Ch 17 - Demand Management (demand-side policies)
Fiscal policy: involves the government changing the levels of taxations and government spending in order to influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity
- AD is the total level of planned expenditure in an economy
Purpose of Fiscal policy:
- Stimulate economic growth during a period of recession
- Keep inflation low
- Stabilise economic growth
- Often simultaneously used monetary policy
- Governments prefer using monetary policy to stabilise the economy
- Fiscal policy depends on size of multiplier
Expansionary fiscal policy:
- Involves increasing AD
- Government will increase spending and cut taxes
- Lower taxes increase government spending → more disposable income
- Will worsen the government budget, governments will need to increase borrowing
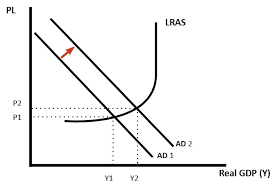
Deflationary Fiscal policy:
- Decreasing AD
- Governments will cut government spending and increase taxes
- Higher taxes → reduce consumer spending
- Improves government budget deficit
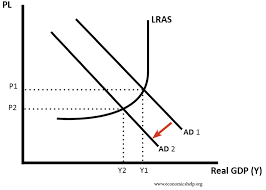
Fine tuning: maintaining a steady rate of economic growth using fiscal policy
- If growth is below the trend rate of growth, governments cut taxes to boost spending and economic growth → tax increases, consumption decreases
- If growth is too fast + inflationary, governments increase tax to decrease/slow down consumer spending and reduce economic growth
Limitations of fine tuning:
- Time lags: government spending takes several to integrate in the economy
- Political costs: increasing taxes imposes problems on consumers
- Difficulty forecasting: predicting the state of the economy requires the government to have plenty of info on the likeliness of growth
Demand Management policies: efforts to influence the level of aggregate demand (AD) in an economy. Main types: monetary and fiscal policy
- Consumer confidence is an indirect factor since it helps encourage investments and encourage consumers to spend
Monetary policy: involves cutting or raising interest rates
- Lower interest rates make it cheaper to borrow leading a boost in consumer spending and investment
- Lower interest rates reduce the value of the exchange rate (making exports more competitive and boosting export demand)
- Set by banks
- Independent in selling rates but have to meet the government inflation target
- Cutting interest rates may fail to boost spending, some banks could be unwilling to offer loans which makes lowering interest rates ineffective
Quantitative easing: when banks buy bonds to lower the interest rates on savings and loans
- Reduces long term interest rates and boosts the money supply
Aim of monetary policy:
- Low inflation: enables higher investments in the long term
- Stable economic growth maintains a sustainable rate of economic growth +keeps unemployment low
Based on the trends of the banks, they can choose:
- Higher inflation + higher growth → increase interest rates
- Lower growth + decrease in inflation rates → lower interest rates
Expansionary monetary policy: expands monetary supply faster than usual or lowering short term interest rates
- If central bank predicts inflation rates dropping below the government’s target, they will cut interest rates
- Lower interest rates stimulate economic activity
- Lower interest rates reduce borrowing costs
- Increases disposable income of consumers
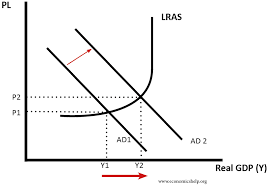
Contractionary monetary policy:
- Central bank increases interest rates to reduce rate of economic growth and reduce inflationary pressure
- Increase in interest rates causes fall in consumer spending and investment leading to lower inflation
Cost push inflation: occurs when the economy experiences rising prices due to higher costs of production and higher costs of raw material
Demand pull inflation: occurs when aggregate demand grows faster than aggregate supply