Databases
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made from Ada comp. sci. and PMT comp. sci. notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What is a data base?
An organised collection of data, possibly containing different types of information (e.g. students, lessons, teachers etc.)
What is a flat file data base?
A data base in which all the required data is stored in a single table
Benefits of databases
They improve the integrity of data…
…reducing the amount of unnecessarily duplicated data…
…making it quicker and easier to keep data up to date
Allows data to be combined in different ways to produce useful information
What is DBMS the abreviation of?
Abreviation of database management system
What is a database management system?
A software application that allows a database administrator to maintain one or more relational databases
Typical features of a database management system
Provides a graphical user interface that allows the user to:
modify the database structure
create indexes
optimise the database
browse data
What are database applications?
Software programs designed to retrieve, manage, distribute, and present information from a database effectively
What is a table?
A collection of related data that represents a group of entities of the same type (e.g. students)
What is an entity?
An item/object of interest about which information is stored
Non-prime attribute
An attribute that is not the primary key / not part of a composite primary key
Candidate key
Any set of one or more fields that uniquely identifies each record in the table. As such it could be used as a primary key.
Primary key
The (set of) field(s) that uniquely identifies each record in the table. Each table can only have one primary key.
Composite key
A combination of 2 or more fields that uniqualy identifies each record in a table
Foreign key
An attribute in a table that appears as the primary key in another table.
It links two tables together
What is the difference between a primary key and a foreign key?
A primary key will only appear once in a table/is a unique identifier
A foreign key may appear multiple times a table/may not be unique
Secondary key
A field that allows a database to be searched quickly
Isn’t necessarily unique
What is an attribute?
A characteristic of an entity and is a column in a table
What are the three main category of relationships?
One-to-one
One-to-many
Many-to-many
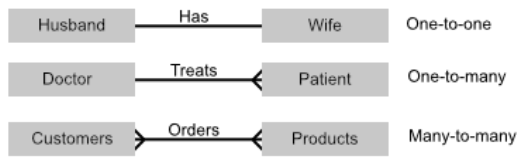
One-to-one relationship
When one instance of an entity is linked to only one instance of another entity
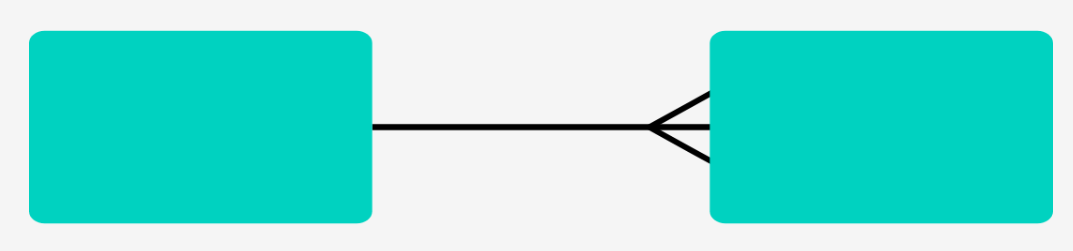
One-to-many relationship
When one instance of an entity is linked with multiple instances of another entity.
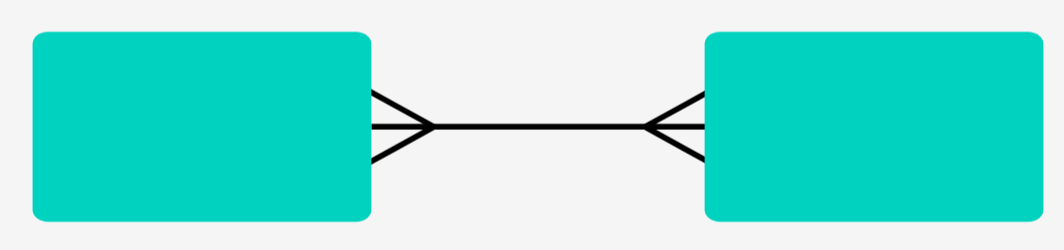
Many-to-many relationship
When multiple instances of an entity are linked with multiple instances of another entity. Not allowed in 3NF
What is ER diagram the abreviation of?
Abreviation of entity-relationship diagram
Entity-relationship diagrams
Entities are represented as boxes
Relationships are represented by lines, which show how many of one entity can be linked to another entity:
Straight line at one end means one
Splayed line (crows foot) means many
Relationship can by labelled
one-to-one ER diagram

one-to-many ER diagram
many-to-many ER diagram
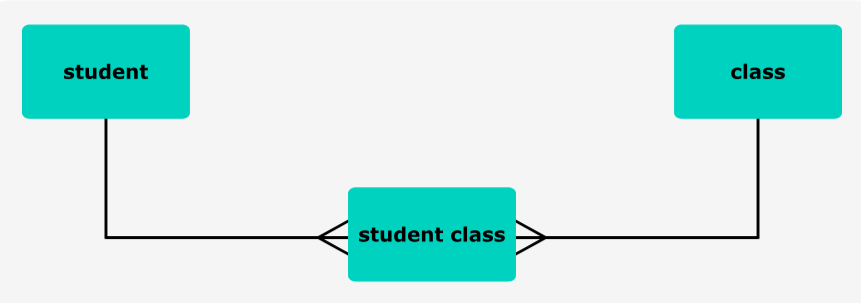
Pupose of a link/junction table
Allows many-to-many relationships to be implemented in a relational database by breaking this relationship into a one-to-many relationship between each of the two entities and the link table.
First normal form (1NF)
A database in which:
All cells are atomic (contains one value)
Has a pimary key - every record is uniquely identified
Each field only holds 1 type of information
No Repeating fields/data
Second normal form (2NF)
Database that is in the 1NF
Database that has no partial dependencies - every field is dependent on the entirety of the primary key.
Partial dependancy
When the value of a non-primary attribute is dependant on only part of a composite primary key
Third normal form (3NF)
Database that is in the 2NF
Database has no transitive dependencies / no non-key dependencies
Transitive / Non-key dependency
When a non-primary attribute depends on another attribute that is also not the primary key or part of the composite primary key
Functional dependency
When the value of one attribute depends on the value of another attribute
What does normalisation aim to achieve?
Aims to minimise redundancy (unnecessary duplicates).
Consistent data throughout linked tables.
Allow records to be added and removed without issues.
Allow complex queries to be carried out
What is normalisation?
The process of coming up with the best possible layout for a relational database
What is data consistency?
When a database transaction can only change data in acceptable ways - ways that follow a pre-defined set of rules
Ensures data is ___
What is data redundancy?
When the same piece of data is stored in more than one table in a database. This can either be by accident or by design
It can lead to inconsistencies in the data and/or wasted storage space
What is data integrity?
The reliability of data in terms of its accuracy, completeness, and consistency
What is a database transaction?
A single logical unit of work performed on a database. Can be made up of multiple steps.
An example is transferring money from a current bank account to a svaings account.
Serialisation
Making sure that when two or more transactions are executed concurrently, the effect is the same as if they had been executed serially (in order, one after the other)
Record locking
Preventing simultaneous access to records in a database.
It prevents data inconsistencies or a loss of updates.
How can record locking be used to achieve isolation when carrying out multiple transactions?
The outcome of concurrent transactions is the same as if transactions were completed sequentially.
Record locking allows one process to access/modify a record at any one time
So data that is being used elsewhere cannot be modified (or data that is being modified elsewhere cannot be used)
What are the disadvantages of record locking?
Can cause delays (as users/processes wait for access)
Can cause deadlock
ACID test
Set of properties of database transactions that will guarantee the integrity of data:
Atomicity - components of a transaction are atomic, i.e. indivisible. The whole transaction must succeed or fail.
Consistency - ensures that an illegal transaction (e.g. one that breaks referential integrity) is rejected so that the integrity of the database is upheld.
Isolation - ensures that each transaction will be isolated and dealt with in a way that does not affect others.
Durability - ensures that data is saved once a transaction has been completed. Even if there is a hardware failure immediately after a transaction, the data will be safe.
What is a durable transaction?
When completed transactions are not lost in case of power failure or system failure
How can durability be achieved for a completed transaction?
Storing completed transactions in secondary storage
What is indexing?
Method used to store the position of each record ordered by a certain attribute (normally a secondary key). This is used to look up and access data quickly.
Relational database
Two or more tables linked using key fields
A different table is used for each entity
Describe the differences between a flat file and a relational database.
Flat file databases:
May have redundant data
Flat file harder to update
No specialist knowledge needed to operate
Relational databases:
Consist of linked tables
Make it easier to change the format of the database
Provide security features
Data Integrity
What is capturing data?
The process of getting the information that will be stored in the database.
What method do banks use to capture data from cheques?
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) is used for all of the details apart from the amount which must be entered manually.
Selecting data
The process of removing excess information to extract only the data you require.
Managing data
Manipulating the information collected in any type of way, such as sorting through it or selecting certain parts using SQL
What is the most common language used to manipulate data in databases?
SQL
What is SQL an abreviation for
Abreviation of Structured Query Language
Structured Query Language (SQL)
A declarative language used to manipulate databases.
It enables creating, removing and updating databases
Record
One entry (row) of a table
It holds all the related fields/information about that one entry (e.g. information about a student)
Field
One item of data in a record
A particular piece of information about the entry (e.g. date of birth of a student)
What is meant by the term referential integrity?
Database/relationships are consistent - each foreign key links to a valid primary key
What is an example of how referential integrity can be broken?
If the primary key is deleted/updated, foreign keys (in other tables that link to this one) become invalid. As such referential integrity is lost.
Is SQL case sensitive?
SQL is not case sensitive
What case are SQL keywords written in, and why?
SQL keywords are written in upercase
This helps with readability
What do SQL statments always end with?
___ statements are terminated with a semicolon
5 SQL data types you need to know
Text
Date fields
Time fields
Numeric fields
Boolean fields
Format of text in SQL
A string value contained in single quotation marks
Example: ‘Some random text’
Format of date field in SQL
Contained in single quotation marks and usually written in the form ‘YYYY-MM-DD’
Example: ‘1912-06-23’
Format of time fields in SQL
Contained in single quotation marks and commonly written in the 24h fromat ‘hh:mm:ss’
Example: ‘21:12:12’
Format of numeric fields in SQL
Stored as pure numbers (so no characters like currency symbols or other formating characters)
Not conatained in quotation marks
Format of boolean fields in SQL
Either TRUE or FALSE
Used without quotation marks
Rules for identifiers in SQL
Names must begin with a letter
Names can only consist of letters, numbers, and underscores
Names cannot be SQL keywords (watch out for ORDER)
Names can’t include spaces
How to create table in SQL
CREATE TABLE TableName
(
Attribute1 INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
Attribute2 VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
…
);What must be specified for each attribute when creating a table in SQL?
Whether it is the primary key
Its data type
Whether it must be filled in (‘NOT NULL’)
CREATE TABLE TableName
(
Attribute1 INTEGER NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY,
Attribute2 VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
…
)How to retrieve fields from a given table in SQL?
SELECT first_name, fav_num, date_of_birth
FROM table_name
WHERE first_name = 'John' AND fav_num > 12 AND date_of_birth < '2012-12-12'
ORDER BY fav_num DESC;How to get all available fields from the table my_table in SQL
Use * wildcard
SELECT *
FROM my_tableFROM statement
Specifies which table is being accessed or modified
WHERE statment
Used to specify the condition used to select which records will be accessed, modified or deleted
ORDER BY statement
Specifies how to sort results
Used with ASC or DESC for ascending and descending respectively
JOIN statement
Provides a method for combining rows from two tables based on a common field between them. For example:
SELECT Movie.MovieTitle, Director.DirectorName, Movie.MovieCompany
FROM Movie JOIN Director
ON Movie.DirectorName = Director.DirectorName;How to add a new record to a table
INSERT INTO table_name
(column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...);INSERT INTO statment
Used to add a new record to a database table
How to update records in a table
UPDATE TableName
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE columnX = some_value, columnY = some_value, ...UPDATE statment
Used to update records in a database table
How to delete records from a table
DELETE FROM TableName
WHERE columnX = some_valueDELETE statement
Used to delete records from a table
How to add a column to a table using SQL
ALTER TABLE TableName
ADD column_name column_datatype;How to delete a column of a table using SQL
ALTER TABLE TableName
DROP COLUMN AttributeXHow to change the data type of a column using SQL
ALTER TABLE TableName
MODIFY COLUMN AttributeX NewDataTypeALTER statement
Used to add, delete or modify the columns in a table
How to delete a table using SQL
DROP TABLE table_name;How to delete a databse using SQL
DROP DATABASE DB_name;What is the % wildcard and when is it used?
The % wildcard represents any number of characters, even zero characters
It is used with the LIKE operator to search for a pattern
What is the _ wildcard and when is it used?
The _ wildcard represents a single character
It is used with the LIKE operator to search for a pattern