Cognition Midterm Exam
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
what are the three components of communication?
1) input (vision/hearing/kinesthetics (body lang)/ proprioception)
2) processing (in brain)
3) output (oro-facial structures, extremities, speech)
how is attention referred to?
in relation to a stimulus
what is the difference between external and internal attention?
external; from the enviro (auditory stim/ light in room)
internal; from inside self (pain/ hunger/ stress)
what are the two important features of attention?
1) capacity limitation (only so many things we can tend to at once)
2) selection of relevant stimuli (irrelevant is ignored)
what type of attention does paced serial addition tasks measure?
sustained attention (1 task without distraction)
what type of attention does the stroop task measure?
selective attention (select only one stimuli while filtering out the other- only looking at the color/ word)
what type of attention does the walk and turn task measure?
divided/ alternating attention (2+ tasks at once/ shift between them- walking and counting and turning around)
which area of the brain is primarily responsible for sustained attention?
bilateral superior temporal gyrus
which area of the brain is primarily responsible for attention allocation?
right inferior frontal gyrus
which area of the brain is primarily responsible for selective attention and attention control?
superior and medial frontal gyrus
how would attention be impacted in RHD? TBI? Dementia? Aphasia?
1) RHD- usually impaired
2) TBI- usually impaired, may have neglect
3) dementia- usually impaired in later stages (except in early stages with lewey body)
4) aphasia- impaired sustained, difficulty allocating
what is memory?
any retention of information beyond the life of the external stimulus
what is immediate memory (aka sensory memory)?
shortest form of memory- highly tied to sensory input (about 1/3- 2 seconds)
what is short term/ working memory?
temporarily store, manipulate, work with information from the immediate memory (20-30 seconds)
how many items can most people actively store in working memory?
7 items (+/- 2 -> between 5-9 items)
what type of information is stored in the articulatory/ phonological loop in working memory?
processing linguistic and acoustic information
what type of information is stored in the visuospatial sketchpad in working memory?
visual, spatial, tactile, kinesthetic signals
what are the three steps for memory formation? (LTM)
1) encoding (strategies: repeat/ rehearsal/ meaningful organization)
2) consolidation (forming the neural network)
3) storage (retain info for future use- more retrieval = stronger memory)
what type of memory does the face recognition test measure?
LTM because of repetition (lots of faces were repeated -> consolidation)
what are the two main types of long term memory (LTM)?
1) declarative/ explicit (semantic/ episodic/ lexical)
2) non-declarative/ implicit (motor/ cognitive skills)
what are the three types of declarative memory?
1) semantic (words and their related concepts)
2) episodic (events and experiences)
3) lexical (words and vocabulary)
what are the two types of non-declarative memory?
1) motor skills memory (performance- walking/biking)
2) cognitive skills memory (win a game/ problem solve)
what is the main brain area for memory?
hippocampus, frontal/temporal/parietal lobe
what are some subcortical areas in the brain for memory?
hippocampus, amygdala, basal ganglia
what are some executive functions?
initiation, problem solving, planning, mental flexibility, judgement, inhibition, reasoning, self-regulation, metacognition
what is the definition of executive functioning?
cognitive functions at a higher-level and more goal directed
how does resource allocation in executive functioning change after a brain injury?
more resources are needed for automatic tasks -> previously simple tasks become more challenging and take longer
which areas of the brain are important for executive functioning?
DORSOLATERAL prefrontal cortex and frontal lobe
what is right hemisphere disorder (RHD)?
group of deficits and changes following insult to the right hemisphere of the brain (in note: cognitive communication disorder 2/2...)
what are the main cognitive behaviors of RHD (6)?
1) neglect
2) anosognosia & prosopagnosia
3) topographical disorientation
4) constructural impairments
5) emotion difficulty
6) fundamental cognitive processes changes
what are the main communicative behaviors of RHD (4)?
1) aprosodia (flat contour/ monotone/ understand emotions)
2) pragmatic difficulty (non-literal interpretation, inferencing)
3) discourse changes (both comprehension and production)
4) conversation difficulties (theory of mind)
what are the neglect types?
personal (of own body -> somatophrenia- inability to perceive own body), peri-personal (within reach), extra-personal (beyond arms reach)
what are the errors seen in neglect?
1) egocentric (viewer centered- miss entire L side)
2) allocentric (object centered- miss L side of object)
3) combination (miss L side object and L side of page)
what is the main difference between neglect and hemianopia?
neglect: unaware, impaired attention
hemianopia: aware, sensory impairment
what is anosognosia?
lack of knowledge/denial of deficits- may deny need for tx
what is prosopagnosia?
inability to recognize faces in the absence of other visual agnosias (face blindness) -> also can impact perception of emotion on face!
what is amusia? how is it impacted in RHD?
impaired recognition, production, reproduction of melodies and pitch
-> in RHD: difficulty recognizing music without lyrics (pitch= bad but language perception = good)
what is topographical disorientation?
confusion about location in space -> difficulty describing how to travel from one place to another (or immediate enviro)
what are constructural impairments?
difficulty assembling components to form objects/ drawings -> spatial relation deficits in RHD -> whole picture distortion
how are emotions impacted in RHD?
difficulty recognizing/ using facial expressions/ poor emotional language or hypoarousal
what are the main cognitive processes that can be impacted in RHD?
orientation/arousal, attention, memory, EF (OAME)
what are some screeners used for RHD?
MoCA, MMSE, SLUMS, CLQT, RBANS
what is the main battery for RHD assessment?
Right Hemisphere Language Battery (RHLB)
what assessments aim at neglect and attention in RHD?
Test of Everyday Attention (TEA) & the Functional Assessment of Verbal Reasoning & Executive Strategies (FAVRES) and use an awareness questionnaire to supplement
what battery aims at prosody in RHD?
Florida Affect Battery (FAB)- look at facial, vocal, cross-modal stimulation and methods
what is Global Coherence in RHD?
the listener's perception of the speakers ability to maintain a unified theme in discourse (analyze C-Unites in utterances)
what are the main treatment approaches for attention and neglect in RHD?
1) visual scanning training
2) lighthouse strategy
3) object centered neglect tx (different size stimuli)
what are the main treatment approaches to target aprosodia in RHD?
1) cognitive affective tx (6 step hierarchy to match facial expression/ description/ definition)
2) motoric-imitative tx (unison, repeat, reading, cued)
what are some etiologies of traumatic acquired brain injuries?
falls, assaults, car accidents, sports injuries, gunshot wounds, abuse/ domestic violence, shaken baby syndrome, military/blast injury
what are some etiologies of non-traumatic acquired brain injuries?
CVA, meningitis/ infection, electric shock, tumors, reduced oxygen to brain, drug OD, neurotoxic poison, metabolic disorders
what are the main types of TBI?
1) contact TBI (open or closed head injury)
2) non-contact TBI (brain moves within skill)
what is the difference between open and closed head brain injuries?
OPEN: ruptures the meninges (focal and diffuse)
CLOSED: non-penetrating the meninges (mostly focal)
what is the coup and countrecoup of contact TBIs?
COUP: localized damage, the point of contact
COUNTRECOUP: 2nd injury, where the brain hits the opposite side
what are the three injuries that can occur during a blast?
PRIMARY: blast wave
SECONDARY: from the objects propelled by the blast
TERTIARY: person landing on solid object/ ground
what is a diffuse axonal injury (DAI)?
extensive damage in the white matter tracts d/t twisting or shearing forces on the neurons
what is the difference between a coma and a vegetative state?
COMA: no signs of awareness and no sleep/wake cycle
VEG STATE: some sleep-wake, return of reflexes, spontaneous eye opening (persistent- 1+ month, permanent- 1+ year)
what are the criterion for a mild TBI (mTBI)?
loss of consciousness is less than 30 mins, GCS= 13-15, PTA= less than 24 hours
what is chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)?
condition where hyperphosphorylated tau proteins build up in the brain (similar to Alzheimer's disease) -> progressive degeneration of neuro function
what is the difference between retrograde and anterograde amnesia?
RETRO: can't remember events before injury (episodic info)
ANTERO: can't remember events after injury (new info)
review the Glasgow Coma Scale!
severe TBI: 3-8
moderate TBI: 9-12
mild TBI: 13-15
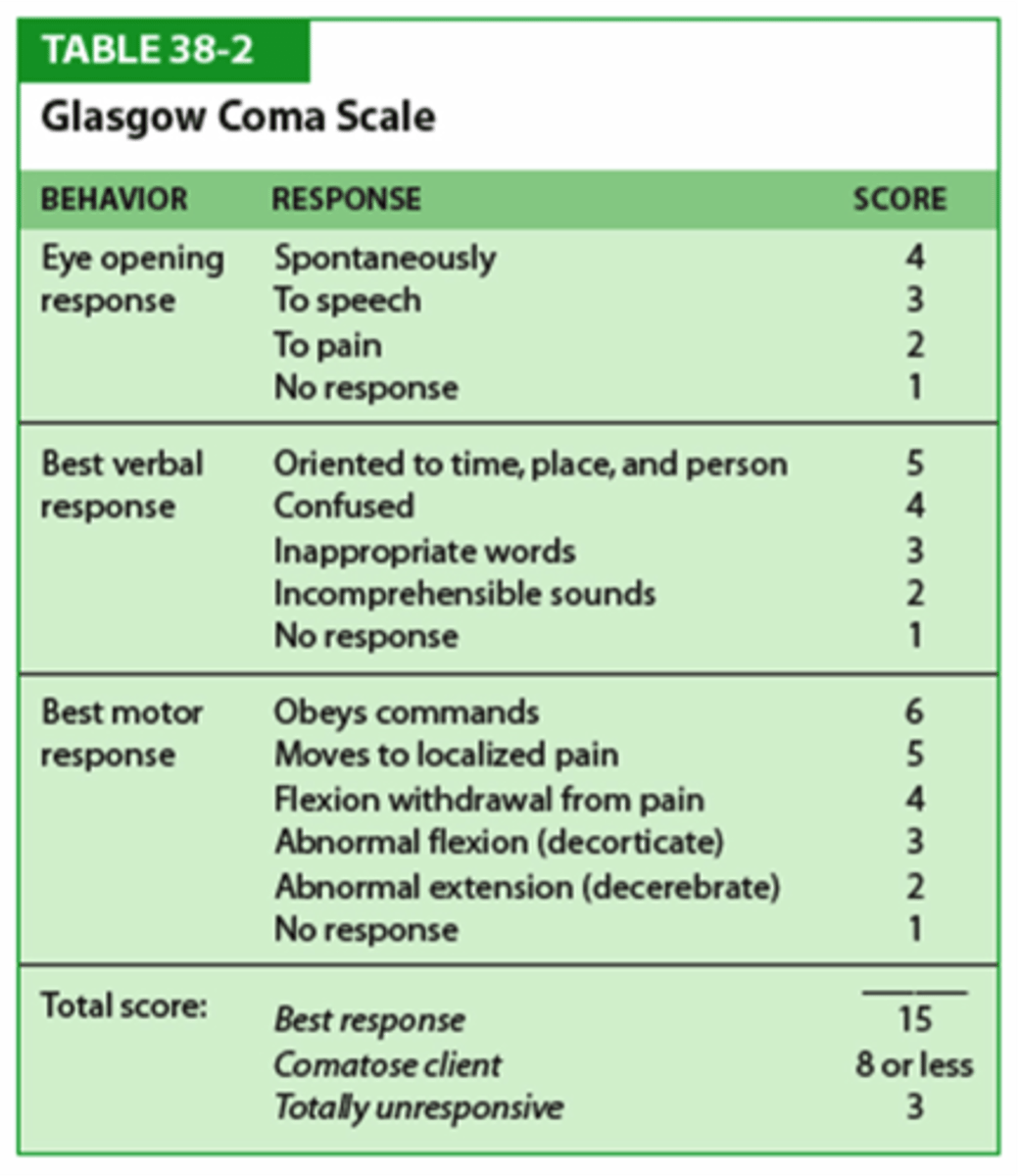
how is post-traumatic amnesia (PTA) measured?
the GOAT! (Galveston Orientation & Amnesia Test)
what are the time frames for PTA for TBI severities?
severe TBI: more than 24 hours
mild TBI: less than or equal to 24 hours
review the Ranchos Los Amigos Levels of Cognitive Function!
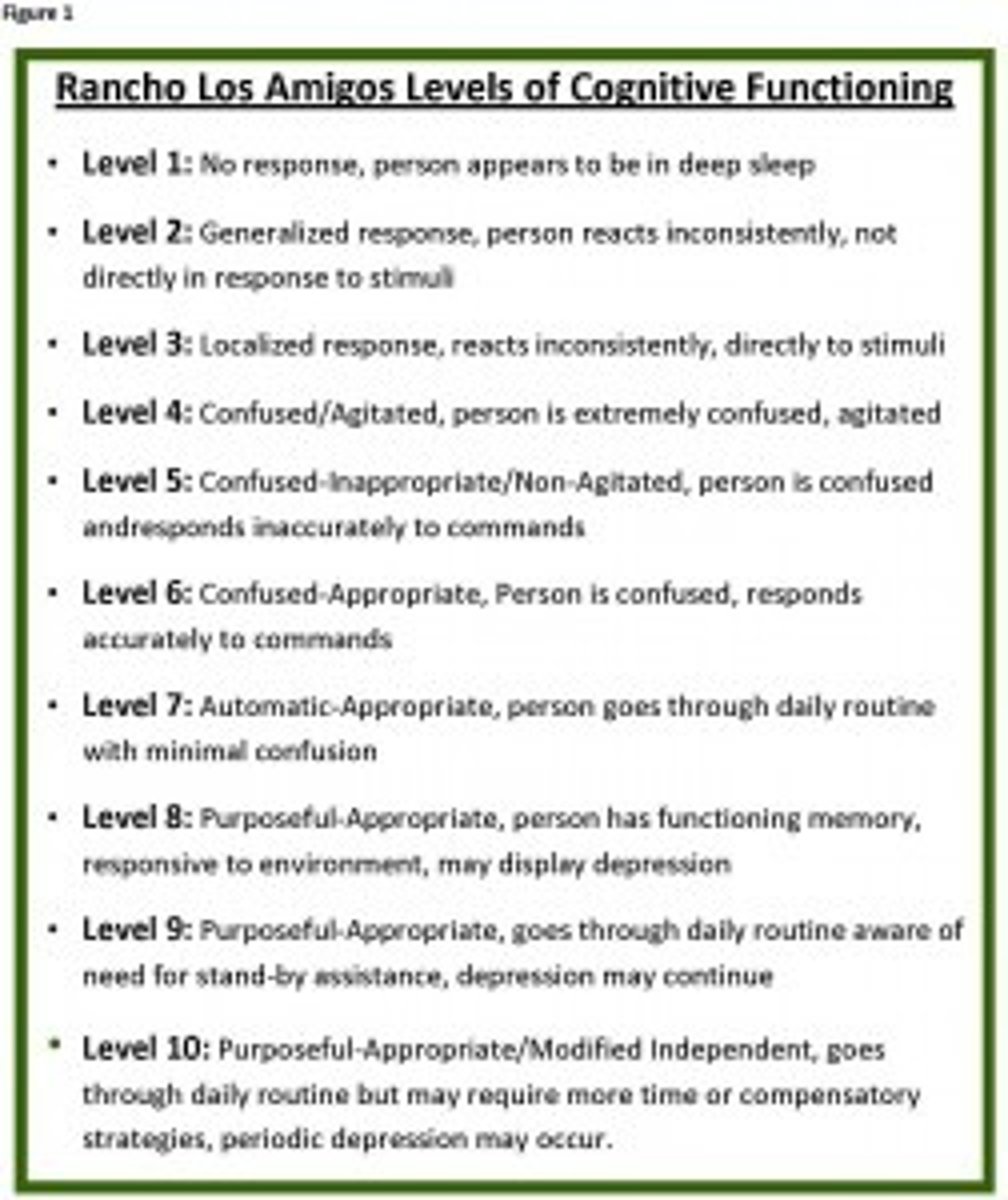
what level on Ranchos do patients need to be at for an SLP eval?
Ranchos= at least a VI (confused but appropriate)
what is a good assessment for memory in TBI?
Rivermeade Behavioral Memory Test (RBMT)
what is controlling sensory stimulation for TBI patient treatment?
to maximize the awareness/ arousal of surroundings in a person with impaired consciousness -> manipulate rate, amount, duration, complexity of stimuli
how do AAC needs change as patients progress through the Rancho levels?
I-III: early AAC, simple y/n, eye gaze
IV-VI: mid AAC, complex choices, voice outputs
VII-X: late AAC, ABC board, text to speech, stored messages
what are the main treatment approaches to target attention in TBI?
direct attention training, metacognitive strategies
what are the main treatment approaches for memory in TBI?
external memory aids, internalized memory strategies, spaced retrieval techniques
what are the main treatment approaches for EF in TBI?
metacognitive strategies, training strategic thinking, multitasking instruction, functional every day approaches!
what is the main treatment approach for social communication in TBI?
supported behavioral self-regulation -> great to do pragmatics in groups!
how does healthy aging change cognition?
language, sustained attention, divided attention (simple tasks), LTM, and procedural memory = INTACT!
-> STM reduced
-> slight reduction in word finding and divided attention on complex tasks
what is the key difference between MCI and dementia?
in MCI- ADLs are not affected, in dementia- ADLs are impacted!
what is a mild cognitive impairment (MCI)?
changes in cognition that are significant enough not to be normal aging, but not severe enough to affect ADLs
what are the three criteria for MCI?
1) self report of memory issues & family or caregiver agree
2) memory impairment scored on a standardized test
3) no impairment of reasoning/ thinking skills/ ADLs
what are the two main types of MCI?
amnesic (memory is impacted) & non-amnestic (memory intact)
what is the most common subtype of MCI?
amnestic single domain (only memory impairment)
what is dementia?
an umbrella term for a collection of symptoms caused by different disorders affecting the brain -> a chronic persistent cognitive disorder
what is Alzheimer's disease?
the most common form of dementia! caused by a beta-amyloid plaques (protein deposits in brain) and neurofibrillary tangles (tau protein build up in neurons) + degeneration of cortex and widening of ventricles
what are the modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer's disease?
MOD: diet, exercise, cognitive/ social engagement, heart health and reducing risk of TBI
NON-MOD: age, family hx, genetics
what characterizes the early, middle, and late stages of Alzheimer's?
EARLY: reduced episodic & WM, reduced attention and EF, reduced w-finding and discourse
MID: reduced ADLs, wanderlust, sundowner syndrome
LATE: reduced motor fx, profound cog and comm deficits, require 24 hour care
what is vascular dementia?
2nd most common dementia type! due to a cerebrovascular or cardiovascular disease or circulatory disturbance that damages areas in the brain for memory or cognition
what is the diagnostic criterion for vascular dementia?
evidence of cardio/vascular condition, cerebrovascular disease tied to onset of symptoms, focal neuro s/s, brain imaging w signs of lesions
what are the primary symptoms of vascular dementia?
confusion, episodic memory impairment, reduced processing, wandering, rapid shuffling gait, difficulty following instructions & sudden onset related to vascular event
what is frontotemporal dementia (FTD)?
a group of rare neurodegenerative disorders c/b behavior, personality and/or language changes
what are the three main subtypes of FTD?
behavioral (bvFTD), language (PPA), motor (mvPPA)
what is primary progressive aphasia (PPA)?
a subtype of FTD where episodic memory is largely preserved, however language impairment is the most negatively impacting ADLs
what are the three subtypes of PPA?
semantic (svPPA), logopenic (lvPPA), and non-fluent (nfvPPA)
what are the hallmark symptoms of semantic PPA (svPPA)?
PRIMARY: picture naming, single-W comprehension deficits
PLUS 3: reduced obj knowledge, surface dsylexia/ dysgraphia, ok repetition, ok grammar, ok motor speech
what are the hallmark symptoms of logopenic PPA (lvPPA)?
PRIMARY: single W retrieval in picture naming, phrase/sent repetition difficulty
PLUS 3: phonemic paraphasias, ok comprehension, ok obj knowledge, ok motor speech, ok syntactic processing
what are the hallmark symptoms of nonfluent PPA (nfvPPA)?
PRIMARY: agrammaticism, apraxia of speech
PLUS 2: reduced syntactic comprehension, ok comprehension of single Ws, ok obj knowledge
what are the hallmark symptoms of the behavioral variant of FTD?
personality changes, apathy, reduced social/ judgment/ self control, reduced awareness of impacts, cognitive deficits are less dramatic than behavioral deficits
what diagnosis commonly co-occurs with bvFTD?
ALS
what are the two subtypes of the motor variant of FTD?
corticobasal degeneration & progressive supranuclear palsy
what are Lewey bodies?
abnormal clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein (accumulate in the F+T lobes, cingulate, insula, SN, amygdala
what are the 4 comprehensive assessments for dementia?
CLQT, RBANS, Dementia Rating Scale (DRS-2), Arizona Battery for Cognitive-Communication Disorders (ABCD-2)
what are additional evaluations for memory and processing?
memory- complex figure drawing and recall
processing- emotional eval subtest of aware of social interference test
what is the standardized assessment for PPA?
Sydney Language Battery (may have to substitute items for more "American" versions)
what is the RAISE framework for person-centered assessment?
R- relationship (useful), A- assessment (dynamic), I- inclusion (complexity), S- support (reveal competency), E- evolve (adapt approach)
what is the difference between direct and indirect interventions?
DIRECT: patient participates themselves
INDIRECT: training to caregivers/ modify enviro/ activities with others