alcohol equation
R-X + NaOH → R-OH + NaX
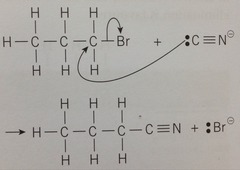
Nucleophilic substitution to form nitriles
Uses the nucleophile :CN-. The halogenoalkane reacts with an aqueous solution of potassium cyanide (KCN). Done with heat under reflux. Adds an extra carbon to the chain so if useful if you need to make a product with one more carbon than the starting material
Halogenoalkane → nitrile equation
R-X + KCN → R-CN + KX
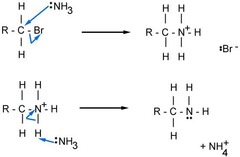
Nucleophilic substitution to form amines
Uses the nucleophile :NH3. The halogenoalkane reacts with excess concentrated solution of ammonia in ethanol. Carried out under pressure
Halogenoalkane → amine equation
R-X + 2NH3 → R-NH2 + NH4X
As you go down group 7, the rate of substitution of halogenoalkanes...
Increases as the bond enthalpy of the C-X bond decreases, so the bonds break more easily
Nucleophilic substitution is most likely to occur for...
Primary halogenoalkanes
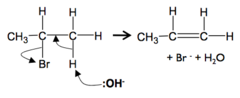
Elimination to form alkenes
The mechanism and type of reaction is elimination. The :OH- ion act as a base as it accepts a proton. The reaction occurs with hot concentrated ethanolic NaOH or KOH without water present (> 170°C). Heat under reflux is required
Halogenoalkanes → alkenes process
The :OH- ion attacks the H on the C next to the C-X. Hydrogen is removed as a H+ ion, so joins with the OH- ion to make water
Halogenoalkanes → alkenes equation
H-C-C-X + KOH → C=C + KX + H2O
Elimination is most likely to occur for...
Tertiary halogenoalkanes
Elimination can produce...
Position isomers
There is competition between...
Substitution and elimination. In general, we produce a mixture of an alcohol and alkene