physics final rdhsbjkdhgb
1/290
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
291 Terms
[…] are more likely to be transferred when the plastic rod is rubbed
Electrons (valence electrons - on outer layer)
Identical objects rubber with identical materials […] each other
repel
Electric interactions are [the same as/different from] magnetic interactions
different from
Methods of charging
friction
conduction
induction
grounding
Friction
two neutral objects acquire opposite charge by rubbing against each other
Conduction
charged object directly transfers some excess charge to another object
objects touch → charges move
one object is initially charged
When charges are transferring between objects they [can/cannot] occur in any amount
cannot
electric charge only comes in multiples of e (charge of an electron). charge is quantized, meaning it only occurs in particular amounts
e = -1.6 × 10^-19 C
is 4.0 × 10^-19 C a possible electric charge?
no
divide value by e
2.5 charge transferred, not possible
is -0.00072 C a possible electric charge?
yes
4.5×10^15 charge transferred, possible
Conductor
electrons are not bound and can move freely
can transfer electrons
excess charge resides on outer surface
Non-Conductors
electrons bound to protons and cannot move freely
can only move around proton
cannot transfer electrons
weaker attraction and repulsion than conductors
Induction
a charged object is brought near a neutral object
neutral object becomes charges
Grounding
path for excess charge to flow to ground
Water is a […]
conductor
polar molecule: has positive and negative end
humidity: tiny water molecules in air → act as conductor → distracting electrons by surrounding charged object
people are ~60% water, making them conductors
k =
9×10^9 Nm²/C²
Coulomb’s Law: Fq =
k q1q2/r²
Imagine 2 charged balls are hanging from threads. Predict what will happen tot he angle between the strings and the vertical.
Increasing the charge on the balls
increases the angle
Imagine 2 charged balls are hanging from threads. Predict what will happen tot he angle between the strings and the vertical.
Increasing the mass of the balls
decreases the angle
Imagine 2 charged balls are hanging from threads. Predict what will happen tot he angle between the strings and the vertical.
Increasing the string length
decreases the angle
source charge
object that created change in its surrounding space
electric field
change in surrounding space created by source charge; are vectors
test charges
object that interacts with electric field
assume they’re positive and do not have fields
force and field
field allows force to be exerted as distance
E =
Fq /q, q - charge in field
k q2/r² , q2 - source charge (only for a point charge; one source charge and one test charge)
Electric field (E-field) lines
represents electric field
number of lines is proportional to strength of object’s charge
can never cross or touch other lines
when there is a positively charged object and a negatively charged object, lines start on positively charged object
positive charge: arrows point away from charge
negative charge: arrows point towards charge
uniform electric field
occurs when E-field vectors and E-field lines in a given area are parallel to each other
faraday cage
external electric field causes electric charges in cage (hollow metal box) to be distributed
electrons move from one part of box to another
part where electrons left is now positive
distribution of charges cancel the field’s effect in the cage’s interior
inside, fields cancel out
Electrostatic equilibrium
state reached by charged conductors
when excess charge is placed on a conductor, charges spread out until they reach the lowest energy state possible
there is no net movement of charge
For objects in electrostatic equilibrium…
excess charge migrates to and remains on the outer surface of conductor
there is no electric field inside the conductor (neutral)
the direction of the electric field is perpendicular to the surface of conductor
there is a greater surface charge density at location of higher curvature
Why are you more likely to get shocked when touching a metal object with your finger as opposed to your entire hand?
the finger is smaller and more curved, therefore there is a greater surface charge density
As you increase the potential on an irregularly shaped conductor, a bluish-purple glow called the cornea forms around a sharp end sooner than a smoother end. Why?
As the sharper ends, more curvature → higher charge density
A person rubs a neutral comb through their hair and the comb becomes negatively charged. Why?
The hair loses electrons to the comb.
Consider four charges, A, B, C, and D, which exist in a region of space. Charge A attracts B, but B repels C. Charge C repels D, and D is positively charged. What is the sign of charge A?
A is negatively charged
Two neutral spheres A and B are near each other. A negatively charged rod is brought near one of the spheres as shown. The far right side of sphere B is
negative
An electroscope is given a positive charge, causing its foil leaves to separate. When an object is brought near the top plate of the electroscope, the foils separate even further. We could conclude
that the object is positively charged.
According to Coulomb’s law, if the electric force between two charges is positive, the force between the charges is [attractive/repulsive]
The force between the charges is repulsive
What methods of charging result in two oppositely charged objects?
Friction and induction
friction: 2 neutral objects acquire opposite charges via rubbing (one gains electrons, other loses electrons)
induction: a charged object is brought near neutral objects, resulting in the separation of charges in the neutral objects
Identify the type of charging: you touch a charged rod to an electroscope
conduction
charged object transfers excess charge to neutral object
Identify the type of charging: you connect a charged object to a much large conductor to neutralize the object
grounding
connecting charged object to larger conductor, which can add or accept excess electrons
Identify the type of charging: you bring a charged object near a neutral soda can. the soda can is attracted to the charged object.
induction
pitch
perception of the frequency of a sound wave
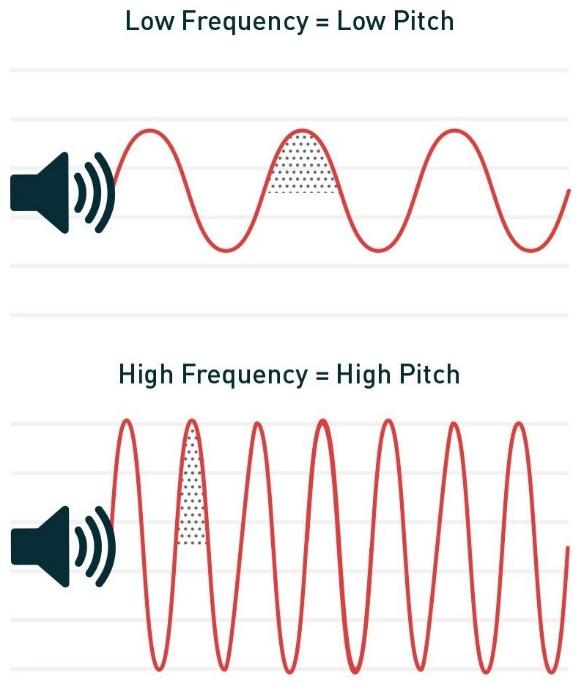
loudness
determined by amplitude of sound wave
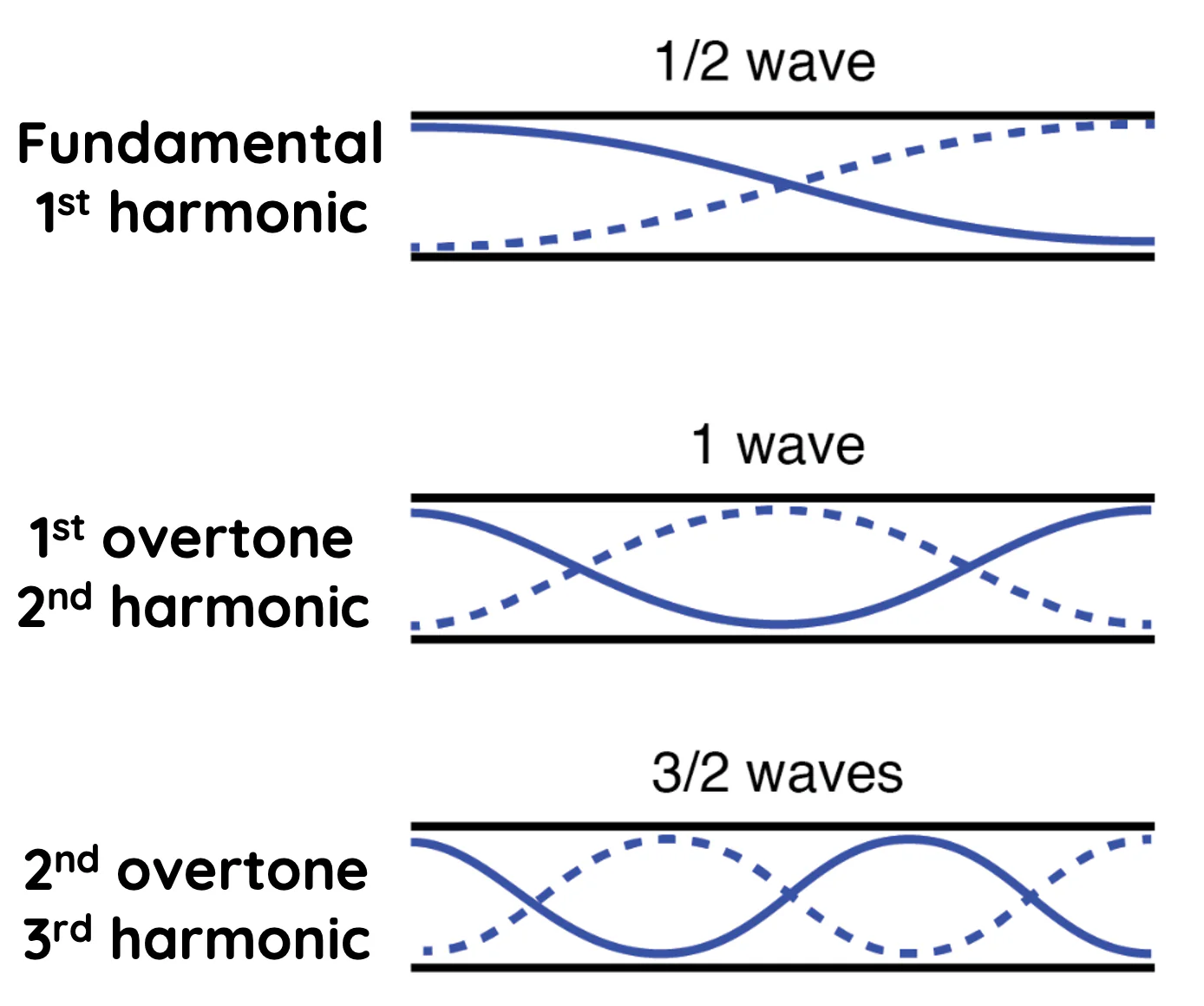
open end pipes
ends of harmonics are antinodes
nodes = n
antinode = n+1
wavelength = 2L/n
frequency = nv/2L
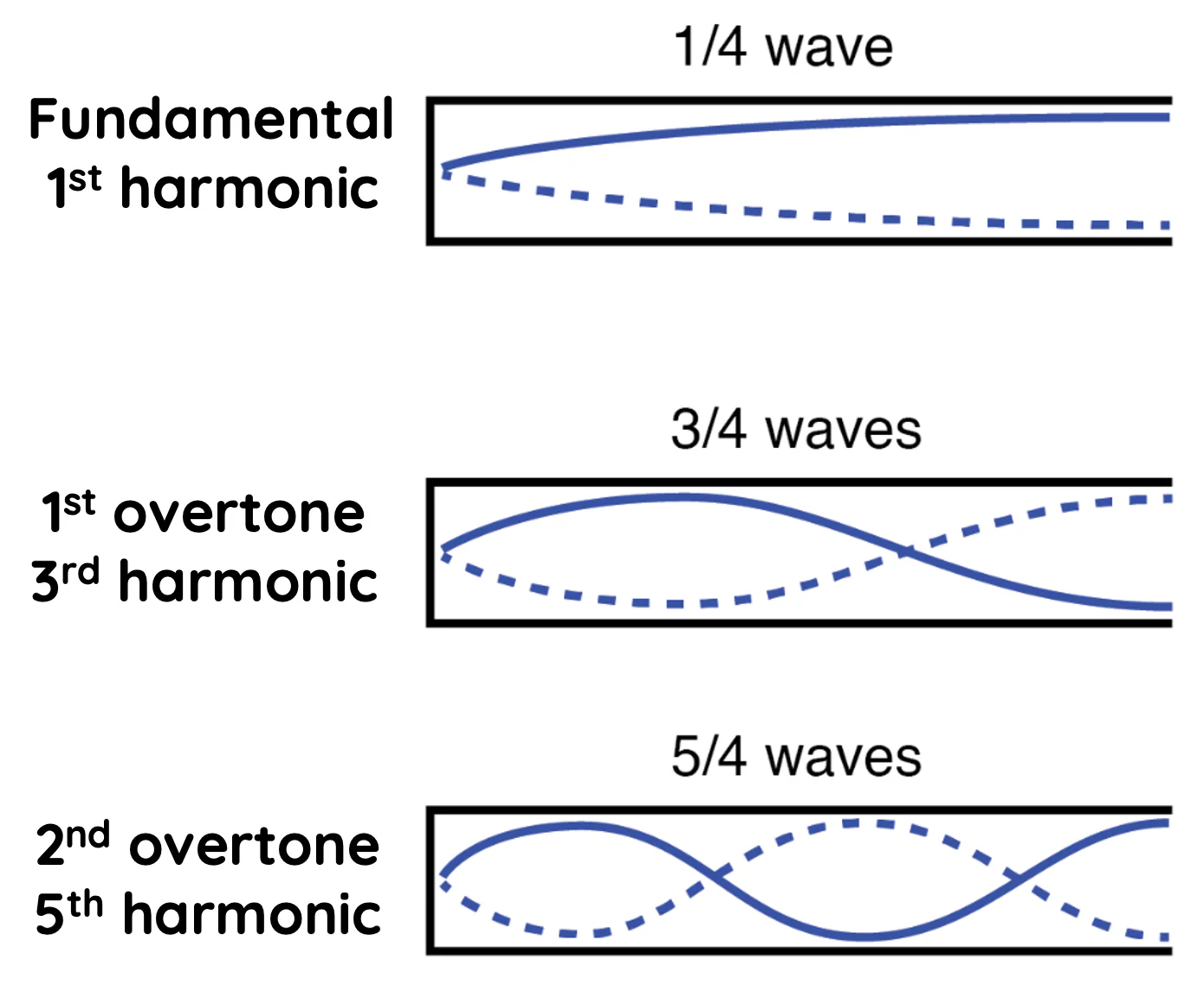
closed end pipes
begins with node
nodes = antinodes = n
wavelength = 4L/n
n is odd
frequency = nv/4L
possible harmonics
open end pipes - any number
closed end pipes - odd numbers
fundamental frequency
n =1 (first harmonic)
relationship with overtones: fn = f1 * n
doppler effect
Frequency of sound (pitch) heard by the observer is higher when the observer and source get closer. When observer and source are farther, frequency gets lower
beat frequency
number of "beats" heard per second
fb = f2-f1
beat
two waves completely in phase
standing wave
stationary
remains in constant position
wave sources
amplitude
frequency
type of waves (transversal or longitudinal)
DO NOT affect speed
wave medium
density
tension
affect speed
traverse wave
disturbance and coil move perpendicular to each other; moves side to side
longitudinal wave
disturbance and coils move parallel to each other
constructive interference
when two pulses meet and they have an amplitude in the same direction → bigger wave
destructive interference
when two pulses meet and they have amplitudes in opposite directions → smaller wave
node (N)
location of minimum/no vibration
antinode (A)
location of max vibration
The SI units for electrical PE are…
joules
What are the accepted symbols for electric potential energy?
U
PE
How would you increase the electrical potential energy of a pair of charged particles of the SAME sign?
decrease their separation
How would you decrease the electrical potential energy of a pair of OPPOSITELY charged particles?
decrease their separation
How would you decrease the electrical potential energy of a pair of charged particles of the SAME sign?
increase their separation
How would you increase the electrical potential energy of a pair of OPPOSITELY charged particles?
increase their separation
Equation for computing the electrical potential energy stored in a pair of charged particles
K\frac{q1q2}{r}
Electric potential energy is a (scalar/vector) quantity
scalar
It may increase or decrease, but it has no compass direction.
When charged particles are released and can move freely, their electric potential energy will be converted to…
kinetic energy
Units for electric potential
volts
Is electric potential a scalar or vector
scalar
volts in terms of joules/coulombs
1 V = 1 J/C
Electric fields point in the direction that ___ charges freely move when released.
positive
Electric fields point towards locations of ___ potential.
lower
Which way do positively charged particles freely move towards?
direction of lower potential
Which way do negatively charged particles freely move towards?
direction of higher potential
Locations of higher electric potential are _____ positively charged bodies than locations of lower potential
closer to
What are equipotential surfaces?
locations of the same potential in an electric field
Equipotential surfaces are ___ to electric field vectors
perpendicular
If a location in an electric field has a potential of 10 V, it means that 1 coulomb of charge would ________ at this location
possess 10 J of potential energy
Is potential constant in an uniform electric field?
no
potential changes as you move from one position to another. an electric field is a potential gradient.
If a charged particle moves freely in an electric field, its PE…
decreases
How does the capacitance of a capacitor increase?
increase area (make plates bigger)
decrease r (decrease separation of plates)
use more polar dielectric
The places of capacitors are (insulators/conductors)
conductors
Dielectric is a (insulator/conductor)
insulator
What do capacitors do?
provide a quick burst of energy in automated external defibrillators
provide a quick burst of current in a computer keyboard
maintain a uniform electric field in air purifiers
How would you increased the energy stored in a capacitor?
charge it with a higher voltage battery
Units for capacitance
farads (F)
Equation for finding sum of capacitors in series
\frac{1}{Ceq} = \frac{1}{C1} + \frac{1}{C2} + … \frac{1}{Cn}
Equation for finding sum of capacitors in parallel
Ceq = C1 + C2 + … Cn
Characteristics of equipotential surfaces/lines/contours
perpendicular to electric field lines
areas where electric potential is the same, regardless of object’s charge
concentric spheres around a single source charge
equipotential contours can never meet or cross
contours are closer = more electric potential energy
test charges seek (higher/lower) energy states
lower
(think of a ball rolling down an incline)
The electric potential energy of interaction of two charged objects is defined to be zero when the distance between them is ____
infinitely far away
If two objects have the same sign charges, their electric potential energy is (positive/negative)
positive
If two objects have opposite charges, their electric potential energy is (positive/negative)
negative
If two oppositely charged objects move closer together, their electric potential bar will (increase/decrease) in size
increase
if the Ue between two equal charges quadruples, what happens to the distance between the particles?
distance decreases by a factor of 4 → 1/4
When is the equation ∆Ue = -qEdcosθ used?
when a charge, q, moves freely in an electric field